Template:Networking tswos manual spanning tree
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails.
Spanning Tree Settings
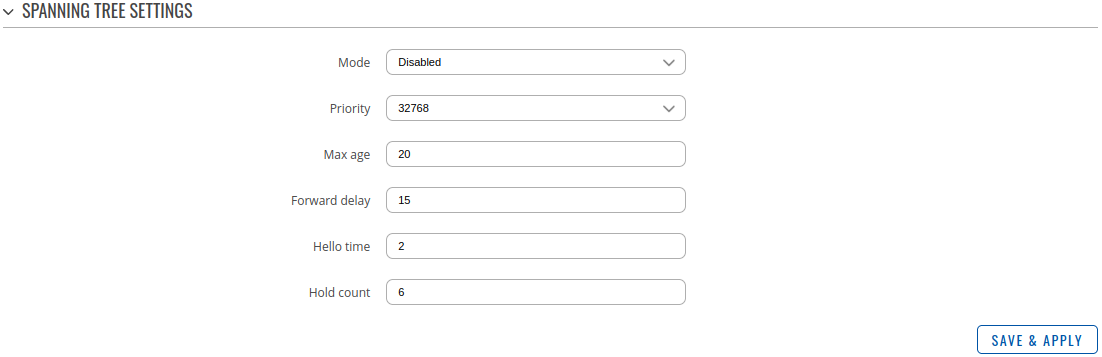
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | Disabled | STP | RSTP; default: Disabled | STP - provides a single path between any two end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. RSTP - detects network topologies to provide faster convergence of the spanning tree. Disabled - turns off spanning tree protocol. |
| Priority | Integer [0..61440]; default: 32768 | STP priority. The lower the number, the higher the priority. |
| Max age | Integer [6..40]; default: 20 | Maximum expected arrival time of hello bridge protocol data units (BPDUs). |
| Forward delay | Integer [4..30]; default: 15 | How long an STP bridge port remains in the listening and learning states before transitioning to the forwarding state. |
| Hello time | Integer [1..10]; default: 2 | Number of seconds between transmissions of configuration BPDUs. |
| Hold count | Integer [1..10]; default: 6 | The number or BPDUs that can be transmitted during every hello time period ranges from a minimum of one and a maximum of not more than defined value. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]