Template:Networking tswos manual qos
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
Quality of Service (QoS) is used to set up priority to specific devices, services or applications within the network through the router, so that the maximum amount of available throughput and speed can be used.
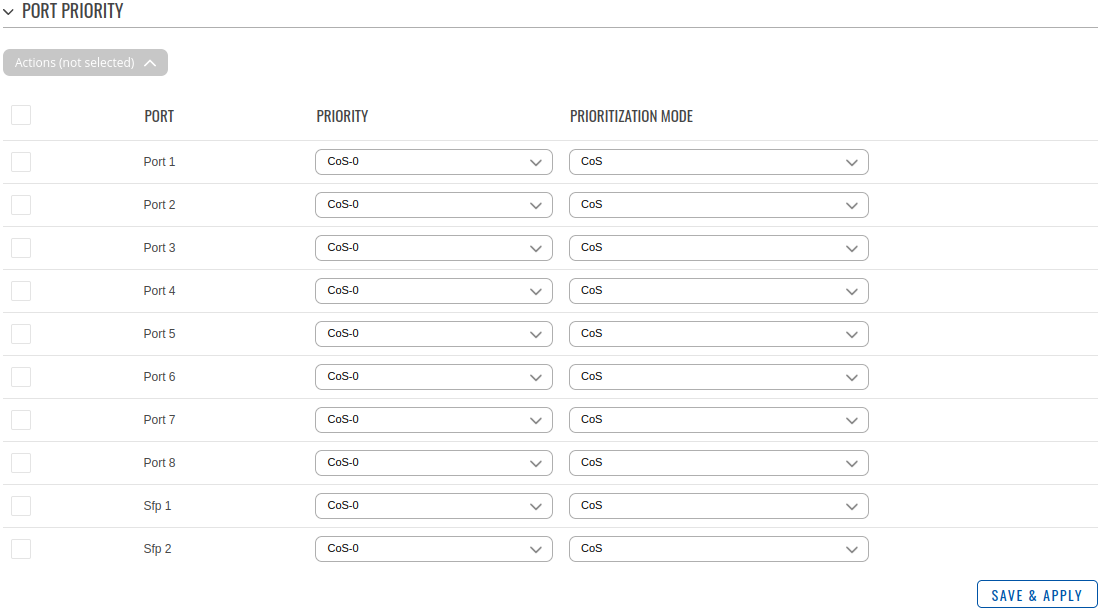
Port priority
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Port | Physical device port | Port ID. |
| Priority | CoS-[0..7]; default: CoS-0 | Port-based priority of the specified port. |
| Prioritization mode | CoS | DSCP | Equal; default: CoS | Utilizes either CoS, DSCP or both markings equally. CoS operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model and consists of eight different classification groups to which Ethernet frames can belong. DSCP serves a similar purpose as CoS, but it does so at the network layer -- Layer 3 -- of the OSI model and uses a 6-bit field, as opposed to only 3 bits. |
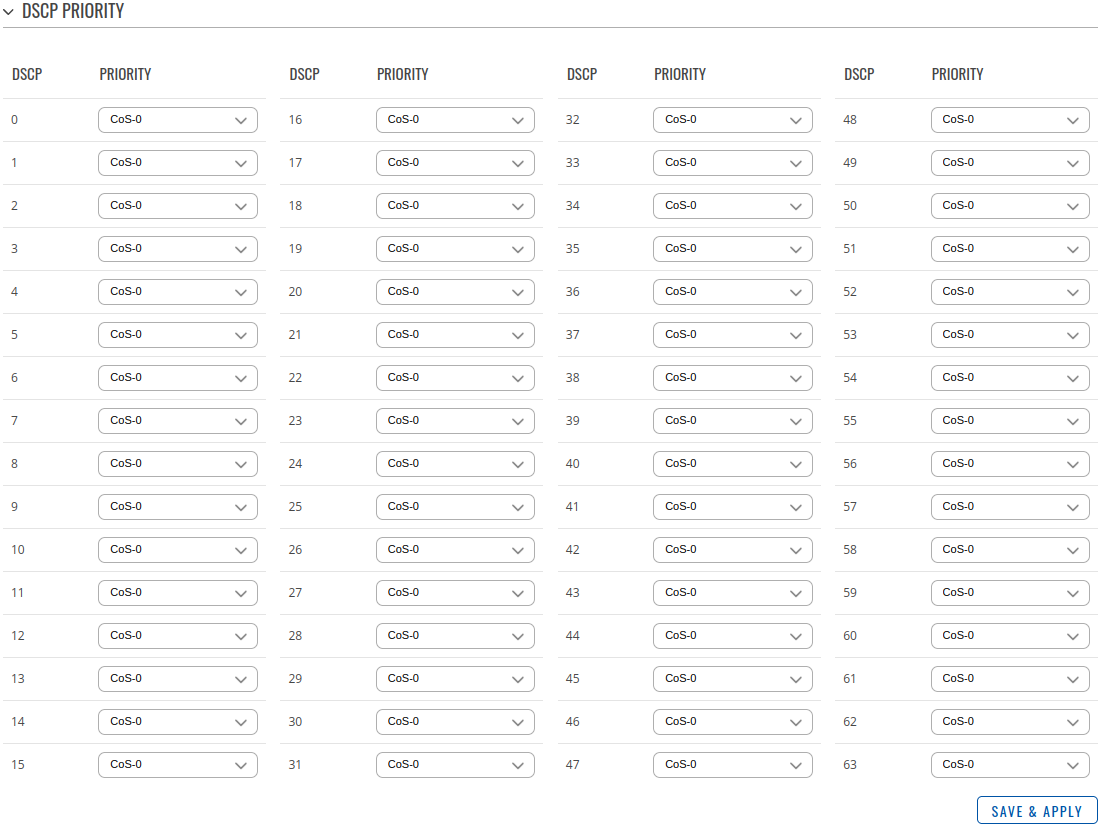
DSCP priority
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) is a means of classifying and managing network traffic and of providing quality of service (QoS) in modern Layer 3 IP networks. It uses the 6-bit Differentiated Services (DS) field in the IP header for the purpose of packet classification.
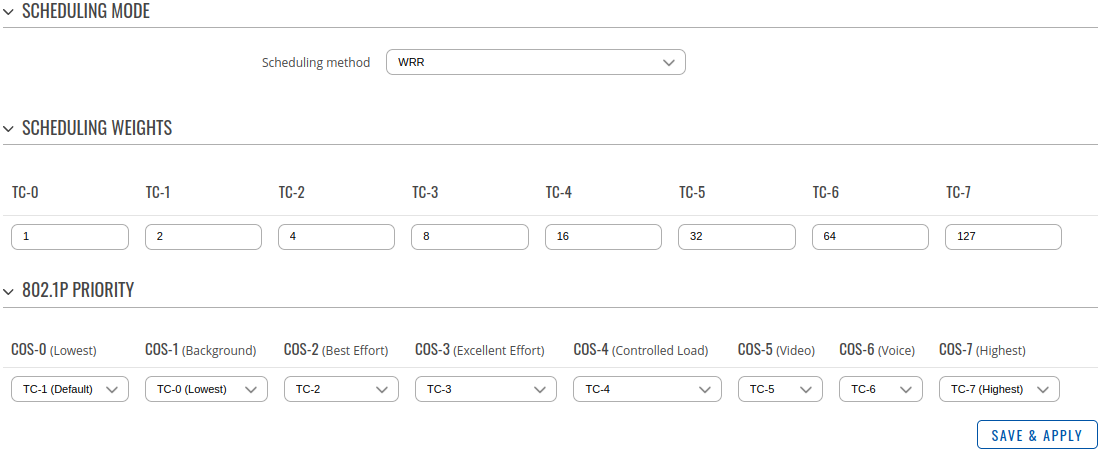
802.1p priority
802.1p is a quality of service (QoS)/class of service (CoS) method that operates at the MAC layer (Layer 2). Equipment that supports 802.1p can add and recognize a value that indicates the priority level of the Ethernet frame. 802.1p—Displays the 802.1p priority tag values to be assigned to an egress queue, where 0 is the lowest and 7 is the highest priority.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scheduling mode | SP | WRR | WFQ; default: WRR | Possible modes:
|
| Scheduling weights | Integer [1..127] | Weight value assignment of specific port queue for WFQ/WRR |
| 802.1P Priority | Integer [0..7] | Internal priority mapping to egress queue ID. By default TC (Traffic Class) queue values are mapped 1 to 1 with CoS values. The higher the CoS marking, the higher will be the packet priority. |
Bandwidth control
In networking, Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms like bandwidth control and storm control are used to manage and control the flow of traffic on a network. They help ensure that critical traffic receives priority and that network resources are used efficiently.
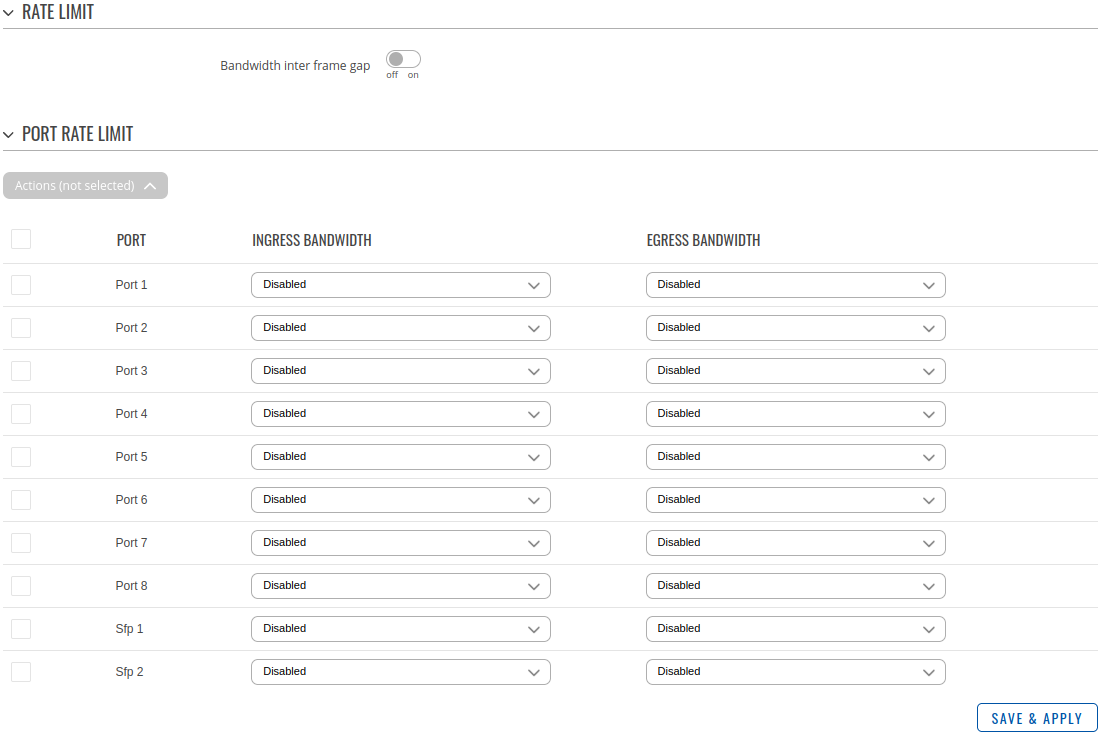
Rate limit
Rate limiting is a specific form of bandwidth control that restricts the rate at which data can be sent or received. It is used to prevent certain traffic flows from exceeding a predefined rate. Rate limiting can be applied to both inbound and outbound traffic. It is commonly used to control traffic such as email, file transfers, or streaming to ensure that it does not consume excessive network resources.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth inter frame gap | off | on; default: off | Bandwidth control rate include IFG (inter frame gap and preamble). |
| Ingress bandwidth | Integer [0..1000000]; default: Disabled | Ingress bandwidth in Kbps units. |
| Egress bandwidth | Integer [0..1000000]; default: Disabled | Egress bandwidth in Kbps units. |
Storm control
Storm control is a feature used to prevent broadcast, multicast, or unknown unicast "storms" from overloading a network. These storms can occur when a network device generates a high volume of these types of traffic, leading to congestion and network performance issues. Storm control mechanisms can include broadcast storm control, multicast storm control, and unknown unicast storm control.
[[File:|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ; default: 1 |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]