TSW202 Network
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version TSW2_R_01.08.
Summary
The Network page contains information related to the device's networking. This chapter is an overview of the Network page in TSW202 devices.
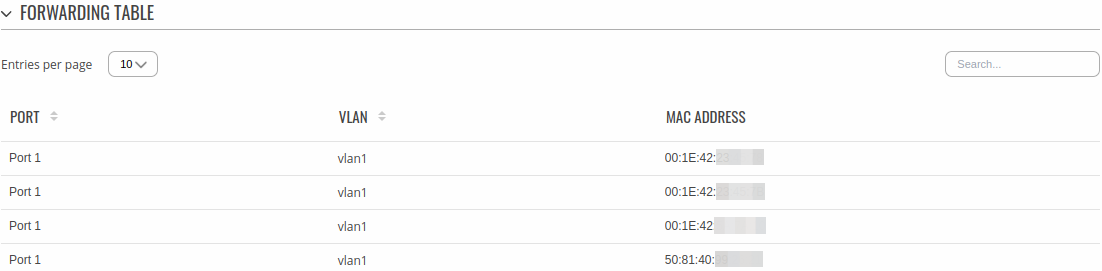
Forwarding Table
The Forwarding Table also known as MAC table, is most commonly used in network bridging, routing, and similar functions to find the proper output network interface controller to which the input interface should forward a packet. It is a dynamic table that maps MAC addresses to ports.
| field name | description |
|---|---|
| Port | Name of physical port. |
| VLAN | VLAN assigned to that port. |
| MAC Address | MAC address of devices connected to that port. |
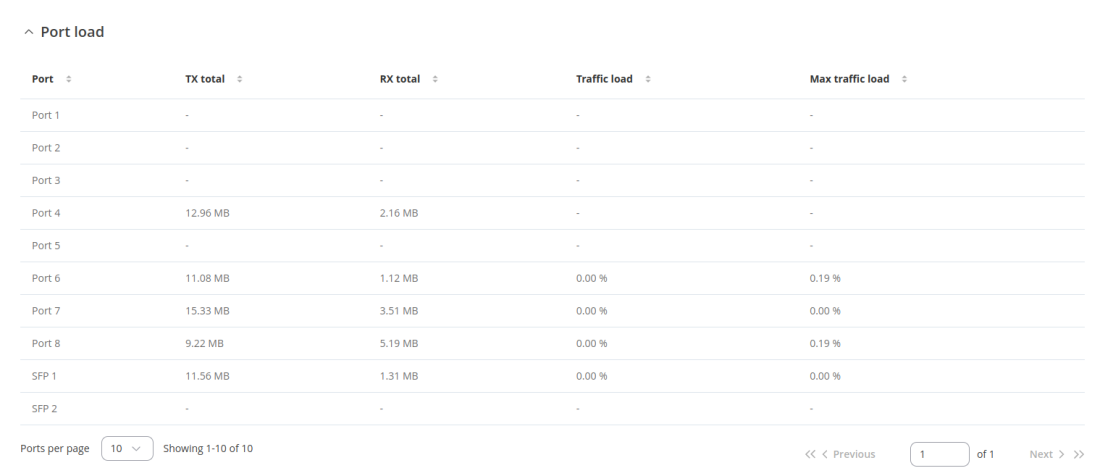
Ports
The Ports table shows usage of the ports. The Port Load Status page provides real-time monitoring and detailed metrics of network port utilization, including traffic load and transmission and reception rates, to ensure optimal network performance
The Port Traffic Error Status table shows if there is any errors in the traffic.
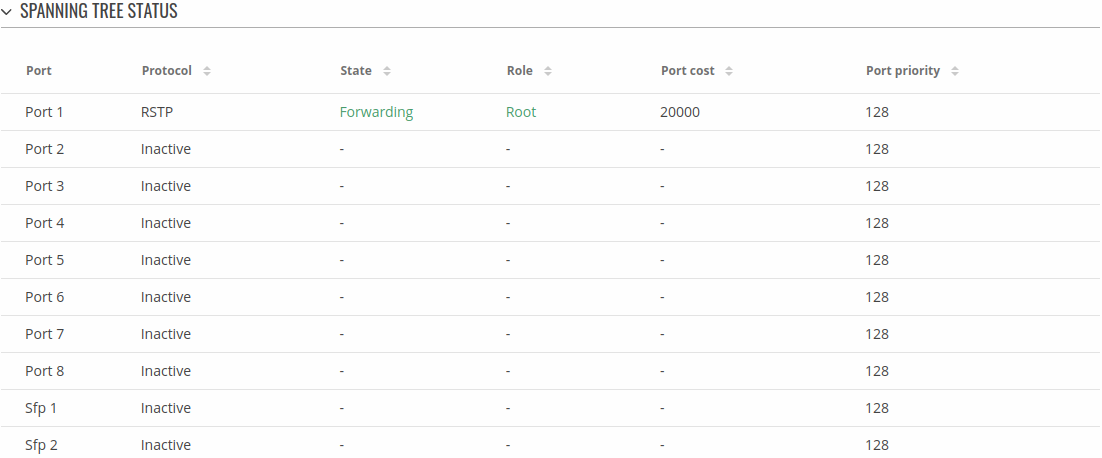
Spanning Tree
The table shows the Spanning Tree states of each port.
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Port | port number | Name of physical port. |
| Protocol | Inactive | STP | RSTP | Protocol used by the port. |
| State | Inactive | Learning | Forwarding | Blocking | Listening | Discarding | State of the port. |
| Role | Inactive | Root | Designated | Alternate | Backup | Role of the port. Roles are used only for RSTP. |
| Port cost | integer | Cost of the port is determined by the port speed. Higher speed ports have lower cost. Lower cost is more preferred by spanning tree. |
| Port priority | integer | Priority of the port is used when costs of the ports are the same. Lower priority is more preferred by spanning tree. Also the lowest priority port is put into forwarding state. |
DHCP Leases
The DHCP Leases table shows information about hosts and the time period for which a DHCP server allocates a network address to a client. User can filter out all leases by interface. Also interface and leasetime remaining fields can be sorted.
| field name | description |
|---|---|
| Host name | Client name. |
| IP address | Leased IP address. |
| MAC address | MAC address of the device. |
| Leasing remaining | Remaining time on the lease. |
| -interactive button "Create Static" | This action will reserve currently assigned IP address for the device in Here |
Routes
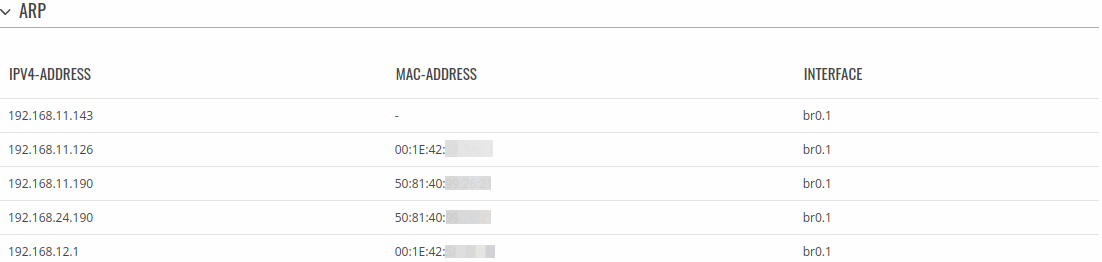
ARP
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine's link layer address (MAC address) belonging to the local network.
The ARP section displays the router's ARP cache (also known as ARP table) data. The ARP cache contains information on each known MAC address and its corresponding IP address. When the router receives a packet destined for a local host, the ARP program attempts to find a physical host or MAC address in the ARP cache that matches the IP address. If the ARP cache doesn't contain the needed IP address, ARP broadcasts a request packet to all LAN machines in order to find the device with the IP address in question.
The figure below is an example of the ARP cache section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IP address | ip; Default: none | IP address of a local host. |
| MAC address | mac; Default: none | MAC address of a local host. |
| Interface | string; Default: none | Interface through which the router is associated with the host. |
You can also view the ARP cache via shell using the arp or ip neigh commands, depending on which output your prefer:
root@Teltonika-TSW202:~# arp IP address HW type Flags HW address Mask Device 192.168.11.126 0x1 0x2 00:1e:42:00:00:00 * br0.1
root@Teltonika-TSW202:~# ip neigh 192.168.11.126 dev br0.1 lladdr 00:1e:42:00:00:00 STALE
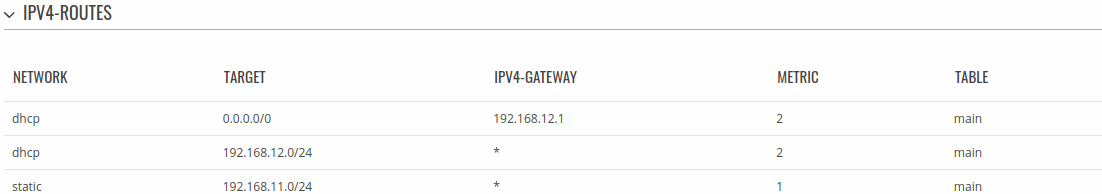
IPv4 Routes
The IPv4 Routes section displays the router's routing table. A routing table contains a list of routes to network destinations associated with and known by the router.
The figure below is an example of the Active IP routes section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Network | string; Default: none | Associated network interface name. |
| Target | ip | ip/netmask; Default: none | Destination network address. |
| IPv4 gateway | ip; Default: none | Indicates the IP address of the gateway through which the target network can be reached. |
| Metric | integer [0..4,294,967,295]; Default: none | Metrics help the router choose the best route among multiple feasible routes to a destination. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric value. |
| Table | string | integer; Default: none | Name or number of the associated routing table. |
You can also view the routing table via shell using the route or ip route commands, depending on which output your prefer:
root@Teltonika-TSW202:~# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface default RUTX12.lan 0.0.0.0 UG 2 0 0 br0.1 192.168.11.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 1 0 0 br0.1 192.168.12.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 2 0 0 br0.1
root@Teltonika-TSW202:~# ip route default via 192.168.12.1 dev br0.1 proto static src 192.168.12.125 metric 2 192.168.11.0/24 dev br0.1 proto static scope link src 192.168.11.2 metric 1 offload 192.168.12.0/24 dev br0.1 proto static scope link src 192.168.12.125 metric 2 offload
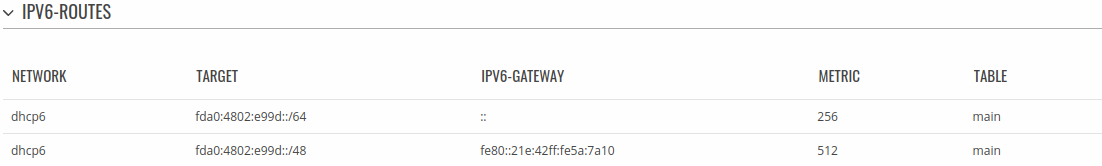
IPv6 routes
The IPv6 Routes section displays the router's IPv6 routing table.
The figure below is an example of the IPv6 routes section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Network | string; Default: none | Associated network interface name. |
| Target | ip6 | ip6/netmask; Default: none | Destination network address. |
| IPv6-Gateway | ip6 | ip6/netmask; Default: none | Source of the network address. |
| Metric | integer [0..4,294,967,295]; Default: none | Metrics help the router choose the best route among multiple feasible routes to a destination. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric value. |
| Table | string | integer; Default: none | Name or number of the associated routing table. |
You can also view the routing table via shell using the route -A inet6 or ip -6 route show commands, depending on which output your prefer:
root@Teltonika-TSW202:~# ip -6 route fda0:4802:e99d::/48 from fda0:4802:e99d::/64 via fe80::21e:42ff:fe5a:7a10 dev br0.1 proto static metric 512 pref medium fda0:4802:e99d::/64 dev br0.1 proto static metric 256 pref medium unreachable fda0:4802:e99d::/64 dev lo proto static metric 2147483647 pref medium fe80::/64 dev eth0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium fe80::/64 dev br0 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium fe80::/64 dev br0.1 proto kernel metric 256 pref medium
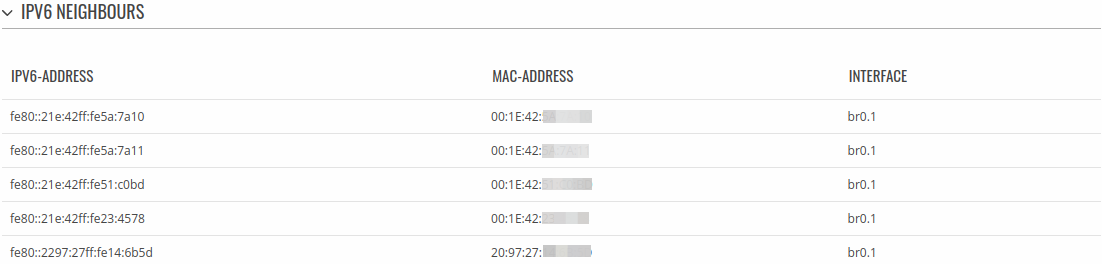
IPv6 Neighbours
The IPv6 Neighbours section displays IPv6 associated neighbours.
The figure below is an example of the Active IPv6 Neighbours section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 Address | ip6; Default: none | IPv6 address of the associated neighbour. |
| MAC Address | ip6; Default: none | MAC address of the associated neighbour. |
| Interface | string; Default: none | Name of the associated network interface. |