Routing
Summary
This chapter is an overview of the Routing section in RUT devices.
Static Leases
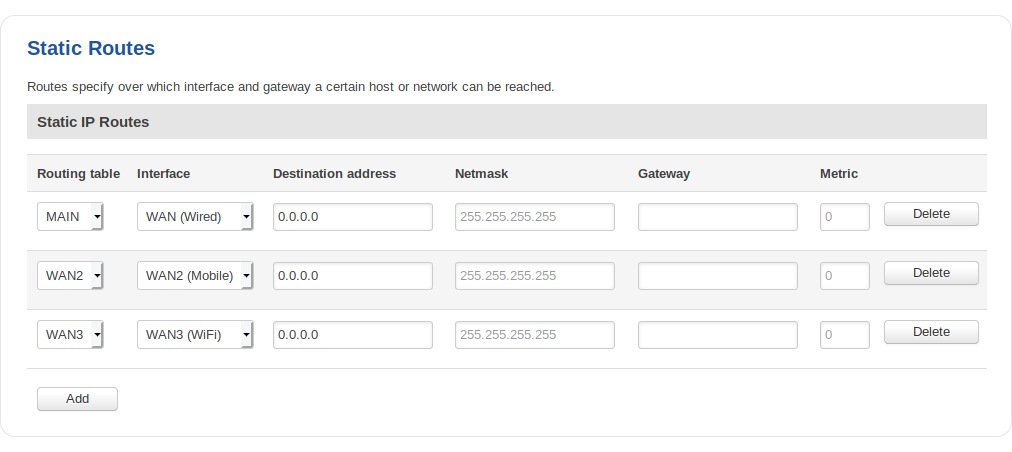
Static routes specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. In this page you can configure your own custom routes.
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Routing table | Main | WAN | WAN2 | WAN3; Default: WAN | Defines which table will be used for the route in question |
| Interface | LAN | WAN(wired) | WAN2(Mobile) | WAN3(WiFi) | VPN instances; Default: WAN(wired) | The zone where the target network resides |
| Destination address* | ip; Default: 0.0.0.0 | The address of the destination network |
| Netmask* | ip; Default: 0.0.0.0 | A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies |
| Gateway | ip; Default: " " | Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule |
| Metric | integer; Default: 0 | A Metric is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied |
*Additional notes on Destination & Netmask:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this: Destination - some IP; Netmask - 255.255.255.255. Furthermore, you can define a rule that applies to a segment of IPs like this: Destination – some IP that STARTS some segment; Netmask – Netmask that defines how large the segment is. e.g.:
| IP | Netmask | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.55.161 | 255.255.255.255 | Only applies to 192.168.55.161 |
| 192.168.55.0 | 255.255.255.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.55.0 - 192.168.55.255 range |
| 192.168.55.240 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.55.240 - 192.168.55.255 |
| 192.168.55.161 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.55.0 - 192.168.55.255 |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
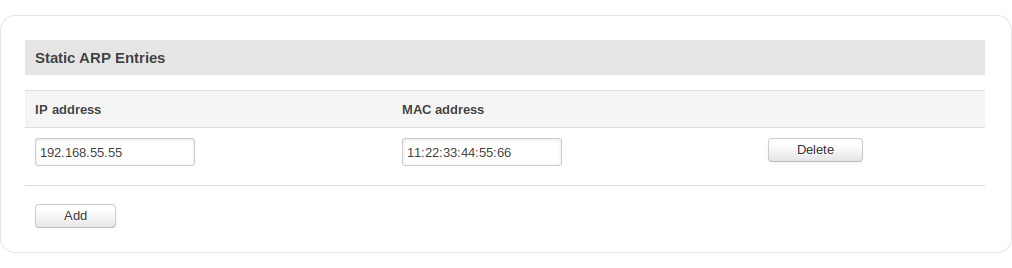
Static ARP entries
Static ARP entries are used to bind a MAC address to a specific IP address. For example, if you want a device to get the same IP every time it connects to the router, you can create a Static ARP entry by binding that device’s MAC address to the desired IP address. The router will then create an entry in the ARP table, which in turn will make sure that that device will get the specified IP address every time.
Dynamic Routes
BGP Protocol
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. The protocol is often classified as a path vector protocol but is sometimes also classed as a distance-vector routing protocol. The Border Gateway Protocol makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator and is involved in making core routing decisions.
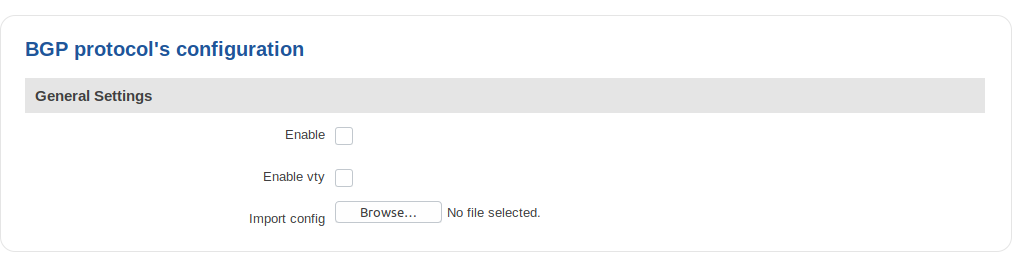
General Settings
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles the BGP protocol ON or OFF |
| Enable vty | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles vty access from LAN ON or OFF |
| Import config | - | Uploads an external BGP configuration |
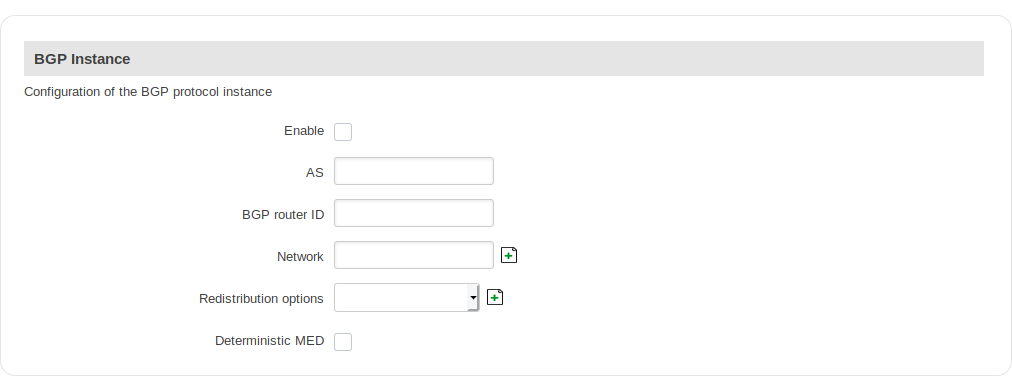
BGP Instance
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles the BGP instance ON or OFF |
| AS | integer: " " | AS number is an identification of an autonomous system. BGP protocol uses the AS number for detecting whether the BGP connection is an internal one or external one. [Required] |
| BGP router ID | string; Default: " " | The router id is used by BGP to identify the routing device from which a packet originated. Default router ID value is selected as the largest IP Address of the interface. |
| Network | string; Default: " " | Add an announcement network(s) |