OpenVPN server on Windows
Introduction
OpenVPN is an open-source software application that implements virtual private network (VPN) techniques for creating secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities.
This article contains step-by-step instructions on how to create and run an OpenVPN server on a PC that runs on Windows OS. The information provided here is geared towards users of almost any knowledge level. The instructions apply to Windows 7 and newer systems.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- A PC or Laptop running on Windows 7 or a later version
- The PC in question must have a Public IP address
- An active Internet connection
Objective:
The purpose of this article is to provide the know-how needed to configure a working OpenVPN server on a Windows PC.
Step 1: installing OpenVPN software
- Download an OpenVPN installer file from here.
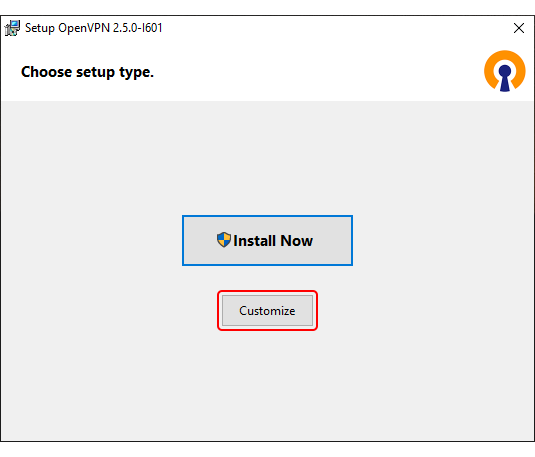
Run the downloaded file. - Before starting the installation process, click 'Customize':
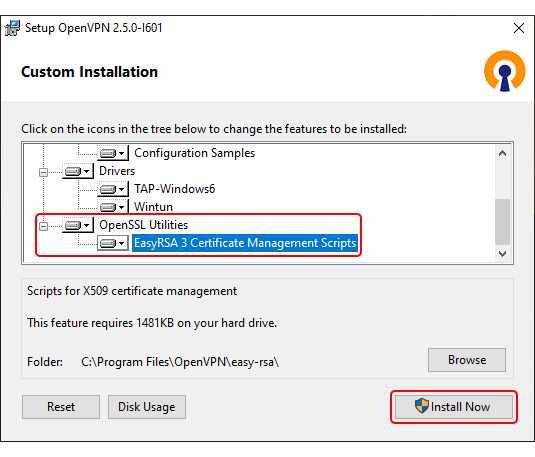
- While in the 'Custom Installation' window, scroll down to find OpenSSL Utilities → EasyRSA 3 Certificate Management Scripts; make sure it is installed along with OpenVPN and click 'Install Now':
Step 2: preparing EasyRSA
- Now we can start preparing to generate certificates and keys. For this we'll be using the EasyRSA application that was installed along with OpenVPN.
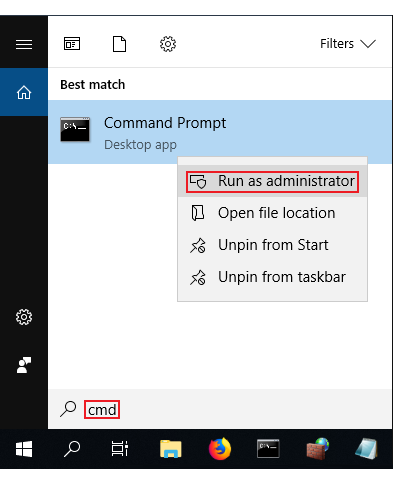
EasyRSA commands have to be executed via the Windows Command Prompt. It can be opened by typing cmd in the Windows search bar (Windows button + S). When you launch it, make sure you run it as administrator: - Change the current directory to the EasyRSA folder. To do so, execute this command:
cd "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\easy-rsa"
init-config
notepad vars.bat
set KEY_COUNTRY=US set KEY_PROVINCE=CA set KEY_CITY=SanFrancisco set KEY_ORG=OpenVPN set [email protected]
set DH_KEY_SIZE=2048
vars
clean-all
Step 3: generating certificates and keys
- Now we can start generating the certificates and keys. Begin with the certificate authority (CA) - the root certificate file that will be used to sign other certificates and keys:
build-ca
NOTE: you can press the "Enter" key when prompted to enter the values set in the vars.bat file earlier. Doing this will set the values to the default specified in vars.bat. However, you should type in a meaningful Common Name.
build-key-server server
NOTE: once again, don't forget to specify a different Common Name (use the name "server" for easier management purposes). When prompted the sign and commit the certificate, type y and press "Enter".
build-key Client1
TIP: use the same Common Name as the certificate name (Client1 in this example). This will help you differentiate different clients easier. Pick meaningful names like "toms_PC", "company_maintenance", etc. Repeat this step as many times as you need, depending on the client quantity.
build-dh