RUT230 Web Filter
Summary
The Web Filter service allows you to set up lists of wanted or unwanted websites (Blacklists or Whitelists). This chapter is a summary of RUT routers' Web Filter function.
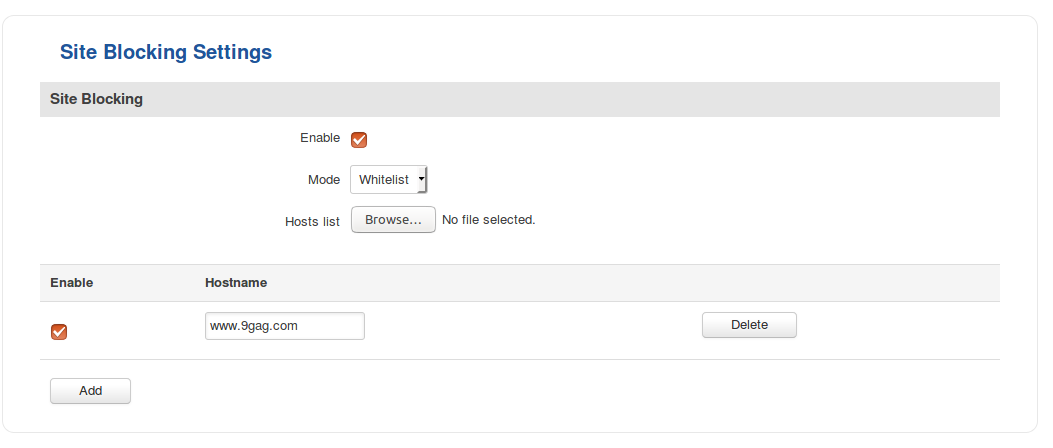
Site Blocking
The Site Blocking tab provides you with the possibility to create a Blacklist or Whitelist that filters out which websites that a local network user can access. Access to sites included in the Blacklist is blocked; access to sites included in the Whitelist is allowed while everything else (not included) is blocked. You can choose only one of these options.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles Blacklist/Whitelist ON or OFF |
| Mode | Blacklist | Whitelist; Default: Whitelist | Whitelist - allow every site included in the list and block everything else Blacklist - block every site included in the list and allow everything else |
| Hosts list | text file; Default: " " | Provides a possibility to upload a text file containing a list of host instead of adding hosts individually via the WebUI. Hosts must be separated by line breaks, i.e., one host per line |
| Enable | yes | no; Default: yes | Toggle an entry of the list active or inactive. Inactive entries are not considered to be a part of the list until they are activated |
| Hostname | host; Default: " " | Website name that is to be added to the list. The formats accepted are either www.example.com or example.com, i.e., the protocol and subdomains can't be specified. The rules will also be applicable for the subdomains of the specified site(s) |
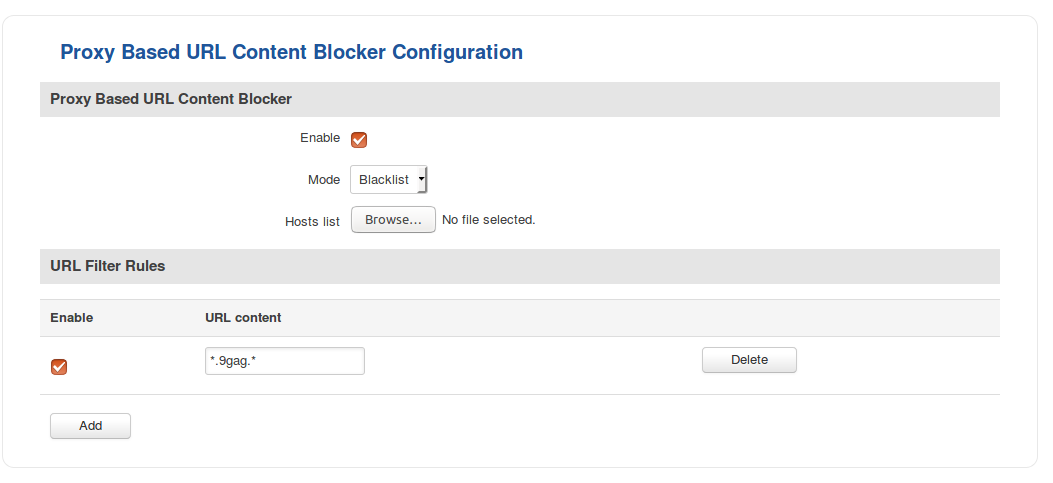
Proxy Based Content Blocker
Proxy Based Content Blocker works in a similar manner to Site Blocking, except with Content Blocker you have the ability to filter out content with more versatility by using the asterisk (*) symbol instead of different extensions and phrases. For example, instead of having to block multiple domains like 'website.com', 'website.net', 'website.org' you can simply create an entry called 'website.*', which would block all websites whose names begin with 'website.'
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles Blacklist/Whitelist ON or OFF |
| Mode | Blacklist | Whitelist; Default: Blacklist | Whitelist - allow every site included in the list and block everything else
Blacklist - block every site included in the list and allow everything else |
| Hosts list | text file; Default: " " | Provides a possibility to upload a text file containing a list of host instead of adding hosts individually via the WebUI. Hosts must be separated by line breaks, i.e., one host per line |
| Enable | yes | no; Default: yes | Toggle an entry of the list active or inactive. Inactive entries are not considered to be a part of the list until they are activated |
| URL content | host; Default: " " | Website name or part of a website name that is to be added to the list. The * symbol can stand for anything. In the given example the URL content is *.9gag.*, which means it blocks all variation of that site's hostname, i.e., 9gag.com, www.9gag.com, 9gag.net, www.9gag.org, etc., while a www.9gag.com entry would only block that specific hostname |
Troubleshooting
Users often find that the Web Filter service doesn't seem to function as expected. In most cases the issue lies not with the functionality of Web Filter itself. Here are some steps to ensure you are using/testing Web Filter correctly (applies to both "Site Blocking" and "Proxy Base URL Content Blocker"):
- Reload your browser. After adding new hostnames to the list, make sure you re-launch your web browser. Web browsers cache previously accessed information so the reason why some sites added to the list don't filter out properly is because the content of those sites had been downloaded and cached prior.
Or you can test immediately after adding new entries to the list with your web browser's non-caching mode. For example, Google Chrome's "Incognito" mode (Ctrl + Shift + N) or Mozilla Firefox's "Private" mode (Ctrl + Shift + P).
- Multiple network interfaces. If your PC has multiple sources for Internet connectivity, make sure it uses the router as its default Internet gateway.
- Multiple domains. Popular sites like Google, Youtube, Facebook, etc. often use multiple domain names. Therefore, sometimes it may be necessary to block more than one domain in order to successfully block a single website.
- Mobile websites. If you're testing Web Filter via a mobile phone, keep in mind that by default mobile devices connect to mobile versions of websites (that usually have names beginning with m.) when they are available. Therefore, it is necessary to also add the mobile hostname as well as the regular one.
- Grammar mistakes. Make sure you have entered the desired hostnames correctly. Often sites aren't blocked because of simple grammar mistakes like typing .comm instead of.com, ww. instead of www. or other general misspellings. If a site is not being blocked properly, check that entry in the Web Filter list.