Template:Networking rutxxx configuration example use LAN as WAN
Introduction
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the [[Media:{{{fw_version}}}_WEBUI.bin|{{{fw_version}}}]] firmware version.
This article provides a guide on how to configure the LAN ports as WAN. It can be usefull as wired ISP redundant connection or even to change the port for physical damage or a custom mounting.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
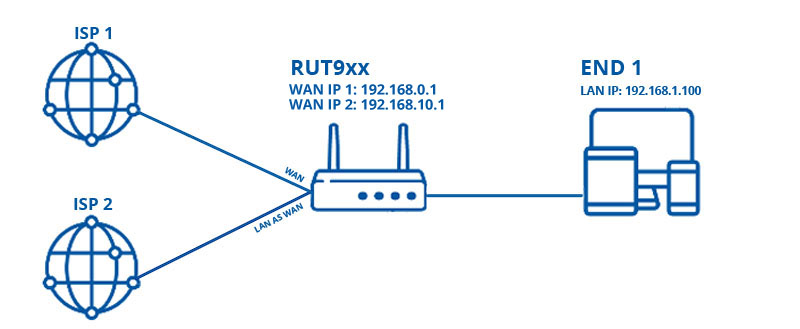
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- One RUTxxx series router (excluding RUT850).
- At least two wired Internet connections.
- An end device for test the configuration.
Configuration scheme:
WebUI Router configuration
Connect to the router’s WebUI navigate to Network -> VLAN -> LAN Network and create a new interface by entering name and clicking “Add New”.
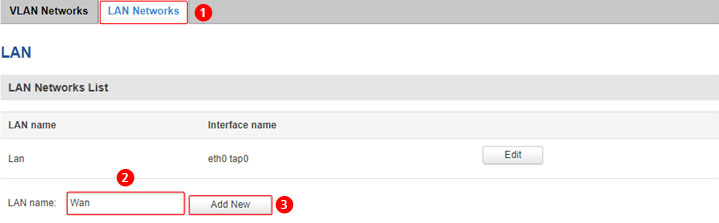
After you clicked “Add New” new configuration window will pop-up, there you leave as default and press “Save”.
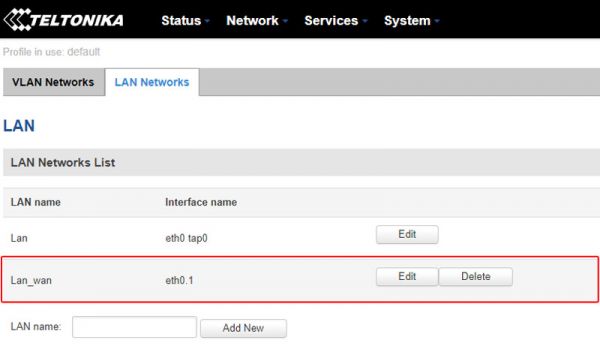
After saving settings, you will be redirected back to Network -> VLAN -> VLAN Networks, now you need to open VLAN Network tab in the same window and you will need to:
- Select VLAN mode: Port based
- Current LAN interface:
- Enable wireless access
- Select your current LAN interface.
- Turn off LAN port 3 (which will be used as WAN port)
- Press “Save”.
Note: Make sure that you are not connected to that LAN port which you going to disable.
- New LAN_WAN interface:
- Click “Add” and new row will appear.
- Turn off LAN ports 1-2 and leave only LAN port 3 on.
- Select “lan_wan” in the LAN section and press “Save”.
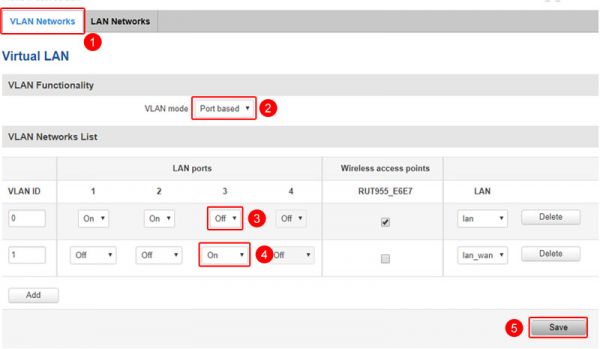
Using DCHP
Leave the settings as default and click save
Using a Static IP
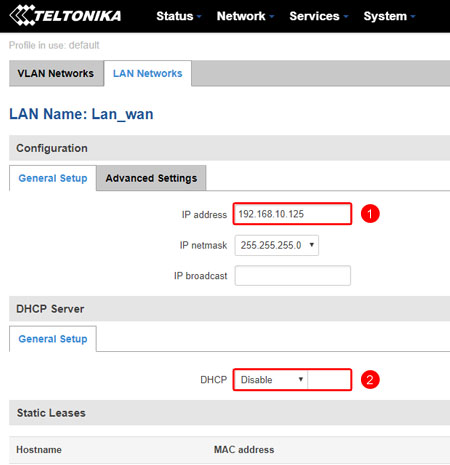
Static IP need to be set as router’s WAN IP.
Static IP should be in the same subnet as gateway’s LAN interface.
For example: if gateway’s LAN subnet is 192.168.10.1, then router’s WAN IP could be for example 192.168.10.125
CLI/SSH Router configuration
For the next part you will be configuring router via SSH. For this you need to use the command line interface (CLI) or a SSH software if you’re using Windows or iOS. In this example software “putty” will be used. Open “putty” enter routers LAN IP address and press “Open”.
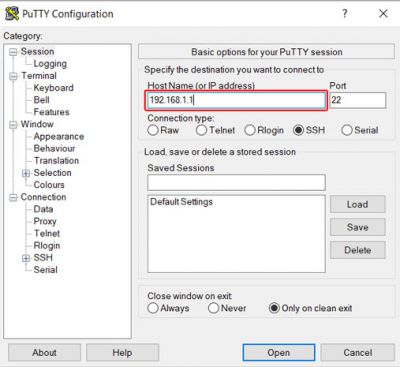
After clicking “Open” you will need to enter router credentials.
Now when you are connected you will need to make changes to network settings, this will be
achieved via SSH command: vi, which allows you to edit settings in the router. Enter following
command in SSH:
Using DHCP
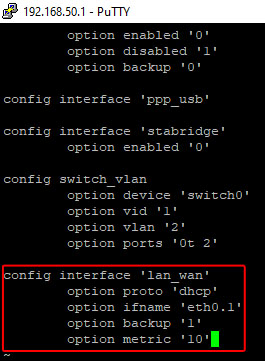
Using arrows navigate and find config interface 'lan_wan' and add two options:
Using Static IP
Using arrows navigate and find config interface 'lan_wan' and add two options:
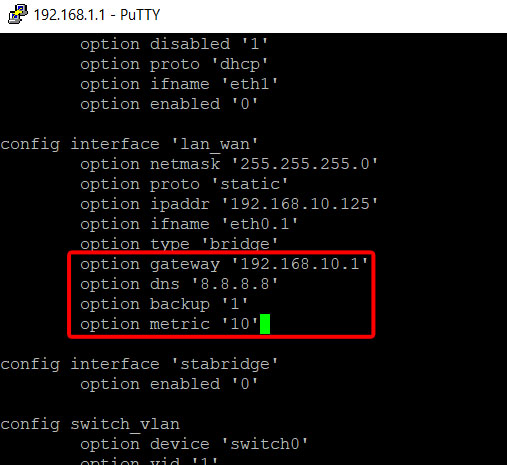
Press Esc and write :wq.
After that you will need to restart network service on the router, for this use command:
![]()
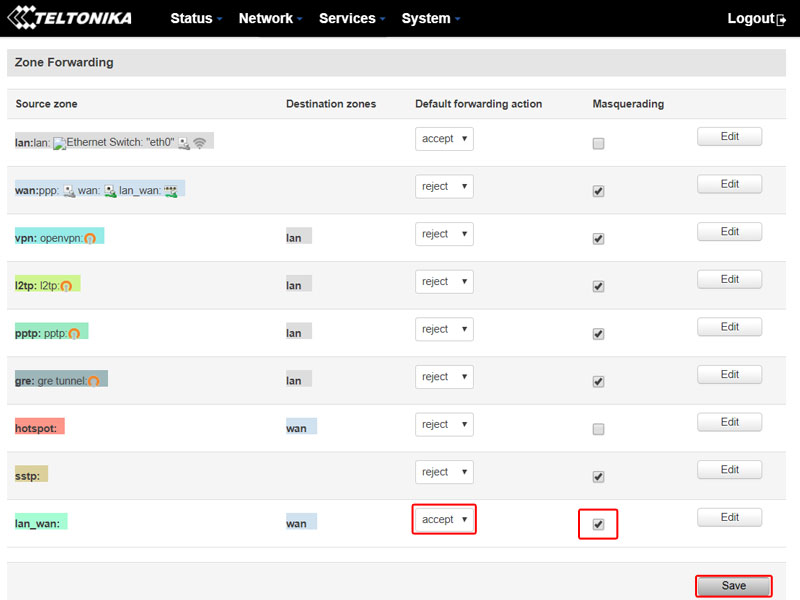
After restart is completed go back to routers WebUI and navigate to Network -> Firewall -> General Settings.
Scroll down, in Zone Forwarding find source zone lan_wan and change “Default forwarding action” from reject to accept and also check Masquerading and save settings.
Testing the configuration
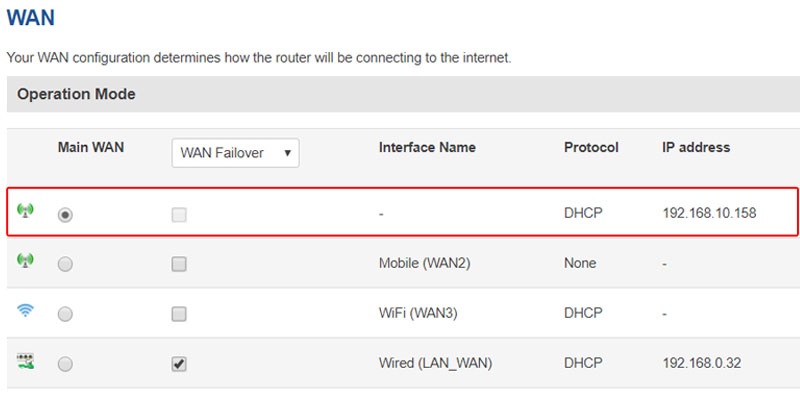
If you did the steps in the right way, your end device should have internet connection according the scheme.
Go to Network --> WAN and check if the new LAN_WAN is enable and if it has an assigned IP
[[Category:{{{name}}} Configuration Examples]]