Template:Networking rutos manual routing
Summary
This chapter is an overview of the Routing section in {{{name}}} devices.
Static Routes
Static routes specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. In this page you can configure your own custom routes.
Static IPv4 Routes
Below is an example and information about Static IPv4 Routes.
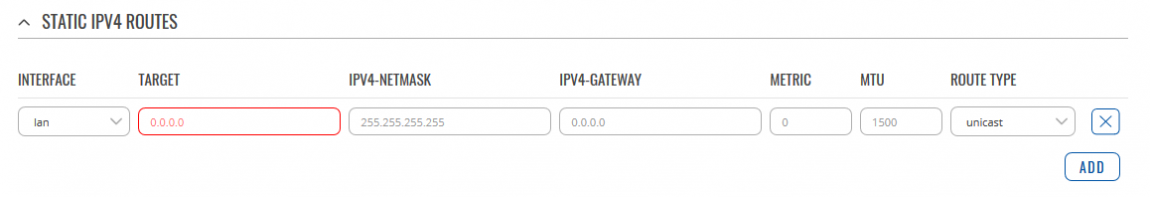
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Default: lan | The zone where the target network resides |
| Target* | IPv4; Default: 0.0.0.0 | The address of the destination network |
| Netmask* | Default: 255.255.255.255 | A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies |
| Gateway | IP; Default: 0.0.0.0 | Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule |
| Metric | Default: 0 | The metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | [64..9000]; Default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | Default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route, available options:
|
*Additional notes on Target & Netmask:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this:
- Target: some IP
- Netmask: 255.255.255.255
Furthermore, you can define a rules that apply to a range of IPs. Refer to the table below for examples.
| Target | Netmask | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.2.0 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.15 range. |
| 192.168.2.240 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.240 - 192.168.2.255 range. |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.55.255 range. |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 range. |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.255 | Only applies to 192.168.2.161. |
Static IPv6 Routes
Settings for Static IPv6 routes are the same as for IPv4 only that the target IP and and gateway are different.

Advanced Static Routes
Advanced static routing includes features and concepts that are used in more complex networks.
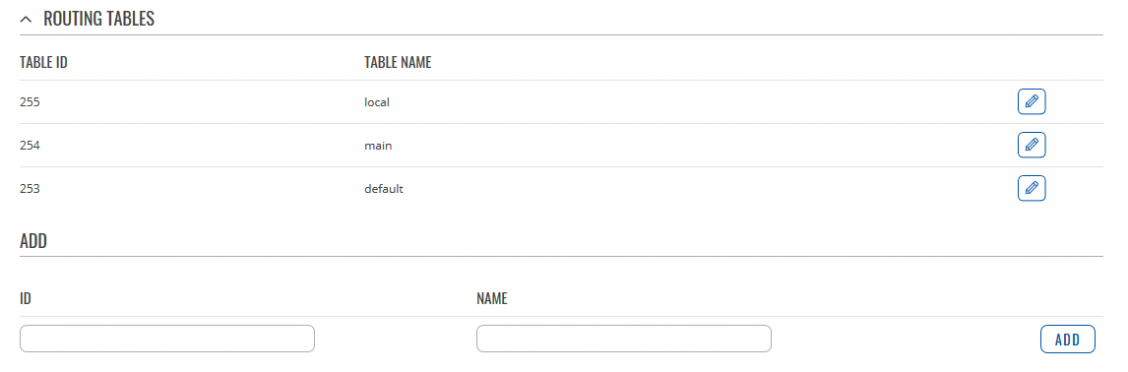
Routing Tables
Below is an example of routing tables. You can create a new one by writing ID (anything you want, but only numbers are allowed), Name and pressing Add button. You can edit them by pressing Edit button
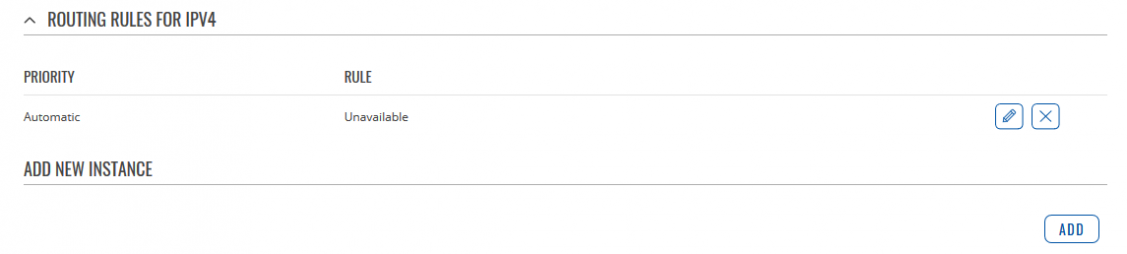
Routing Rules For IPv4
Below is an example of routing rules for IPv4. You can create a new rule by pressing Add button, also you can edit them by pressing Edit button.
An example of rule editing window and meanings of all the configurations are presented below.
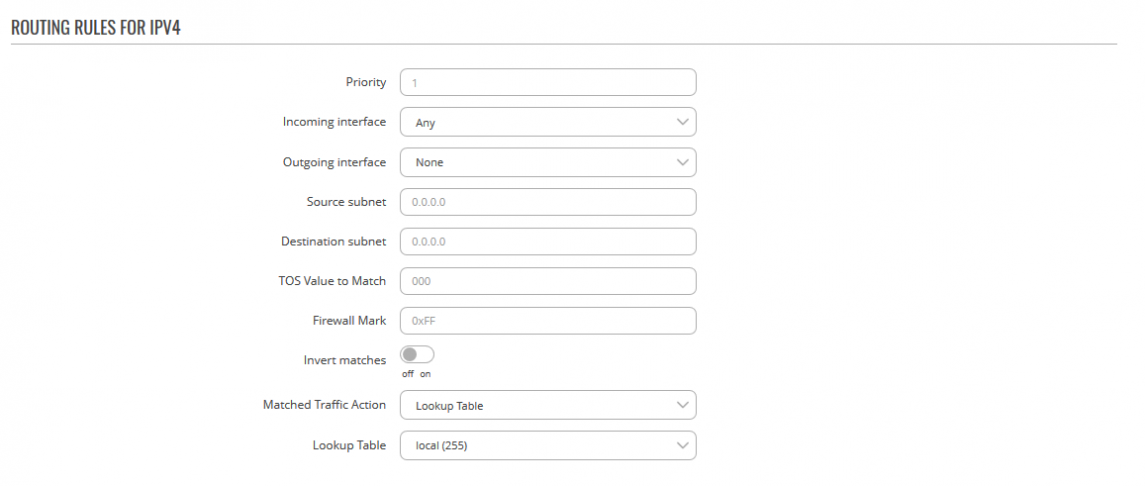
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Priority | Default: auto-assigned | Controls the order of the IP rules, by default the priority is auto-assigned so that they are processed in the same order. |
| Incoming interface | Default: Any | Specifies the incoming logical interface name |
| Outgoing interface | Default: None | Specifies the outgoing logical interface name |
| Source subnet | IPv4; Default: 0.0.0.0 | Specifies the source subnet to match (CIDR notation) |
| Destination subnet | IPv4; Default: 0.0.0.0 | Specifies the destination subnet to match (CIDR notation) |
| TOS Value to Match | Default: 0 | Specifies the TOS value to match in IP headers |
| Firewall Mark | Default: 0xFF | Specifies the fwmark and optionally its mask to match, e.g. 0xFF to match mark 255 or 0x0/0x1 to match any even mark value |
| Invert matches | off | on; Default: off | If enabled, the meaning of the match options (Firewall Mark, TOS Value, Source and Destination subnets) is inverted |
| Matched Traffic Action | Default: Lookup Table | Available options:
|
| Lookup Table | Default: " " | The rule target is a table lookup |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]
