Template:Networking rut manual gps
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the RUT9XX_R_00.06.07 firmware version.
Summary
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based radionavigation system. This page is an overview of the GPS service in {{{name}}} routers.
Map
The Map page displays the device's current coordinates and position on the map. To see the device's location on the map, make sure to attach the GPS antenna on the router and enable GPS in the [[{{{name}}}_GPS#General|General]] page.
The figure below is an example of the Map page:
[[File:{{{file_map}}}]]
General
The General section is used to enable the GPS service and the support for different types satellites. Once you turn on GPS, you can check the [[{{{name}}}_GPS#Map|Map]] page in order to see if the router has obtained a GPS fix. It is very important to attach the GPS antenna on the router and place it outside (not inside of a building). The router will not be likely to obtain a GPS fix otherwise.
The figure below is an example of the General page and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that page:
[[File:{{{file_general}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; default: no | Turns the GPS service on or off. |
| Galileo NMEA support* | yes | no; default: no | Turns support for Galileo satellites on or off. |
| Glonass NMEA support* | yes | no; default: no | Turns support for Glonass satellites on or off. |
| BeiDou NMEA support* | yes | no; default: no | Turns support for BeiDou satellites on or off. |
*Changing these options requires a modem reboot. Therefore, if you make changes to these options and save them, the router will lose cellular connectivity for about 30 seconds.
NMEA
The NMEA page is used to configure settings related to NMEA sentence collecting and forwarding.
NMEA forwarding
The NMEA forwarding section is used to configure and enable NMEA forwarding. The figure below is an example of the NMEA forwarding section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
[[File:{{{file_nmea_forwarding}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; default: no | Turns NMEA forwarding on or off |
| Hostname | ip | host; default: 192.168.1.5 | IP address or hostname of the server to which NMEA data will be forwarded |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 8500 | Port number off the server to which NMEA data will be forwarded |
| Protocol | TCP | UDP; default: TCP | Protocol that will be used to send NMEA data |
| Contain Connection | yes | no; default: no | Contain active session with a remote server |
NMEA forwarding cache
The router caches NMEA forwarding information if NMEA forwarding is enabled. This section is used to select the memory type where the cache will be stored and the maximum amount of data that will be saved:
[[File:{{{file_nmea_cache}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Type | ram | flash; default: ram | Selects which type of memory will be used for storing NMEA forwarding cache. |
| Maximum sentences | integer; default: 5000 | Maximum amount of NMEA sentences that will be saved in the cache before older entries are deleted and replaced by new ones. |
| File | filepath; default: none | Location of the file where NMEA forwarding cache information will be stored. This field becomes visible only when the selected memory type is "flash". |
NMEA collecting
The NMEA collecting section is used to enable NMEA sentence gathering and storing. The figure below is an example of the NMEA collecting section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
[[File:{{{file_nmea_collecting}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; default: no | Turns NMEA sentence collecting on or off. |
| Location | filepath; default: none | Location of the file where NMEA sentences will be stored. This field becomes visible only when NMEA collecting is enabled. |
NMEA sentence settings
The NMEA sentence settings section provides the possibility to configure which NMEA sentences will be forwarded or collected and at what frequency. The figure below is an example of the NMEA sentence settings section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
[[File:{{{file_nmea_sentence}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Forwarding enabled | yes | no; default: no | Enables forwarding for the adjacent NMEA sentence. |
| Forwarding interval | integer; default: 5 | NMEA sentence forwarding frequency in seconds. |
| Collecting enabled | yes | no; default: no | Enables collecting for the adjacent NMEA sentence. |
| Collecting interval | integer; default: 5 | NMEA sentence collecting frequency in seconds. |
NMEA sentence reference table:
| NMEA sentence name | Description |
|---|---|
| GPGSV | Number of GPS satellites in view. |
| GPGGA | GPS fix data. |
| GPVTG | Track made good and speed relative to the ground. |
| GPRMC | Recommended minimum specific GPS/Transit data. |
| GPGSA | GPS DOP and active satellites. |
| GLGSA | GLONASS DOP and active satellites. |
| GLGSV | Number of GLONASS satellites in view. |
| GNGNS | GNSS position fix from more than one constellation (e.g., GPS + GLONASS). |
| GAGSV | Number of Galileo satellites in view. |
| PQGSV | Detailed satellite data (used in BeiDou sentences). |
| PQGSA | Overall satellite data (used in BeiDou sentences). |
HTTPS
The HTTPS page can be used to configure data sending to an HTTP(S) server.
HTTPS/HTTP Server Settings
The HTTPS/HTTP Server Settings section is used to enable GPS data sending to an HTTP or HTTPS server:
[[File:{{{file_https_settings}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; default: no | Turns data sending to an HTTP/HTTPS server on or off. |
| URL | ip | host; default: 192.168.1.5 | IP address or hostname of the HTTP/HTTPS server. |
TAVL Settings
The TAVL Settings section is used to select which data will be sent to the TAVL server:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Send GSM signal | yes | no; default: no | Includes GSM signal strength information in the GPS data sent to server. |
| Send analog input | yes | no; default: no | Includes analog input state in GPS data package to be sent to server. |
| Send digital input (1) | yes | no; default: no | Includes digital input #1 state in the GPS data sent to server. |
| Send digital input (2) | yes | no; default: no | Includes digital input #2 state in GPS data package to be sent to server. |
AVL
The AVL page is used to set up GPS data sending to an AVL server.
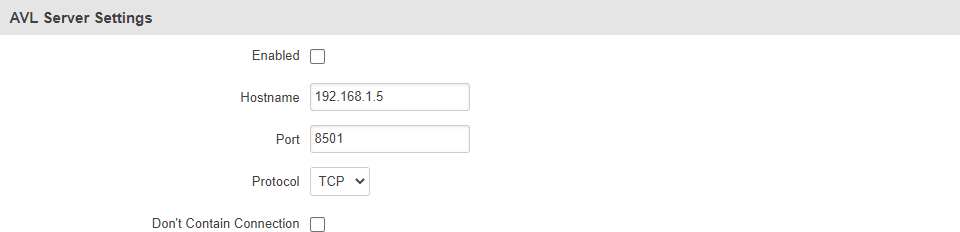
AVL Server Settings
The AVL Server Settings section is used to configure the main parameters of data sending to an AVL server. The figure below is an example of the AVL Server Settings section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; default: no | Turns data sending to AVL server on or off. |
| Hostname | ip | host; default: 192.168.1.5 | IP address or hostname of an AVL server. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 8501 | TCP/UDP port number of the AVL server to which the router will be connecting. |
| Protocol | TCP | UDP; default: TCP | Protocol that will be used for communication with the AVL server. |
| Don't Contain Connection | yes | no; default: no | When turned on, closes the TCP/UDP socket each time after transferring data. |
Main rule
The Main rule section defines how and when GPS data will be collected and sent to a specified AVL server. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the configuration fields of Main Rule.
[[File:{{{file_main_rule}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: yes | Turns the main rule on or off. |
| Rule priority | Low priority level | High priority level | Panic priority level | Security priority level; default: Low priority level | The rule's priority. Different priority settings add different flags to event packets, so they can be displayed differently in the receiving system. The router sends data of higher priority first. Priority levels from highest to lowest are as follows:
|
| Collect period | integer [1..999999]; default: 50 | How often (in seconds) data will be collected. |
| Min distance | integer [1..999999]; default: 50 | Minimum distance change (in meters) before sending records. |
| Min angle | integer [1..360]; default: 50 | Minimum angle change (in degrees) before sending records. |
| Min saved records | integer [1..32]; default: 20 | Minimum amount of gathered records before sending. |
| Send period | integer [0..999999]; default: 20 | How often (in seconds) gathered data is sent. |
Secondary Rules
The Secondary rules section provides you with the possibility to create additional data sending rules. The difference from the main rule is that the secondary rules only send data when the router uses a specified type of WAN and when the digital isolated output is in the specified state.
Refer to the figure and table below for information on the configuration fields of the Secondary rules section.
[[File:{{{file_secondary_rules}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: yes | Turns the rule on or off. |
| WAN | Mobile Both | Mobile Home | Mobile Roaming | WiFi | Wired; default: Mobile Home | Selects which type of WAN will trigger the rule. |
| Digital Isolated Input | Low logic level | High logic level | Both; default: High logic level | Selects which input state will trigger the rule. |
| Rule priority | Low priority level | High priority level | Panic priority level | Security priority level; default: Low priority level | The rule's priority. Different priority settings add different flags to event packets, so they can be displayed differently in the receiving system. The router sends data of higher priority first. Priority levels from highest to lowest are as follows:
|
| Collect period | integer [1..999999]; default: 10 | How often (in seconds) data will be collected. |
| Min distance | integer [1..999999]; default: 25 | Minimum distance change (in meters) before sending records. |
| Min angle | integer [1..360]; default: 25 | Minimum angle change (in degrees) before sending records. |
| Min saved records | integer [1..32]; default: 10 | Minimum amount of gathered records before sending. |
| Send period | integer [0..999999]; default: 10 | How often (in seconds) gathered data is sent. |
AVL Configuration
The AVL Configuration section is used to add additional secondary GPS data sending rules.
[[File:{{{file_gps_configuration}}}]]
TAVL Settings
The TAVL Settings section is used to select which data will be sent to the TAVL server:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Send GSM signal | yes | no; default: no | Includes GSM signal strength information in the GPS data sent to server. |
| Send analog input | yes | no; default: no | Includes analog input state in GPS data package to be sent to server. |
| Send digital input (1) | yes | no; default: no | Includes digital input #1 state in the GPS data sent to server. |
| Send digital input (2) | yes | no; default: no | Includes digital input #2 state in GPS data package to be sent to server. |
| Send digital input (3) | yes | no; default: no | Includes digital input #3 state in GPS data package to be sent to server. |
AVL I/O
The AVL I/O tab provides you with the possibility to configure input rules.
Check Analog
The Check Analog section is used to set how often the router checks the value of the analog input. This is relevant to input rules related to the analog input.
[[File:{{{file_avl_io_analog}}}]]
Input Rules
The Input Rules section displays existing input rules. To create a new input rule look to the section below (AVL Input Configuration), select input type, trigger and click the 'Add' button.
To configure an input rule click the 'Edit' button located next to it. The figure below represents a newly added rule with default settings. Refer to the table below for information on the fields contained in the input rule configuration section.
[[File:{{{file_avl_io_rules}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Turns the input rule on or off. |
| Input type | Digital | Digital isolated | analog; default: Digital | Selects to which input the rule will apply. |
| Trigger | Input open | Input shorted | Both; default: Input open | The event that will trigger the rule. |
| Priority | Low | High | Panic; default: Low | The rule's priority. Different priority settings add different flags to event packets, so they can be displayed differently in the receiving system. The router sends data of higher priority first. Priority levels from highest to lowest are as follows:
|
GPS Geofencing
A geofence is a virtually defined boundary for a real-world geographic area. The GPS Geofencing page provides you with the possibility to set this custom area and apply rules that will inform you when the device leaves or enters the geofence.
[[File:{{{file_geofencing_add}}}]]
The figure below is an example of GPS Geofencing configuration and the table below provides information related to that configuration:
[[File:{{{file_geofencing_details}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Turns the Geofence rule on or off |
| Longitude (X) | degrees [-180.000000..180.000000]; default: 0.000000 | East-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. Combining this and the Latitude information will produce a point on the world map that will serve as the center of the geofence area. |
| Latitude (Y) | degrees [-90.000000..90.000000]; default: 0.000000 | North-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Combining this and the Longitude information will produce a point on the world map that will serve as the center of the geofence area. |
| Radius | integer [1..999999]; default: 200 | Radius (in meters) of the geofence area. |
| Generate event on | Exit | Enter | Enter/exit; default: Exit | Specifies whether the rule should be triggered when the device enters the geofence area, leaves it or on both events. |
| Get current coordinates | - (interactive button) | Obtains the device's current coordinates and places them in the Longitude and Latitude fields. |
See also
- [[{{{name}}} GPS Protocols]]
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]