Relayd
Introduction
Relayd is a daemon to relay and dynamically redirect incoming connections to a target host. Its main purpose in RUT routers is extending the wireless network. For example, when RUT is in STA (Wireless Station) mode, it can be used to bridge WAN and LAN interfaces to create a larger Wireless network.
This article will provide an extensive configuration example of a basic Relayd usage scenario with RUT devices.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- Two RUT routers
- An end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone)
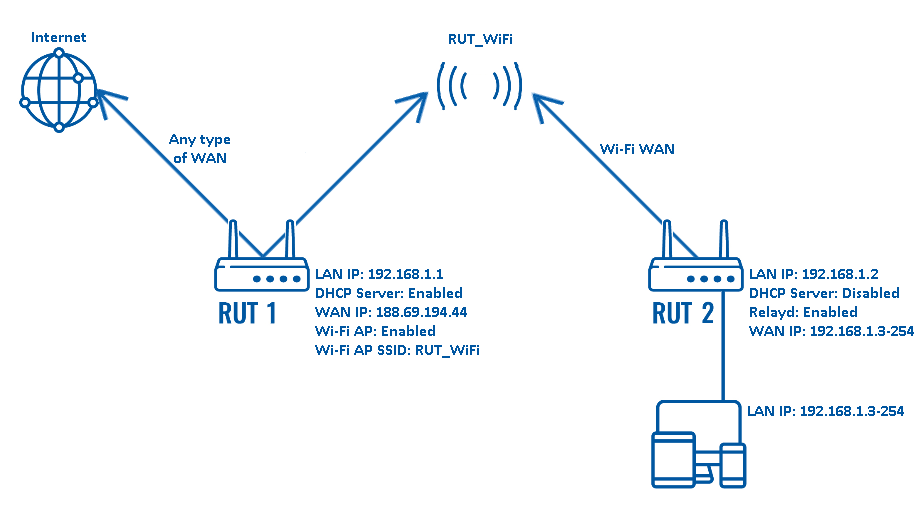
Configuration scheme:
The scheme depicts two RUT routers - RUT1 and RUT2. RUT1 has access to the Internet through an undefined type of WAN (it can be any). RUT2 acts as a Wi-Fi Station (STA) and gains access to the Internet via RUT1's Wi-Fi Access Point (AP) (SSID: RUT_WiFi). RUT2's DHCP Server is disabled. This is done so that the end devices connected to RUT2 get IP addresses from RUT1's DHCP Server with the help of Relayd.
So in short, this type of configuration connects devices from different networks into a single network, making it possible for the devices to communicate with each other and providing the devices with an Internet connection.