RUTX DMVPN
Introduction
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) is a dynamic tunneling form of a virtual private network (VPN) supported on Cisco routers. This article contains step-by-step instructions on how to configure DMVPN between a "HUB" and two "Spokes" using RUTXxx routers.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- At least two RUTXxx routers
- A PC to configure the routers
- HUB has to be reachable from spokes (HUB must have Public IP address, or has to be in the same WAN network as Spokes)
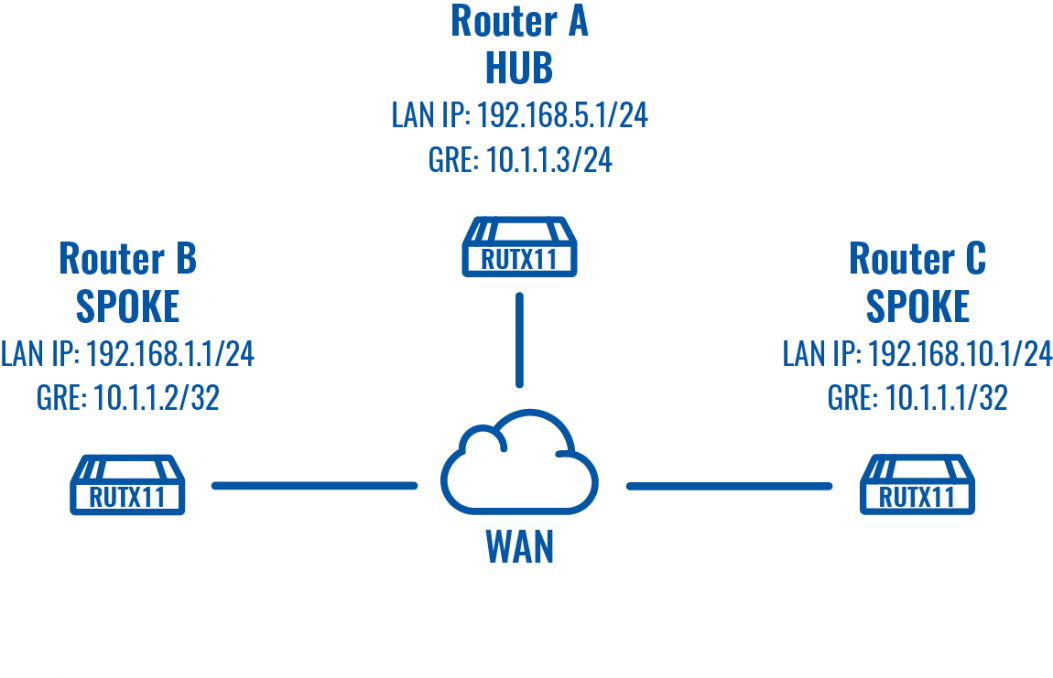
Configuration scheme
Spoke configuration
This section contains information on how to configure DMVPN Spokes. Firstly, we'll configure the DMVPN instance to make the connection possible. Then we'll set the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) parameters as our dynamic routing solution.
Note: at the moment, BGP is the only stable dynamic routing solution that can work with DMVPNs.
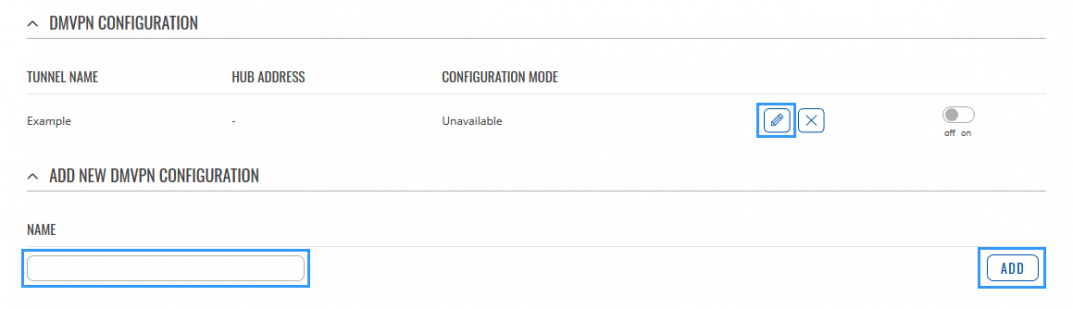
STEP 1: Connect to router's WebUI, go to Services > VPN > DMVPN. Enter a name for your DMVPN instance, click ADD and when instance appears in DMVPN CONFIGURATION field, click Edit.
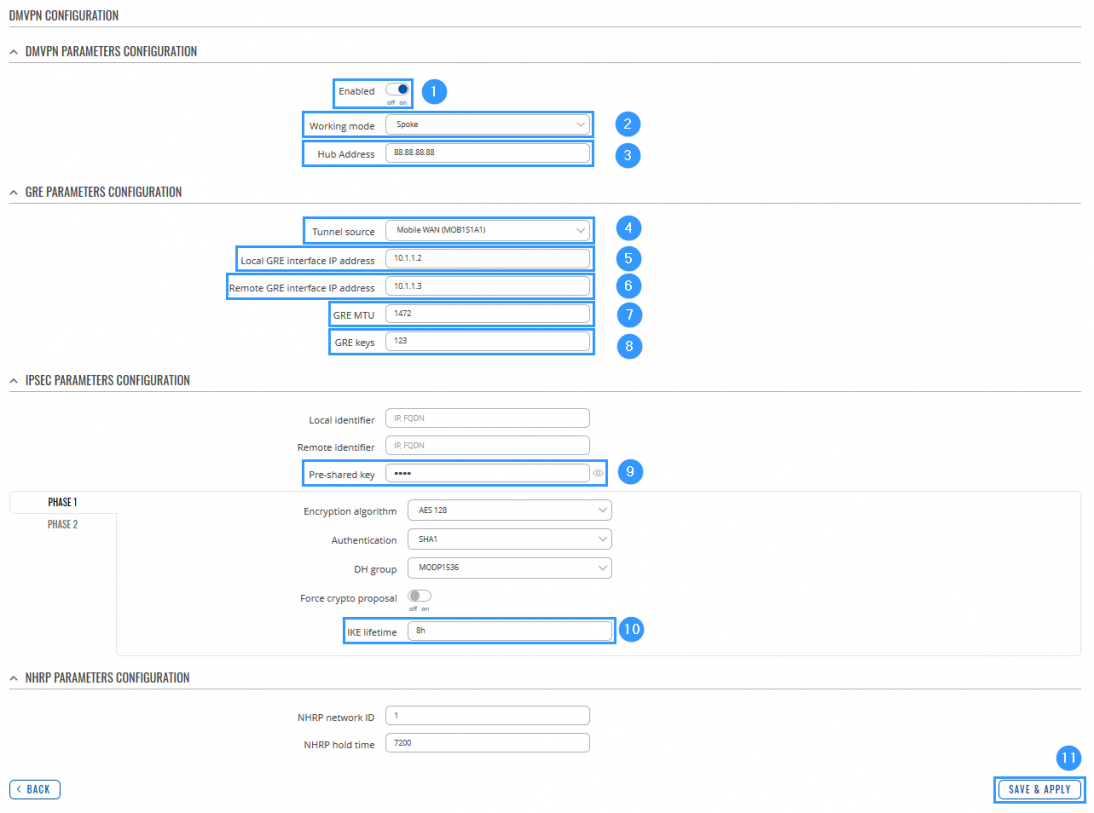
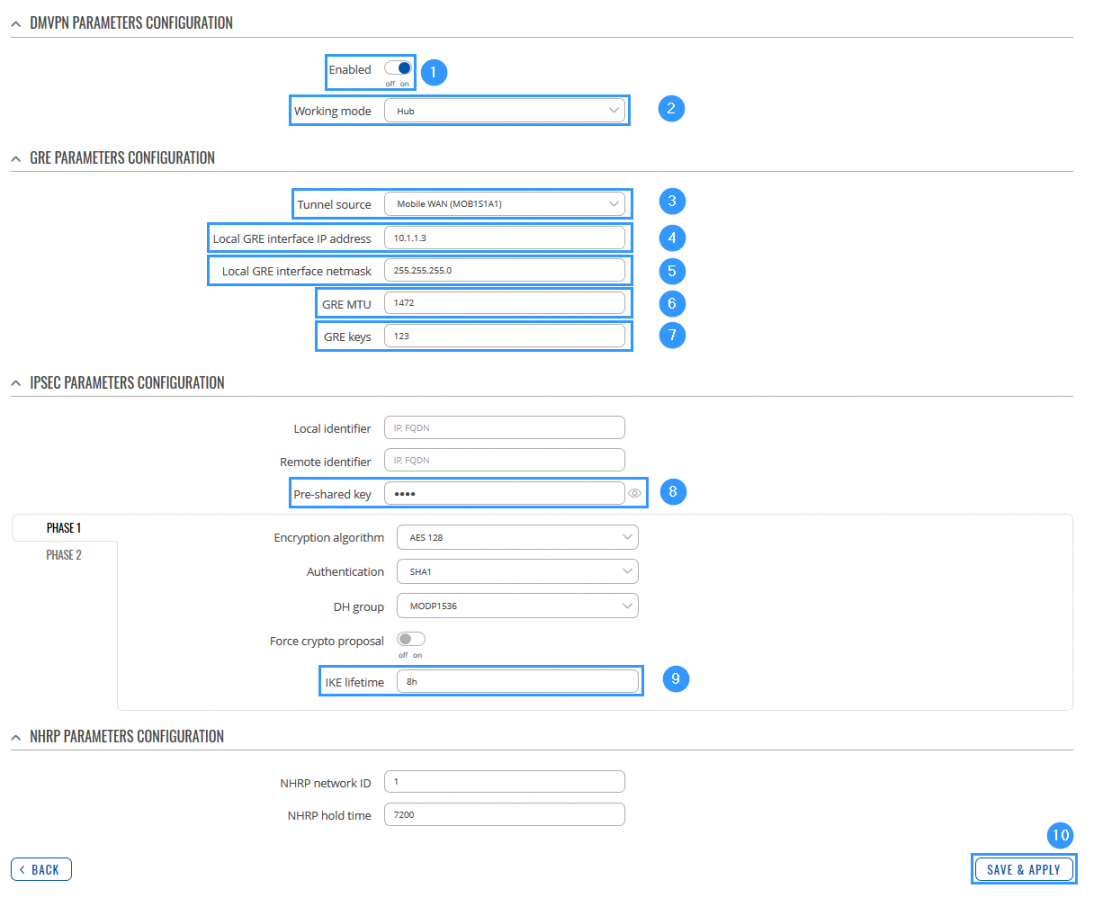
STEP 2: Configure DMVPN settings.
- Enable instance.
- Select Working mode (Spoke).
- Enter HUB Address (HUB WAN IP).
- Select Tunnel source (select your WAN interface).
- Write Local GRE interface IP address (create GRE tunnel IP address or just use the same as in the example).
- Write Remote GRE interface IP address (create GRE tunnel IP address or just use the same as in the example).
- Add GRE MTU (largest PDU size of any single transaction).
- Write GRE keys (it must match with HUB and other Spokes).
- Add Pre-shared key (it must match HUB and other Spokes).
- Write IKE lifetime (how long the keying channel of a connection should last before being renegotiated). P.S. do that in PHASE 1 and PHASE 2.
- Leave everything else as default and click Save & Apply.
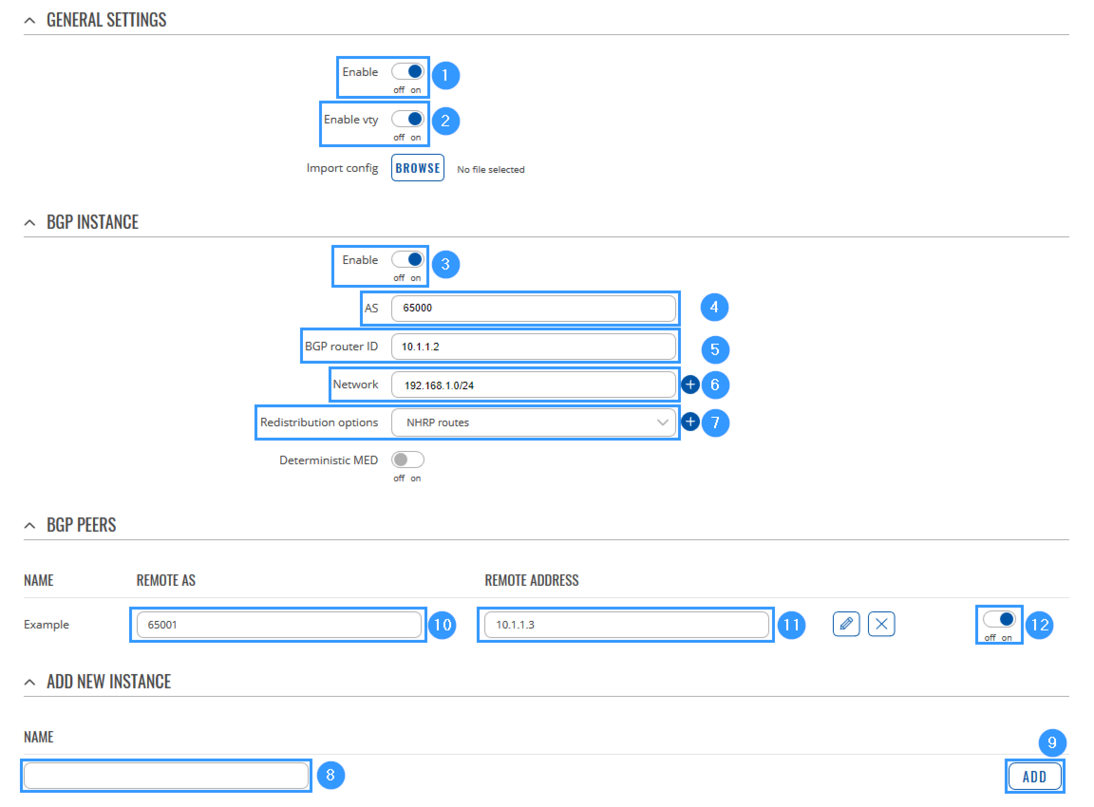
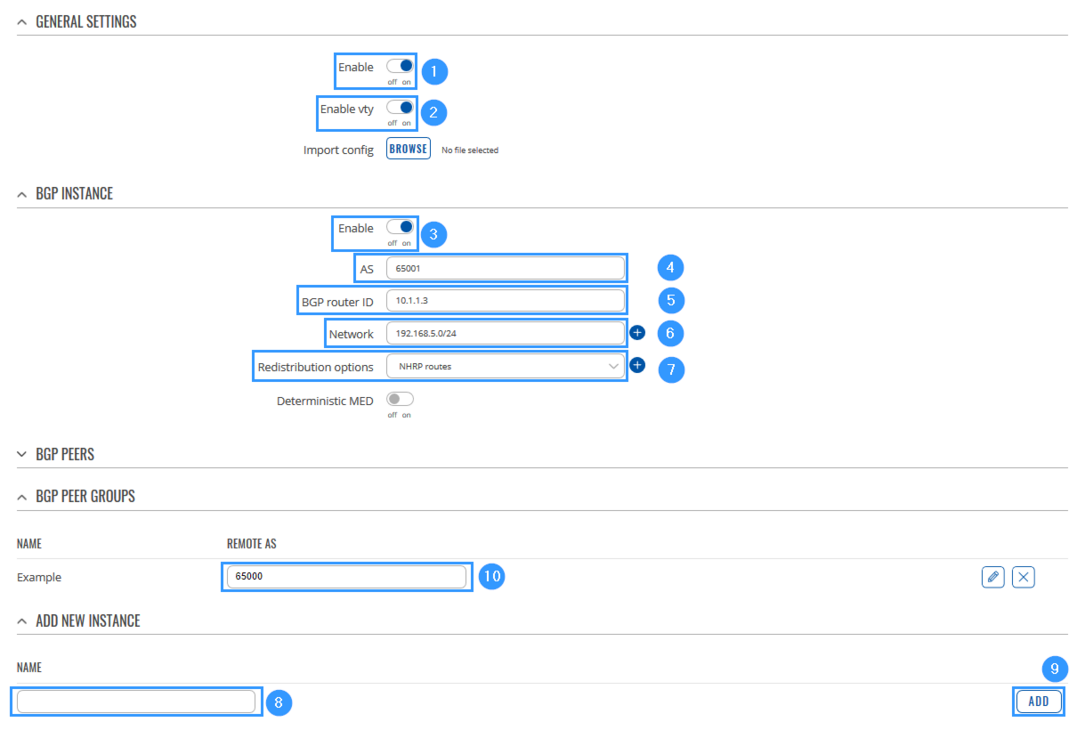
STEP 3: Go to Network > Routing > Dynamic Routes > BGP and make the necessary configuration.
- Enable instance.
- Enable vty instance.
- Enable BGP Instance.
- Add AS (Autonomous system name, it must match with other Spokes).
- Write BGP router ID (SPOKE GRE Tunnel IP).
- Add Network (SPOKE LAN network IP with subnet mask).
- Select Redistribution options.
- Write a Name of the new instance (anything you want).
- Press Add button and then new BGP peer will appear.
- Add REMOTE AS (HUB GRE Tunnel IP).
- Write REMOTE ADDRESS (HUB GRE IP).
- Enable peer.
- Leave everything else as default and click Save & Apply.
Repeat this on different routers as many times as the number of Spokes that you need. Remember that other Spokes will have different LAN, WAN and GRE IP addresses.
HUB configuration
This section contains information on how to configure DMVPN HUB.
STEP 1: Connect to router's WebUI, go to Services > VPN > DMVPN. Enter a name for your DMVPN instance, click ADD and when instance appears in DMVPN CONFIGURATION field, click Edit.
STEP 2: Configure DMVPN settings.
- Enable instance.
- Select Working mode.
- Select Tunnel source (select your WAN interface).
- Write Local GRE interface IP address (create GRE tunnel IP address or just use the same as in the example).
- Write Local GRE interface netmask.
- Add GRE MTU (largest PDU size of any single transaction).
- Write GRE keys (it must match with HUB and other Spokes).
- Add Pre-shared key (it must match HUB and other Spokes).
- Write IKE lifetime (how long the keying channel of a connection should last before being renegotiated). P.S. do that in PHASE 1 and PHASE 2.
- Leave everything else as default and click Save & Apply.
STEP 3: Go to Network > Routing > Dynamic Routes > BGP and make the necessary configuration.
- Enable instance.
- Enable vty instance.
- Enable BGP Instance.
- Add AS (Autonomous system name).
- Write BGP router ID (HUB GRE Tunnel IP).
- Add Network (HUB LAN network IP with subnet mask).
- Select Redistribution options.
- Write BGP PEER GROUP NAME (anything you want).
- Press ADD button and then new BGP PEER GROUP will appear.
- Add REMOTE AS (it must match AS of other DMVPN spokes).
- Leave everything else as default and click Save & Apply.
Testing configuration
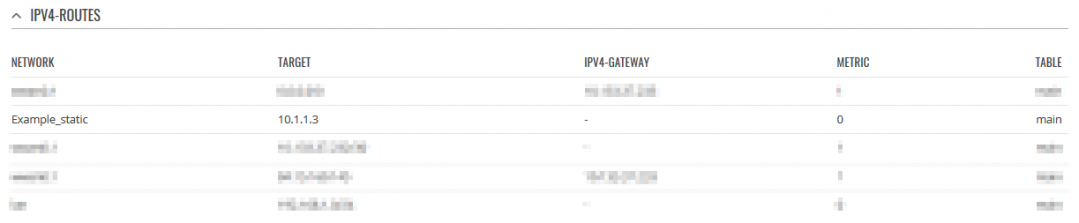
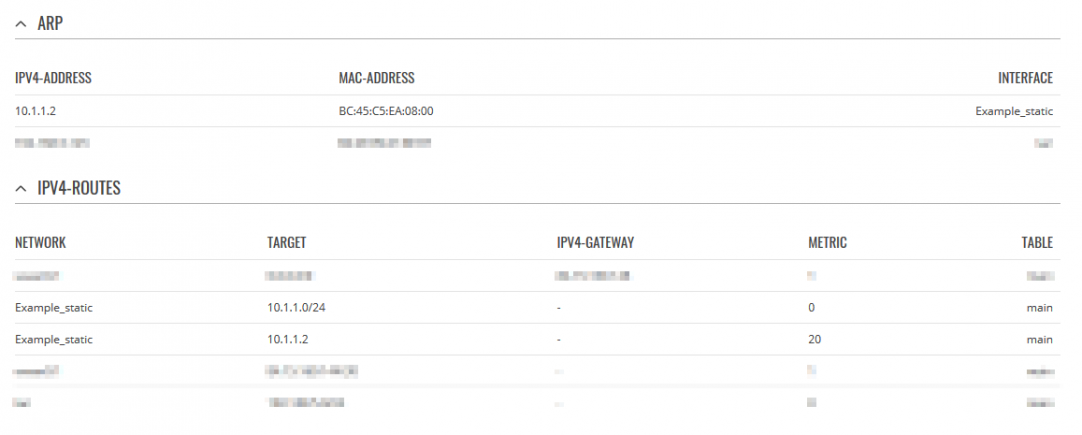
Access HUB and Spoke WebUI, check whether new routes appeared (it should look similar to the examples).
SPOKE:
HUB: