Difference between revisions of "Command line interfaces"
(Redirected page to Command Line Interfaces) Tag: New redirect |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | #REDIRECT [[Command Line Interfaces]] | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
A '''command line interface''' ('''CLI''') is a means of interacting with a computer program or system where the user (or client) issues commands to the program in the form of successive lines of text (command lines). A program which handles the interface is called a '''command language interpreter''' or '''shell'''. | A '''command line interface''' ('''CLI''') is a means of interacting with a computer program or system where the user (or client) issues commands to the program in the form of successive lines of text (command lines). A program which handles the interface is called a '''command language interpreter''' or '''shell'''. | ||
| − | + | RUTxxx routers support a variety of different command line interfaces all of which will be described in this article. Only the methods of reaching and logging in via a specified CLI will be described here and not any specific command usage. | |
| − | In all cases, CLI login information for | + | In all cases, CLI login information for RUTxxx routers is: |
* User name: '''root''' | * User name: '''root''' | ||
| − | * Password: '''router's admin password''' | + | * Password: '''router's admin password''' |
==CLI (WebUI)== | ==CLI (WebUI)== | ||
| − | + | RUTxxx routers have a command line interface built-in to their '''Web User Interfaces''' ('''WebUI'''). This is the most accessible method because all you need is web browser. | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | * Simply login to the WebUI by typing the router's LAN IP address into the URL field of your web browser and press "Enter" on your keyboard: | ||
| − | + | [[File:Enabling remote access for rms part 1 v2.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
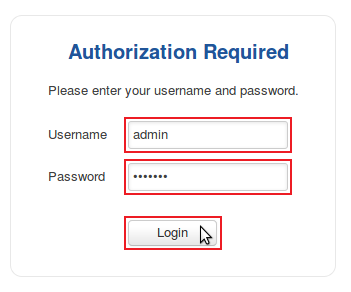
| − | * After this, you will be greeted with the | + | * After this, you will be greeted with the login window. Type in the user name '''admin''' and the router's admin password and click "Login": |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Rut login page configuration examples version.png]] |
---- | ---- | ||
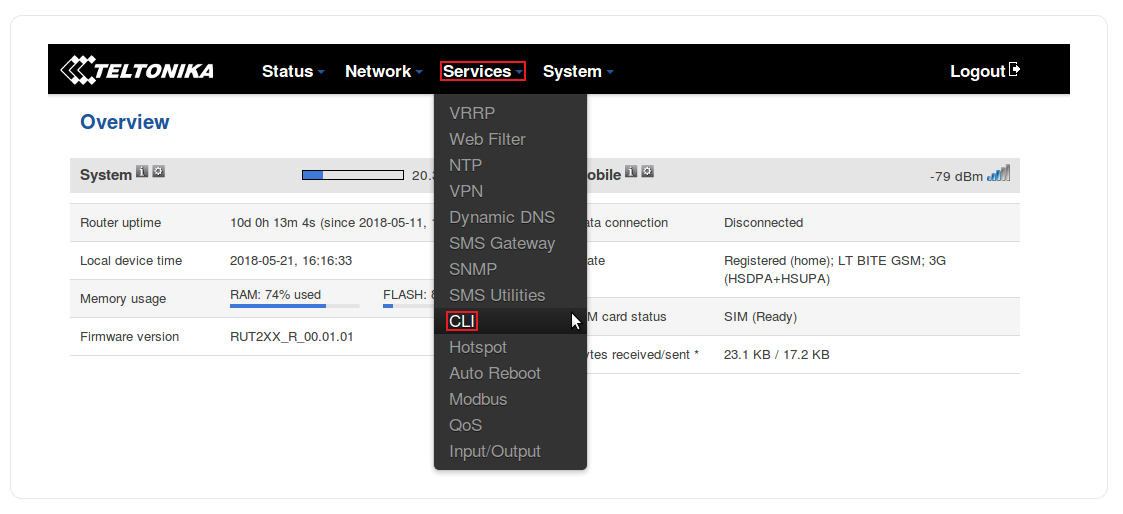
| − | * Then locate CLI under the Services tab: | + | * Then locate the CLI section under the Services tab: |
| − | [[File:How to locate cli.png]] | + | [[File:How to locate cli v2.png]] |
---- | ---- | ||
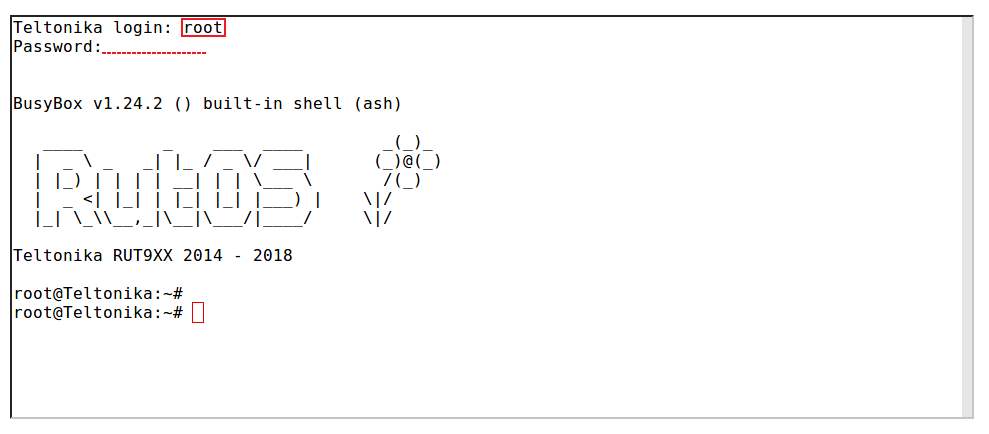
| − | * Type in the | + | * Type in the login name ''root'', press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. You should be greeted with a message such as this: |
| − | [[File:Cli rutos.PNG]] | + | [[File:Cli rutos v3.PNG]] |
==SSH== | ==SSH== | ||
| − | '''Secure Shell''' (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. The best known example application is for remote login to computer systems by users. The login process is different for different operating systems. Therefore, this section is split into two | + | '''Secure Shell''' (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. The best known example application is for remote login to computer systems by users. The login process is different for different operating systems. Therefore, this section is split into two parts: '''Linux''' and '''Windows'''. |
===Linux=== | ===Linux=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | Linux operating systems support many applications that can be used to | + | Linux operating systems support many applications that can be used to login to a RUTxxx router via SSH, but the most common is '''Terminal''', which we'll be using for this example. |
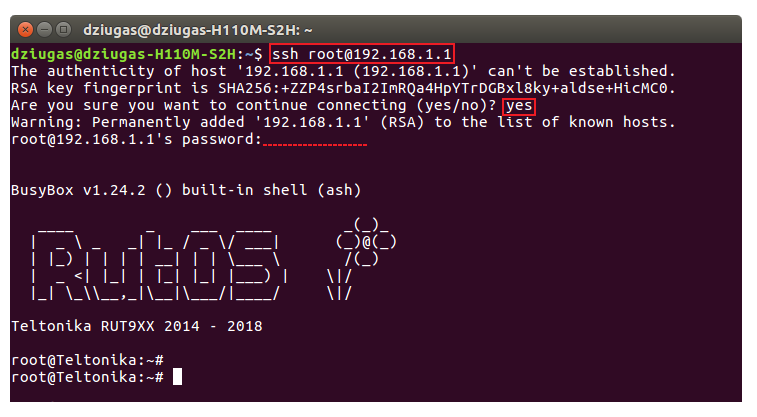
| − | * Open a new Terminal window, type '''ssh [email protected]''' and press "Enter". If this is your first time logging in, you might be asked to clarify whether you really want to | + | * Open a new Terminal window, type '''ssh [email protected]''' and press "Enter". If this is your first time logging in, you might be asked to clarify whether you really want to login. In that case, just type '''yes''' and press "Enter". Then type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" to finish the login process: |
| − | [[File:Ssh linux login.png]] | + | [[File:Ssh linux login v2.png]] |
After this you should be greeted with a window such as the one depicted in the figure above. | After this you should be greeted with a window such as the one depicted in the figure above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====RSA key==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is a possibility to use an RSA key instead of a password when logging in via SSH. This process is described '''[[SSH RSA key authentication (Linux)|here]]''' in detail. | ||
===Windows=== | ===Windows=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | To | + | To login to a RUTxxx router via SSH using a Windows OS you will need an SSH client application. The most common is '''PuTTY''' - free, open source SSH and Telnet client, which we'll be using for this example. You can download PuTTY from '''[https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html here]'''. |
| + | ---- | ||
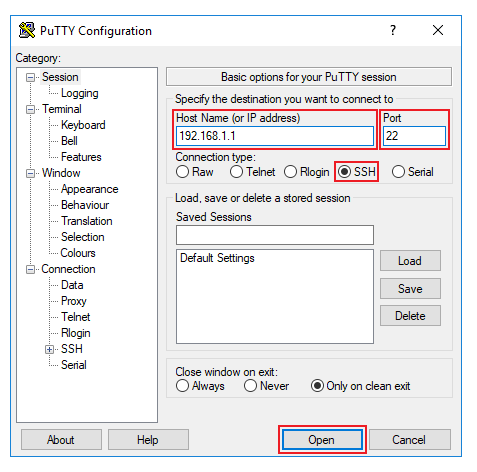
| + | * Launch PuTTY and select the '''SSH''' option under the "Connection type" field. Type in the router's LAN IP address into the "Host Name (or IP address)" field, specify the SSH port into the "Port" field ('''22''' by default) and click "Open": | ||
| − | * | + | [[File:Putty login 1 v2.PNG]] |
| + | ---- | ||
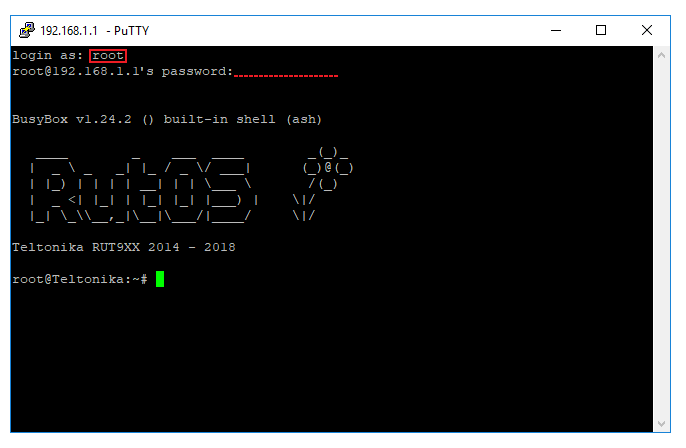
| + | * In the next window type in the login name ''root'', press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. You should be greeted with a message such as this: | ||
| − | [[File:Putty login | + | [[File:Putty login 2 v2.PNG]] |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | ====RSA key==== | |
| − | [[ | + | There is a possibility to use an RSA key instead of a password when logging in via SSH. This process is described '''[[SSH RSA key authentication (Windows)|here]]''' in detail. |
==RS232/RS485 console (only with RUT955)== | ==RS232/RS485 console (only with RUT955)== | ||
| − | It is also possible to control a RUT955 router via | + | It is also possible to control a RUT955 router via RS232 or RS485 consoles. For this, however, you will need the adequate cables: |
<font size="-1"> | <font size="-1"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid white; background: white" | {| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid white; background: white" | ||
| Line 64: | Line 73: | ||
| style="border:1px solid white; width: 400px" | '''Straight-through Female/Male RS232 cable''' <br> [[File:Services rs232 connector female male.PNG|300px|left]] | | style="border:1px solid white; width: 400px" | '''Straight-through Female/Male RS232 cable''' <br> [[File:Services rs232 connector female male.PNG|300px|left]] | ||
| style="border:1px solid white; width: 400px" | '''Null-modem (crossed) Male/Male RS232 cable''' <br> [[File:Male male rs232 cable.jpg|230px|left]] | | style="border:1px solid white; width: 400px" | '''Null-modem (crossed) Male/Male RS232 cable''' <br> [[File:Male male rs232 cable.jpg|230px|left]] | ||
| − | | style="border:1px solid white; width: 400px" | '''USB to RS232 ( | + | | style="border:1px solid white; width: 400px" | '''USB to RS232 (Male) cable''' <br> [[File:Usb to rs232 male.png|187px|left]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
</font> | </font> | ||
| − | You can | + | You can login to the RS485 console with a 2-wire cable. You can use the RS485 jack that comes with the router for one end; the other end of the cable basically depends on your end device's capabilities (it can be USB, RS232, etc.) |
===Router configuration=== | ===Router configuration=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
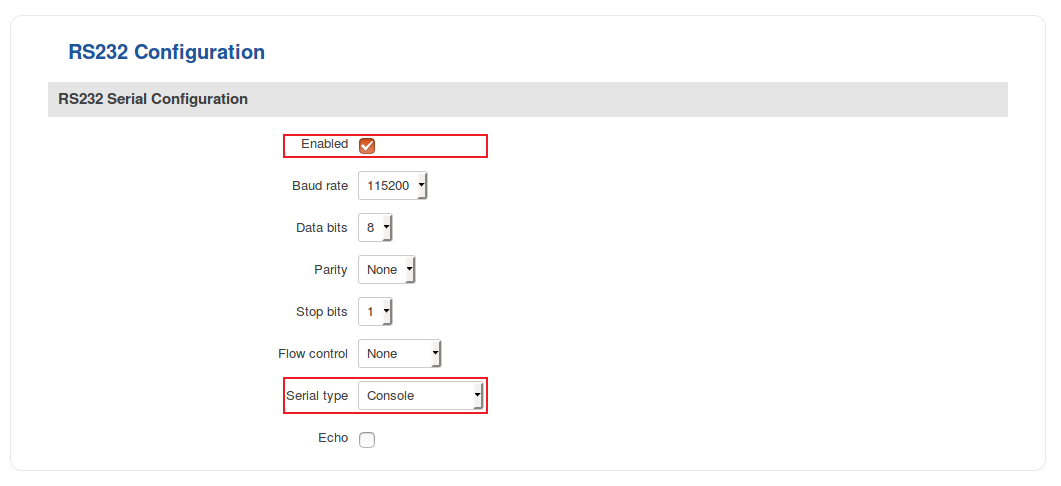
| − | The configuration for the router's side is fairly simple. Just | + | * The configuration for the router's side is fairly simple. Just login to the router's WebUI, go to '''Services → RS232/RS485''', place a check mark next to the "Enable" field and select "Serial type: Console" (the same is true for both RS232 and RS485): |
| − | [[File:Rs232 console configuration.png]] | + | [[File:Rs232 console configuration v2.png]] |
You can leave the rest of the settings as defaults or set them in accordance with your needs. Don't forget to click save after you have made the changes. | You can leave the rest of the settings as defaults or set them in accordance with your needs. Don't forget to click save after you have made the changes. | ||
| Line 81: | Line 90: | ||
===Linux=== | ===Linux=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | To | + | * To login from a Linux PC, you'll need an application for serial communication like '''minicom''' or '''gtkterm'''. For this example we'll be using minicom. You can download it by typing these lines into the Terminal: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
$ sudo apt-get update | $ sudo apt-get update | ||
| Line 90: | Line 97: | ||
'''update''' downloads a list of newest software packages; '''install minicom''' downloads and installs minicom. | '''update''' downloads a list of newest software packages; '''install minicom''' downloads and installs minicom. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
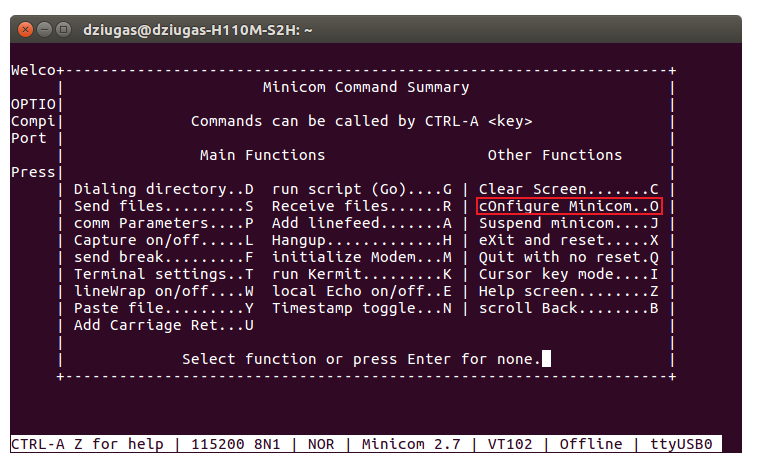
| − | * Once you've installed minicom, you can run it with the command '''sudo minicom'''. This will open a new console window where you will need to set some things up. Press '''Ctrl + A''' at once on your keyboard, then press | + | * Once you've installed minicom, you can run it with the command '''sudo minicom''' from the Linux Terminal. This will open a new console window where you will need to set some things up. Press '''Ctrl + A''' at once on your keyboard, then press "Z" which will direct you to the settings menu: |
| − | [[File:Minicom settings.png]] | + | [[File:Minicom settings v2.png]] |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | * | + | * Press "O" on your keyboard. This will direct you to the main settings menu. From there you should specify the name of the serial device and the same parameters that you entered in the router's configuration. A picture with corresponding parameters is presented below: |
| − | [[File:Minicom settings port.png]] | + | [[File:Minicom settings port v2.png]] |
| − | Once done press "Enter". In the next menu you can save these settings as defaults by selecting '''Save setup as dfl''' so that you wouldn't need to set everything up the next time you use the console. | + | Once done, press "Enter". In the next menu you can save these settings as defaults by selecting '''Save setup as dfl''' so that you wouldn't need to set everything up the next time you use the console. |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | * Press "Esc" on your keyboard to return to the console window and type in the | + | * Press "Esc" on your keyboard to return to the console window and type in the login name ''root'', press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. After this, you will be able to use the RS232/RS485 console. |
===Windows=== | ===Windows=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | To | + | To login from a Windows PC, you'll need an application for serial communication. The most common is '''PuTTY''' - free, open source SSH and Telnet client, which we'll be using for this example. You can download PuTTY from '''[https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html here]'''. |
| + | ---- | ||
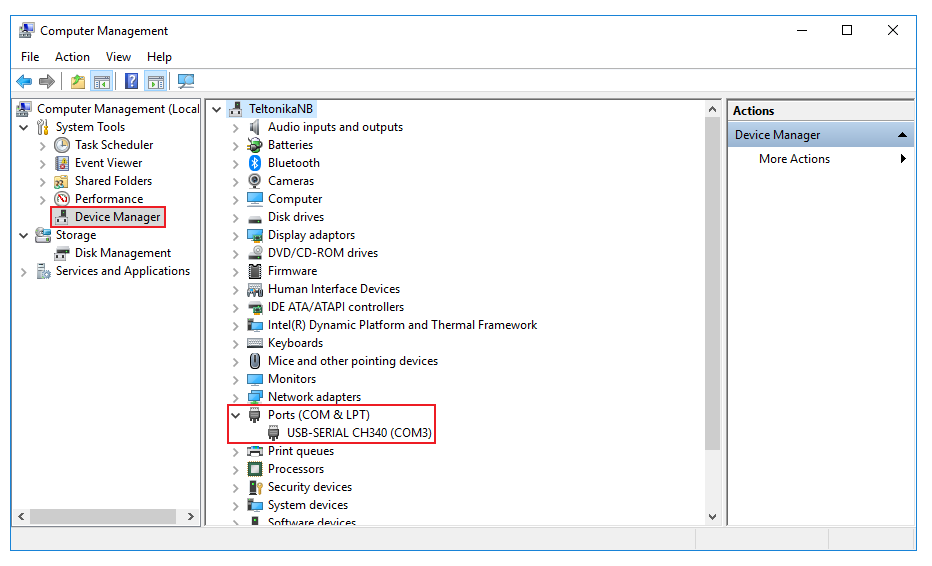
| + | * First you must find out which '''Serial line''' (or '''COM port''') your cable uses. To do so, go to Windows '''Device Manager''' (you can find it easily via the search field or in the Control Panel). Find '''Ports (COM & LPT)''' in the device list and expand that section. Locate your serial device (depends on the type of cable) and take note of its '''COM port number''' ('''COM3''' in our example): | ||
| − | * | + | [[File:Putty serial login 1 v2.PNG]] |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | * Launch PuTTY and select the '''Serial''' option under the "Connection type" field. Specify the COM port ('''COM3''' from our example) in the "Serial line" field and the Baud rate from your router's configuration in the "Speed" field ('''115200''' from our example) and click "Open": | ||
| − | [[File:Putty serial login | + | [[File:Putty serial login 2 v2.PNG]] |
---- | ---- | ||
| − | * | + | * In the next window type in the login name ''root'', press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. You should be greeted with a message such as this: |
| − | [[File:Putty serial login | + | [[File:Putty serial login 3 v2.PNG]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==See also== | |
| − | [[ | + | * [[SSH RSA key authentication (Linux)]] |
| + | * [[SSH RSA key authentication (Windows)]] | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html - PuTTY | + | * https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html - PuTTY downloads page |
Latest revision as of 12:45, 17 June 2020
Pages with broken file links > Command line interfacesRedirect to:
Introduction
A command line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with a computer program or system where the user (or client) issues commands to the program in the form of successive lines of text (command lines). A program which handles the interface is called a command language interpreter or shell.
RUTxxx routers support a variety of different command line interfaces all of which will be described in this article. Only the methods of reaching and logging in via a specified CLI will be described here and not any specific command usage.
In all cases, CLI login information for RUTxxx routers is:
- User name: root
- Password: router's admin password
CLI (WebUI)
RUTxxx routers have a command line interface built-in to their Web User Interfaces (WebUI). This is the most accessible method because all you need is web browser.
- Simply login to the WebUI by typing the router's LAN IP address into the URL field of your web browser and press "Enter" on your keyboard:
- After this, you will be greeted with the login window. Type in the user name admin and the router's admin password and click "Login":
- Then locate the CLI section under the Services tab:
- Type in the login name root, press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. You should be greeted with a message such as this:
SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. The best known example application is for remote login to computer systems by users. The login process is different for different operating systems. Therefore, this section is split into two parts: Linux and Windows.
Linux
Linux operating systems support many applications that can be used to login to a RUTxxx router via SSH, but the most common is Terminal, which we'll be using for this example.
- Open a new Terminal window, type ssh [email protected] and press "Enter". If this is your first time logging in, you might be asked to clarify whether you really want to login. In that case, just type yes and press "Enter". Then type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" to finish the login process:
After this you should be greeted with a window such as the one depicted in the figure above.
RSA key
There is a possibility to use an RSA key instead of a password when logging in via SSH. This process is described here in detail.
Windows
To login to a RUTxxx router via SSH using a Windows OS you will need an SSH client application. The most common is PuTTY - free, open source SSH and Telnet client, which we'll be using for this example. You can download PuTTY from here.
- Launch PuTTY and select the SSH option under the "Connection type" field. Type in the router's LAN IP address into the "Host Name (or IP address)" field, specify the SSH port into the "Port" field (22 by default) and click "Open":
- In the next window type in the login name root, press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. You should be greeted with a message such as this:
RSA key
There is a possibility to use an RSA key instead of a password when logging in via SSH. This process is described here in detail.
RS232/RS485 console (only with RUT955)
It is also possible to control a RUT955 router via RS232 or RS485 consoles. For this, however, you will need the adequate cables:
| Straight-through Female/Male RS232 cable |
Null-modem (crossed) Male/Male RS232 cable |
USB to RS232 (Male) cable |
You can login to the RS485 console with a 2-wire cable. You can use the RS485 jack that comes with the router for one end; the other end of the cable basically depends on your end device's capabilities (it can be USB, RS232, etc.)
Router configuration
- The configuration for the router's side is fairly simple. Just login to the router's WebUI, go to Services → RS232/RS485, place a check mark next to the "Enable" field and select "Serial type: Console" (the same is true for both RS232 and RS485):
You can leave the rest of the settings as defaults or set them in accordance with your needs. Don't forget to click save after you have made the changes.
Linux
- To login from a Linux PC, you'll need an application for serial communication like minicom or gtkterm. For this example we'll be using minicom. You can download it by typing these lines into the Terminal:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install minicom
update downloads a list of newest software packages; install minicom downloads and installs minicom.
- Once you've installed minicom, you can run it with the command sudo minicom from the Linux Terminal. This will open a new console window where you will need to set some things up. Press Ctrl + A at once on your keyboard, then press "Z" which will direct you to the settings menu:
- Press "O" on your keyboard. This will direct you to the main settings menu. From there you should specify the name of the serial device and the same parameters that you entered in the router's configuration. A picture with corresponding parameters is presented below:
File:Minicom settings port v2.png
Once done, press "Enter". In the next menu you can save these settings as defaults by selecting Save setup as dfl so that you wouldn't need to set everything up the next time you use the console.
- Press "Esc" on your keyboard to return to the console window and type in the login name root, press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. After this, you will be able to use the RS232/RS485 console.
Windows
To login from a Windows PC, you'll need an application for serial communication. The most common is PuTTY - free, open source SSH and Telnet client, which we'll be using for this example. You can download PuTTY from here.
- First you must find out which Serial line (or COM port) your cable uses. To do so, go to Windows Device Manager (you can find it easily via the search field or in the Control Panel). Find Ports (COM & LPT) in the device list and expand that section. Locate your serial device (depends on the type of cable) and take note of its COM port number (COM3 in our example):
- Launch PuTTY and select the Serial option under the "Connection type" field. Specify the COM port (COM3 from our example) in the "Serial line" field and the Baud rate from your router's configuration in the "Speed" field (115200 from our example) and click "Open":
File:Putty serial login 2 v2.PNG
- In the next window type in the login name root, press "Enter", type in the router's admin password and press "Enter" again. You should be greeted with a message such as this:
File:Putty serial login 3 v2.PNG
See also
External links
- https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html - PuTTY downloads page