Difference between revisions of "How to use UBUS commands for Bluetooth device scanning / pairing"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
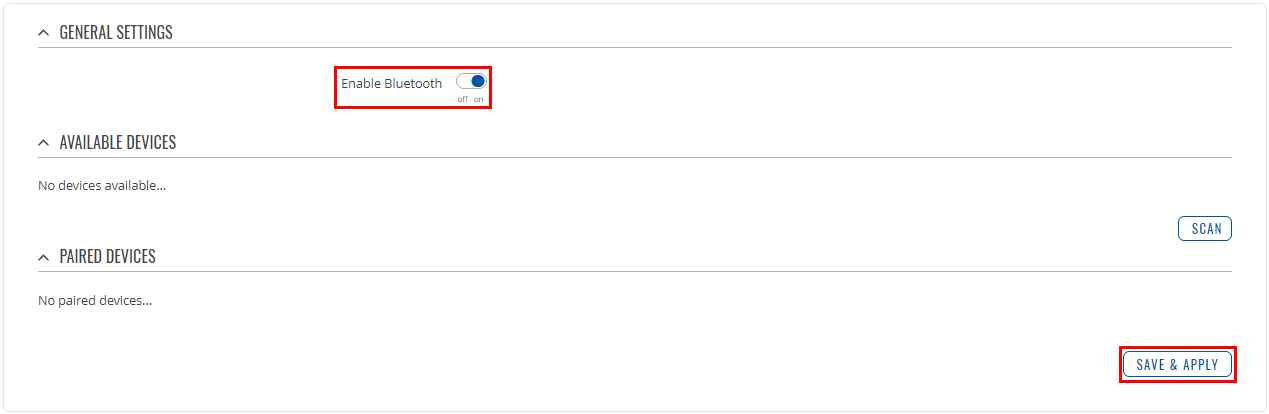
| − | Before you start using ubus commands to control Bluetooth, make sure to enable it in '''Network -> Bluetooth -> General''' settings. Click '''Save & Apply'''. | + | Before you start using ubus commands to control Bluetooth, make sure to enable it. You can do that in '''Network -> Bluetooth -> General''' settings. Click '''Enable Bluetooth''' and press '''Save & Apply'''. |
[[File:Networking_rutx_configuration_example_bluetooth_enable_v1.png]] | [[File:Networking_rutx_configuration_example_bluetooth_enable_v1.png]] | ||
| − | * | + | *Now login to [[CLI]] or SSH and run '''scan.start''' command to start Bluetooth scan: |
... | ... | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 24 April 2020
Main Page > General Information > Configuration Examples > Hardware application > How to use UBUS commands for Bluetooth device scanning / pairingThis page contains instructions on how to use ubus commands in CLI / SSH to scan and pair Bluetooth devices on RUTX10/11.
The ubus command line tool allows to interact with the ubusd server (with all currently registered services). It's useful for investigating/debugging registered namespaces as well as writing shell scripts. For calling procedures with parameters and returning responses it uses the user-friendly JSON format.
Before you start using ubus commands to control Bluetooth, make sure to enable it. You can do that in Network -> Bluetooth -> General settings. Click Enable Bluetooth and press Save & Apply.
- Now login to CLI or SSH and run scan.start command to start Bluetooth scan:
... ubus call blesem scan.start ...
- To see scan results, use command scan.result:
... ubus call blesem scan.result ...
The scan takes about 30 seconds. The "scanning": 1 output shows us that scan still in progress. After it finishes you should see a similar output:
...
{
"scanning": 0,
"devices": [
{
"name": "RT_T",
"rssi": -72,
"address": "FF:CB:FA:6A:23:CB"
}
]
}
...
The list of devices always contains "rssi" and "address", but "name" output might be missing:
...
{
"scanning": 0,
"devices": [
{
"rssi": -42,
"address": "28:21:06:02:72:AD"
},
{
"name": "RT_T",
"rssi": -77,
"address": "C6:0D:52:5E:35:D7"
}
]
}
...
- Device pairing command:
...
ubus call blesem pair '{"address":"FF:CB:FA:6A:23:CB"}'
...
On success pairing you should see output:
...
{
"success": "device successfully paired"
}
...
On success pairing new device info will be written in blesem service config:
...
config device
option address "FF:CB:FA:6A:23:CB"
...
- Device unpairing command:
...
ubus call blesem unpair '{"address":"FF:CB:FA:6A:23:CB"}'
...
- To get statistic from paired devices, use stat command:
...
ubus call blesem stat '{"address":"FF:CB:FA:6A:23:CB"}'
...
You should see output:
...
{
"success": "successfully requested status",
"model": "3901",
"battery": 98,
"temperature": "20.34",
"humidity": 20,
"firmware": "23",
.
}
...