TRB140 Powering Options
This chapter contains information on powering options supported by TRB140 devices.
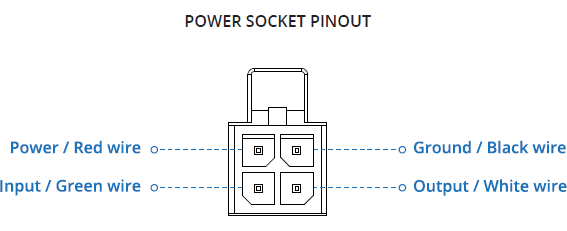
Power socket
The TRB140 device can be powered over the 4 pin connector using a 9-30 VDC power supply unit (PSU). Refer to the image below for the power socket pinout information:
If you decide not to use the standard 9 VDC PSU and want to power the device from a higher voltage, please make sure that you choose a power supply of high quality. Some power supplies can produce voltage peaks significantly higher than the declared output voltage, especially during connection and disconnection.
While the device is designed to accept input voltage in the range of 9-30 VDC, high voltage power supplies can harm the device. If you want to use high voltage power supplies it is recommended to also use additional safety equipment to suppress voltage peaks from the power supply.
Passive PoE
The device may also be powered via the Ethernet port:
- TRB140 devices support PPoE from HW revision 0007
- The device is NOT COMPLIANT with the IEEE 802.3af-2003 standard: powering the device from an IEEE 802.3af-2003 power supply will damage the device as it is not rated for input voltages of the PoE standard.
- The device is NOT COMPLIANT with the IEEE 802.3at standard: it cannot power other devices over Ethernet.
Simultaneous powering
The device can be powered from the power socket and over Ethernet simultaneously. If device batch number is between 1 and 11, both PSUs should have similar output voltages. Meanwhile, devices manufactured from batch number 12 can have different voltage PSUs connected to its power socket and Ethernet port. The power socket has higher priority meaning that the device will draw power from the power socket as long as it is available. When the device is switching from one power source to another it loses power for a fraction of a second and may reboot. The device will function correctly after the reboot.
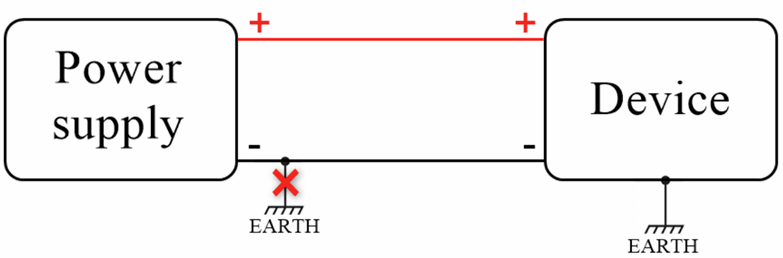
Ground loops
Do not connect the power supply negative terminal of our device to the chassis or earth exclusively.
This connection could cause ground loops. For example, if the antenna shield and power supply negative terminal are connected to the chassis or earth, it forms a ground loop, therefore unwanted current could flow through a device PCB ground and may cause damage.