Difference between revisions of "Template:Networking rut cloud of things"
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 3.png]] | [[Image:Cloud of things adding device 3.png]] | ||
| − | There are two ways to register your device(s) '''Bulk''' and '''General'''. Bulk is used | + | There are two ways to register your device(s) '''Bulk''' and '''General'''. Bulk is used when you are registering a lot of devices at once. In this example we will be using the '''General''' option. |
[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 4.png]] | [[Image:Cloud of things adding device 4.png]] | ||
| + | In '''Device ID''' section write the serial number of your router. You can add more than one item by pressing '''Add another device''' button. There is a possibility to assign your routers to groups, but we are not doing that in this example.[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 5.png]] | ||
| − | + | If everything was done correctly, it will show you that the registration was successful. | |
[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 6.png]] | [[Image:Cloud of things adding device 6.png]] | ||
| − | Then | + | Then you will need to '''Accept''' the '''Pending Acceptance'''. |
[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 7.png]] | [[Image:Cloud of things adding device 7.png]] | ||
| − | + | Finally you will receive a message showing that the device has been accepted.d. | |
| + | |||
[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 8.png]] | [[Image:Cloud of things adding device 8.png]] | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Image:Cloud of things adding device 9.png]] | [[Image:Cloud of things adding device 9.png]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
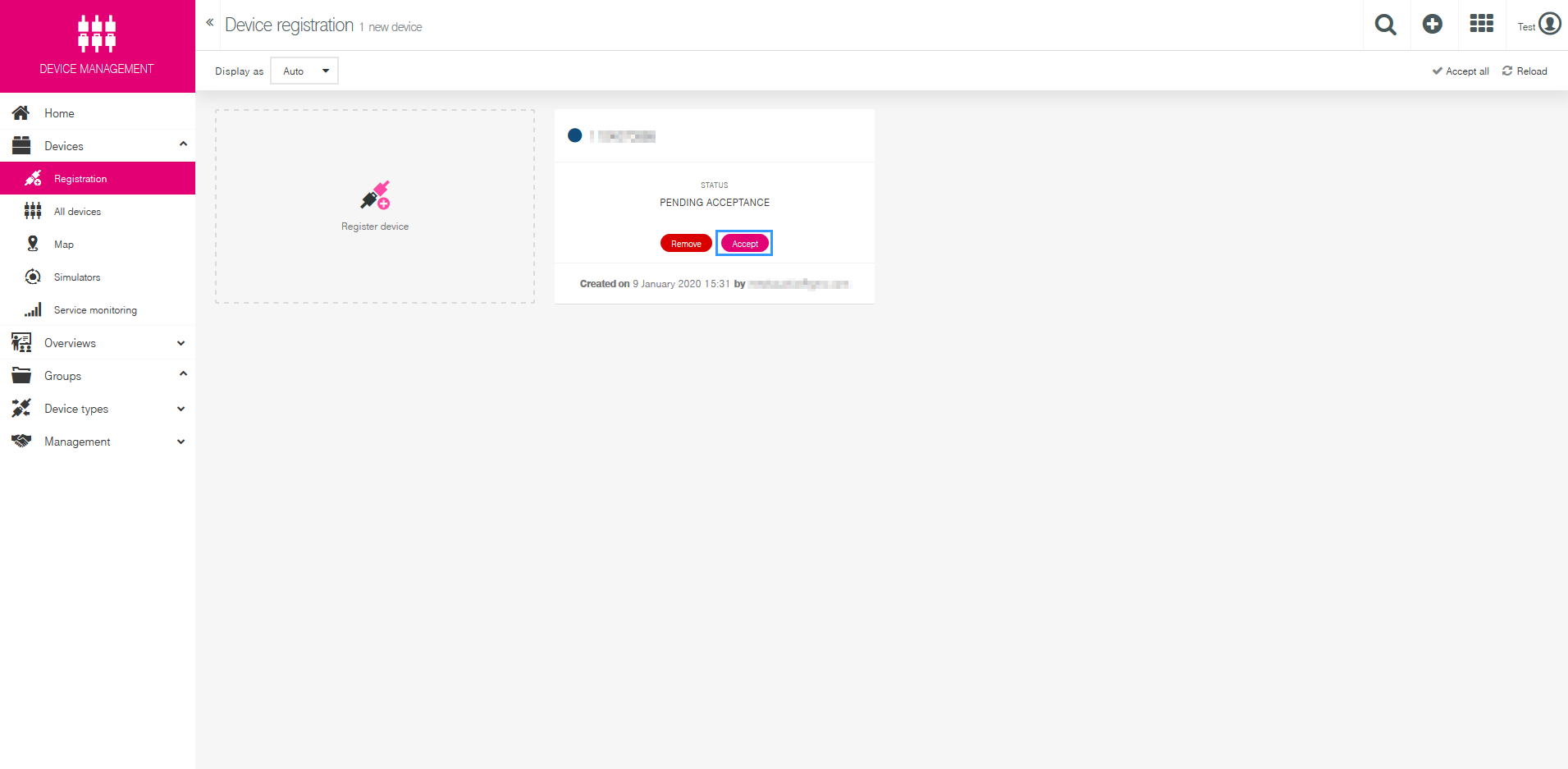
Click „Accept“ button to accept this device. | Click „Accept“ button to accept this device. | ||
Revision as of 17:03, 27 November 2019
Telekom Cloud of Things is now compatible with Teltonika RUT routers.
Description
The Cloud of Things is cloud platform for the Internet of Things. It allows you to remotely monitor, manage and control your connected devices and machines – plug-and-play, without extensive installation.
Summary
This example application streams some information from the router device. Once it is enabled you should be able to the following things in Cloud of Things Cockpit the following information from your router:
Device Model, Revision and Serial Number
Mobile Cell ID, ICCID, IMEI, Connection Type, Operator, Signal Strength
WAN Type and IP
Mobile and WAN information are sent from “stream” Lua script, while Device information - from stream application. This information (except Device) is being sent to the main Cumulocity server continuously: at 10 seconds interval.
????????????????????????????????
Creating an account
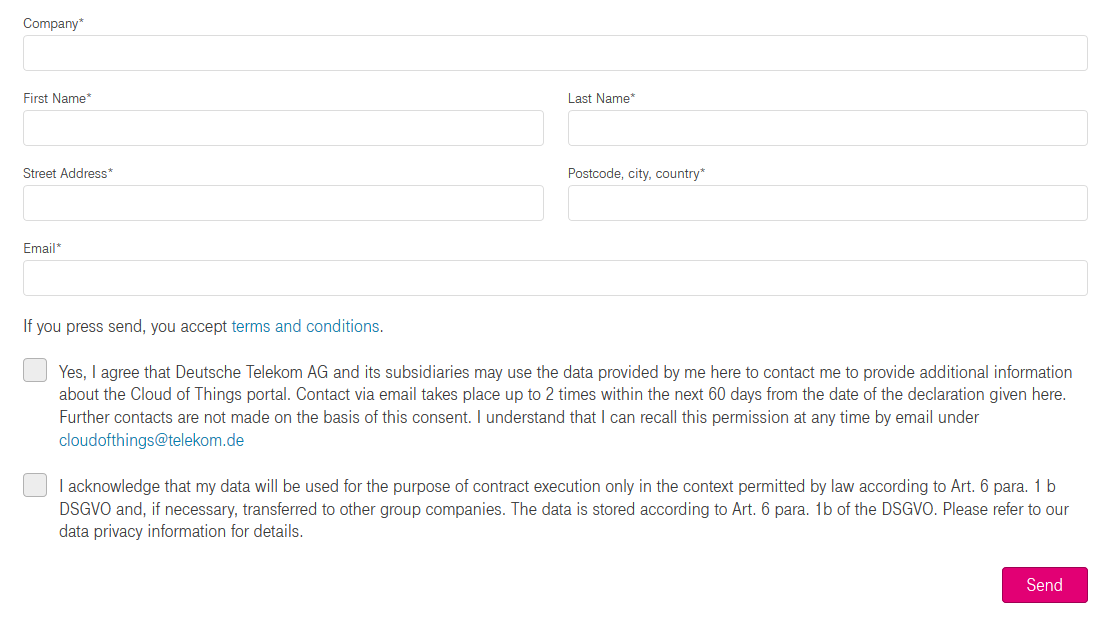
First of all, you need to create an account. After registration, you will receive free 60 days Cloud of Things trial. Registration form can be found here: https://support.ram.m2m.telekom.com/apps/demotenant/index.html#/ . Below you can see registration form:
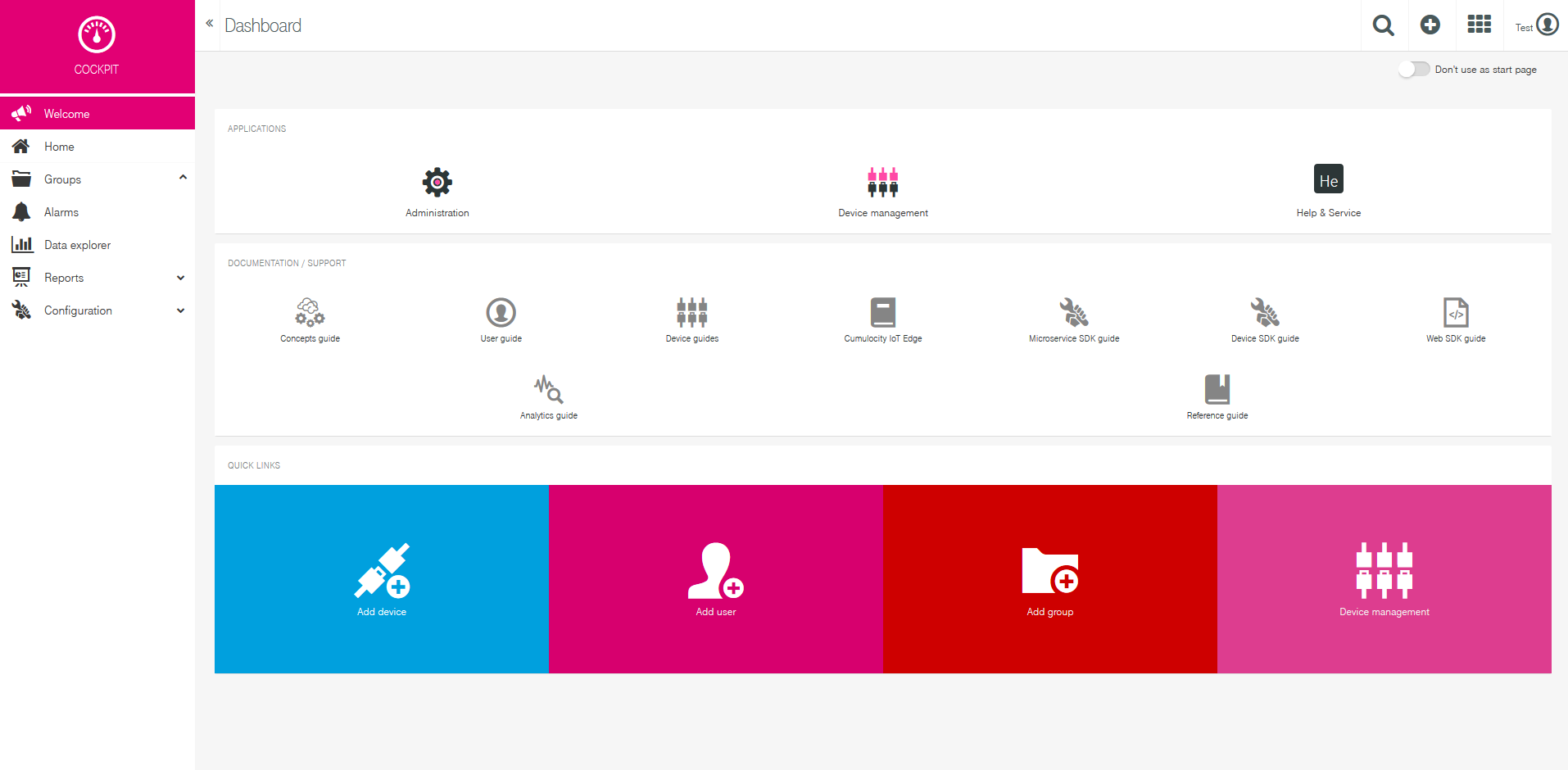
After successful registration you will receive an email with your account details (URL, username, password) and after logging in, you will be redirected to Cloud of Things Cockpit portal, see below:
Package installing and device registering
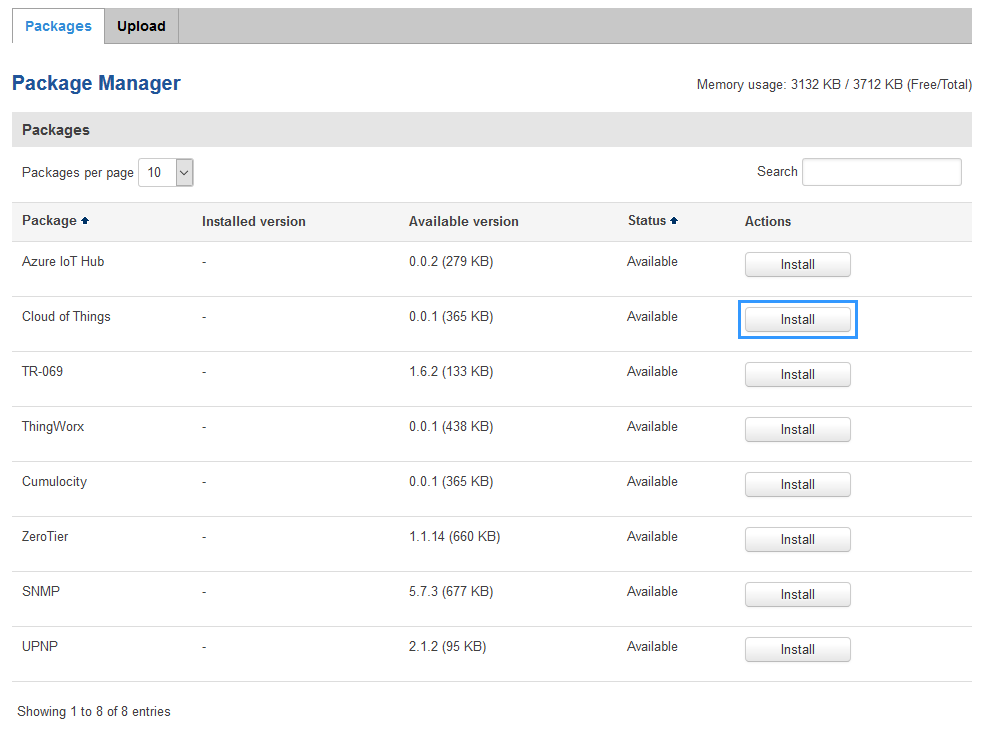
Cloud of Things IoT platform is not included in standart software package. So it order to use it you will need to install it first. Go to System>Package Manager.
There you will find all the available packages. The one you need is called Cloud of Things. In order to install it press Install button.
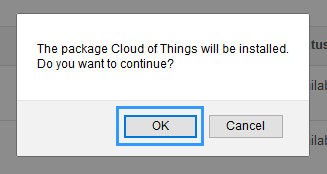
Then it will ask your confirmation, whether you want to install the package. Press OK to continue.
It will take a moment to install, but when it is done, you will receive a message.
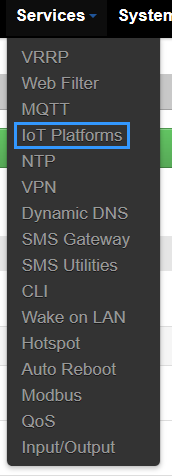
When the package is installed, a new window in Services section will appear, IoT Platforms.
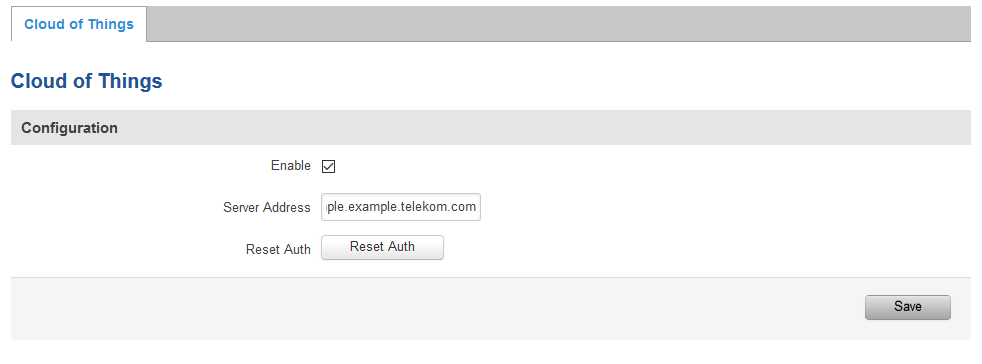
In order to use the feature you will need to enable it, write Server Address and press Save. The server address is the link which was provided by Cloud of Things.
(E.g. example.example.example.telekom.com)
P.S. In order to re-register a device on Cloud of Things platform, you need to press Reset Auth button. If you are registering the device for the first time, pressing the button is not necessary.
Adding devices on Cloud of Things platform
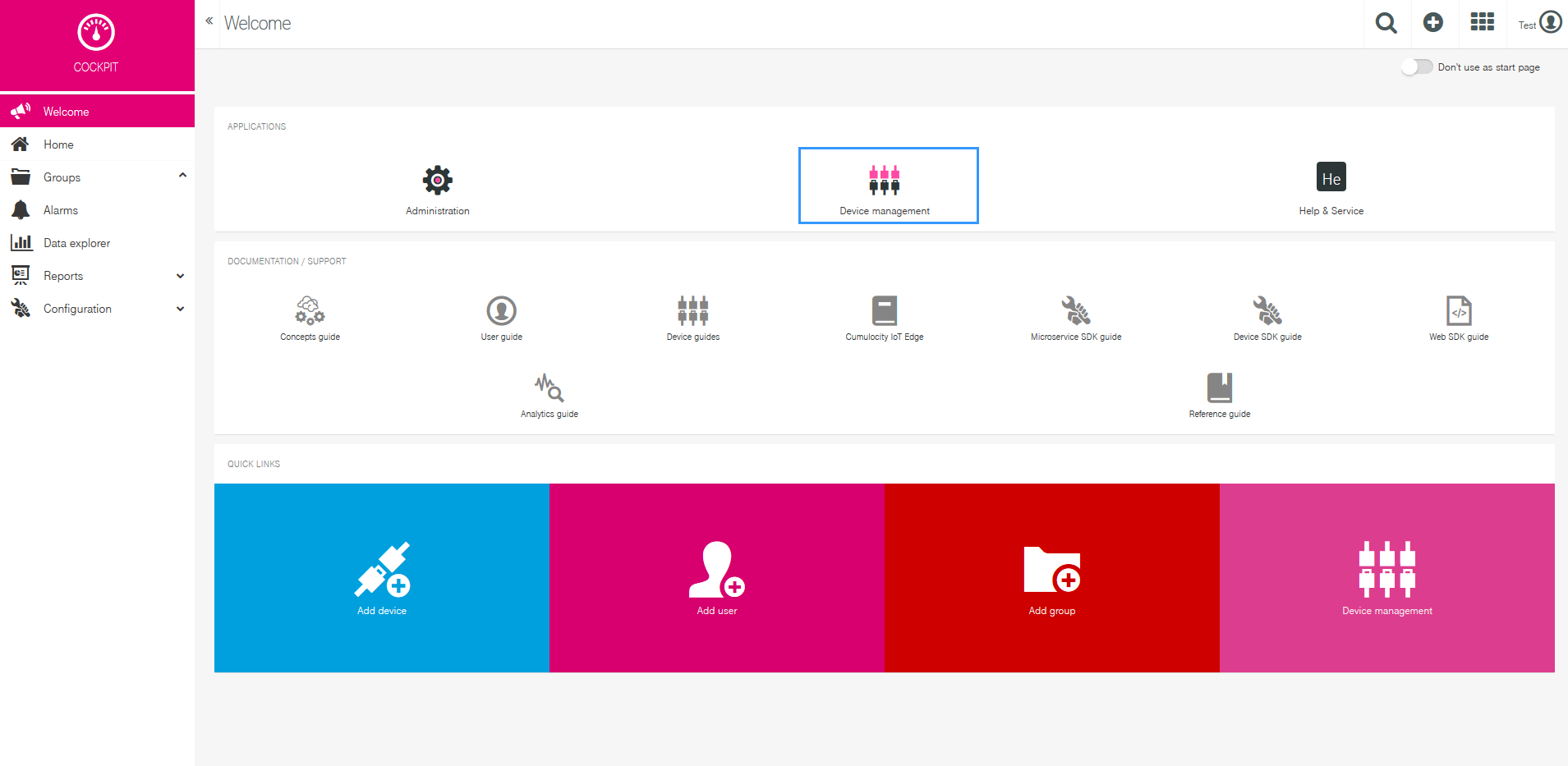
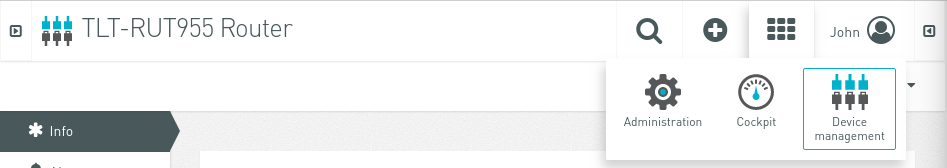
After successfully installing the package and making the required configuration on the router, you now can add the device on Cloud of Things platform. After logging in to the website you are forwarded to Cockpit page. There press Device manager.
Then select Devices and press Registration.
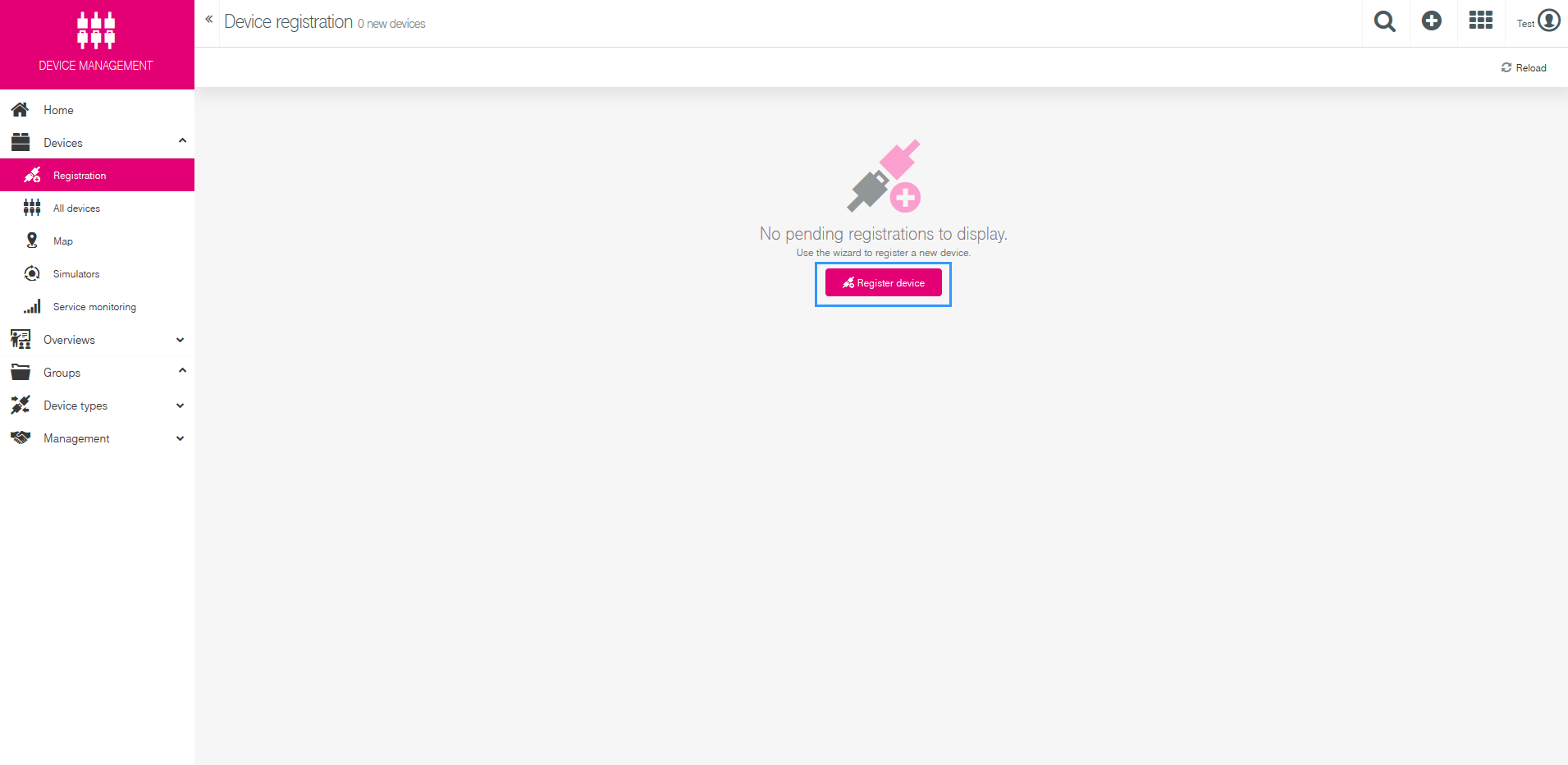
Press Register device.
There are two ways to register your device(s) Bulk and General. Bulk is used when you are registering a lot of devices at once. In this example we will be using the General option.
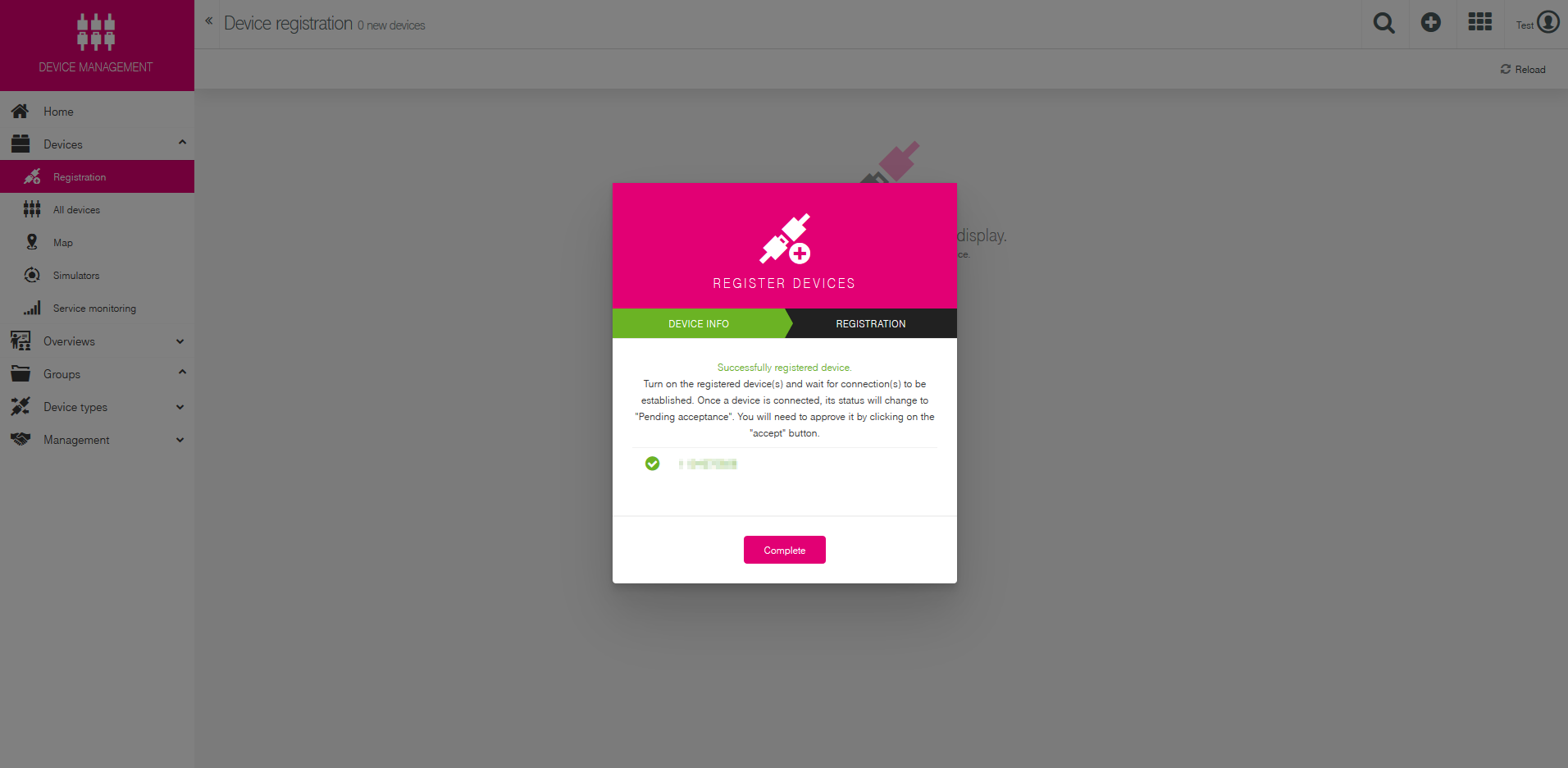
In Device ID section write the serial number of your router. You can add more than one item by pressing Add another device button. There is a possibility to assign your routers to groups, but we are not doing that in this example.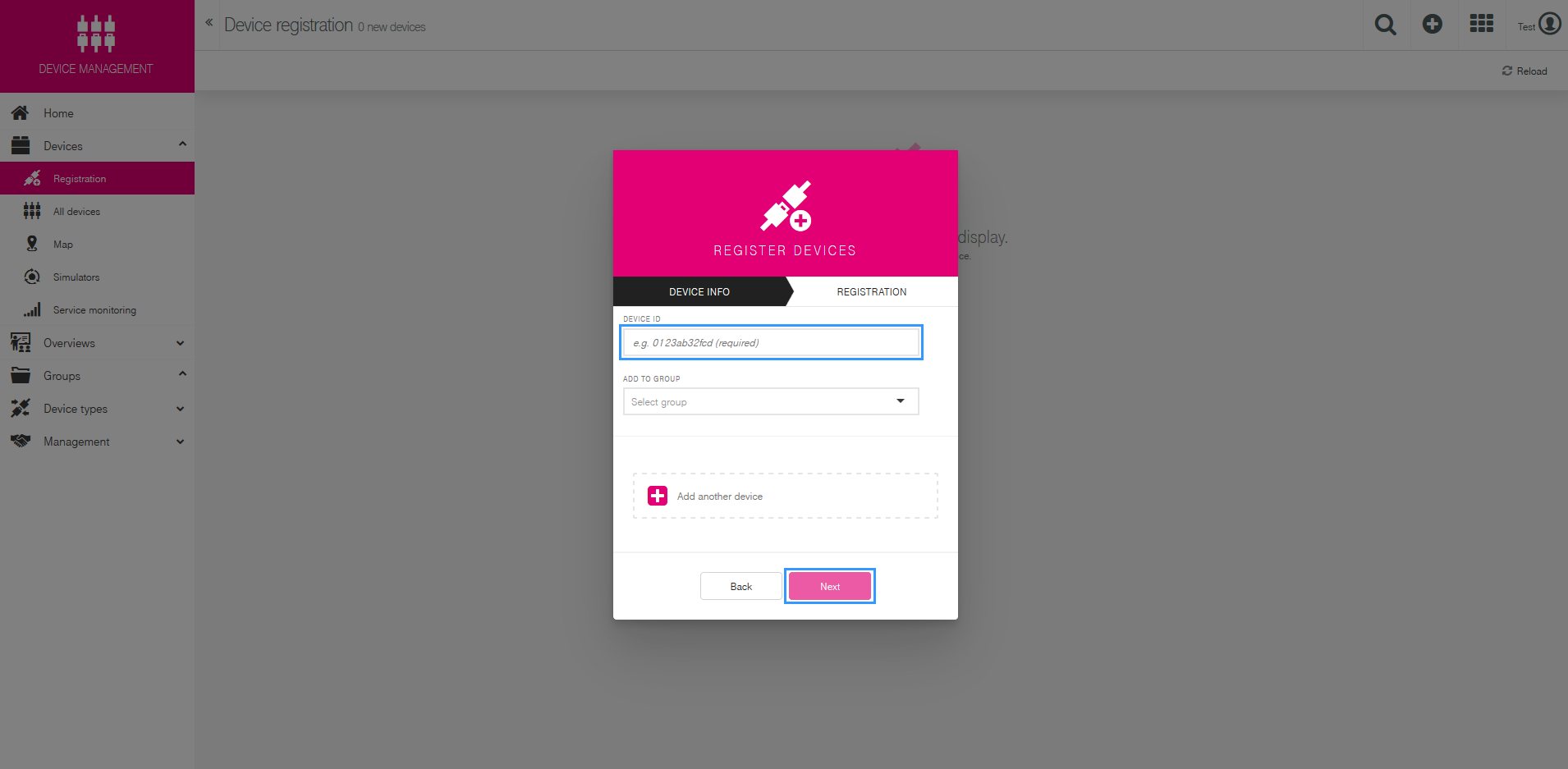
If everything was done correctly, it will show you that the registration was successful.
Then you will need to Accept the Pending Acceptance.
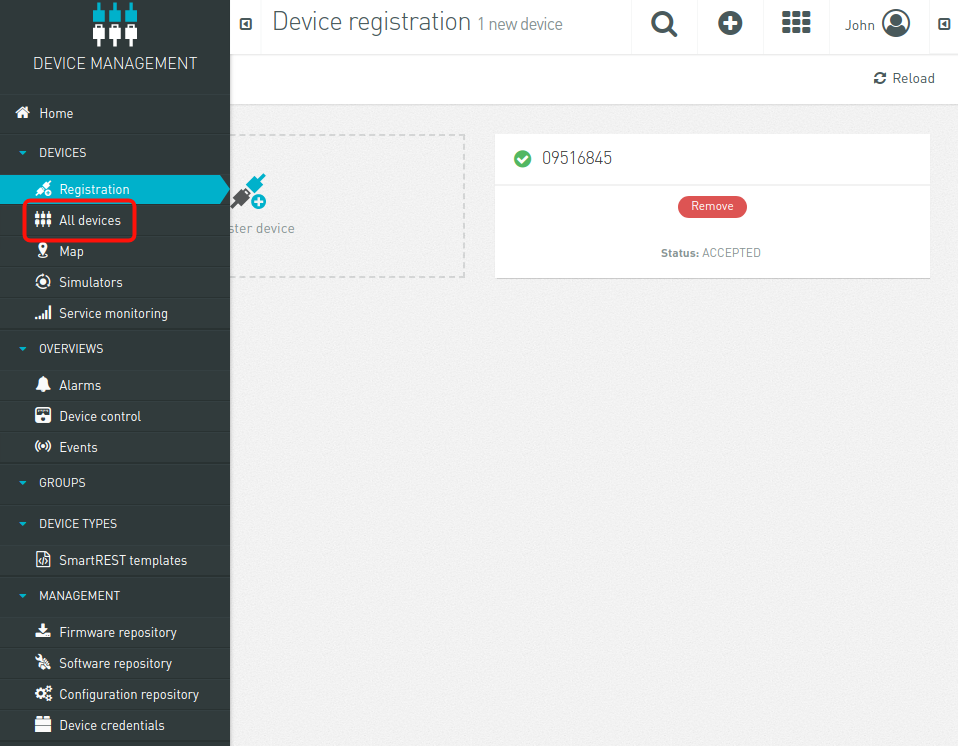
Finally you will receive a message showing that the device has been accepted.d.
Click „Accept“ button to accept this device.
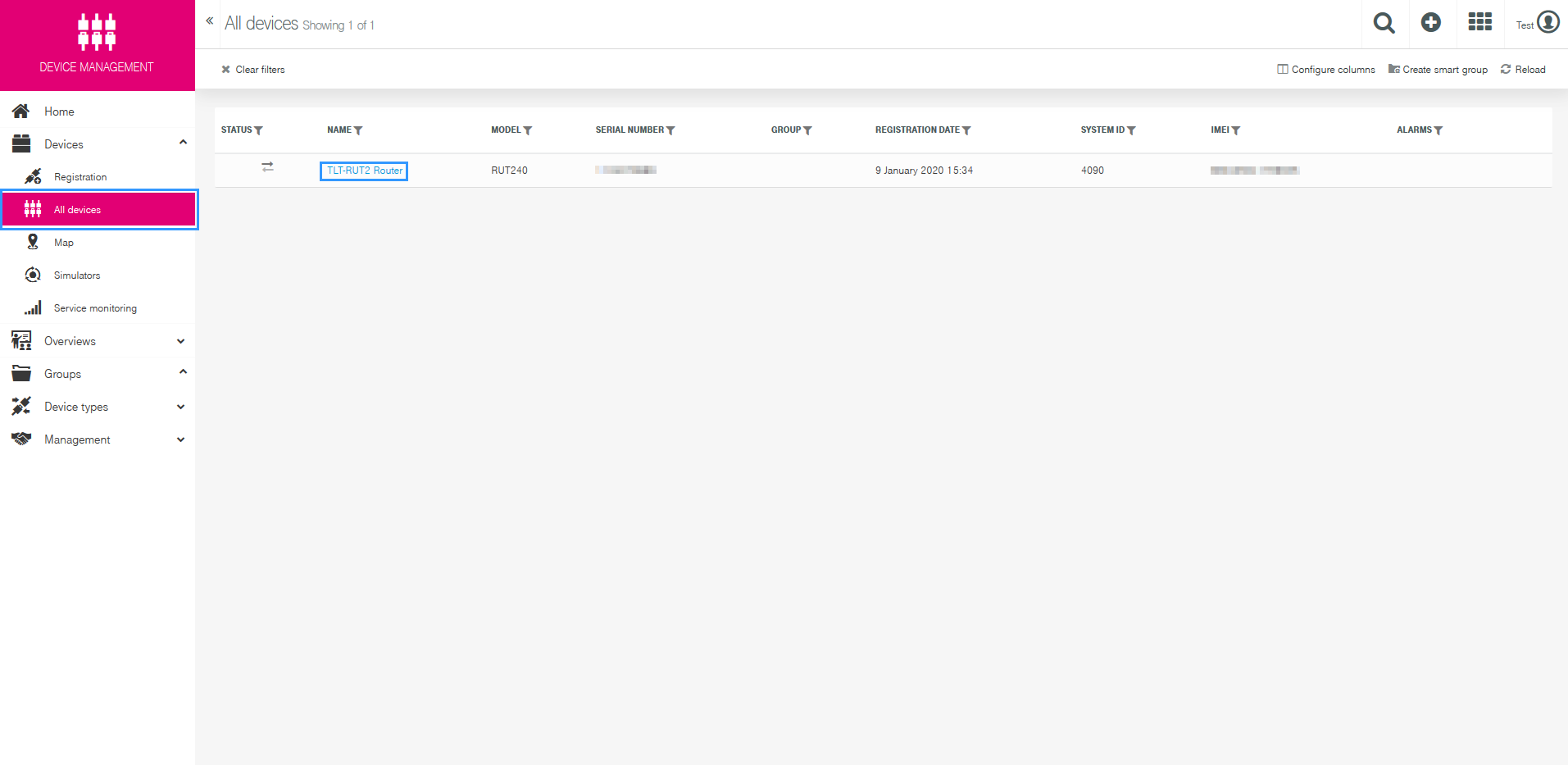
Now navigate to „All devices“ page:
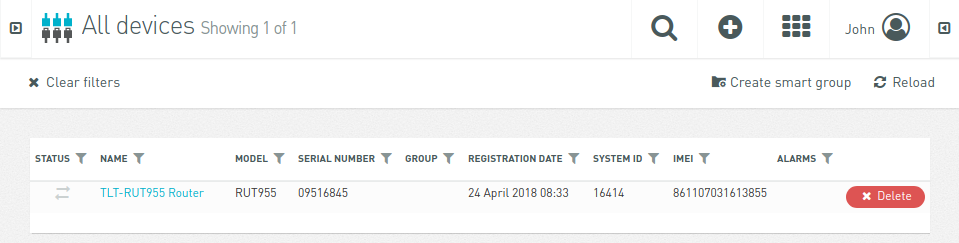
Here you should be able to see list of all registered devices:
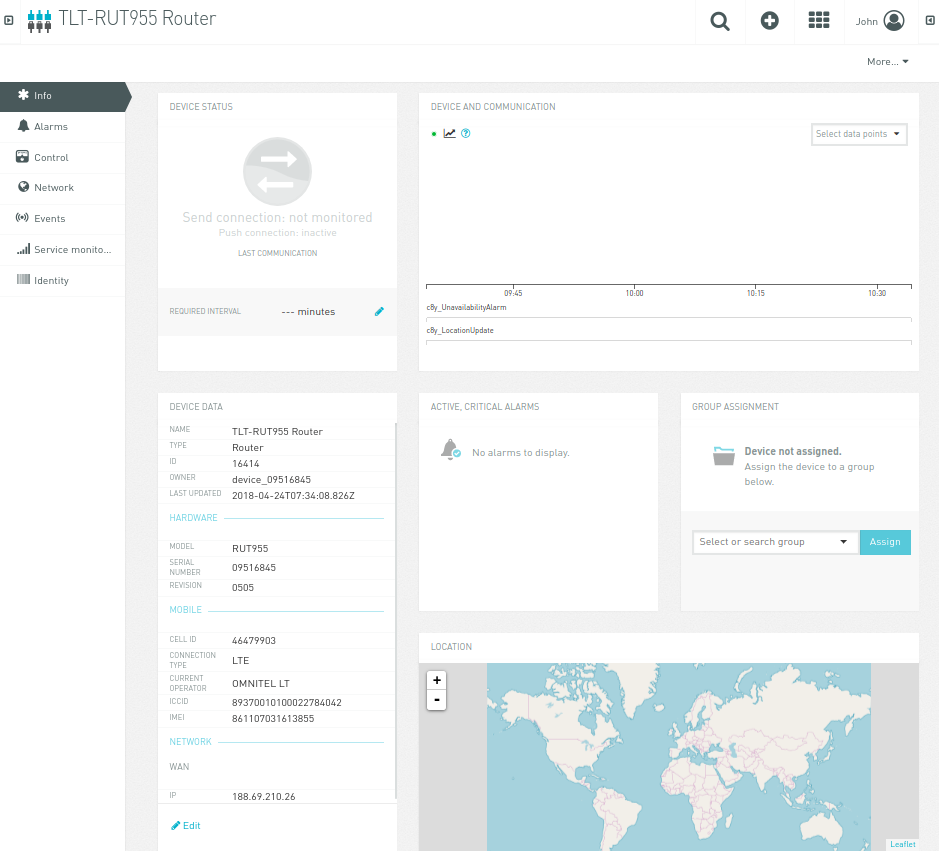
Click on „TLT-RUT955 Router“ name to get into information page:
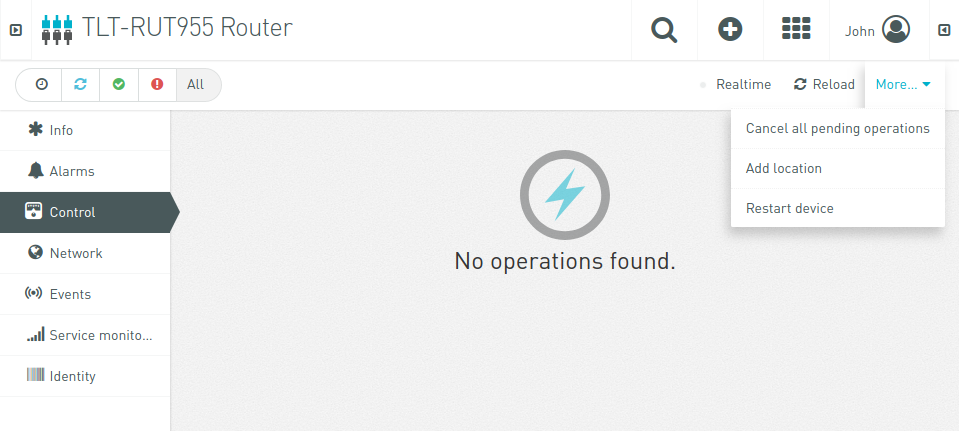
Notice „Device Data“ widget, it contains information from the router device. By navigating to „Control“ tab, you can restart device by clicking „More → Restart Device“:
You can go back to Cumulocity Cockpit page the same way you entered Device managemant page:
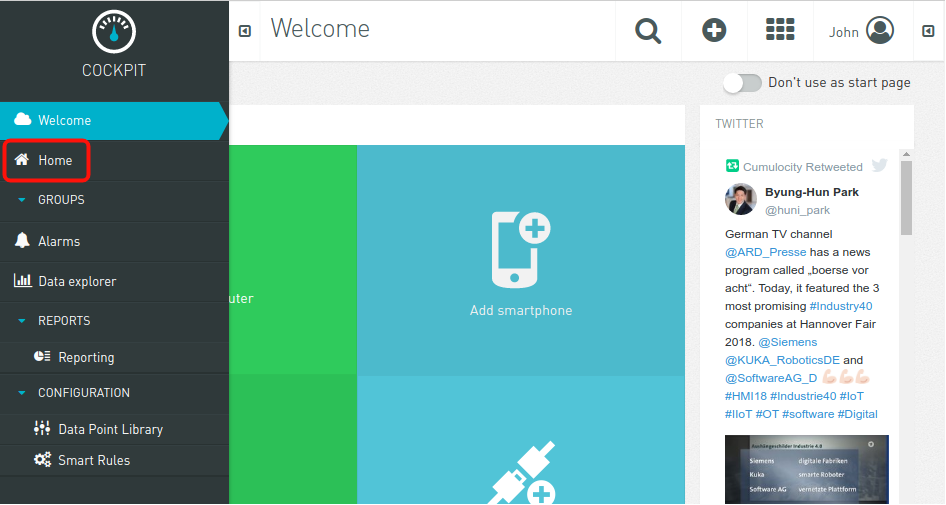
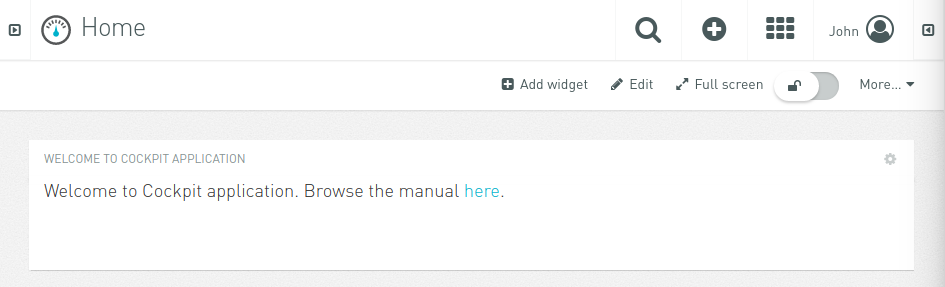
Then navigate to „Home“ page:
And then click „Add widget“:
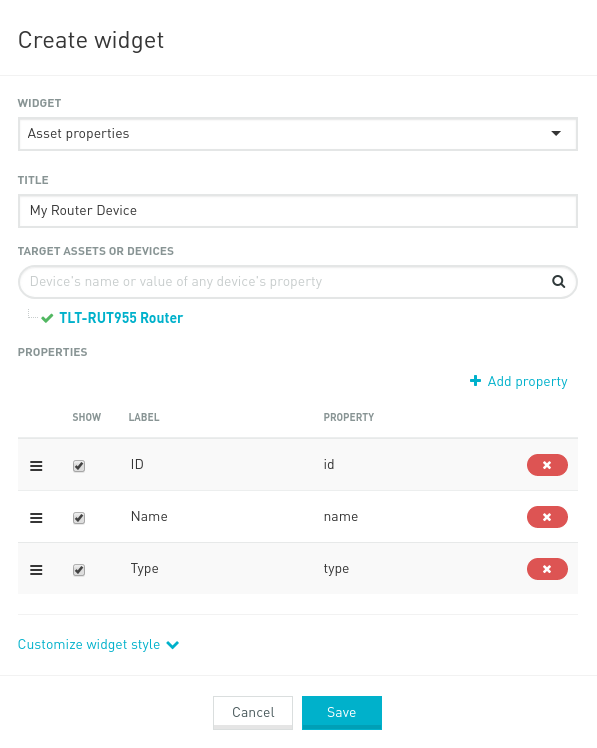
Select „Asset properties“ widget and type title, then select „TLT-RUT955 Router“ in „Target Assets or Devices“:
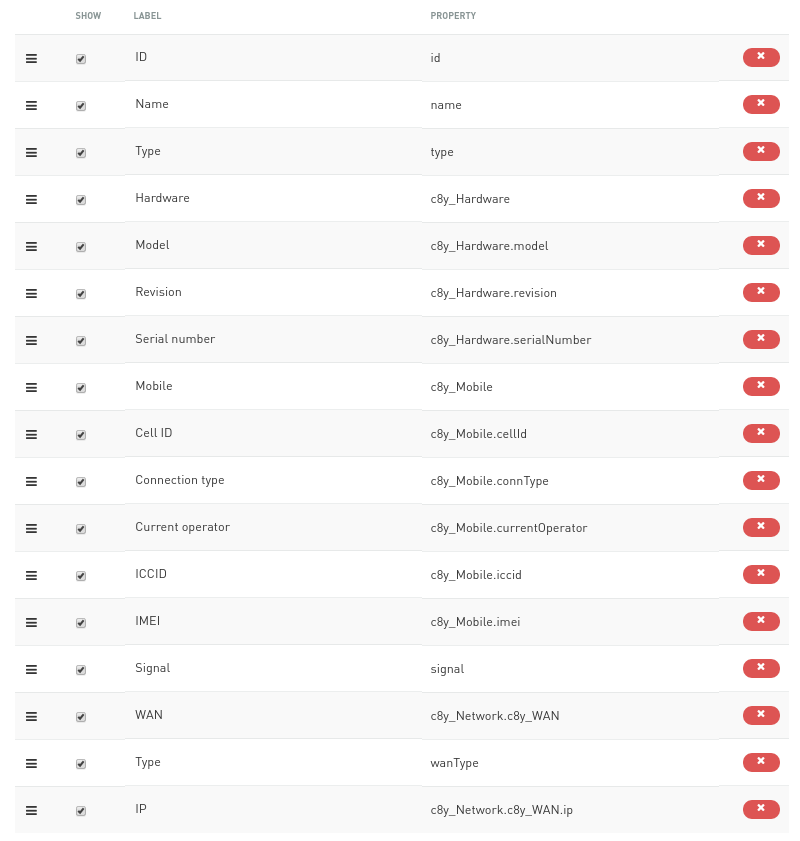
To add more information into widget, click „Add property“ and click on „Show“ to add that property.
In example application, these properties are used:
Hardware – Model, Revision, Serial Number
Mobile – Cell ID, Connection Type, Current Operator, ICCID, IMEI and Signal
WAN – IP and Wan Type
Total properties:
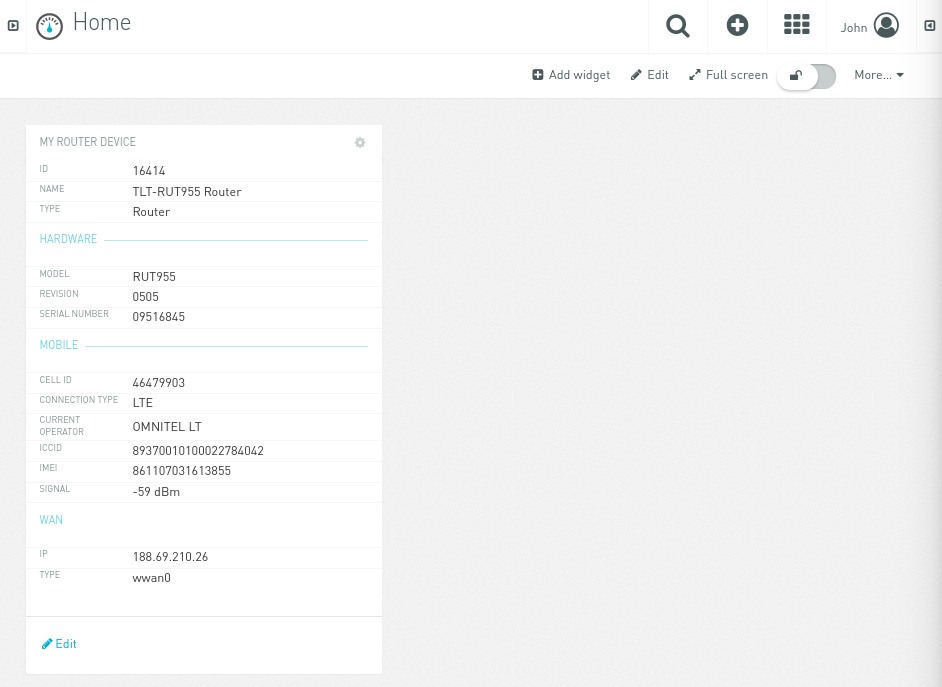
Then click „Save“ and you should be able to see widget with properties you have set:
Explanation of example application
There are two steps when adding new properties:
1. Writing template
2. Writing lua script which will stream information.
By default, template location inside router is „/usr/lib/lua/cm/srtemplate.txt“. It contains such content:
rut955-v0.01
10,100,GET,/identity/externalIds/SerialNumber/%%,,application/json,%%,STRING,
10,101,POST,/inventory/managedObjects,application/json,application/json,%%,STRING,"{""name"":""%%"",""c8y_IsDevice"":{},""com_cumulocity_model_Agent"":{}}"
10,102,POST,/identity/globalIds/%%/externalIds,application/json,application/json,%%,STRING STRING,"{""externalId"":""%%"",""type"":""SerialNumber""}"
10,103,PUT,/inventory/managedObjects/%%,application/json,application/json,%%,STRING STRING STRING,"{""name"": ""%%"", ""type"": ""%%""}"
10,104,PUT,/inventory/managedObjects/%%,application/json,application/json,%%,STRING STRING STRING STRING,"{""c8y_Hardware"": {""model"":""%%"",""revision"":""%%"",""serialNumber"":""%%""}}"
10,105,PUT,/inventory/managedObjects/%%,application/json,application/json,%%,STRING STRING STRING STRING STRING STRING STRING,"{""c8y_Mobile"": {""imei"":""%%"",""cellId"":""%%"",""iccid"":""%%"",""connType"":""%%"",""currentOperat or"":""%%""},""signal"":""%%""}"
10,106,PUT,/inventory/managedObjects/%%,application/json,application/json,%%,STRING STRING STRING,"{""c8y_Network"":{""c8y_WAN"":{""ip"":""%%""}},""wanType"":""%%""}"
10,107,PUT,/inventory/managedObjects/%%,application/json,application/json,%%,UNSIGNED STRING,"{""c8y_SupportedOperations"":[""%%""]}"
10,108,PUT,/devicecontrol/operations/%%,application/json,application/json,%%,UNSIGNED STRING,"{""status"":""%%""}"
11,500,$.managedObject,,$.id 11,501,,$.c8y_IsDevice,$.id 11,502,,$.c8y_Restart,$.id,$.deviceId
First line contains template version. In this case it is „rut955-v0.01“.
When template is updated, version must be updated aswell, otherwise device will use non-updated template version.
The following lines contains requests starting with a number „10“ and responses - starting with a number „11“. Now explanation of request:
Type - 10
Code - 101
Method - POST
URL - /inventory/managedObjects
Content Type - application/json
Accept - application/json
Placeholder - %%
Params - STRING STRING
Template - JSON
Type – requests are identified by a number 10
Code – request code number, each request must contain unique number
Method – HTTP method of request
URL – URL that will be used in request
Content Type – it is Content-Type header field value
Accept – it is Accept header field value, mostly equal to Content Type
Placeholder - string which will be replaced in URL or Template JSON
Params – what kind of params are replaced, JSON template contains two strings
Template – JSON template which will be sent
Explanation of response:
Type - 11
Code - 502
Cond - <none>
Value 1 - $.c8y_Restart
Value 2 - $.id
Value3 - $.deviceId
Type – responses are identified by a number 11
Code – response code, each response must contain unique number
Cond – JSON path base pointing to an object or object list from which values are extracted
Value… - JSON values
Take a look for more information about templates: https://www.cumulocity.com/guides/reference/smartrest.
Now explanation of logic inside lua script. By default, example application’s lua script location is „/usr/bin/lua/cm“. Application will scan this folder for any *.lua files and load them if they contains „init“ function. Script’s „stream.lua“ content:
-- stream.lua local utl = require "luci.util" local sys = require "luci.sys" local DEVICE_NAME = 'TLT-RUT955 Router' local DEVICE_TYPE = 'Router'
function restart(r)
local deviceId = r:value(2)
c8y:send('108,'..deviceId..',SUCCESSFUL')
sys.exec("reboot")
end
function init()
srInfo('*** Stream Init ***')
-- set device name and type
c8y:send('103,'..c8y.ID..','..DEVICE_NAME..','..DEVICE_TYPE)
-- set restart as supported operation
c8y:send('107,'..c8y.ID..',c8y_Restart')
-- set imei, cellid and iccid first time
mobileDataStream()
-- create timer which will stream mobile info data
local m_timer = c8y:addTimer(10 * 1000, 'mobileDataStream')
m_timer:start()
-- register restart handler
c8y:addMsgHandler(502, 'restart')
return 0
end
function mobileDataStream()
local imei = utl.trim(sys.exec("gsmctl -i"))
local cell = utl.trim(sys.exec("gsmctl -C"))
local icc = utl.trim(sys.exec("gsmctl -J"))
local type = utl.trim(sys.exec("gsmctl -t"))
local oper = utl.trim(sys.exec("gsmctl -o"))
local sign = utl.trim(sys.exec("gsmctl -q"))..' dBm'
local req = '105,'..c8y.ID
req = req..','..imei
req = req..','..cell
req = req..','..icc
req = req..','..type
req = req..','..oper
req = req..','..sign
-- send mobile info
c8y:send(req)
local wantype = utl.trim(sys.exec("uci get -q network.wan.ifname"))
local wanip = utl.trim(sys.exec("curl -s http://whatismyip.akamai.com"))
-- send wan info
c8y:send('106,'..c8y.ID..','..wanip..','..wantype)
end
Once application finds lua script, it will call „init“ function. This is where all initialization of timers and other stuff should be.
Sending information is quite simple:
c8y:send('103,'..c8y.ID..','..DEVICE_NAME..','..DEVICE_TYPE)
By using „c8y:send“ function, first string contains request code, which was defined in the template, earlier. Then comma must appear after each value. The above line shows how we update device name and device type with our own.
For more information about Lua API, download Cumulocity C++ SDK: https://bitbucket.org/m2m/cumulocity-sdk-c/downloads and look up inside „sdk/doc/lua.html“ with a browser.
External Links
https://www.cumulocity.com/try-for-free
https://www.cumulocity.com/guides/reference/smartrest
https://bitbucket.org/m2m/cumulocity-sdk-c/downloads
Disclaimer:
Any of the trademarks, service marks, collective marks, design rights or similar rights that are mentioned, used or cited in the articles are the property of their respective owners.