Testing Trap With Linux Operating System
Summary
This chapter is a guide on configuring SNMP Trap listening service on Linux OS.
Preconditions
To configure Trap listening service these packages are required: snmp , snmpd, snmptt, snmptrapd.
To install these packages run command for each package:
$ sudo apt install <package_name>
Also you need to download and load MIB files. Use this command:
$ sudo apt-get install snmp-mibs-downloader
Important note: before continuing make sure that SNMP Trap package is configured. SNMP configuration example can be found here.
Editing configuration files
Snmpd.conf
This is not required for Trap listening service, but with this configuration snmpget command will be able to establish connection without requiring port number in the command line. If you want to configure SNMP so it would listen to the port globally, not locally follow these steps:
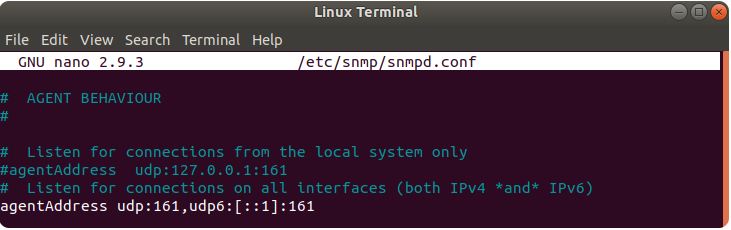
Edit snmpd.conf file, it can be found in /etc/snmp/ directory. Example of the command:
$ sudo nano /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
Find a line containing "agenAddress udp:127.0.0.1:161" and comment it by adding # symbol at the beginning of the line. Then find the line "agenAddress udp:161,udp6[::1]:161" and uncomment it. If you chose different SNMP port change 161 into your chosen port. Make sure to use exactly the same port as in SNMP package configuration on Teltonika device.
Snmptrapd.conf
This is required to specify community you described in SNMP Trap package configuration, to describe Trap port and how to handle caught Trap messages.
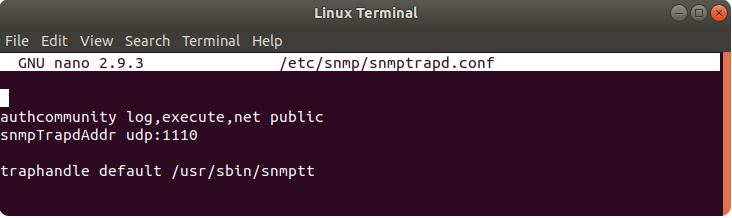
Edit snmptrapd.conf file, it can be found in /etc/snmp/ directory. Example of the command:
$ sudo nano /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf
Add these lines at the beginning of the file:
authcommunity log,execute,net public
snmpTrapdAddr udp:1110
traphandle default /usr/sbin/snmptt
In the first line change public to your community group described in SNMP Trap package configuration. In the second line change 1110 port number to your described port number in SNMP Trap package of the Teltonika device.
Also you can change first line to disableAuthorization yes. This will disable all authorizations and any group will be able to send traps to the SNMP Manager.
Creating Trap listening service
This is required for launching Trap listening service with extra configurations, we will use it to describe the log file to which all traps will be recorded.
Use this command:
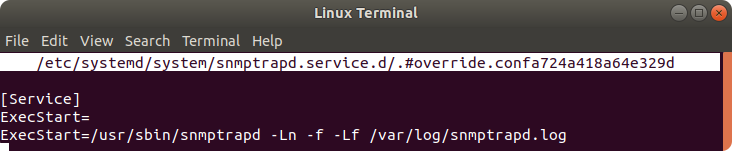
$ sudo systemctl edit snmptrapd.service
Write these lines into the file:
[Service]
ExecStart=
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/snmptrapd -Ln -f -Lf /var/log/snmptrapd.log
This configuration will write the log of caught Trap messages into /var/log/ folder and into snmptrapd.log file. You can change the log file directory and file name.
Loading MIB file
MIB file will be used to translate OID codes to more readable format.
If you dont have the MIB file, download it from SNMP packge WebUI window, example here
After downloading the MIB file, place it in /usr/share/snmp/mib directory, you can use this command:
$ sudo cp Downloads\TLT-MIB.txt /usr/share/snmp/mibs/TLT-MIB.txt
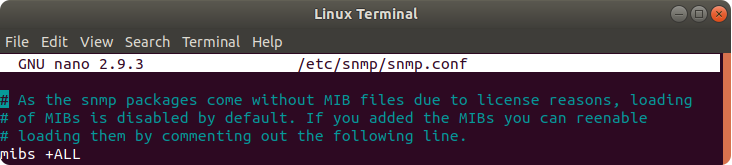
Now edit file /etc/snmp/snmp.conf . Example of the command:
$ sudo nano /etc/snmp/snmp.conf
Find this line: mibs : and change it to: mibs +ALL to load all existing MIB files in /usr/share/snmp/mibs directory.
Launching Trap listening service
Important note: Trap listening service will stop on system shutdown or restart.
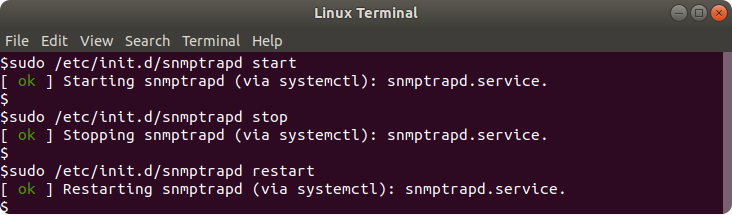
To launch SNMP Trap listening service use this command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/snmptrapd start
To stop the service use this command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/snmptrapd stop
To restart or launch the service you can use this command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/snmptrapd restart
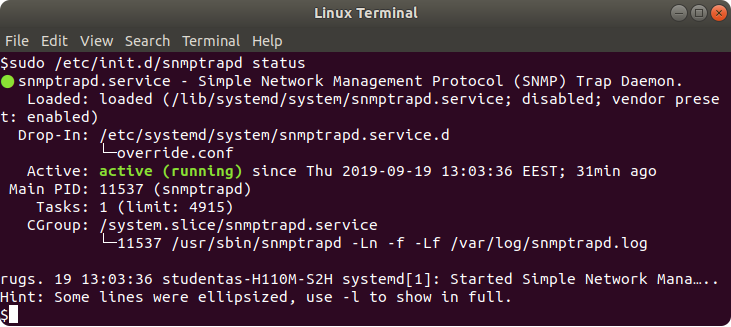
To read service status use this command:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/snmptrapd status
If SNMP manager caught any traps, connection information can be represented with service status information.
Important note: if status shows failed message, one solution could be changing the SNMP Trap port, some other process might be using the described port.
Testing if SNMP Trap listening service works
First make sure that SNMP Trap package has Trap rules configured in order to test if listening service works correctly. More information here
If any Trap was triggered, you can check, if Trap message was caught and logged. Check service status to see if any connections were established.
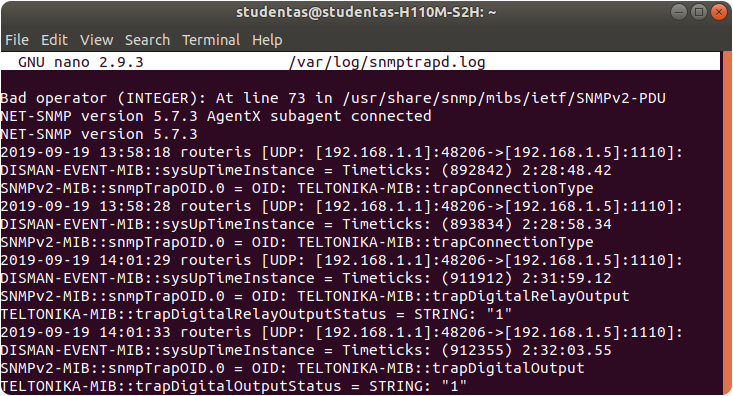
Open /var/log/snmptrapd.log . If you specified different directory and file name, open it. Example commands:
$ sudo cat /var/log/snmptrapd.log $ sudo more /var/log/snmptrapd.log $ sudo nano /var/log/snmptrapd.log
snmptrapd.log file after triggering some trap rules: