Template:Networking rutos manual dnp3
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. It is primarily used for communications between a master station and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs).
This manual page provides an overview of the DNP3 functionality in {{{name}}} devices.
Note: DNP3 is additional software that can be installed from the Services → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
DNP3 Parameters
DNP3 parameters are held within indexes. The index numbers and corresponding system values are described in the table below:
| required value | index | group type |
|---|---|---|
| Uptime | 0 | Octet String |
| Hostname | 3 | Octet String |
| Router Serial Number | 5 | Octet String |
| LAN MAC Address | 6 | Octet String |
| Router name | 7 | Octet String |
External Modem Parameters
If you are using an external modem on your device, use these index numbers for corresponding system values:
| required value | index | group type |
|---|---|---|
| Modem VID and PID | 100 + 50 * modem_number | Octet String |
| Mobile data received today (SIM1) | 101 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent today (SIM1) | 102 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received this week (SIM1) | 103 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent this week (SIM1) | 104 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received this month (SIM1) | 105 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent this month (SIM1) | 106 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received last 24h (SIM1) | 107 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent last 24h (SIM1) | 108 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received last week (SIM1) | 109 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent last week (SIM1) | 110 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received last month (SIM1) | 111 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent last month (SIM1) | 112 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received today (SIM2) | 113 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent today (SIM2) | 114 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received this week (SIM2) | 115 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent this week (SIM2) | 116 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received this month (SIM2) | 117 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent this month (SIM2) | 118 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received last 24h (SIM2) | 119 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent last 24h (SIM2) | 120 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received last week (SIM2) | 121 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent last week (SIM2) | 122 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data received last month (SIM2) | 123 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Mobile data sent last month (SIM2) | 124 + 50 * modem_number | Counter |
| Modem temperature (in 0.1 °C) | 125 + 50 * modem_number | Octet String |
| Operator | 126 + 50 * modem_number | Octet String |
| Network state | 127 + 50 * modem_number | Octet String |
| Connection state | 128 + 50 * modem_number | Octet String |
| Signal Strength | 129 + 50 * modem_number | Octet String |
The modem_number of the external modem is 1 (internal modem is skipped).
To get the exact index of a parameter, use the formula in the table above. For example, the index of an external modem operator is 176. Formula is: 126 + 50 * 1.
TCP Master
A master in DNP3 is a component that communicates (requests data) with a single outstation via a communication channel. By default, the master list is empty. To add a new master, click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added master's configuration page.
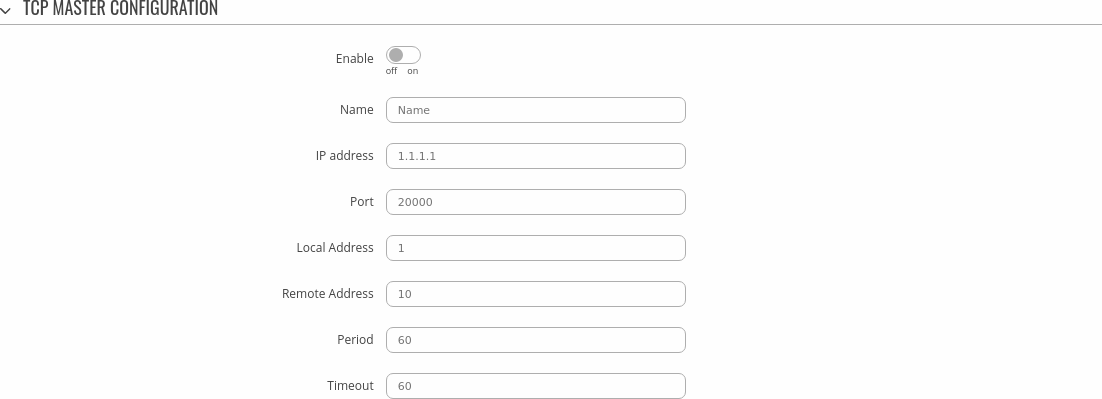
TCP Master Configuration
The TCP Master Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of a DNP3 Outstation that the Master (this {{{name}}} device) will be querying with requests. The figure below is an example of the TCP Master Configuration and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns communication with the outstation device on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the TCP master, used for easier management purposes. |
| IP address | ip; default: none | DNP3 Outstation IP address. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | DNP3 Outstation Port. |
| Local Address | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Master Link-Layer address. |
| Remote Address | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Outstation Link-Layer address. |
| Period | integer [1..60]; default: none | Interval at which requests are sent to the outstation device. |
| Timeout | integer [1..60]; default: none | Maximum response wait time. |
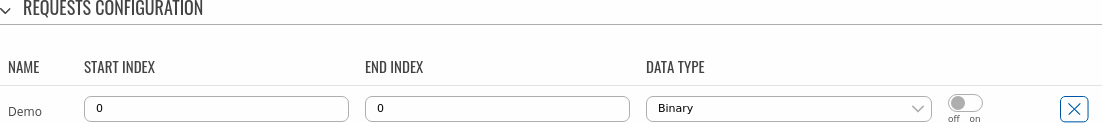
Requests Configuration
A DNP3 request is a way of obtaining data from DNP3 Outstations. The master sends a request to an outstation specifying the function codes to be performed. The outstation then sends the requested data back to the DNP3 master.
The Request Configuration list is empty by default. To add a new Request Configuration look to the Add New Instance section. Enter a custom name into the 'New Configuration Name' field and click the 'Add' button:
The new Request Configuration should become visible in the list:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: Unnamed | Name of this Request Configuration. Used for easier management purposes. |
| Start Index | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Start index of the data subarray. |
| End Index | integer [0..65535]; default: none | End index of the data subarray. |
| Data Type | Binary | Double Binary | Counter | Frozen Counter | Analog | Octet String | Analog Output Status | Binary Output Status; default: Binary | Data object group of the requested index(-es). |
| off/on slider | off | on; default: off | Turns the request on or off. |
Serial Master
The Serial Master page is used to configure the device as a DNP3 RTU Master. DNP3 RTU (remote terminal unit) is a serial communication protocol mainly used in communication via serial interfaces.
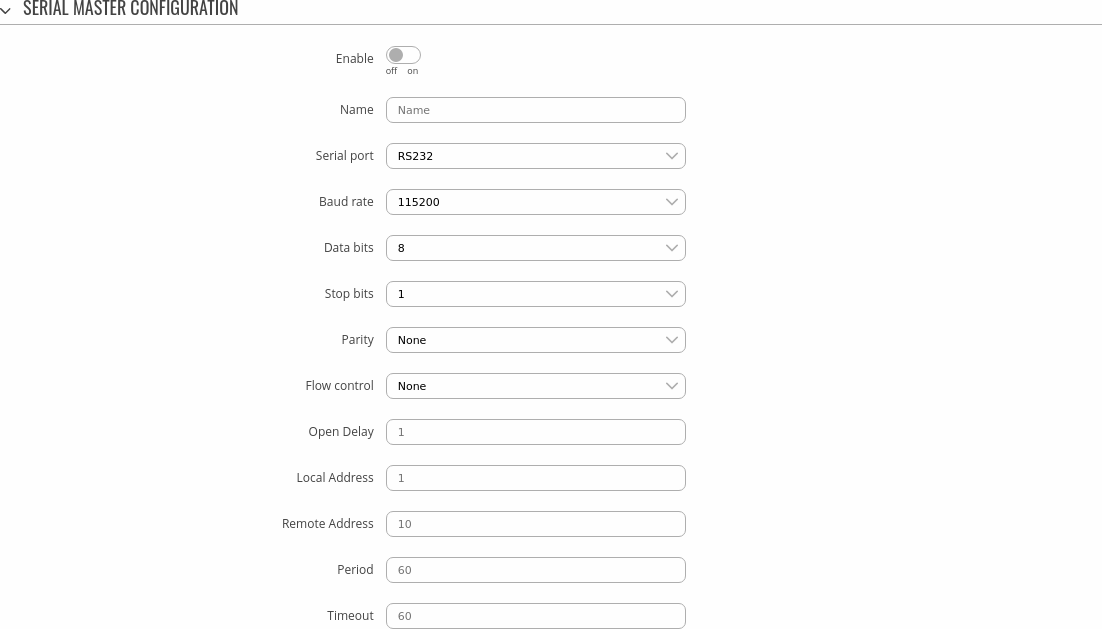
Serial Master Configuration
The Serial Master Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of a DNP3 Outstation that the Master (this {{{name}}} device) will be querying with requests. The figure below is an example of the Serial Master Configuration and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns communication with the outstation device on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the Serial master, used for easier management purposes. |
| Serial port | ; default: RS485 | DNP3 Outstation IP address. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200; default: 115200 | Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second). |
| Data bits | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | None | 1 | 1.5 | 2; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | None | Even | Odd; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None | RTS/CTS | Xon/Xoff; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking.
|
| Open delay | integer [0..10000]; default: none | Some physical layers need time to 'settle' so that the first tx isn't lost. |
| Local Address | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Master Link-Layer address. |
| Remote Address | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Outstation Link-Layer address. |
| Period | integer [1..60]; default: none | Interval at which requests are sent to the outstation device. |
| Timeout | integer [1..60]; default: none | Maximum response wait time. |
Requests Configuration
A DNP3 request is a way of obtaining data from DNP3 Outstations. The master sends a request to an outstation specifying the function codes to be performed. The outstation then sends the requested data back to the DNP3 master.
The Request Configuration list is empty by default. To add a new Request Configuration look to the Add New Instance section. Enter a custom name into the 'New Configuration Name' field and click the 'Add' button:
The new Request Configuration should become visible in the list:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: Unnamed | Name of this Request Configuration. Used for easier management purposes. |
| Start Index | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Start index of the data subarray. |
| End Index | integer [0..65535]; default: none | End index of the data subarray. |
| Data Type | Binary | Double Binary | Counter | Frozen Counter | Analog | Octet String | Analog Output Status | Binary Output Status; default: Binary | Data object group of the requested index(-es). |
| off/on slider | off | on; default: off | Turns the request on or off. |
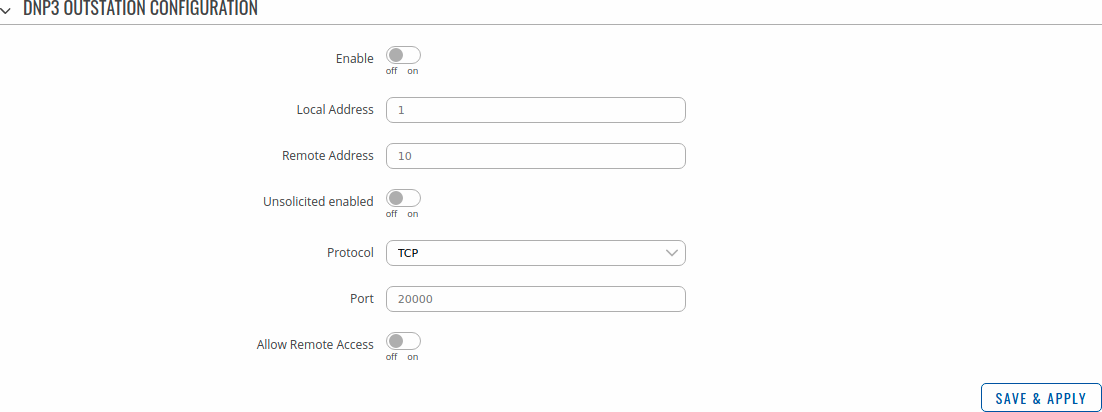
DNP3 Outstation
An outstation in DNP3 is a component that communicates with a single master via a communication channel. It makes measurements of the physical world and then sends them to a master upon request (solicited) or on its own accord (unsolicited). Occasionally a master requests that it do something by sending it a control. This provides the user with the possibility to get system parameters.
The figure below is an example of the DNP3 Outstation window section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that window:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns DNP3 Outstation on or off. |
| Local Address | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Outstation Link-Layer address. |
| Remote Address | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Master Link-Layer address. |
| Unsolicited enabled | off | on; default: none | Enables the transmission of unsolicited messages. |
| Protocol | TCP | UDP; default: TCP | Protocol used for DNP3 communications. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 502 | Port used for DNP3 communications. |
| UDP response address | ipv4; default: none | UDP response address. |
| UDP response port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | UDP response port. |
| Allow Remote Access | off | on; default: off | Allows remote DNP3 connections by adding an exception to the device's firewall on the port specified in the field above. |