Difference between revisions of "RUT900 MQTT"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
For in-depth MQTT configuration examples, refer to this page: '''[[Monitoring via MQTT]]''' | For in-depth MQTT configuration examples, refer to this page: '''[[Monitoring via MQTT]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Template: Networking_rutxxx_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| + | | fw_version = RUT9XX_R_00.06.06 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
==MQTT Broker== | ==MQTT Broker== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 23: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Toggles MQTT Broker ON or OFF</td> | <td>Toggles MQTT Broker ON or OFF</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Local Port</td> | <td>Local Port</td> | ||
| − | <td>integer [0..65535]; Default: " | + | <td>integer [0..65535]; Default: "1883"</td> |
<td>Specifies the local port that the MQTT broker will listen to</td> | <td>Specifies the local port that the MQTT broker will listen to</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable Remote Access</td> | <td>Enable Remote Access</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>If enabled, MQTT Broker will be reachable by remote user (from WAN)</td> | <td>If enabled, MQTT Broker will be reachable by remote user (from WAN)</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 52: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Use TLS/SSL</td> | <td>Use TLS/SSL</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Toggles the use of TLS/SSL certificates ON or OFF</td> | <td>Toggles the use of TLS/SSL certificates ON or OFF</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>CA File</td> | <td>CA File</td> | ||
| − | <td>.ca file; | + | <td>.ca file; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>'''Certificate authority''' is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate</td> | <td>'''Certificate authority''' is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>CERT File</td> | <td>CERT File</td> | ||
| − | <td>.crt file; | + | <td>.crt file; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>Certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. Client certificates play a key role in many mutual authentication designs, providing strong assurances of a requester's identity</td> | <td>Certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. Client certificates play a key role in many mutual authentication designs, providing strong assurances of a requester's identity</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Key File</td> | <td>Key File</td> | ||
| − | <td>.key file; | + | <td>.key file; default: '''none'''</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Private key for client to establish connection</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 90: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Use TLS/SSL</td> |
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Toggles MQTT Bridge ON or OFF</td> | <td>Toggles MQTT Bridge ON or OFF</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Connection Name</td> | <td>Connection Name</td> | ||
| − | <td>string; | + | <td>string; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>Name of the Bridge connection. Although this is used for easier management purposes, this field is mandatory</td> | <td>Name of the Bridge connection. Although this is used for easier management purposes, this field is mandatory</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote Address</td> | <td>Remote Address</td> | ||
| − | <td>ip; | + | <td>ip; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>Remote Broker’s address</td> | <td>Remote Broker’s address</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 111: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Use Remote TLS/SSL</td> | <td>Use Remote TLS/SSL</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Enables the use of TSL/SSL certificates of the remote broker. If this is checked, you will be prompted to upload TLS/SSL certificates. More information can be found in the [[#Security|Security]] section of this chapter</td> | <td>Enables the use of TSL/SSL certificates of the remote broker. If this is checked, you will be prompted to upload TLS/SSL certificates. More information can be found in the [[#Security|Security]] section of this chapter</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Use Remote Bridge Login</td> | <td>Use Remote Bridge Login</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Enables the use of Remote login data. If this is checked, you will be prompted to enter a remote client ID, username and password</td> | <td>Enables the use of Remote login data. If this is checked, you will be prompted to enter a remote client ID, username and password</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Topic</td> | <td>Topic</td> | ||
| − | <td>string; | + | <td>string; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>Specifies the names of the Topics that your Broker will subscribe to</td> | <td>Specifies the names of the Topics that your Broker will subscribe to</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Try Private</td> | <td>Try Private</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Check if the remote Broker is another instance of a daemon</td> | <td>Check if the remote Broker is another instance of a daemon</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Clean Session</td> | <td>Clean Session</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Check to discard session state after connecting or disconnecting</td> | <td>Check to discard session state after connecting or disconnecting</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 140: | ||
The last section of MQTT Broker parameters is called '''Miscellaneous'''. It contains parameters that are related to neither Security nor Bridge. | The last section of MQTT Broker parameters is called '''Miscellaneous'''. It contains parameters that are related to neither Security nor Bridge. | ||
| − | [[Image:Services mqtt broker settings misc.PNG]] | + | [[Image:Services mqtt broker settings misc.PNG| border| class=tlt-border]] |
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 145: | Line 150: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>ACL File</td> | <td>ACL File</td> | ||
| − | <td>.ACL file; | + | <td>.ACL file; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>The contents of this file are used to control client access to topics of the broker</td> | <td>The contents of this file are used to control client access to topics of the broker</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Password File</td> | <td>Password File</td> | ||
| − | <td>password file; | + | <td>password file; default: '''none'''</td> |
| − | <td>The Password file stores user names and corresponding passwords, used for authentication</td> | + | <td>The Password file stores user names and corresponding passwords, used for authentication. The file can be produced by mosquitto_passwd on the ssh command line, see https://mosquitto.org/man/mosquitto_passwd-1.html</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Persistence</td> | <td>Persistence</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>If enabled, connection, subscription and message data will be written to the disk. Otherwise, the data is stored in the router’s memory only</td> | <td>If enabled, connection, subscription and message data will be written to the disk. Otherwise, the data is stored in the router’s memory only</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Allow Anonymous</td> | <td>Allow Anonymous</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''yes'''</td> |
<td>If enabled, the Broker allows anonymous access</td> | <td>If enabled, the Broker allows anonymous access</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 169: | Line 174: | ||
An '''MQTT Publisher''' is a client that sends messages to the Broker, who then forwards these messages to the Subscriber. | An '''MQTT Publisher''' is a client that sends messages to the Broker, who then forwards these messages to the Subscriber. | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Networking_rut955_manual_mqtt_publisher_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] |
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 179: | Line 184: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
| − | <td>yes | no; | + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> |
<td>Toggles the MQTT Publisher ON or OFF</td> | <td>Toggles the MQTT Publisher ON or OFF</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Hostname</td> | <td>Hostname</td> | ||
| − | <td>host | ip; | + | <td>host | ip; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>Broker’s IP address or hostname</td> | <td>Broker’s IP address or hostname</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Port</td> | <td>Port</td> | ||
| − | <td>integer [0..65535]; | + | <td>integer [0..65535]; default: '''1883'''</td> |
<td>Specifies the port used for connecting to the Broker</td> | <td>Specifies the port used for connecting to the Broker</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Username</td> | <td>Username</td> | ||
| − | <td>string; | + | <td>string; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>User name used for authentication when connecting to the Broker</td> | <td>User name used for authentication when connecting to the Broker</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Password</td> | <td>Password</td> | ||
| − | <td>string; | + | <td>string; default: '''none'''</td> |
<td>Password used for authentication when connecting to the Broker</td> | <td>Password used for authentication when connecting to the Broker</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>TLS</td> | ||
| + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
| + | <td>Toggles the TLS authentication between ON or OFF.</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Allow insecure connection</td> | ||
| + | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
| + | <td>If enabled, router will be allowed to not verify server's authenticity.</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>CA file</td> | ||
| + | <td>.ca file; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
| + | <td>'''Certificate authority''' is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate.</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Certificate file</td> | ||
| + | <td>.crt file; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
| + | <td>Certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. Client certificates play a key role in many mutual authentication designs, providing strong assurances of a requester's identity.</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Key file</td> | ||
| + | <td>.key file; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
| + | <td>Private key for client to establish connection.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:RUT900 Services section]] | [[Category:RUT900 Services section]] | ||
Revision as of 09:07, 27 August 2020
Main Page > RUT Routers > RUT900 > RUT900 Manual > RUT900 WebUI > RUT900 Services section > RUT900 MQTTSummary
MQTT (MQ Telemetry Transport or Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is an ISO standard (ISO/IEC PRF 20922) publish-subscribe-based "lightweight" messaging protocol for use on top of the TCP/IP protocol. It is designed to send short messages from one client (publisher) to another (subscriber) through brokers, which are responsible for message delivery to the end point. RUT routers support this functionality via an open source Mosquitto broker. The messages are sent this way: a client (subscriber) subscribes to a topic(s); a publisher posts a message to that specific topic(s). The broker then checks who is subscribed to that particular topic(s) and transmits data from the publisher to the subscriber. This chapter is a summary of the MQTT function in RUT routers.
For in-depth MQTT configuration examples, refer to this page: Monitoring via MQTT
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the RUT9XX_R_00.06.06 firmware version.
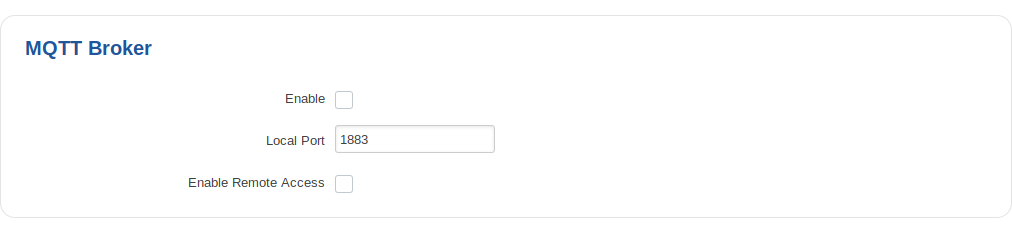
MQTT Broker
The Broker will “listen” for connections on the specified Local port. In order to accept connections from WAN, you also need to check Enable Remote Access.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles MQTT Broker ON or OFF |
| Local Port | integer [0..65535]; Default: "1883" | Specifies the local port that the MQTT broker will listen to |
| Enable Remote Access | yes | no; default: no | If enabled, MQTT Broker will be reachable by remote user (from WAN) |
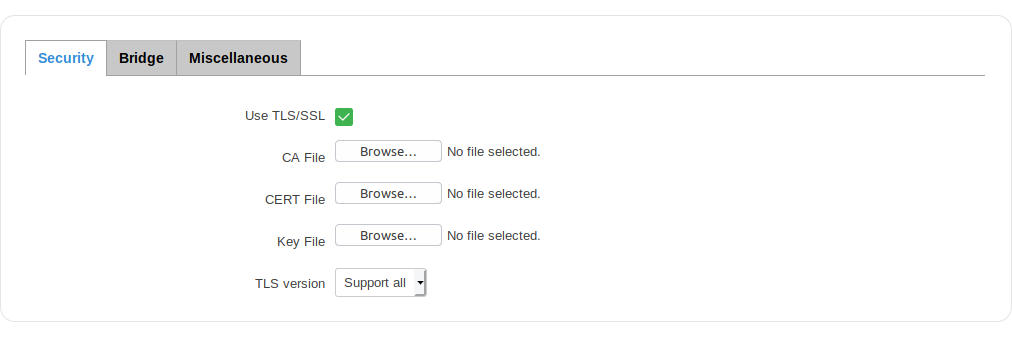
Security
The MQTT Security tab is used to establish MQTT connection security via TLS/SSL.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Use TLS/SSL | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the use of TLS/SSL certificates ON or OFF |
| CA File | .ca file; default: none | Certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate |
| CERT File | .crt file; default: none | Certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. Client certificates play a key role in many mutual authentication designs, providing strong assurances of a requester's identity |
| Key File | .key file; default: none | Private key for client to establish connection |
| TLS version | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2 | Support all; Default: Support all | Authenticates a client to a server and establishes precisely who they are |
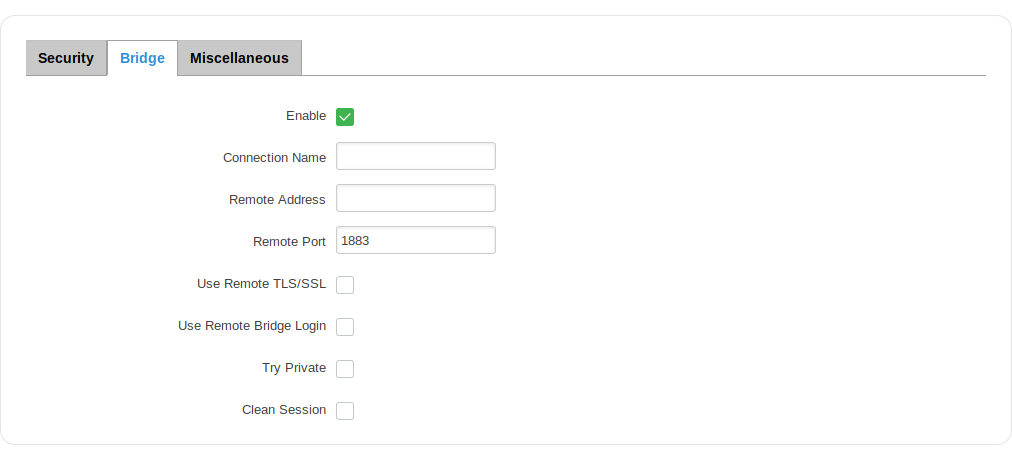
Bridge
The MQTT Broker also supports a functionality called Bridge. An MQTT Bridge is used for the communication between two MQTT Brokers. The window of Bridge parameters is presented below. Some of these are mandatory as they are needed to create a connection: Connection Name, Remote Address and Remote Port. For more information on MQTT Bridge parameters you can read the official mosquitto.conf manual page.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Use TLS/SSL | yes | no; default: no | Toggles MQTT Bridge ON or OFF |
| Connection Name | string; default: none | Name of the Bridge connection. Although this is used for easier management purposes, this field is mandatory |
| Remote Address | ip; default: none | Remote Broker’s address |
| Remote Port | integer [0..65535]; Default: 1883 | Specifies which port the remote broker uses to listen for connections |
| Use Remote TLS/SSL | yes | no; default: no | Enables the use of TSL/SSL certificates of the remote broker. If this is checked, you will be prompted to upload TLS/SSL certificates. More information can be found in the Security section of this chapter |
| Use Remote Bridge Login | yes | no; default: no | Enables the use of Remote login data. If this is checked, you will be prompted to enter a remote client ID, username and password |
| Topic | string; default: none | Specifies the names of the Topics that your Broker will subscribe to |
| Try Private | yes | no; default: no | Check if the remote Broker is another instance of a daemon |
| Clean Session | yes | no; default: no | Check to discard session state after connecting or disconnecting |
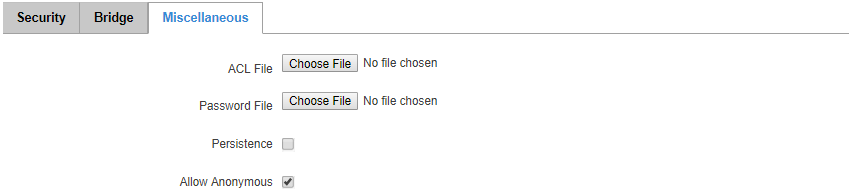
Micellaneous
The last section of MQTT Broker parameters is called Miscellaneous. It contains parameters that are related to neither Security nor Bridge.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| ACL File | .ACL file; default: none | The contents of this file are used to control client access to topics of the broker |
| Password File | password file; default: none | The Password file stores user names and corresponding passwords, used for authentication. The file can be produced by mosquitto_passwd on the ssh command line, see https://mosquitto.org/man/mosquitto_passwd-1.html |
| Persistence | yes | no; default: no | If enabled, connection, subscription and message data will be written to the disk. Otherwise, the data is stored in the router’s memory only |
| Allow Anonymous | yes | no; default: yes | If enabled, the Broker allows anonymous access |
MQTT Publisher
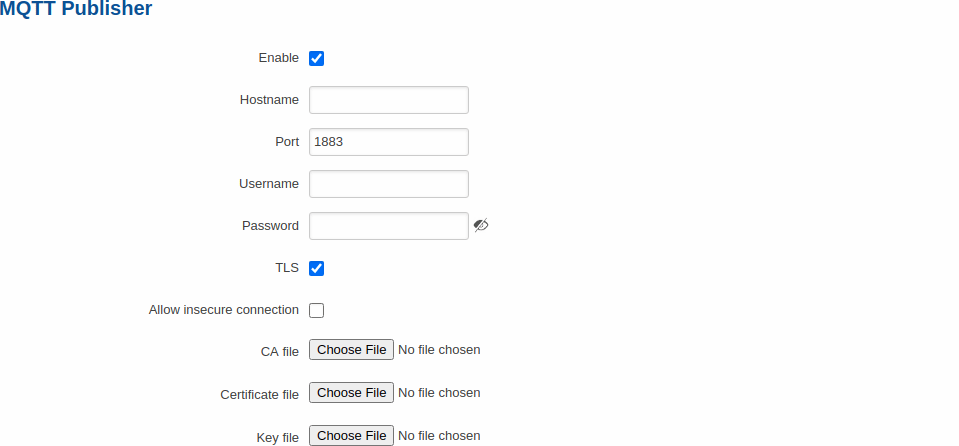
An MQTT Publisher is a client that sends messages to the Broker, who then forwards these messages to the Subscriber.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the MQTT Publisher ON or OFF |
| Hostname | host | ip; default: none | Broker’s IP address or hostname |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Specifies the port used for connecting to the Broker |
| Username | string; default: none | User name used for authentication when connecting to the Broker |
| Password | string; default: none | Password used for authentication when connecting to the Broker |
| TLS | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the TLS authentication between ON or OFF. |
| Allow insecure connection | yes | no; default: no | If enabled, router will be allowed to not verify server's authenticity. |
| CA file | .ca file; default: none | Certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. |
| Certificate file | .crt file; default: none | Certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. Client certificates play a key role in many mutual authentication designs, providing strong assurances of a requester's identity. |
| Key file | .key file; default: none | Private key for client to establish connection. |