Difference between revisions of "TRB140 Static Routes"
From Teltonika Networks Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| − | + | <b>Static routes</b> specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. This chapter is an overview of the Static Routes page in {{{name}}} gateways. | |
| − | ==Static | + | {{Template: Networking_trb_manual_fw_disclosure |
| − | [[File:Networking trb manual static routes v1.png| | + | | fw_version = {{{fw_version}}} |
| − | <br /><table class="nd-mantable"><tr><th> | + | }} |
| + | ==Static routes== | ||
| + | To find information on static route configuration, refer to the figure and table below: | ||
| + | [[File:Networking trb manual static routes v1.png|left|frameless|1096x1096px]] | ||
| + | <br /><table class="nd-mantable"><tr><th>Field</th><th>Value</th><th>Description</th></tr><tr><td>Interface</td><td>mobile | lan; default: <b>mobile</b></td><td>The zone where the target network resides</td></tr><tr><td>Target<span class="asterisk">*</span></td><td>ip4; default: <b>0.0.0.0</b></td><td>The address of the destination network</td></tr><tr><td>Netmask<span class="asterisk">*</span></td><td>netmask; default: <b>255.255.255.255</b></td><td>A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies</td></tr><tr><td>Gateway</td><td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td><td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule</td></tr><tr><td>Metric</td><td>integer; default: <b>0</b></td><td>The <b>metric</b> value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the lower metric is applied.</td></tr><tr><td>MTU</td><td>integer [64..9000]; default: <b>1500</b></td><td>Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction.</td></tr><tr><td>Route Type</td><td>unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast | -- custom -- ; default: <b>unicast</b></td><td>Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:<ul><li><b>unicast</b> -</li><li><b>local</b> - routes of this type are added to the 'local' routing table and used only for locally hosted IPs.</li><li><b>broadcast</b> - routes of this type are added to the 'local' routing table and used by link layer devices that support the broadcast address principle.</li><li><b>multicast</b> -</li><li><b>unreachable</b> -</li><li><b>prohibit</b> - used to prohibit traffic to specified host or network. When a destination is prohibited, the kernel sends a 'Network is unreachable' response the source address.</li><li><b>blackhole</b> - packets that match this type of route are discarded without any response.</li><li><b>anycast</b> -</li><li><b>-- custom --</b> -</li></ul></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <span class="asterisk">*</span><b>Additional notes on Target & Netmask:</b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this:<ul><li><b>Target</b>: some IP</li><li><b>Netmask</b>: 255.255.255.255</li></ul>Furthermore, you can define a rules that apply to a range of IPs. Refer to the table below for examples.<table class="nd-mantable"><tr><th>Target</th><th>Netmask</th><th>Description</th></tr><tr><td>192.168.2.0</td><td>255.255.255.240</td><td>Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.15 range.</td></tr><tr><td>192.168.2.240</td><td>255.255.255.240</td><td>Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.240 - 192.168.2.255 range.</td></tr><tr><td>192.168.2.161</td><td>255.255.255.0</td><td>Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.55.255 range.</td></tr><tr><td>192.168.0.0</td><td>255.255.0.0</td><td>Applies to IPs in the 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 range.</td></tr><tr><td>192.168.2.161</td><td>255.255.255.255</td><td>Only applies to 192.168.2.161.</td></tr></table><br /> | ||
Revision as of 18:36, 21 November 2019
Summary
Static routes specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. This chapter is an overview of the Static Routes page in {{{name}}} gateways.
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the [[Media:{{{fw_version}}}.bin|{{{fw_version}}}]] firmware version.
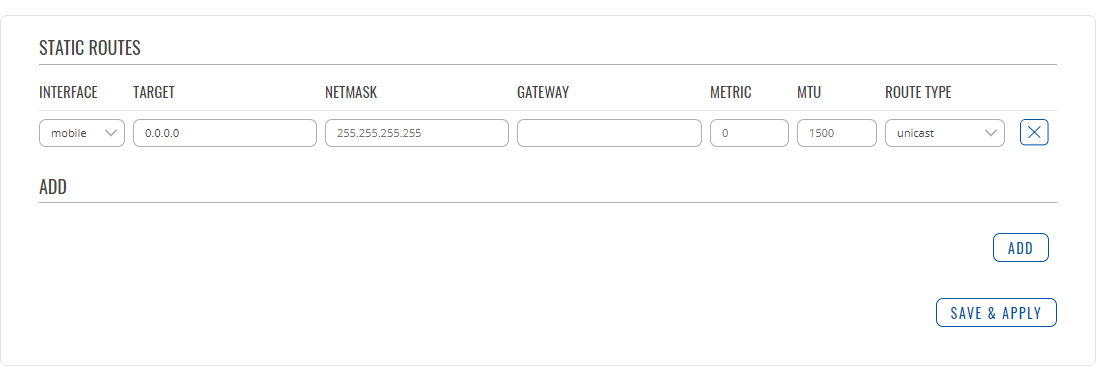
Static routes
To find information on static route configuration, refer to the figure and table below:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | mobile | lan; default: mobile | The zone where the target network resides |
| Target* | ip4; default: 0.0.0.0 | The address of the destination network |
| Netmask* | netmask; default: 255.255.255.255 | A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies |
| Gateway | ip; default: none | Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule |
| Metric | integer; default: 0 | The metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | integer [64..9000]; default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast | -- custom -- ; default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:
|
*Additional notes on Target & Netmask:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this:
- Target: some IP
- Netmask: 255.255.255.255
Furthermore, you can define a rules that apply to a range of IPs. Refer to the table below for examples.
| Target | Netmask | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.2.0 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.15 range. |
| 192.168.2.240 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.240 - 192.168.2.255 range. |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.55.255 range. |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 range. |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.255 | Only applies to 192.168.2.161. |