Template:Networking rutos manual network: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_latest_fw | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| name = {{{name}}} | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} Network (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: | {{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} Network (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT2 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} Network (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: | {{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT2 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} Network (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT2XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 21: | ||
The <b>Mobile</b> tab displays information about the mobile connection. The figure below is an example of the Mobile tab: | The <b>Mobile</b> tab displays information about the mobile connection. The figure below is an example of the Mobile tab: | ||
{{#switch: {{{series}}} | {{#switch: {{{series}}} | ||
| RUTX | RUTM | | RUTX | RUTM = | ||
{{#switch: {{{name}}} | {{#switch: {{{name}}} | ||
| RUTX09|RUTX11|RUTXR1|RUTX50|RUTM09|RUTM11|RUTM50 | | RUTX09|RUTX11|RUTXR1|RUTX50|RUTM09|RUTM11|RUTM50|RUTX14 = [[File:Networking rutx manual network mobile v4.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| RUTX12|RUTM12 = [[File:Networking rutx12 manual network mobile | | RUTX12|RUTM12 = [[File:Networking rutx12 manual network mobile v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| TRB1|RUT2|RUT2M|RUT36X| | | TRB1|RUT2|RUT2M|RUT36X = [[File:Networking_trb14x_manual_network_v4.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| | | TRB2|RUT9|RUT9M = [[File:Networking_trb2XX_manual_network_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| TRB5 = [[File:Networking_trb5_manual_network_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| TCR1 = [[File:Networking_rutx_manual_network_mobile_v4.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
{{#switch: {{{series}}} | {{#switch: {{{series}}} | ||
|RUTX|RUTM | |RUTX|RUTM= | ||
{{#switch:{{{name}}} | {{#switch:{{{name}}} | ||
|RUTX12= | |RUTX12= | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Data connection state</td> | <td>Data connection state</td> | ||
<td>Indicates whether the device has a mobile data connection or not | <td>Indicates whether the device has a mobile data connection or not</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 113: | Line 109: | ||
<td>Mobile network type. Possible values are: | <td>Mobile network type. Possible values are: | ||
<ul>{{#ifeq: {{{5g}}} | 1 | | <ul>{{#ifeq: {{{5g}}} | 1 | | ||
<li> <b>5G</b>: | <li> <b>5G</b>: 5G (NSA), 5G (SA)</li>|}} | ||
<li> <b>4G</b>: | <li> <b>4G</b>: | ||
{{# | {{#ifeq: {{{name}}} | TRB255 | | ||
4G (NB), 4G (M1) | 4G (NB), 4G (M1) | ||
| | | 4G (LTE) }} | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
{{# | {{#ifeq: {{{name}}} | TRB255 | | | ||
<li> <b>3G</b>: 3G (WCDMA), 3G (HSDPA), 3G (HSUPA), 3G (HSPA), 3G (HSPA+), 3G (DC-HSPA+), 3G (HSDPA+HSUPA), UMTS</li> | <li> <b>3G</b>: 3G (WCDMA), 3G (HSDPA), 3G (HSUPA), 3G (HSPA), 3G (HSPA+), 3G (DC-HSPA+), 3G (HSDPA+HSUPA), UMTS</li> | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{ | {{#ifeq: {{{2G}}} | 1 | <!-- add variable for rut9 devices --> | ||
<li><b>2G</b>: 2G (GSM), 2G (GPRS), 2G (EDGE)</li> | <li><b>2G</b>: 2G (GSM), 2G (GPRS), 2G (EDGE)</li> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 136: | Line 132: | ||
By combining more than one carrier together, either in the same or different bands it is possible to increase the bandwidth available and in this way increase the capacity of the link. | By combining more than one carrier together, either in the same or different bands it is possible to increase the bandwidth available and in this way increase the capacity of the link. | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Connected band</td> | <td>Connected band</td> | ||
<td>Currently used mobile frequency band.</td> | <td>Currently used mobile frequency band.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Signal strength</td> | ||
<td>Received signal strength indicator (<b>[[RSSI]]</b>) measured in dBm. Values closer to 0 indicate a better signal strength</td> | <td>Received signal strength indicator (<b>[[RSSI]]</b>) measured in dBm. Values closer to 0 indicate a better signal strength</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Bytes received</td> | ||
<td>Amount of data received through the mobile interface</td> | <td>Amount of data received through the mobile interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Bytes sent</td> | ||
<td>Amount of data sent through the mobile interface</td> | <td>Amount of data sent through the mobile interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 154: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>LAC | <td>LAC</td> | ||
<td | <td>The Location Area Code, abbreviated as LAC is the unique number given to each location area within the network. The served area of a cellular radio access network is usually divided into location areas, consisting of one or several radio cells.</td> | ||
</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 174: | Line 162: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>EARFCN</td> | ||
<td>In | <td>In GSM cellular networks, an absolute radio-frequency channel number (ARFCN) is a code that specifies a pair of physical radio carriers used for transmission and reception in a land mobile radio system, one for the uplink signal and one for the downlink signal.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Mobile country code</td> | <td>Mobile country code</td> | ||
<td>The Mobile Country Code, abbreviated as MCC, is the code uniquely identifying the home country of a (Glossary:Mobile network operator (MNO | <td>The Mobile Country Code, abbreviated as MCC, is the code uniquely identifying the home country of a (Glossary:Mobile network operator (MNO|mobile network operator (MNO).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 186: | Line 174: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
{{#switch: {{{series}}} | RUTX | RUTM= | |||
====Modem layout==== | |||
The <b>Modem layout</b> section visually indicates where the internal and external modems are positioned. | |||
{{#switch: {{{name}}} | |||
[[File: | |RUTX09|RUTM09 = [[File:Networking_rutx09_manual_network_mobile_modem_layout.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
|RUTX11|RUTM11 = [[File:Networking_rutx11_manual_network_mobile_modem_layout.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
|RUTX12|RUTM12 = [[File:Networking_rutx12_manual_network_mobile_modem_layout.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
|RUTXR1 = [[File:Networking_rutxr1_manual_network_mobile_modem_layout.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}}|#defaul=}} | |||
====Bands==== | ====Bands==== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<table class="nd-othertables"> | <table class="nd-othertables"> | ||
| Line 206: | Line 199: | ||
<td>Overall signal quality for different network types is defined by different measurements. Short explanations and recommendations are provided below. Click <b>[[Mobile Signal Strength Recommendations|here]]</b> for more in-depth information or click on one of the links below: | <td>Overall signal quality for different network types is defined by different measurements. Short explanations and recommendations are provided below. Click <b>[[Mobile Signal Strength Recommendations|here]]</b> for more in-depth information or click on one of the links below: | ||
<ul>{{#ifeq: {{{5g}}} | 1 | | <ul>{{#ifeq: {{{5g}}} | 1 | | ||
<li> <b>5G</b | <li> <b>5G</b> </li>|}} | ||
<li><b>4G</b> | <li><b>4G</b> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 220: | Line 208: | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
{{# | {{#ifeq: {{{name}}} | TRB255 | | | ||
<li><b>3G</b> | <li><b>3G</b> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 229: | Line 217: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{ | {{#ifeq: {{{2G}}} | 1 | | ||
<li><b>2G</b> | <li><b>2G</b> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 247: | Line 235: | ||
This tab displays information about the device's local network(s). The figure below is an example of the '''Network''' window: | This tab displays information about the device's local network(s). The figure below is an example of the '''Network''' window: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_network_lan_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-othertables"> | <table class="nd-othertables"> | ||
| Line 258: | Line 246: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>IP address</td> | ||
<td>IP address of the LAN interface</td> | <td>IP address of the LAN interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 267: | Line 255: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th colspan="2">dhcp leases</th> | <th colspan="2">dhcp leases</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 287: | Line 271: | ||
<td>Leasetime Remaining</td> | <td>Leasetime Remaining</td> | ||
<td>Remaining lease time for a DHCP client. Active DHCP lease holders will try to renew their DHCP leases after a half of the lease time passes. </td> | <td>Remaining lease time for a DHCP client. Active DHCP lease holders will try to renew their DHCP leases after a half of the lease time passes. </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Firewall== | |||
This tab displays information about the device's firewall. The figure below is an example of the '''Firewall''' page: | |||
[[File:Networking rutos manual network | [[File:Networking rutos manual status network firewall nat.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
[[File:Networking rutos manual status network firewall raw.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
= | [[File:Networking rutos manual status network firewall mangle.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
[[File:Networking rutos manual status network firewall filter.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{wifi}}} | 1 | | |||
==Wireless== | |||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_status_network_wifi_{{{wifi}}}_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd- | <table class="nd-othertables"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th width="250">Field name</th> | <th width="250">Field name</th> | ||
| Line 365: | Line 299: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>SSID</td> | ||
<td> | <td>The broadcasted SSID (Service Set Identifier) of the wireless network</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
< | <td>Wireless MAC</td> | ||
< | <td>The MAC (Media Access Control) address of the access point radio</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Band</td> | ||
<td> | <td>The band defines which frequency used </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Signal</td> | ||
<td> | <td>The signal quality between router's radio and some other device that is connected to the router</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Bit rate</td> | ||
<td> | <td>The maximum possible physical throughput that the router's radio can handle. Bit rate will be shared between router and other possible devices which connect to local Access Point (AP) </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Mode</td> | ||
<td> | <td>Connection mode. Can either be Access Point (AP) or Client. In AP mode others can connect to this router's wireless connection. In client mode router connects to other wireless networks</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td> | <td>Encryption</td> | ||
<td> | <td>The type of WiFi encryption used</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Hostname</td> | ||
<td> | <td>Device's hostname</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>IP address</td> | ||
<td> | <td>Shows what IP address leased for device</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>MAC address</td> | ||
<td> | <td>Device's MAC (Media Access Control) address</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Signal</td> | ||
<td> | <td>Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). Signal's strength measured in dBm</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>RX rate</td> | ||
<td> | <td>The rate at which packets are received from associated interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
< | <td>TX rate</td> | ||
< | <td>The rate at which packets are sent to associated interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
|}} | |||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Status section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} Status section]] | ||
Revision as of 08:45, 14 September 2023
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The Network page contains information related to the device's networking. This chapter is an overview of the Network page in {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
mobile network operator (MNO). Mobile network code Mobile Network Code (MNC) is a unique two- or three-digit number used to identify a home Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) to. MNC is allocated by the national regulator.
Bands
| bands information | |
|---|---|
| Name | Connected band |
| Other signal level measurements | Overall signal quality for different network types is defined by different measurements. Short explanations and recommendations are provided below. Click here for more in-depth information or click on one of the links below:
|
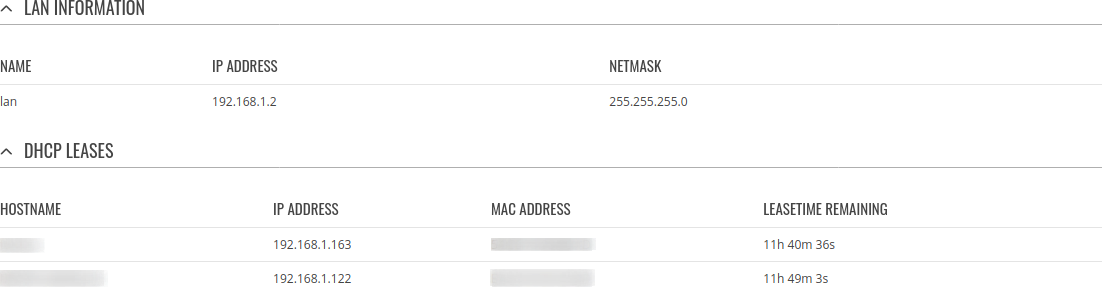
LAN
This tab displays information about the device's local network(s). The figure below is an example of the Network window:
| lan information | |
|---|---|
| Name | LAN interface name |
| IP address | IP address of the LAN interface |
| Netmask | Netmask of the LAN interface. In a sense, a netmask specifies the size of a network. In other words, it indicates which part of the IP address denotes the network, and which denotes the device |
| dhcp leases | |
| Hostname | Hostname of a LAN client |
| IP Address | IP address of a LAN client |
| MAC Address | MAC address of a LAN client |
| Leasetime Remaining | Remaining lease time for a DHCP client. Active DHCP lease holders will try to renew their DHCP leases after a half of the lease time passes. |
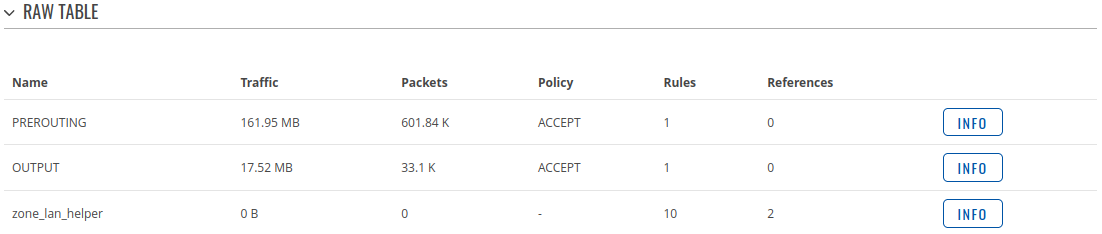
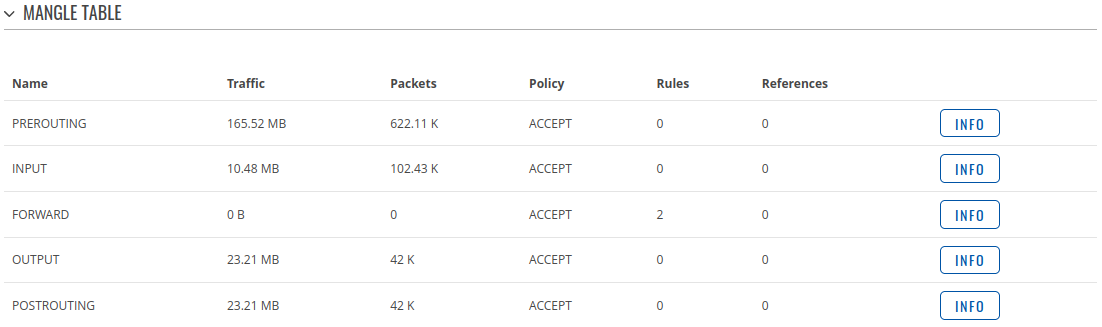
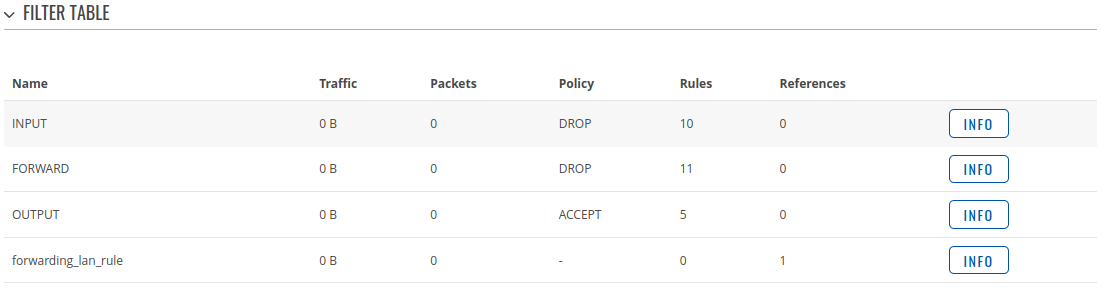
Firewall
This tab displays information about the device's firewall. The figure below is an example of the Firewall page:
[[Category:{{{name}}} Status section]]