TSW212 Ports: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Template: Networking_tswos_manual_ports <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> | name = TSW212 | series = TSW2 <!----------------------SEPARATORS--...") |
m (Vainius.l moved page Draft:TSW212 Ports to TSW212 Ports without leaving a redirect) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| series = TSW2 | | series = TSW2 | ||
<!----------------------SEPARATORS---------------------> | <!----------------------SEPARATORS---------------------> | ||
| poe = 0 | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:32, 25 October 2023
Main Page > TSW Switches > TSW212 > TSW212 Manual > TSW212 WebUI > TSW212 Network section > TSW212 PortsThe information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version TSW2_R_00.01.03.1.
Summary
The Ports page provides information related to the status of the device's physical ports, as well as the ability to edit port settings, security, loopback detection.
General
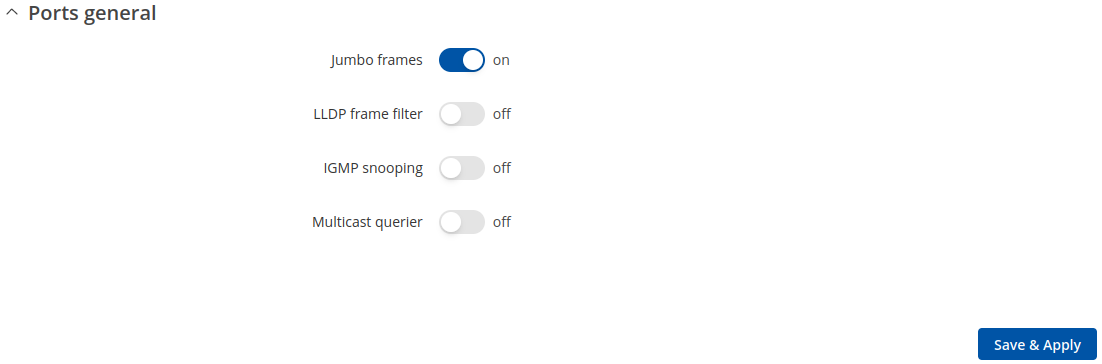
In this section you can enable Jumbo frames and LLDP frame filter services.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Jumbo frames | off | on; default: on | Allow ethernet frame with a payload greater than the standard maximum transmission unit (MTU) of 1500 bytes. This may improve network performance by making data transmissions more efficient. |
| LLDP frame filter | off | on; default: off | Enable to stop the forwarding of LLDP frames. |
| IGMP snooping | off | on; default: off | Enables IGMP snooping. |
| Multicast querier | off | on; default: off | Enables multicast querier. |
Port Settings
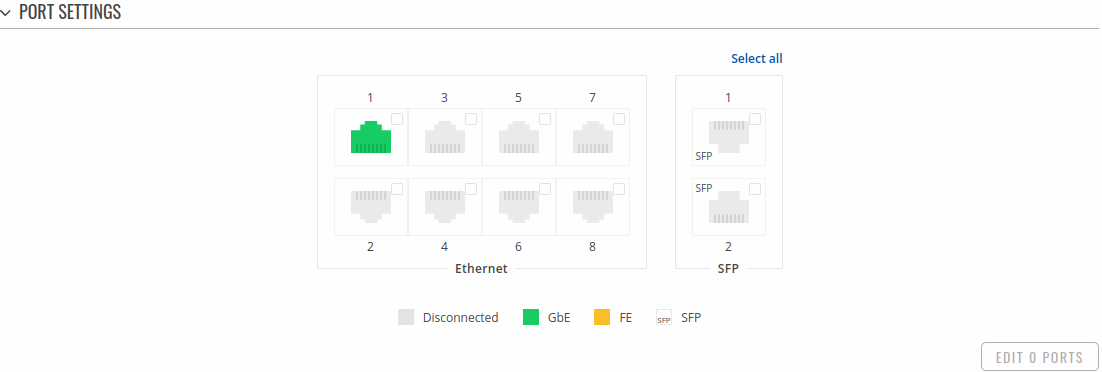
This section displays information about the status of the device's ports with the ability to configure port settings.
Port Settings
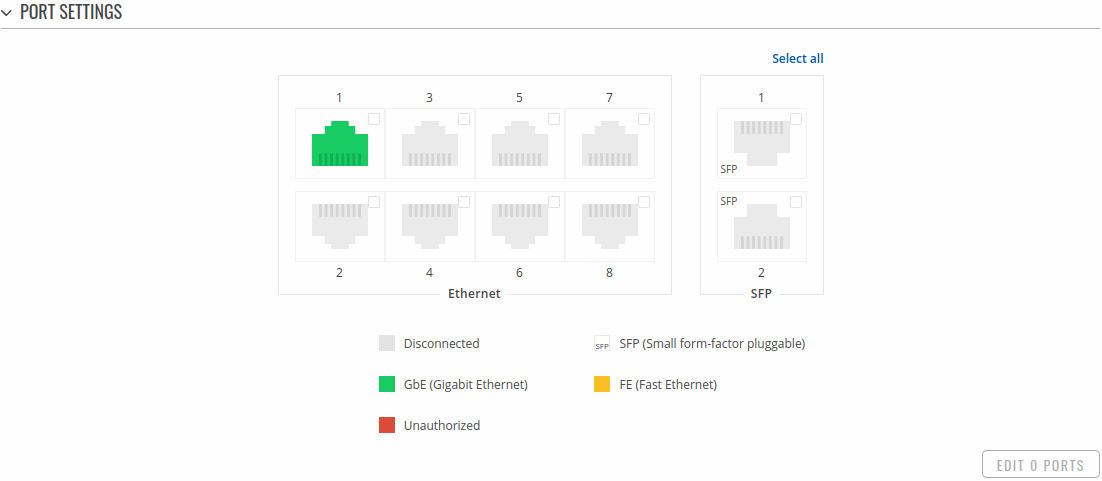
The figure below is an example of the All Ports window, color indicates port speed and status:
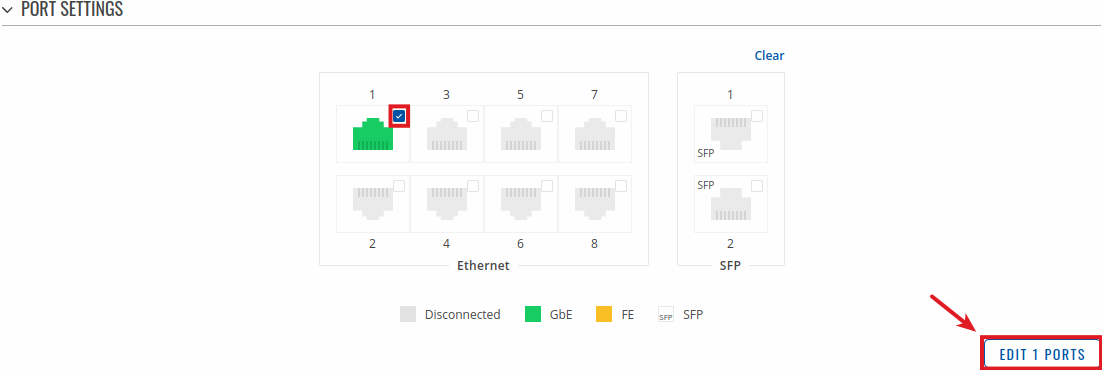
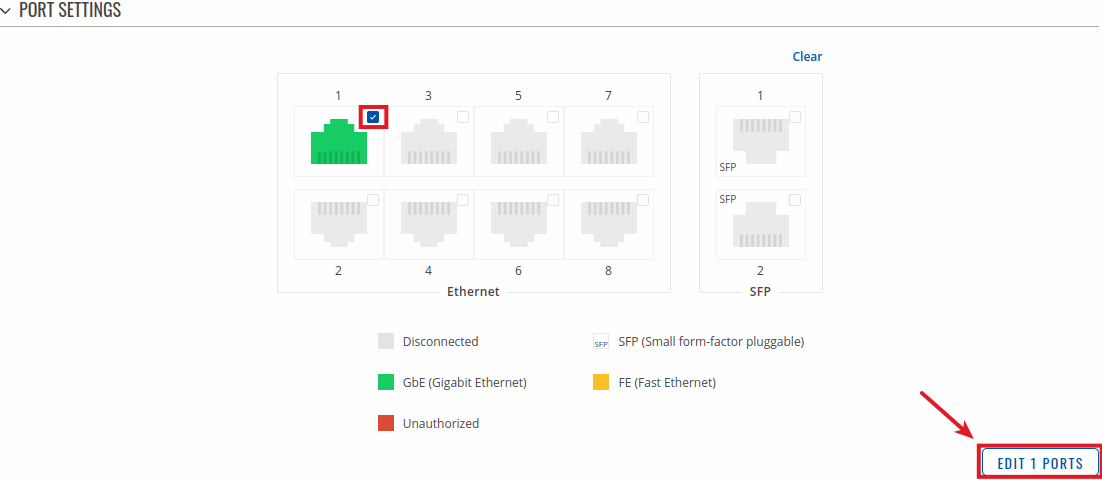
To change port settings select port and press `edit (number of ports) ports` button:
You will be redirected to `Port settings`. From here you can enable/disable ports or change settings:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Toggle port on or off. |
| Port name | string; default: none | Name of the port. This is only used for easier management purposes. |
| EEE | off | on; default: on | Enable Energy-Efficient Ethernet. |
| Isolate port | off | on; default: off | When enabled port will be isolated from other isolated ports. Traffic between isolated ports will droped. Traffic between isolated and normal ports will be sent as normal. |
| Link speed | Auto | 10Mbps (E) | 100Mbps (FE) | 1000Mbps (GbE); default: Auto | A measure of how fast ports are able to transmit and receive data. |
| Duplex | Full | Half; default: | Advertises preferred duplex mode and speed for negotiation with other devices. |
Port Status
This section displays port status information. There is also an option to select, enable ports, enable/disable PoE, EEE and Isolation options:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Port | Port ID. |
| Enabled | Enable/Disable port. |
| Status | Port status. |
| Speed | Port link speed.
|
| PoE (W) | PoE port power usage in watts. |
| EEE | Enable/Disable Energy-Efficient Ethernet. |
| Isolation | When enabled port will be isolated from other isolated ports. Traffic between isolated ports will be droped. Traffic between isolated and normal ports will be sent as normal. |
| TX sum | Total upload. |
| RX sum | Total download. |
| TX rate | Upload speed. |
| RX rate | Download speed. |
Port Mirroring
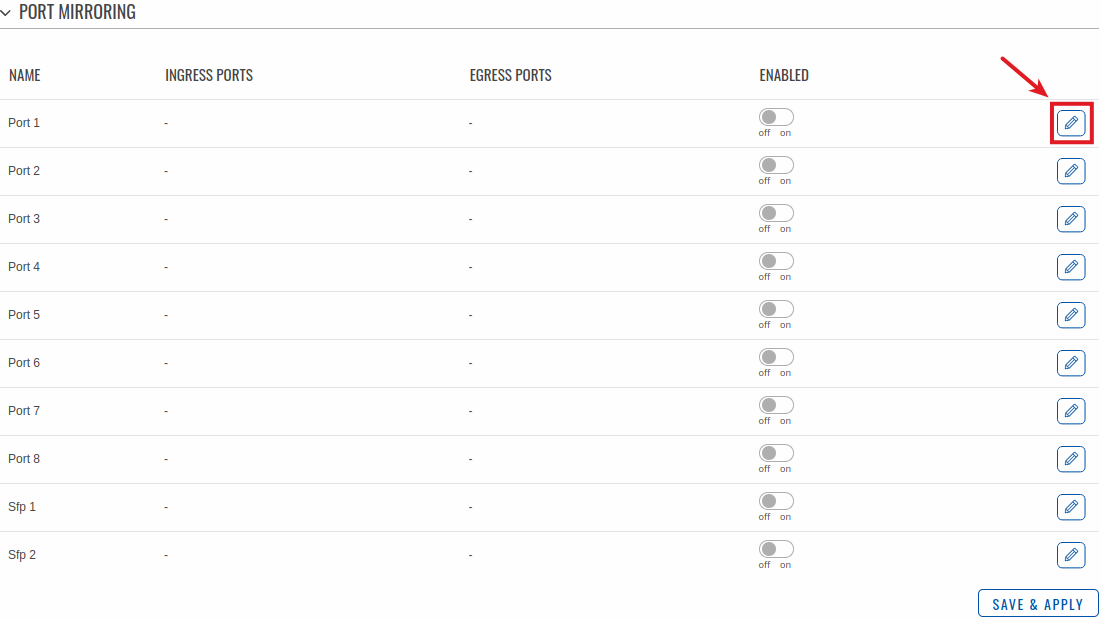
Port Mirroring is a service that mirrors incoming and outgoing packets on one Ethernet port (Source Port) to another (Monitoring Port).
To change port mirroring settings select port and press `Edit` button:
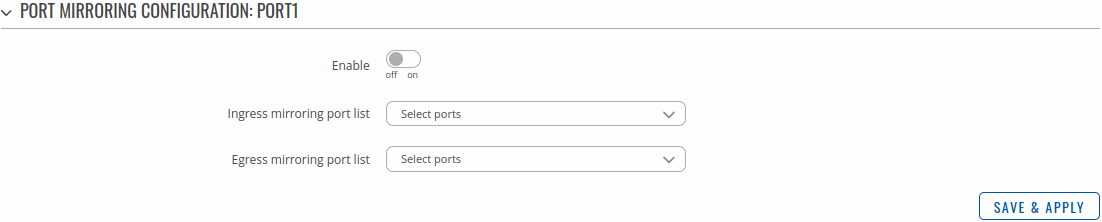
You will be redirected to `Port mirroring settings`, from here you can select ingress and egress ports:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | The port which will mirror the packets. |
| Ingress mirroring port list | port; default: none | Specify which port incoming traffic is mirrored. |
| Egress mirroring port list | port; default: none | Specify which port outcoming traffic is mirrored. |
Loopback Detection
Loopback Detection
A port-based loopback detection service that using its own distinctive packets, seeks to identify and break a network loop by shutting down troublesome ports.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enable loopback detection. |
| Broadcast interval | integer [1..10000]; default: none | Send detection packets in an given interval from 1 to 10000 seconds. |
| Auto-recovery interval | integer [60..10000]; default: none | Restores disabled ports in an given interval from 60 to 10000 seconds. |
Port Tracking
Tracks specific port status. Notes:
![]() To change port tracking setting press on port and you will be redirected to `Port tracking configuration`:
To change port tracking setting press on port and you will be redirected to `Port tracking configuration`:
![]()
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Enable port tracking. |
| Recovery mode | Auto | Manual; default: Auto | Manages port unblocking type.Possible modes:
|
802.1X
This section displays information about the status of the device's ports with the ability to configure port `802.1x` settings.
General
Port Status
The figure below is an example of the Port Status window, color indicates port speed and status:
To change port `802.1x` settings select port and press `edit (number of ports) ports` button:
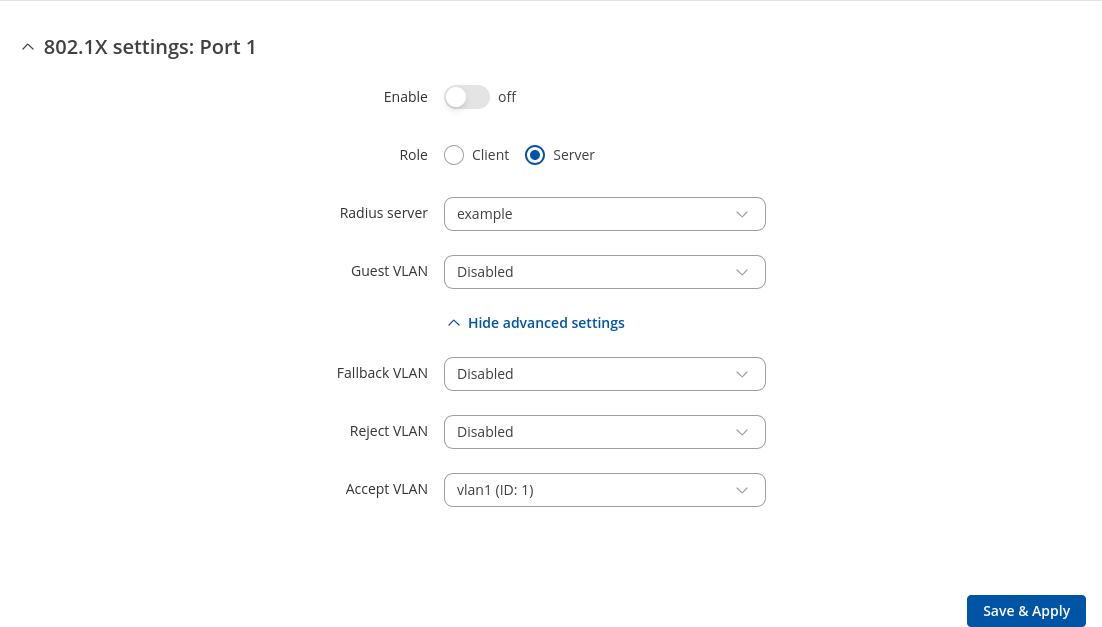
You will be redirected to `Port 802.1x settings`. From here you can enable/disable 802.1x protocol or change role:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Toggle 802.1x on or off. |
| Role | Client | Server; default: Server | Toggle 802.1x role. |
| Radius sever | radius server ID; default: example | Radius server ID. |
| Guest VLAN | Disabled | VLAN; default: Disabled | Select guest VLAN for 802.1x server service. |
| Fallback VLAN | Disabled | VLAN; default: Disabled | Select fallback VLAN 802.1x for server service. |
| Reject VLAN | Disabled | VLAN; default: Disabled | Select reject VLAN 802.1x for server service. |
| Accept VLAN | Radius assigned | VLAN; default: VLAN | Select accept VLAN 802.1x for server service |
| Client: Authentication type | MD5 | TLS | PWD | Tunneled TLS | Protected EAP (PEAP); default: MD5 | Authentication type. |
| Client: Identity (Username) | string; default: none | Used as the username for authentication. |
| Client: MD5, PWD, Tunneled TLS, Protected EAP (PEAP): Password | string; default: none | Used for authentication. |
| Client:TLS: CA Certificate | .crt file; default: none | Radius server CA certificate. |
| Client:TLS: User certificate | .crt file; default: none | TLS client certificate. |
| Client:TLS: Private Key | .key file; default: none | TLS Private Key. |
| Client:TLS: Private Key Password | string; default: none | TLS Private Key Password. |
| Client:Tunneled TLS: Inner authentication | PAP | MSCHAP | MSCHAPv2 | MSCHAPv2 (no EAP) | CHAP | MD5 | GTC; default: PAP | Inner authentication type. |
| Client:Protected EAP (PEAP): Inner authentication | MSCHAPv2 | MD5 | GTC; default: MSCHAPv2 | Inner authentication type. |
| Client:Protected EAP (PEAP): Peap version | auto | 0 | 1; default: auto | Peap version. |
| Client:Tunneled TLS, Protected EAP (PEAP): Anonymous identity | string; default: none | Shown as username outside the encrypted tunnel. Not used for authentication. |
| Client:Tunneled TLS, Protected EAP (PEAP): CA Certificate | .crt file; default: none | Radius server CA certificate. |
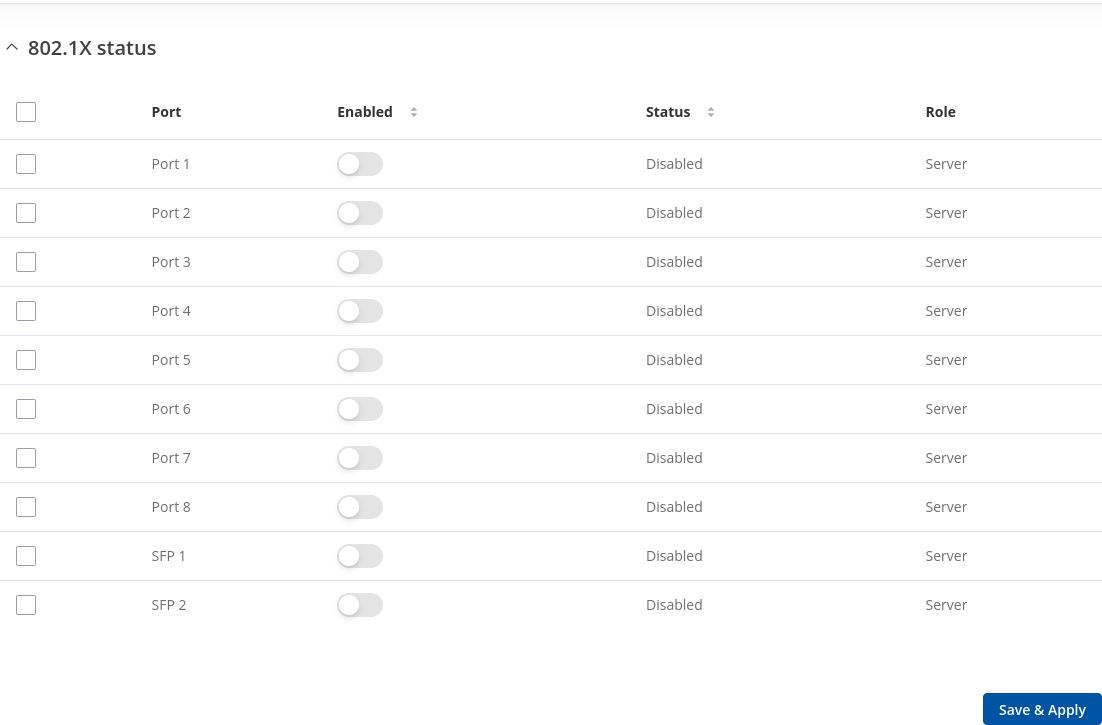
802.1X Status
This section displays port `802.1x` status information. There is also an option to select, enable 802.1x for ports:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Port | Port ID. |
| Enabled | Enables port security on this port. |
| Status | Port status. |
| Role | Shows the role of the port. |
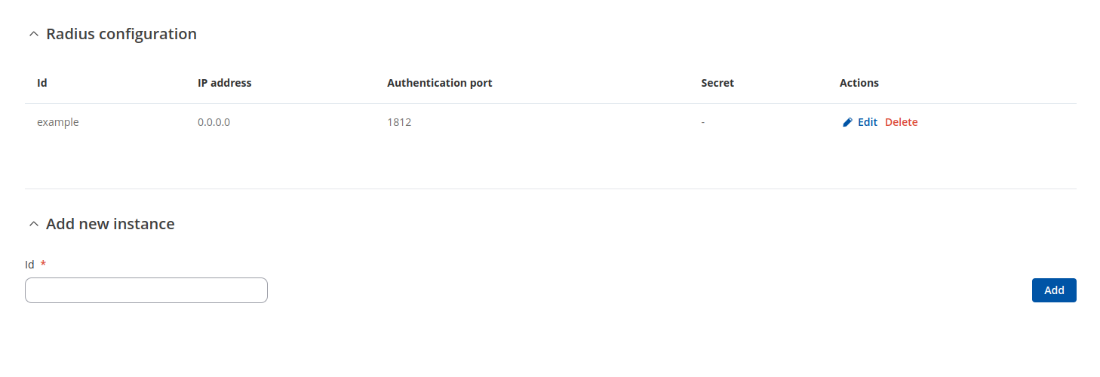
RADIUS
The RADIUS page is used to create and manage radius servers:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | RADIUS server ID. |
| Address (IPv4) | RADIUS server IP. |
| Authentication port | RADIUS server athentication port. |
| Secret | RADIUS server secret. |
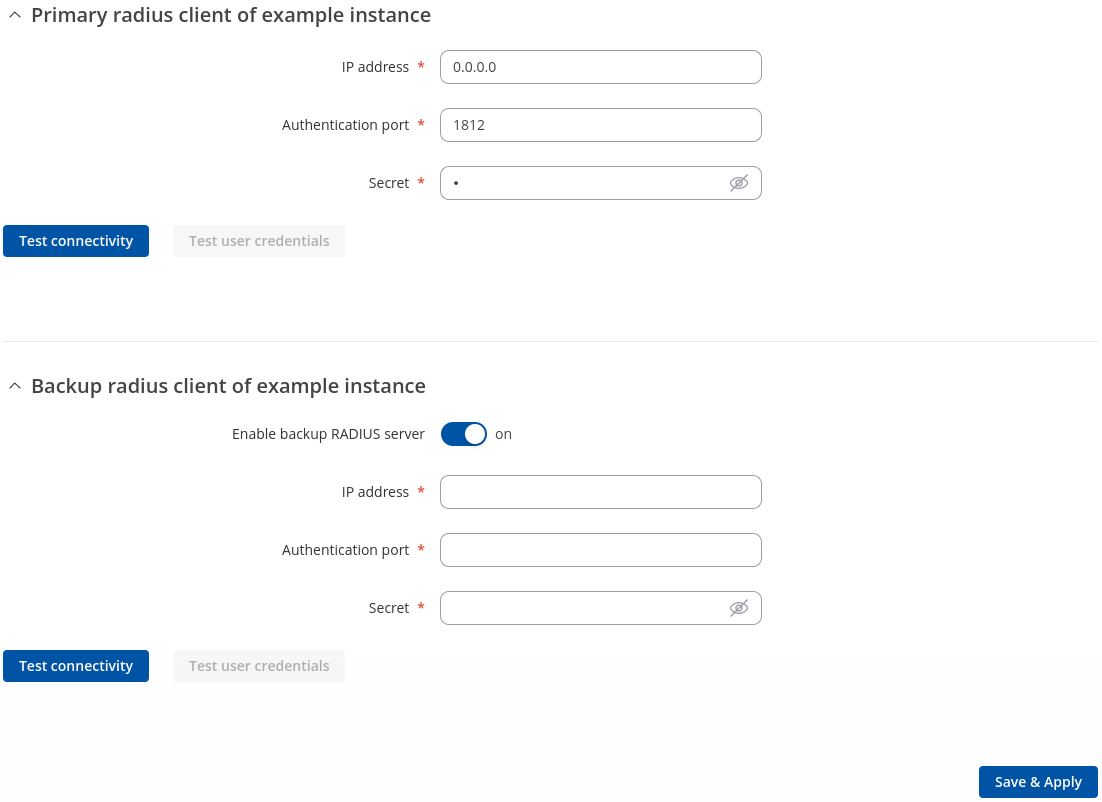
Radius Configuration
The RADIUS configuration window should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IP address | ip; default: 0.0.0.0 | RADIUS server IP. |
| Authentication port | integer [1.. 65535]; default: 1812 | RADIUS server athentication port. |
| Secret | string; default: - | RADIUS server secret. |
| Test connectivity | -(interactive) button | Test connectivity to RADIUS server. |
| Test user credentials | -(interactive) button | Test credentials to RADIUS server. |
| Enable backup RADIUS server | off | on; default: off | Enable backup RADIUS server. |
| IP address | ip; default: none | Backup RADIUS server IP. |
| Authentication port | integer [1.. 65535]; default: none | Backup RADIUS server authentication port. |
| Secret | string; default: - | Backup RADIUS server secret. |
| Test connectivity | -(interactive) button | Test connectivity to backup RADIUS server. |
| Test user credentials | -(interactive) button | Test credentials to backup RADIUS server. |