Template:RutOS configuration example MQTT Gateway: Difference between revisions
m added name variables |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
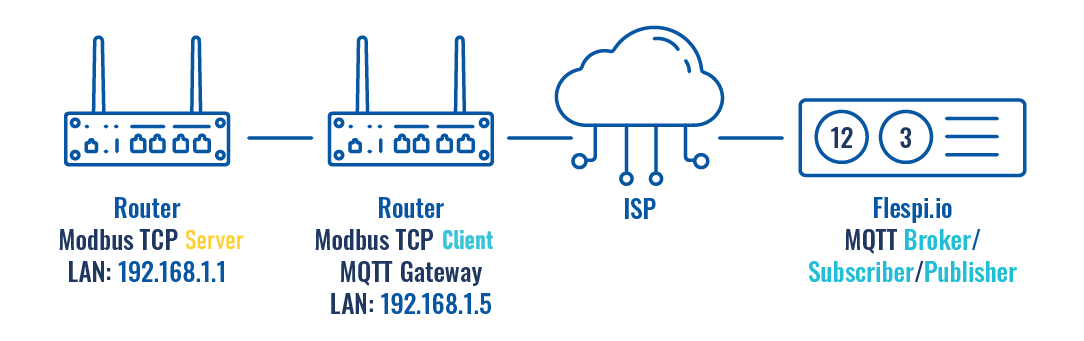
This guide will demonstrate how to configure the MQTT Gateway on a Modbus TCP Client using two different types of MQTT Brokers. The first configuration involves using a third-party MQTT Broker service "'''''Flespi.io'''''". The second setup uses the RUT241 router as the MQTT Broker. In this scenario, two routers will serve as the Modbus TCP Client and Server, while a PC will act as both the MQTT Publisher and Subscriber. | |||
==Configuration overview & prerequisites== | ==Configuration overview & prerequisites== | ||
*Two | *Two routers - '''RUT1''' as Modbus TCP Server (Slave) and '''RUT2''' as Modbus TCP Client (Master) | ||
*Flespi.io account to act as an MQTT Broker/Publisher/Subscriber (for first configuration example) | *Flespi.io account to act as an MQTT Broker/Publisher/Subscriber (for first configuration example) | ||
* | *RUT241 with a Public IP address to act as MQTT Broker (for second configuration example) | ||
*An end device (PC, Laptop) to act as MQTT Subscriber/Publisher (for second configuration example) | *An end device (PC, Laptop) to act as MQTT Subscriber/Publisher (for second configuration example) | ||
==Configuration using flespi.io as MQTT Broker== | ==Configuration using flespi.io as MQTT Broker== | ||
===Configuring | [[File:Networking Topology MQTT MODBUS flespi configuration v2.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
===Configuring Modbus TCP Server=== | |||
---- | ---- | ||
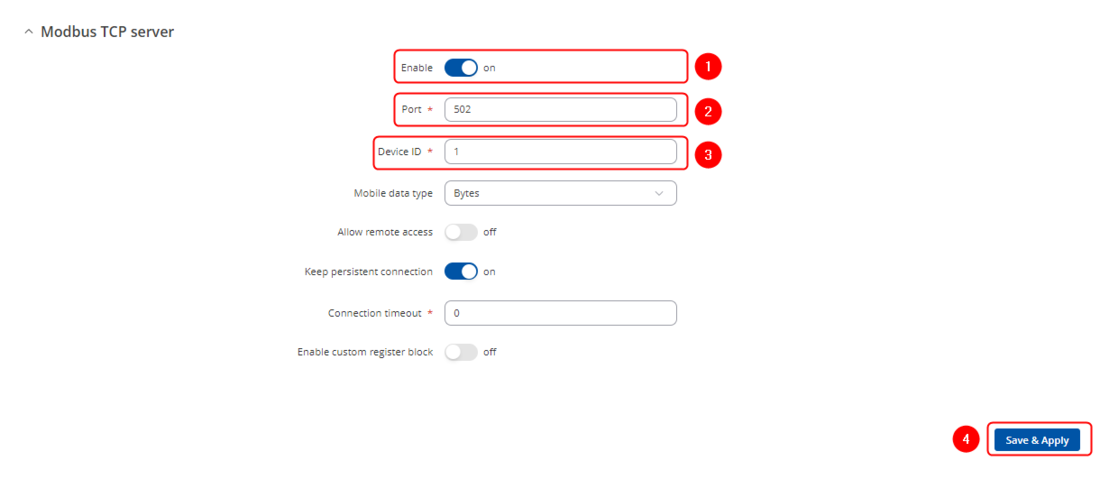
Open RUT1 router's WebUI and navigate to '''Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Server''' | |||
#Check '''Enable''' | #Check '''Enable''' | ||
#Enter port that will be used, in this example 502 will be used | #Enter port that will be used, in this example 502 will be used | ||
#Enter device ID | #Enter device ID | ||
#Press | #Press [[File:Save & Apply.png|90px]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking MQTT MODBUS flespi configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
''*In this configuration LAN port is used hence “Allow Remote Access” is not needed'' | ''*In this configuration LAN port is used hence “Allow Remote Access” is not needed'' | ||
''Modbus TCP | ''Modbus TCP Server is now configured''. | ||
===Configuring | ===Configuring Modbus TCP Client=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
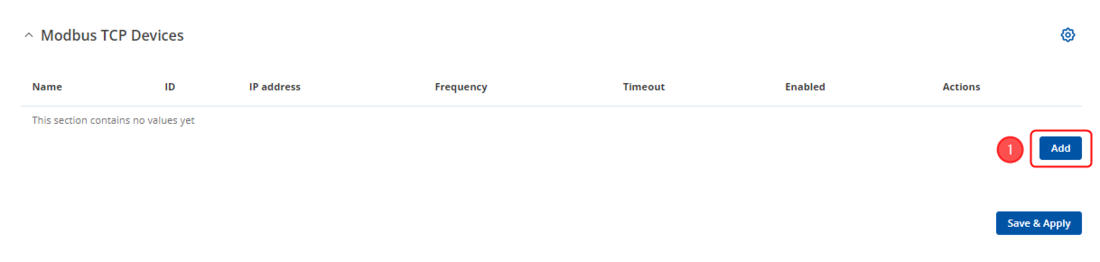
Open RUT2 router's WebUI and navigate to '''Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Client''' | |||
#Press | #Press [[File:Add Button.png|50px]] | ||
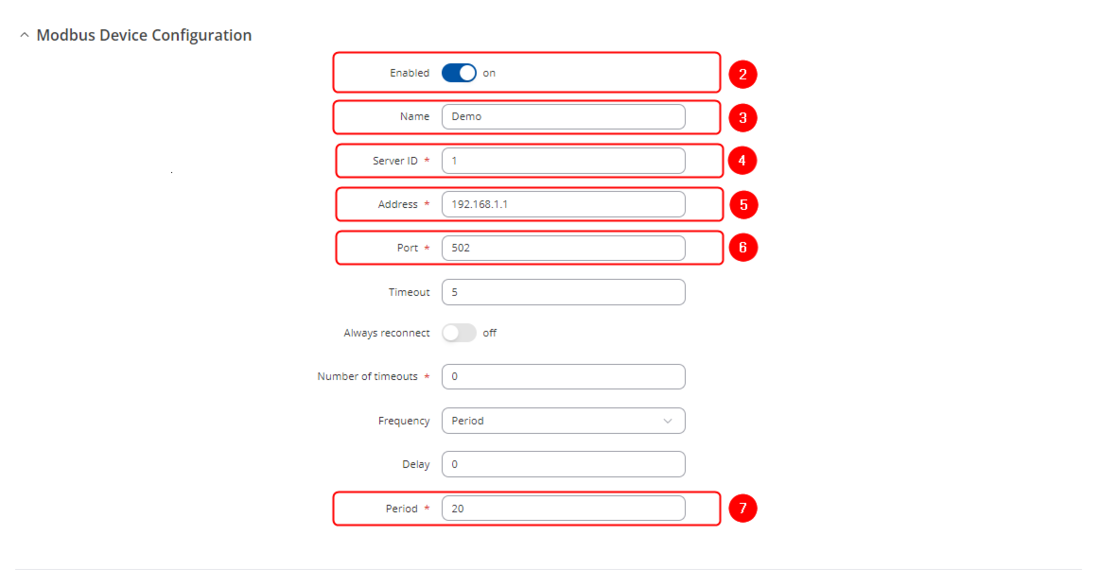
# Check '''Enable''' | [[File:MQTT gateway modbus client configuration v1.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | ||
# Enter the name for the | #<li value="2"> Check '''Enable''' | ||
# | #Enter the name for the Server device | ||
#Enter the IP address of the Modbus TCP | #Server ID must match with the previously configured Modbus TCP Server device ID | ||
#Chose same Port as in | #Enter the IP address of the Modbus TCP Server device | ||
#Enter Period in seconds, how often requests will be sent to the | #Chose same Port as in Server device - 502 | ||
#Enter new request name and press | #Enter Period in seconds, how often requests will be sent to the Server device | ||
#Choose Data type | [[File:MQTT gateway modbus client configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | ||
#Press the Test button in Request Configuration Testing to see if the | #<li value="8">Enter new request name and press [[File:Add Button.png|50px]] in Requests configurations | ||
#Press Save & Apply | [[File:MQTT gateway modbus client configuration v2.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | ||
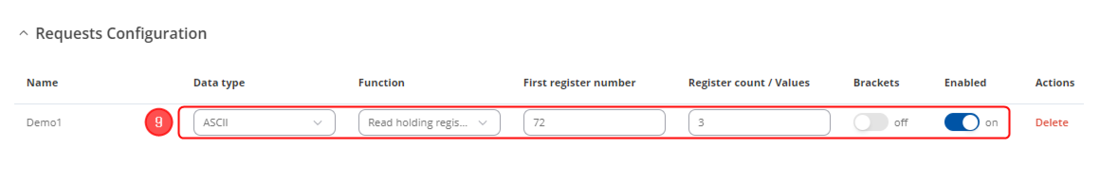
''List of available Modbus parameters can be found [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/ | #<li value="9">Choose "Data type" - '''ASCII''', "Function" - '''Read holding resgiter (3)''', enter "First register number" - '''72''' and "Register count/Values" - '''3''' You can name each individual configuration, and then select enable on configurations that you want to use. In this example, register to get Routers name is used. | ||
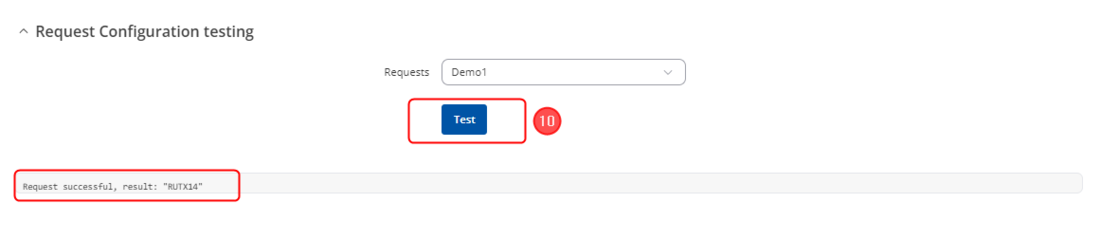
#Press the "'''Test'''" button in Request Configuration Testing to see if the Server device responds to requests, a response similar to the image below should be shown. | |||
[[File:MQTT gateway modbus client configuration v3.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | |||
[[File:MQTT gateway modbus client configuration v4.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | |||
#<li value="11">Press [[File:Save & Apply.png|90px]] to save the configuration | |||
''List of available Modbus parameters can be found [[https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/RUTX14_Modbus#Modbus_Registers here]]'' | |||
===Configuring Flespi.io MQTT Broker=== | |||
---- | ---- | ||
Log in or create an account on https://flespi.io | |||
[[File:Flespi login.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
Once logged in: | Once logged in: | ||
#Navigate to MQTT Board on the left side of the screen and press it. | #Navigate to MQTT Board on the left side of the screen and press it. | ||
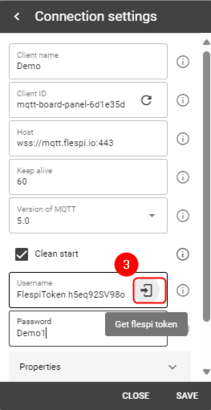
#On the right-hand panel, top right corner, next to the name of the MQTT board, press the cogwheel-looking icon to open ''Connection Settings'' | #On the right-hand panel, top right corner, next to the name of the MQTT board, press the cogwheel-looking [[File:Flespi cogwheel.png|20px]] icon to open ''Connection Settings'' | ||
#In the opened window, press "Get flespi token" to generate a username | #In the opened window, press "Get flespi token" to generate a username | ||
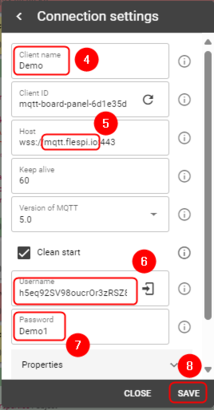
#Enter Client name | #Enter Client name | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
#Create a password | #Create a password | ||
#Press Save | #Press Save | ||
=== Configuring MQTT Gateway | [[File:Flespi mqtt left pane.png|border|class=tlt-border|410x410px]] [[File:Flespio mqtt board cogwheel.png|border|class=tlt-border|410x410px]] [[File:Flespi_generate_username_token.png|border|class=tlt-border|410x410px]] [[File:Flespi mqtt broker config.png|border|class=tlt-border|410x410px]] | ||
=== Configuring MQTT Modbus Gateway=== | |||
---- | ---- | ||
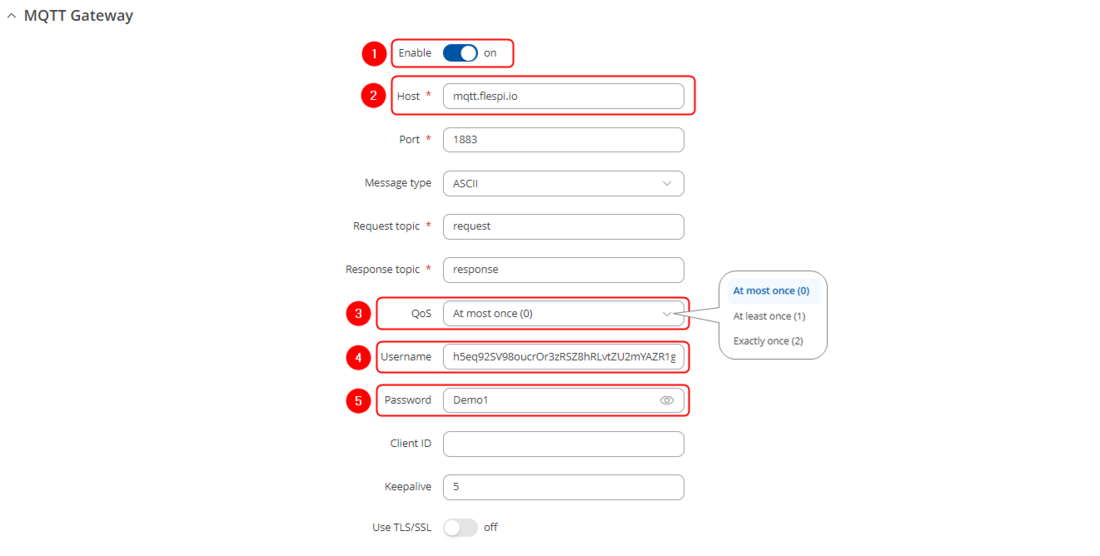
Open | Open RUT2 router's WebUI and navigate to '''Services → Modbus → MQTT Modbus Gateway''' | ||
#Select Enable | #Select Enable | ||
#Enter Host (copied from flespi connection settings without 'wss://' and port) | #Enter Host (copied from flespi connection settings without 'wss://' and port) | ||
#Select QoS (Quality of Service) level | |||
#Enter Username (Copied from flespi Connection settings generated token) | #Enter Username (Copied from flespi Connection settings generated token) | ||
#Enter Password | #Enter Password | ||
#Press [[File:Save & Apply.png|90px]] to save the configuration | |||
[[File:MQTT modbus gateway config.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | |||
''You can change Request and Response topics that you will have to publish and subscribe to get information from Modbus TCP Client through MQTT Gateway, but for this example, they are left on default topics'' | |||
===Message format for MQTT Publisher=== | |||
===Message format for MQTT | |||
---- | ---- | ||
The format is in the text - heavier and slower, but less difficult to edit. | The format is in the text - heavier and slower, but less difficult to edit. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 104: | ||
|from '''1''' to '''999''' | |from '''1''' to '''999''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|7. | |7. Server ID - Indicates to which Server request is sent | ||
|from '''1''' to '''255''' | |from '''1''' to '''255''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 117: | Line 119: | ||
If function is 16 - from '''1''' to '''123''' (first register + registry value can not go out of range), Registry values separated by commas without spaces. Example.: '''1,2,3,654,21,789'''. There has to be as many values, as specified number of registers, and each value must be between '''0''' and '''65535'''. If number of registries is 0, there should be '''no registry values''' | If function is 16 - from '''1''' to '''123''' (first register + registry value can not go out of range), Registry values separated by commas without spaces. Example.: '''1,2,3,654,21,789'''. There has to be as many values, as specified number of registers, and each value must be between '''0''' and '''65535'''. If number of registries is 0, there should be '''no registry values''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[File:Networking MQTT modbus message format publisher | [[File:Networking MQTT modbus message format publisher v2.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | ||
====Examples==== | ====Examples==== | ||
| Line 133: | Line 135: | ||
Log in and navigate to MQTT Board on https://flespi.io | Log in and navigate to MQTT Board on https://flespi.io | ||
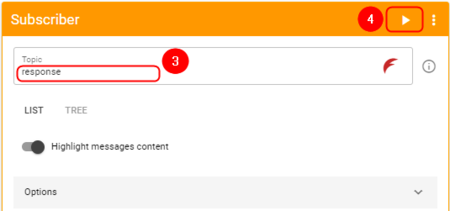
Add a Subscriber: | '''Add a Subscriber:''' | ||
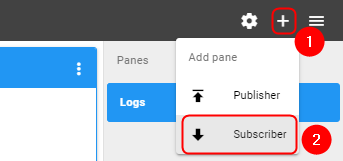
#Press '''''<nowiki/> | #Press '''''<nowiki/>[[File:Flespi-plus-button.png]]''''' button on the top right corner | ||
#Select '''''<nowiki/>'Subscriber'''''' | #Select '''''<nowiki/>'Subscriber'''''' | ||
# In the topic field enter '''''<nowiki/>'response'''''' | # In the topic field enter '''''<nowiki/>'response'''''' | ||
#Press '''''<nowiki/>'Subscribe'''''' button | #Press '''''<nowiki/>'Subscribe'''''' button | ||
[[File: | [[File:Flespi mqtt add subscriber.png|border|class=tlt-border|450px]] [[File:Flespi-mqtt subscriber config.png|border|class=tlt-border|450px]] | ||
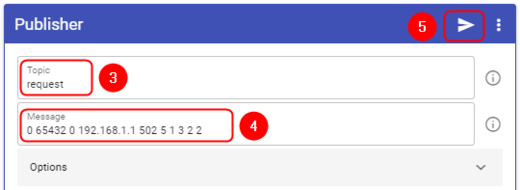
Add a Publisher: | '''Add a Publisher:''' | ||
#Press '''''<nowiki/> | #Press '''''<nowiki/>[[File:Flespi-plus-button.png]]''''' button on the top right corner | ||
#Select '''''<nowiki/>'Publisher'''''' | #Select '''''<nowiki/>'Publisher'''''' | ||
# In the topic field enter '''''<nowiki/>'request'''''' | # In the topic field enter '''''<nowiki/>'request'''''' | ||
| Line 150: | Line 152: | ||
#Press '''''<nowiki/>'Publish'''''' button | #Press '''''<nowiki/>'Publish'''''' button | ||
[[File: | [[File:flespi-mqtt_publisher_config.png|border|class=tlt-border|450x450px]] [[File:Flespi-mqtt publisher config v1.png|border|class=tlt-border|520x520px]] | ||
| Line 156: | Line 158: | ||
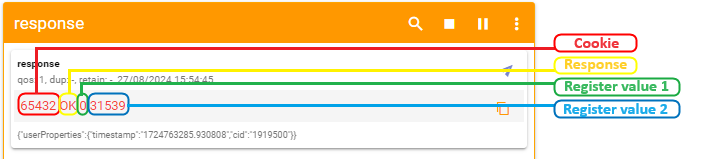
[[File: | [[File:flespi-mqtt_response.png|border|class=tlt-border|931x931px]] | ||
When the value climbs over 65535 the counter resets and the value held by the first register increases by '''1'''. So one way to interpret the results would be to multiply the value in the first register by '''2<sup>16</sup>''' and add it to the value of the second register. In this example: ''' | When the value climbs over 65535 the counter resets and the value held by the first register increases by '''1'''. So one way to interpret the results would be to multiply the value in the first register by '''2<sup>16</sup>''' and add it to the value of the second register. In this example: '''0 * 65536 + 31539 = 31539s''' or '''0 days 8 hours 45 minutes and 39 seconds.''' | ||
''This Means that MQTT Gateway on Modbus TCP | ''This Means that MQTT Gateway on Modbus TCP Client router is working correctly and Modbus TCP Server receives requests.'' | ||
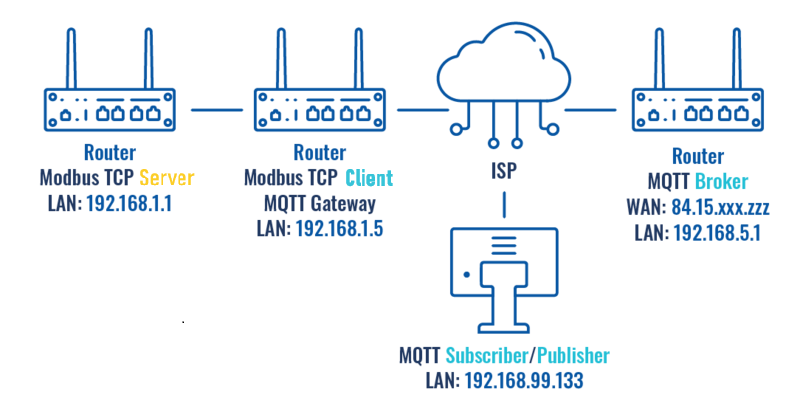
==Configuration using | ==Configuration using RUT241 router as MQTT Broker== | ||
[[File:Networking Topology MQTT | [[File:Networking Topology MQTT broker configuration v1.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
''The same configuration will be used for Modbus TCP Client and Server routers as in the previous example, only settings in Modbus TCP Client router will be changed to match MQTT Broker on RUT241 router'' | |||
===Configuring MQTT Modbus Gateway settings=== | |||
---- | ---- | ||
' | Open RUT2 router's WebUI and navigate to '''Services → MQTT Modbus Gateway''' | ||
#'''Enable''' | #'''Enable''' | ||
# Host: '''Enter Public IP address of MQTT Broker ( | # Host: '''Enter Public IP address of the new MQTT Broker (RUT241)''' | ||
#Username: '''N/A''' | #Username: '''N/A''' | ||
#Password: '''N/A''' | #Password: '''N/A''' | ||
#Press | #Press [[File:Save & Apply.png|90px]] | ||
[[File:Networking MQTT Modbus MQTT gateway config v1.png|border|class=tlt-border| | [[File:Networking MQTT Modbus MQTT gateway config v1.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
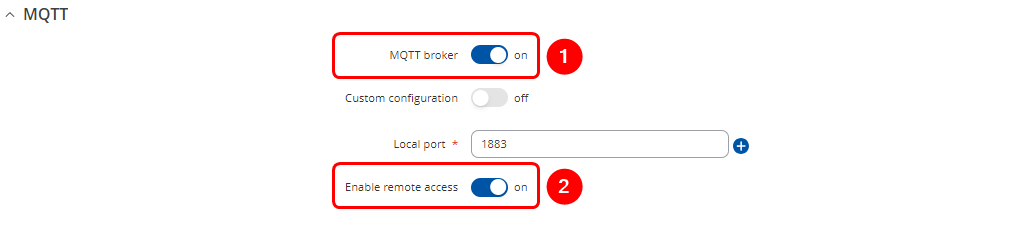
===Configuring | ===Configuring MQTT Broker settings on RUT241 device=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Open RUT241 router's WebUI and navigate to '''Services → MQTT → Broker''' | |||
#Select '''Enable''' | #Select '''Enable''' | ||
#Check '''Enable Remote Access''' | #Check '''Enable Remote Access''' | ||
# | [[File:MQTT gateway broker settings p01.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
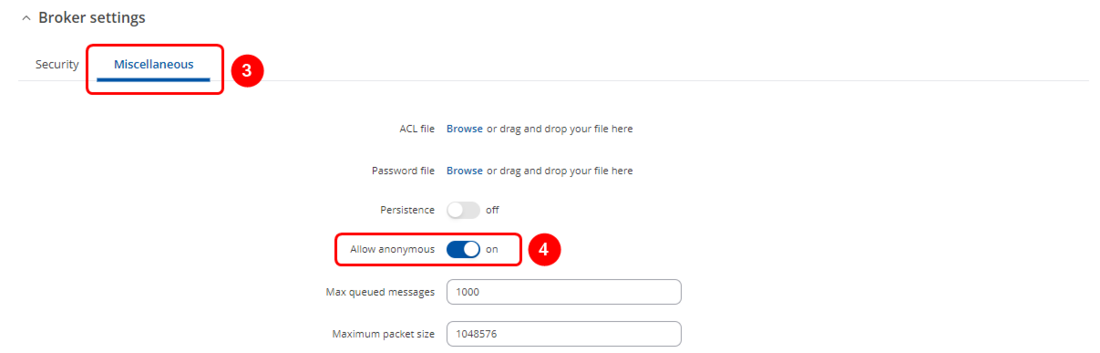
#<li value="3"> Scroll down to "'''Broker settings'''" and select "'''Miscellaneous'''" tab | |||
#Enable "'''Allow anonymous'''" | |||
[[File:MQTT gateway broker settings p02.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | |||
#<li value="5">Press [[File:Save & Apply.png|90px]] to save the configuration | |||
===Configuring MQTT Publisher/Subscriber on PC & testing MQTT Gateway=== | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 212: | Line 217: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Modbus Master RutOS configuration example]] | *[[Modbus Master RutOS configuration example]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Monitoring via Modbus]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:29, 2 October 2024
Summary
This guide will demonstrate how to configure the MQTT Gateway on a Modbus TCP Client using two different types of MQTT Brokers. The first configuration involves using a third-party MQTT Broker service "Flespi.io". The second setup uses the RUT241 router as the MQTT Broker. In this scenario, two routers will serve as the Modbus TCP Client and Server, while a PC will act as both the MQTT Publisher and Subscriber.
Configuration overview & prerequisites
- Two routers - RUT1 as Modbus TCP Server (Slave) and RUT2 as Modbus TCP Client (Master)
- Flespi.io account to act as an MQTT Broker/Publisher/Subscriber (for first configuration example)
- RUT241 with a Public IP address to act as MQTT Broker (for second configuration example)
- An end device (PC, Laptop) to act as MQTT Subscriber/Publisher (for second configuration example)
Configuration using flespi.io as MQTT Broker
Configuring Modbus TCP Server
Open RUT1 router's WebUI and navigate to Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Server
*In this configuration LAN port is used hence “Allow Remote Access” is not needed
Modbus TCP Server is now configured.
Configuring Modbus TCP Client
Open RUT2 router's WebUI and navigate to Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Client
- Check Enable
- Enter the name for the Server device
- Server ID must match with the previously configured Modbus TCP Server device ID
- Enter the IP address of the Modbus TCP Server device
- Chose same Port as in Server device - 502
- Enter Period in seconds, how often requests will be sent to the Server device
- Choose "Data type" - ASCII, "Function" - Read holding resgiter (3), enter "First register number" - 72 and "Register count/Values" - 3 You can name each individual configuration, and then select enable on configurations that you want to use. In this example, register to get Routers name is used.
- Press the "Test" button in Request Configuration Testing to see if the Server device responds to requests, a response similar to the image below should be shown.
List of available Modbus parameters can be found [here]
Configuring Flespi.io MQTT Broker
Log in or create an account on https://flespi.io

Once logged in:
- Navigate to MQTT Board on the left side of the screen and press it.
- On the right-hand panel, top right corner, next to the name of the MQTT board, press the cogwheel-looking
 icon to open Connection Settings
icon to open Connection Settings - In the opened window, press "Get flespi token" to generate a username
- Enter Client name
- Copy Host address
- Copy Username
- Create a password
- Press Save
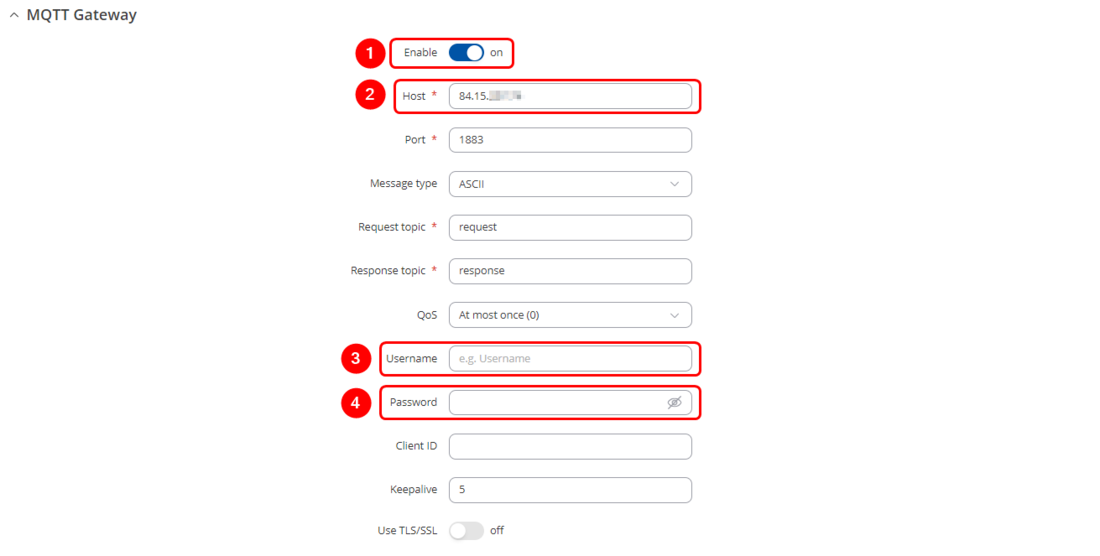
Configuring MQTT Modbus Gateway
Open RUT2 router's WebUI and navigate to Services → Modbus → MQTT Modbus Gateway
- Select Enable
- Enter Host (copied from flespi connection settings without 'wss://' and port)
- Select QoS (Quality of Service) level
- Enter Username (Copied from flespi Connection settings generated token)
- Enter Password
- Press
 to save the configuration
to save the configuration
You can change Request and Response topics that you will have to publish and subscribe to get information from Modbus TCP Client through MQTT Gateway, but for this example, they are left on default topics
Message format for MQTT Publisher
The format is in the text - heavier and slower, but less difficult to edit.
| 1. Format version | 0 |
| 2. Cookie | from 0 to 264 -1 |
| 3. IP Type | 0 - IPv4; 1 - IPv6; 2 - hostname |
| 4. IP | IPv6 must be in full format (for example: 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334) |
| 5. Port | Port number (for example: 502) |
| 6. Timeout in seconds (time to wait for response) | from 1 to 999 |
| 7. Server ID - Indicates to which Server request is sent | from 1 to 255 |
| 8. Function | 3 - read registers; 6 - write single register; 16 - write multiple registers |
| 9. Number of the first register from which information will be read or written | from 1 to 65535 |
| 10. Registry value | If function is 3 - from 1 to 123 (first register + registry value can not go out of range);
If function is 6 - from 0 to 65535 If function is 16 - from 1 to 123 (first register + registry value can not go out of range), Registry values separated by commas without spaces. Example.: 1,2,3,654,21,789. There has to be as many values, as specified number of registers, and each value must be between 0 and 65535. If number of registries is 0, there should be no registry values |
Examples
| Setting relay (on) (Relay address is 202, which means 'Number of first register will be 203) | 0 65432 0 192.168.1.1 502 5 1 6 203 1 |
| Getting uptime | 0 65432 0 192.168.1.1 502 5 1 3 2 2 |
Testing MQTT Publisher and Subscriber on flespi.io
Log in and navigate to MQTT Board on https://flespi.io
Add a Subscriber:
- Press
 button on the top right corner
button on the top right corner - Select 'Subscriber'
- In the topic field enter 'response'
- Press 'Subscribe' button
Add a Publisher:
- Press
 button on the top right corner
button on the top right corner - Select 'Publisher'
- In the topic field enter 'request'
- In the message field enter message, for this example 'Getting uptime' is used
- Press 'Publish' button
Check the response in the 'Subscriber' tab, you should receive a message similar to the one below.
When the value climbs over 65535 the counter resets and the value held by the first register increases by 1. So one way to interpret the results would be to multiply the value in the first register by 216 and add it to the value of the second register. In this example: 0 * 65536 + 31539 = 31539s or 0 days 8 hours 45 minutes and 39 seconds.
This Means that MQTT Gateway on Modbus TCP Client router is working correctly and Modbus TCP Server receives requests.
Configuration using RUT241 router as MQTT Broker
The same configuration will be used for Modbus TCP Client and Server routers as in the previous example, only settings in Modbus TCP Client router will be changed to match MQTT Broker on RUT241 router
Configuring MQTT Modbus Gateway settings
Open RUT2 router's WebUI and navigate to Services → MQTT Modbus Gateway
- Enable
- Host: Enter Public IP address of the new MQTT Broker (RUT241)
- Username: N/A
- Password: N/A
- Press

Configuring MQTT Broker settings on RUT241 device
Open RUT241 router's WebUI and navigate to Services → MQTT → Broker
- Select Enable
- Check Enable Remote Access
- Scroll down to "Broker settings" and select "Miscellaneous" tab
- Enable "Allow anonymous"
Configuring MQTT Publisher/Subscriber on PC & testing MQTT Gateway
For testing purposes, two terminal windows will be used on the same PC.
To get Ubuntu terminal on Windows 10/11, refer to the following link for instructions: https://tutorials.ubuntu.com/tutorial/tutorial-ubuntu-on-windows#0
- Open first terminal, which will act as Subscriber. Type in:
mosquito_sub -h [Host_address] -p [Port] -t [Topic]
- Open second terminal, which will act as Publisher. Type in:
mosquito_pub -h [Host] -h [Host_address] -p [Port] -m [‘Message’] -t [Topic]
- On the first window - Subscriber, a response should appear