IBGP configuration example: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "<p style="color:red">The information on this page is updated in accordance with the [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.06.10'''] firmware v...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Topology== | ==Topology== | ||
[[File: | [[File:BGP topology_v1.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|1000x1000px]] | ||
=iBGP Configuration= | =iBGP Configuration= | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Navigate to <b>Network -> Routing -> Dynamic routes -> BGP</b>. | Navigate to <b>Network -> Routing -> Dynamic routes -> BGP</b>. | ||
Enable <b>"BGP - Global Settings"</b> and <b>"vty"</b>. | Enable <b>"BGP - Global Settings"</b> and <b>"vty"</b>. | ||
[[File:BGP enable.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border| | [[File:BGP enable.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|700x700px]] | ||
Configure <b>BGP Instance</b> tab like this: | |||
[[File:IBGP instance v2.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|700x700px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
 1. <b>Enable</b> - on |  1. <b>Enable</b> - on | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
Go to <b>BGP peers</b> tab and add new instance. For <b>Name</b> write any name you desire and press <b>Add</b>. | Go to <b>BGP peers</b> tab and add new instance. For <b>Name</b> write any name you desire and press <b>Add</b>. | ||
[[File: | [[File:IBGP peer.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
On popped up window select these options: | On popped up window select these options: | ||
[[File: | [[File:IBGP peer config RUT1.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border]] | ||
 1. <b>Enable</b> - on |  1. <b>Enable</b> - on | ||
| Line 65: | Line 64: | ||
[[File:BGP Firewall edit.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | [[File:BGP Firewall edit.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|1100x1100px]] | ||
On popped up window add <b>lan</b> on <b>Allow forward to destination zones</b> field and press | On popped up window add <b>lan</b> on <b>Allow forward to destination zones</b> field and press <b>Save & Aplly</b>. | ||
[[File:BGP Firewall WAN zone .png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|900x900px]] | [[File:BGP Firewall WAN zone .png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border|900x900px]] | ||
| Line 72: | Line 71: | ||
If you have followed the steps correctly, the configuration should be complete. Here are the results you can expect to receive: | If you have followed the steps correctly, the configuration should be complete. Here are the results you can expect to receive: | ||
PC1 to PC2: | <b>PC1 to PC2:</b> | ||
Pinging 192.168.2.10 from 192.168.1.10 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.2.10 from 192.168.1.10 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
| Line 80: | Line 79: | ||
Reply from 192.168.2.10: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=62 | Reply from 192.168.2.10: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=62 | ||
PC2 to PC1: | <b>PC2 to PC1:</b> | ||
Pinging 192.168.1.10 from 192.168.2.10 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.1.10 from 192.168.2.10 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
Latest revision as of 14:11, 24 May 2024
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.06.10 firmware version .
Introduction
BGP, or Border Gateway Protocol, is a fundamental routing protocol used in large-scale networks, particularly the internet, to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (ASes). This article provides a guide on how to configure iBGP or internal Border Gateway routing which uses one autonomous system on our two routers.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Prerequisites:
- Routers must be connected through WAN-WAN connection
- At least two end devices (PCs, Laptops) to configure the routers and test the set up
- Both routers must be on "Advanced mode"

Topology
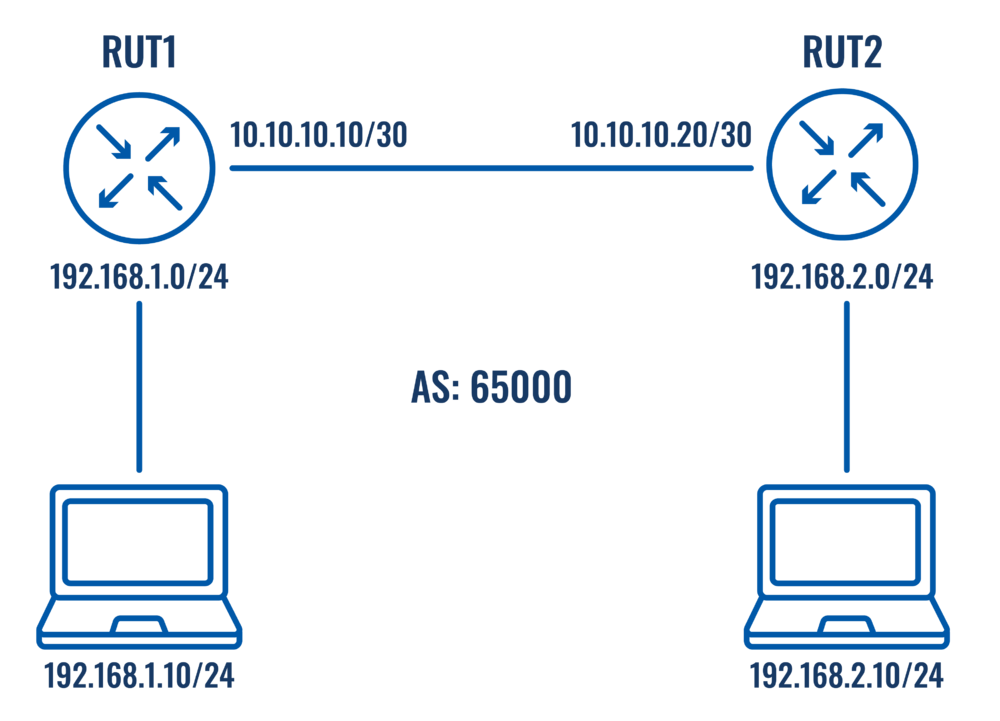
iBGP Configuration
RUT1 BGP Configuration
Navigate to Network -> Routing -> Dynamic routes -> BGP. Enable "BGP - Global Settings" and "vty".
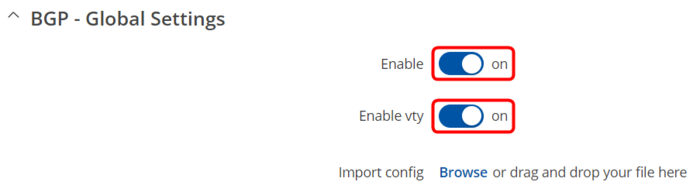
Configure BGP Instance tab like this:
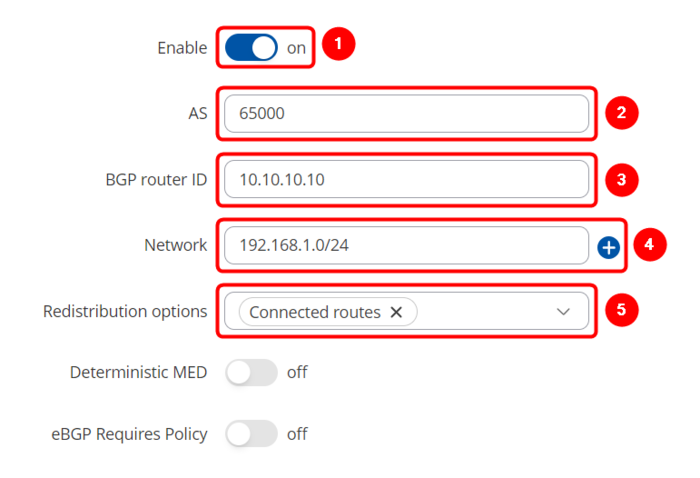
1. Enable - on
2. AS - 65000 (it must be the same on both routers)
3. BGP router ID - 10.10.10.10 (RUT1 WAN IP)
4. Network - 192.168.1.0/24 (RUT1 LAN subnet)
5. Redistribution options - Connected routes
Go to BGP peers tab and add new instance. For Name write any name you desire and press Add.

On popped up window select these options:
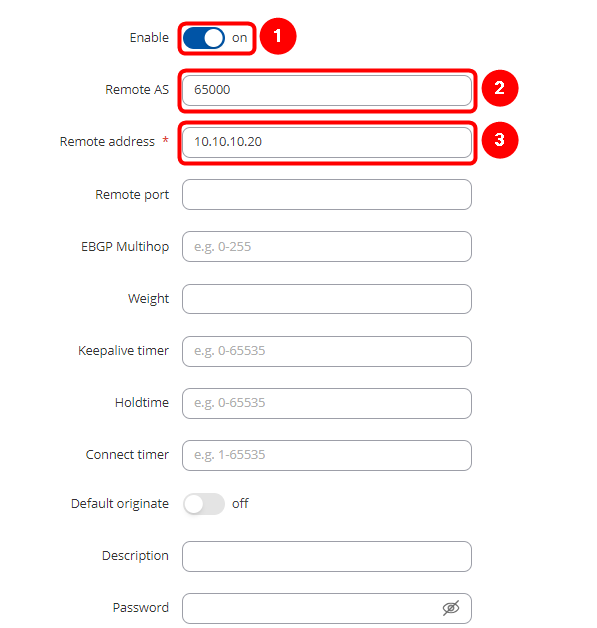
1. Enable - on
2. AS - 65000 (it must be the same on both routers)
3. Remote address - 10.10.10.20 (RUT2 WAN IP)
RUT2 BGP Configuration
For RUT2, the configuration is very similar, all we need to do is just change the BGP router ID to 10.10.10.20, Network to 192.168.2.0/24 on the BGP Instance, and the Remote address to 10.10.10.10 on the Peer Configuration.
BGP Instance should look like this:
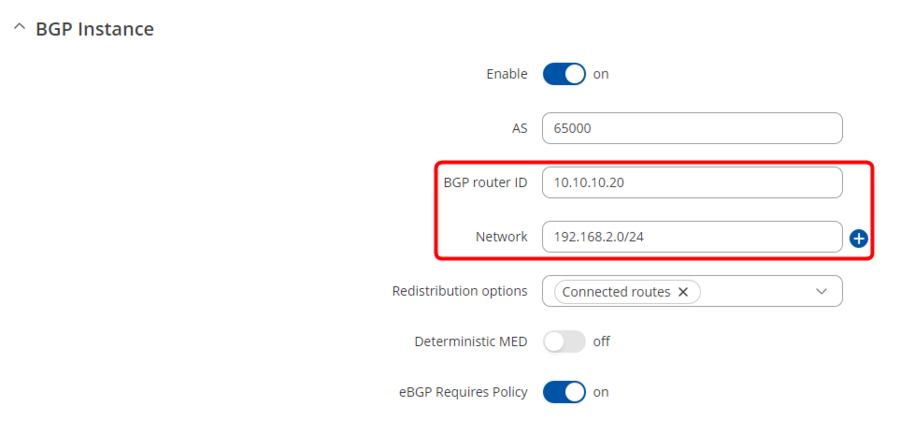
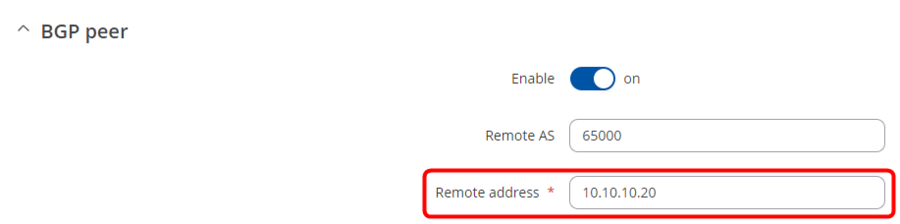
And Peer Configuration like this:
Firewall Zones
Now we can reach only routers by them self to reach their whole network we need to edit Firewalls WAN Zone to add lan on forward to destination zones field.
On both routers navigate to Network -> Firewall -> General Settings -> Zones and press edit on wan zone.
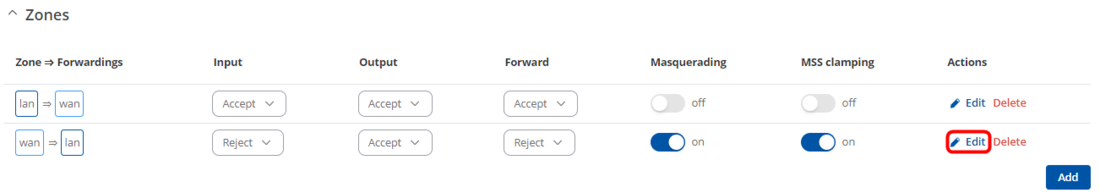
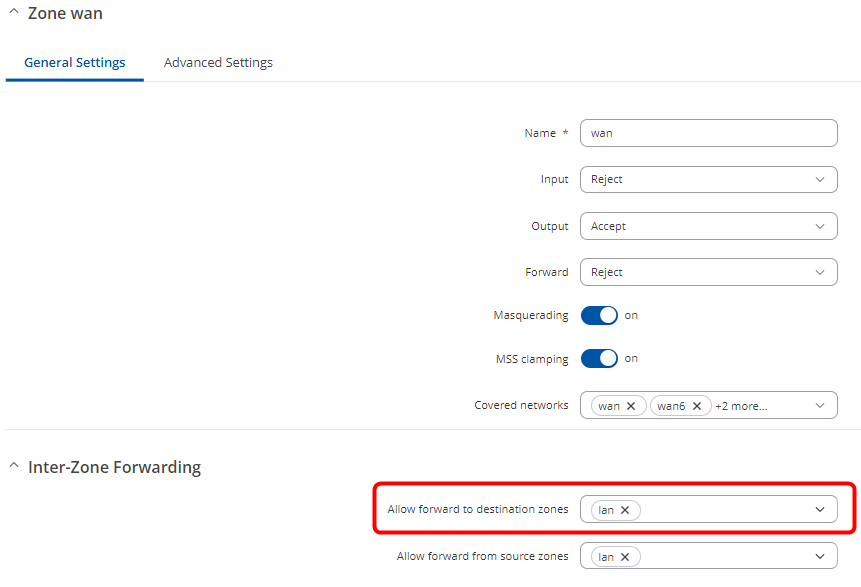
On popped up window add lan on Allow forward to destination zones field and press Save & Aplly.
Testing the setup
If you have followed the steps correctly, the configuration should be complete. Here are the results you can expect to receive:
PC1 to PC2:
Pinging 192.168.2.10 from 192.168.1.10 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.2.10: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.2.10: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.2.10: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.2.10: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=62
PC2 to PC1:
Pinging 192.168.1.10 from 192.168.2.10 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time=9ms TTL=124 Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=124 Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=124 Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=124
See also
External links
https://frrouting.org/ - additional information about FRRouting that our device routing is based on.
