Modbus TCP Server Send SMS example: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
In order to configure Modbus TCP Slave follow the steps provided below: | In order to configure Modbus TCP Slave follow the steps provided below: | ||
[[File:Networking rut configuration modbus tcp slave | [[File:Networking rut configuration modbus tcp slave v2.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | ||
'''Explanation:''' | '''Explanation:''' | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Lets continue with the configuration, now we will configure Modbus TCP Master on the same device. Navigate to '''Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Master'''. Press the button '''ADD''' and follow the steps provided below: | Lets continue with the configuration, now we will configure Modbus TCP Master on the same device. Navigate to '''Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Master'''. Press the button '''ADD''' and follow the steps provided below: | ||
[[File:Networking rut configuration modbus tcp master | [[File:Networking rut configuration modbus tcp master v2.png|border|class=tlt-border|1100px]] | ||
'''Explanation:''' | '''Explanation:''' | ||
Revision as of 12:11, 26 January 2023
Main Page > General Information > Configuration Examples > Modbus > Modbus TCP Server Send SMS exampleIntroduction
The information on this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.03.2 firmware version. .
Modbus is a serial communications protocol. Simple and robust, it has become a de facto standard communication protocol and is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices.
In this configuration example, we will configure Modbus TCP Slave and Modbus TCP Master. We will send a Set Parameters request from Modbus TCP Master to Modbus TCP Slave, which will send an SMS message provided in the Modbus TCP Master Set PArameter request.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Basic" button under "Mode", which is located at the top-right corner of the WebUI.
Prerequisites
- At least one TRB/RUT device with the SIM card, for this example we will be using one device
- One end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone) to configure the router
- One Mobile Phone in order to test the configuration
Configuring Modbus TCP Slave and Modbus TCP Master
Firstly, we will configure Modbus TCP Slave on the router and then on the same device we will configure Modbus TCP Master in order to send Modbus requests to the same device.
Configuring Modbus TCP Slave
In order to start our configuration you will need to open your device's WebUI (by entering the device's IP address of your device), then navigate to Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Slave.
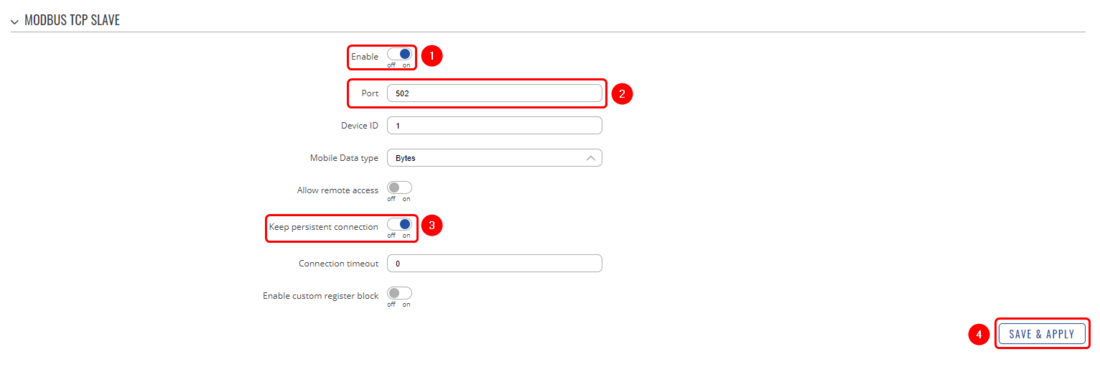
In order to configure Modbus TCP Slave follow the steps provided below:
Explanation:
- Enable the Modbus TCP Slave
- Select the port on which Modbus TCP Slave will communicate with the Modbus TCP Master (for this example: 502)
- Enable persistent connection (not mandatory)
- Save the configuration
Configuring Modbus TCP Master
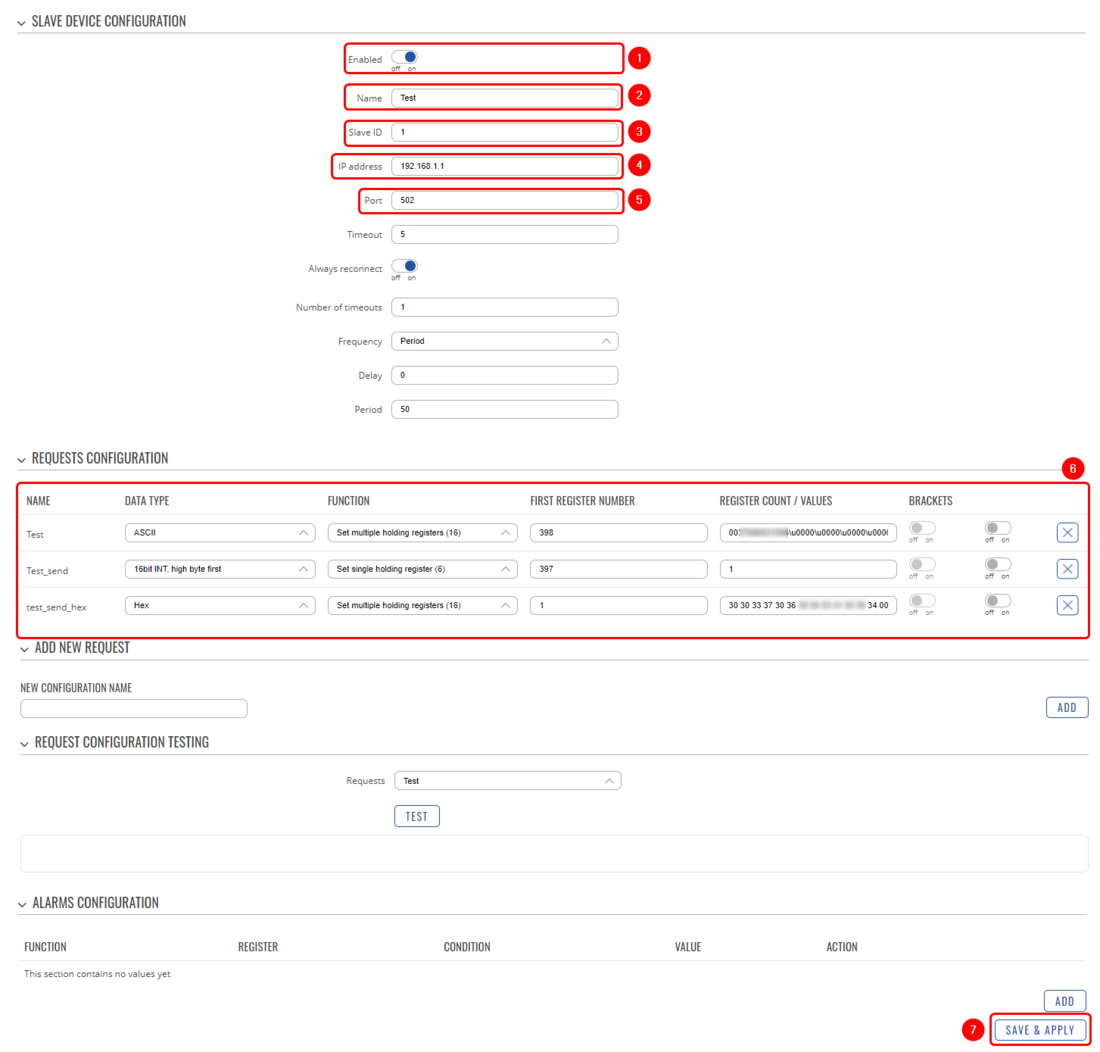
Lets continue with the configuration, now we will configure Modbus TCP Master on the same device. Navigate to Services → Modbus → Modbus TCP Master. Press the button ADD and follow the steps provided below:
Explanation:
- Enable the instance
- Create a name for Modbus TCP Master
- Provide the Slave ID (in this case: 1)
- Provide IP address of the Slave ID, in this case, this router's IP (192.168.1.1)
- Provide Modbus TCP Slave ID (in this case 502)
- In this part we will configure two different SMS messages (hex and ASCII formats) and one send a request to send those messages, we will configure it a little bit later, so leave this part empty for now.
- Save the configuration