Difference between revisions of "Default IPsec route configuration between Teltonika and Fortigate devices"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Topology== | ==Topology== | ||
| − | '''Fortinet''' – The '''Fortinet''' will act as a "default gateway" for the RUT device. '''Fortinet''' has a LAN subnet of 192.168.5.0/24 and WAN subnet of 192.168.10.2/24 configured on it, which should be reachable by the | + | '''Fortinet''' – The '''Fortinet''' will act as a "default gateway" for the RUT device. '''Fortinet''' has a LAN subnet of 192.168.5.0/24 and WAN subnet of 192.168.10.2/24 configured on it, which should be reachable by the RUT. |
'''RUT''' – The '''RUTX11''' in this case will be connected to '''Fortinet''' for basic internet access. '''RUT''' has a LAN subnet of 192.168.1.0/24 and WAN subnet of 192.168.10.1/24 configured on it. | '''RUT''' – The '''RUTX11''' in this case will be connected to '''Fortinet''' for basic internet access. '''RUT''' has a LAN subnet of 192.168.1.0/24 and WAN subnet of 192.168.10.1/24 configured on it. | ||
| − | ==Fortinet | + | ==Fortinet configuration== |
| − | Start by configuring the | + | Start by configuring the '''Fortinet''' device. Login to the WebUI, navigate to '''VPN → IPsec Tunnels → Create new → IPsec Tunnel → Template Custom'''. Configure everything as follows. |
'''Note:''' ''Not specified fields can be left as is or changed according to your needs.'' | '''Note:''' ''Not specified fields can be left as is or changed according to your needs.'' | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th width=330; style="border-bottom: 1px solid white;></th> | <th width=330; style="border-bottom: 1px solid white;></th> | ||
| − | <th width=800; style="border-bottom: 1px solid white;" rowspan=2>[[File: | + | <th width=800; style="border-bottom: 1px solid white;" rowspan=2>[[File:Fortinet_IPsec_Add_route_to_blackhole.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]]</th> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
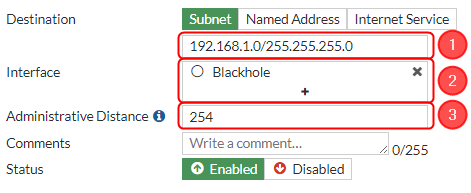
# Destination - '''''192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0;''''' | # Destination - '''''192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0;''''' | ||
# Interface - '''''Blackhole;''''' | # Interface - '''''Blackhole;''''' | ||
| + | # Administrative distance - '''''254;''''' | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | ==RUT | + | ==RUT configuration== |
| − | Start by configuring the | + | Start by configuring the '''RUT''' device. Login to the WebUI, navigate to '''Services → VPN → IPsec and add a new IPsec instance.''' Configure everything as follows. |
'''Note:''' ''Not specified fields can be left as is or changed according to your needs.'' | '''Note:''' ''Not specified fields can be left as is or changed according to your needs.'' | ||
===Instance configuration=== | ===Instance configuration=== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 109: | ||
# Remote endpoint - '''''Fortinet WAN IP;''''' | # Remote endpoint - '''''Fortinet WAN IP;''''' | ||
# Authentication method - '''''Pre-shared key;''''' | # Authentication method - '''''Pre-shared key;''''' | ||
| − | # Pre-shared key - the '''''same password''''' you have '''''set on Fortinet''''' when configuring the '''''Fortinet | + | # Pre-shared key - the '''''same password''''' you have '''''set on Fortinet''''' when configuring the '''''Fortinet IPsec instance;''''' |
# Local identifier – '''''RUT WAN IP;''''' | # Local identifier – '''''RUT WAN IP;''''' | ||
# Remote identifier – '''''Fortinet WAN IP;''''' | # Remote identifier – '''''Fortinet WAN IP;''''' | ||
| Line 169: | Line 170: | ||
If you have followed all the above steps, your configuration should be finished. But as with any other configuration, it is always wise to test the setup in order to make sure that it works properly. | If you have followed all the above steps, your configuration should be finished. But as with any other configuration, it is always wise to test the setup in order to make sure that it works properly. | ||
| − | Using the <code><span class="highlight">'''ipsec status'''</span></code> command we can see that IPsec tunnel is successfully established on RUT router. The command output on a ''' | + | Using the <code><span class="highlight">'''ipsec status'''</span></code> command we can see that IPsec tunnel is successfully established on RUT router. The command output on a '''RUT''' device: |
[[File:Networking_ssh_manual_IPsec_configuration_IPsec_statusall_test_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border|971x135px|center]] | [[File:Networking_ssh_manual_IPsec_configuration_IPsec_statusall_test_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border|971x135px|center]] | ||
| Line 176: | Line 177: | ||
[[File:RutIpsecCurlPingTest.png|border|class=tlt-border|506x133px|center]] | [[File:RutIpsecCurlPingTest.png|border|class=tlt-border|506x133px|center]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | To check if IPsec tunnel is working properly from | + | To check if IPsec tunnel is working properly from '''Fortinet''', we can try pinging our '''RUT''' device by using this command in command line interface on Fortinet<code><span class="highlight" >'''exec ping 192.168.1.1'''</span></code>, if you are not able to ping '''RUT''' device, try changing the source interface from which we try pinging, by executing this command <code><span class="highlight" >'''exec ping-options source 192.168.5.99'''</span></code>: |
[[File:Fortinet_IPsec_test_ping.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | [[File:Fortinet_IPsec_test_ping.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 19 June 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.07.2 firmware version.
Introduction
Normally we configure IPsec for LAN-to-LAN communication, also known as split-tunnel VPN, when only specific hosts should be reachable via a VPN tunnel. However, we may also take a different approach and configure a VPN tunnel using the full tunnel method. This means that any non-directly connected network (i.e. lan interface) will be reachable only via IPsec tunnel and not via the typical default route.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's look at the configuration we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- One RUT/RUTX series router or TRB gateway with RUTOS firmware;
- One Fortinet series router;
- An end device (PC, Laptop) for configuration;
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Topology
Fortinet – The Fortinet will act as a "default gateway" for the RUT device. Fortinet has a LAN subnet of 192.168.5.0/24 and WAN subnet of 192.168.10.2/24 configured on it, which should be reachable by the RUT.
RUT – The RUTX11 in this case will be connected to Fortinet for basic internet access. RUT has a LAN subnet of 192.168.1.0/24 and WAN subnet of 192.168.10.1/24 configured on it.
Fortinet configuration
Start by configuring the Fortinet device. Login to the WebUI, navigate to VPN → IPsec Tunnels → Create new → IPsec Tunnel → Template Custom. Configure everything as follows.
Note: Not specified fields can be left as is or changed according to your needs.
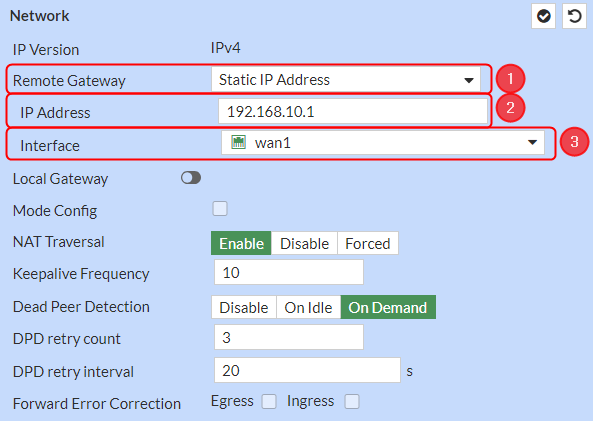
Network configuration
Make the following changes:
- Remote Gateway – Static IP Address;
- IP Address – 192.168.10.1;
- Interface – wan1;
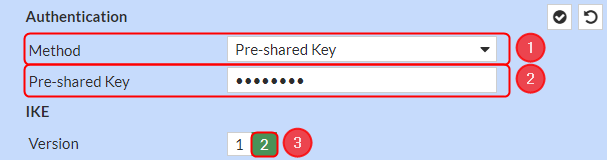
Authentication configuration
Make the following changes:
- Method – Pre-shared Key;
- Pre-shared Key – your desired password;
- Version – 2;
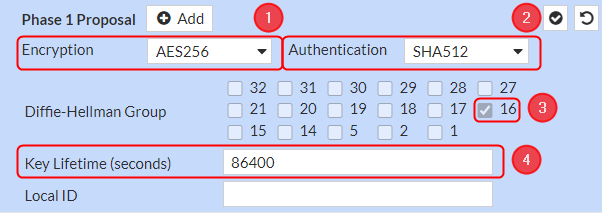
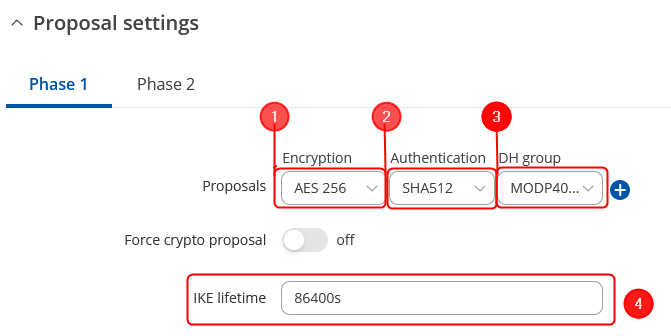
Phase 1 Proposal configuration
Make the following changes:
- Encryption – AES256;
- Authentication - SHA512;
- Diffie-Hellman Group – 16;
- Key Lifetime (seconds) – 86400;
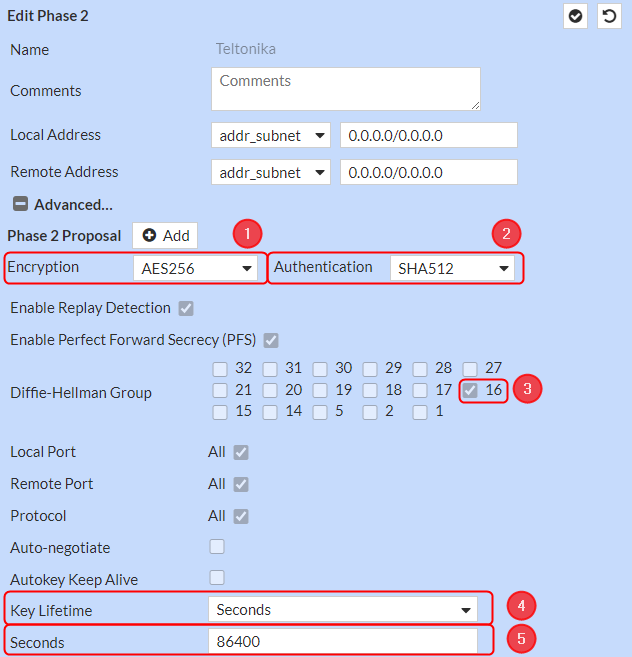
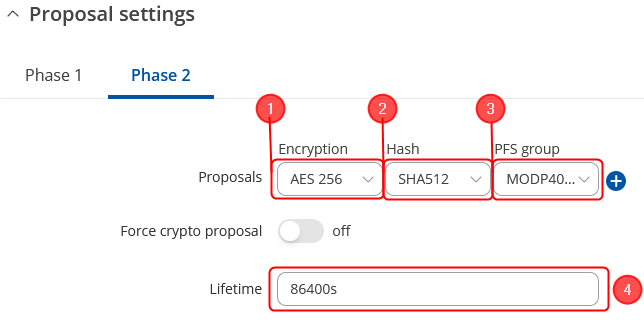
Phase 2 Selectors configuration
Make the following changes: Click on Advanced settings;
- Encryption – AES256;
- Authentication - SHA512;
- Diffie-Hellman Group – 16;
- Key Lifetime – Seconds;
- Seconds – 86400;
Firewall configuration
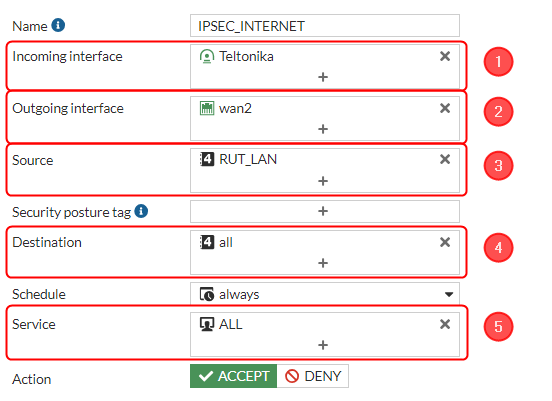
After setting up our IPsec instance, we will need to configure our firewall accordingly. Navigate to Policy & Objects → Firewall Policy → and click on a Create new button.. Configure everything as follows.
Make the following changes:
- Incoming interface - Tunnel interface name (In this case it is Teltonika);
- Outgoing interface - wan2 (choose WAN port from which Fortinet gets internet);
- Source - 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0;
- Destination - all;
- Service - ALL;
Static Routes configuration
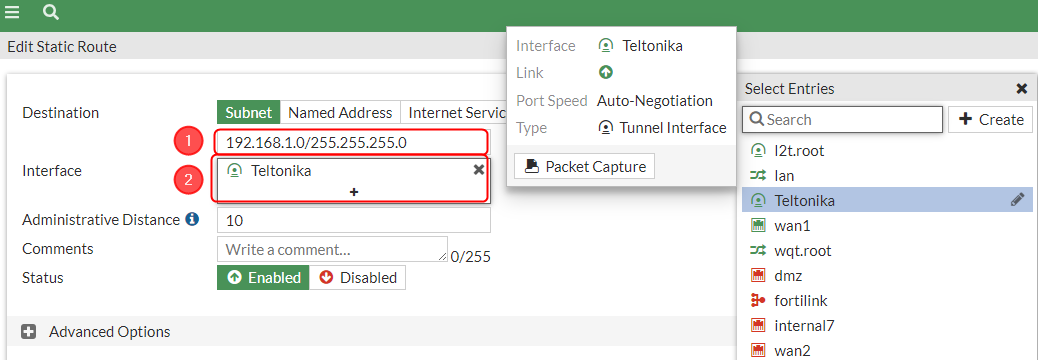
After setting up our IPsec instance and firewall, we will need to configure our static route accordingly. Navigate to Network → Static routes → and click on a Create new button.. For that we will need to create two static routes, one for blackhole and one for accessing our RUT device, configure everything as follows.
Make the following changes:
|
Then create a new static route for blackhole. Make the following changes:
|
RUT configuration
Start by configuring the RUT device. Login to the WebUI, navigate to Services → VPN → IPsec and add a new IPsec instance. Configure everything as follows. Note: Not specified fields can be left as is or changed according to your needs.
Instance configuration
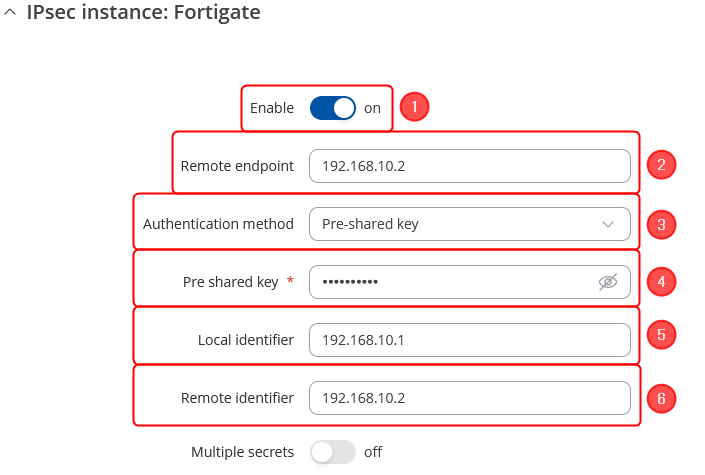
Make the following changes:
- Enable instance;
- Remote endpoint - Fortinet WAN IP;
- Authentication method - Pre-shared key;
- Pre-shared key - the same password you have set on Fortinet when configuring the Fortinet IPsec instance;
- Local identifier – RUT WAN IP;
- Remote identifier – Fortinet WAN IP;
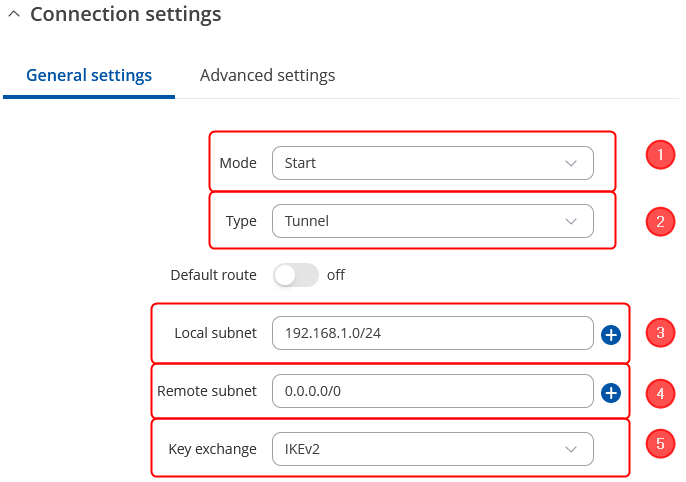
Connection general section configuration
Make the following changes:
- Mode - Start;
- Type - Tunnel;
- Local subnet – 192.168.1.0/24;
- Remote subnet – 0.0.0.0/0;
- Key exchange - IKEv2;
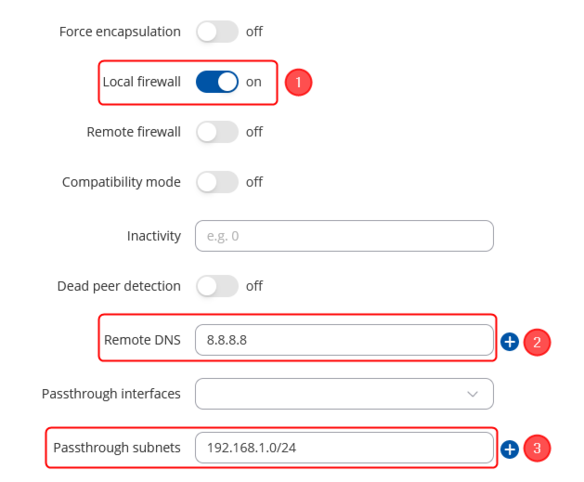
Connection advanced section configuration
Make the following changes:
- Enable local firewall
- Remote DNS – 8.8.8.8;
- Passthrough subnets – 192.168.1.0/24;
Proposal configuration
Make the following changes:
|
|
Testing the configuration
If you have followed all the above steps, your configuration should be finished. But as with any other configuration, it is always wise to test the setup in order to make sure that it works properly.
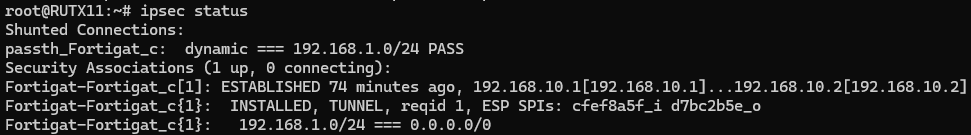
Using the ipsec status command we can see that IPsec tunnel is successfully established on RUT router. The command output on a RUT device:
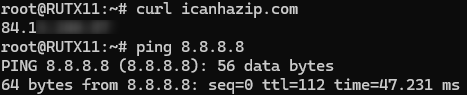
Also, we should be able to access internet routed via Fortigate, we can check it out by pinging 8.8.8.8 and checking what public IP we get by executing this command via command line on RUT device: curl icanhazip.com and ping 8.8.8.8:
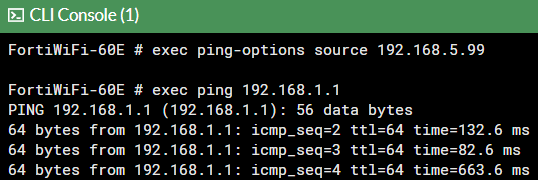
To check if IPsec tunnel is working properly from Fortinet, we can try pinging our RUT device by using this command in command line interface on Fortinetexec ping 192.168.1.1, if you are not able to ping RUT device, try changing the source interface from which we try pinging, by executing this command exec ping-options source 192.168.5.99:
See also
IPsec on Teltonika Networks devices