Mobile Signal Strength Recommendations: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*EC/IO | *EC/IO | ||
More on these measurements in separate service mode sections. | |||
==2G (GSM)== | ==2G (GSM)== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
For 3G service mode, there are three relevant measurements: | For 3G service mode, there are three relevant measurements: | ||
*RSSI - | *RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator | ||
*EC/IO - indicates the downlink carrier-to-interference ratio (signal quality) | *EC/IO - indicates the downlink carrier-to-interference ratio (signal quality) | ||
*RSCP - indicates the | *RSCP - indicates the Received Signal Code Power | ||
The RSSI standard values for 3G are basically the same as 2G | The RSSI standard values for 3G are basically the same as 2G | ||
| Line 89: | Line 91: | ||
==4G (LTE)== | ==4G (LTE)== | ||
For 4G service mode, there are | For 4G service mode, there are four relevant measurements: | ||
*RSSI - | *RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator | ||
*RSRP - the Reference Signal Received Power is the power of the LTE Reference Signals spread over the full bandwidth and narrowband | *RSRP - the Reference Signal Received Power is the power of the LTE Reference Signals spread over the full bandwidth and narrowband | ||
*RSRQ - Reference Signal Received Quality is a C/I type of measurement and it indicates the quality of the received reference signal (similar to EC/IO) | |||
*SINR - Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (A minimum of -20 dB SINR is needed to detect RSRP/RSRQ). Indicates the throughput capacity of the channel. As the name implies, SINR is the strength of the signal divided by | *SINR - Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (A minimum of -20 dB SINR is needed to detect RSRP/RSRQ). Indicates the throughput capacity of the channel. As the name implies, SINR is the strength of the signal divided by | ||
the strength of any interference | the strength of any interference | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 186: | Line 187: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==How do I check the signal quality on a RUT device?== | |||
===WebUI=== | |||
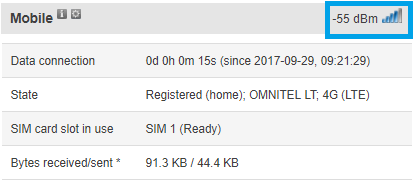
The fastest and easiest way to find out your '''RSSI''' is by checking the Overview window of your router's WebUI (web user interface). The Overview window can be reached simply by accessing your router's WebUI (the default log in information is: address: '''192.168.1.1'''; Username: '''admin'''; Password: '''admin01'''). Once you've logged in, you will be redirected to Overview window automatically. The Overview window contains widgets that display various information summaries about the status of your router. The RSSI value can be checked by looking at the Mobile widget that is located in the top right corner of the Overview window by default. | |||
[[Image:Status overview mobile.PNG]] | |||
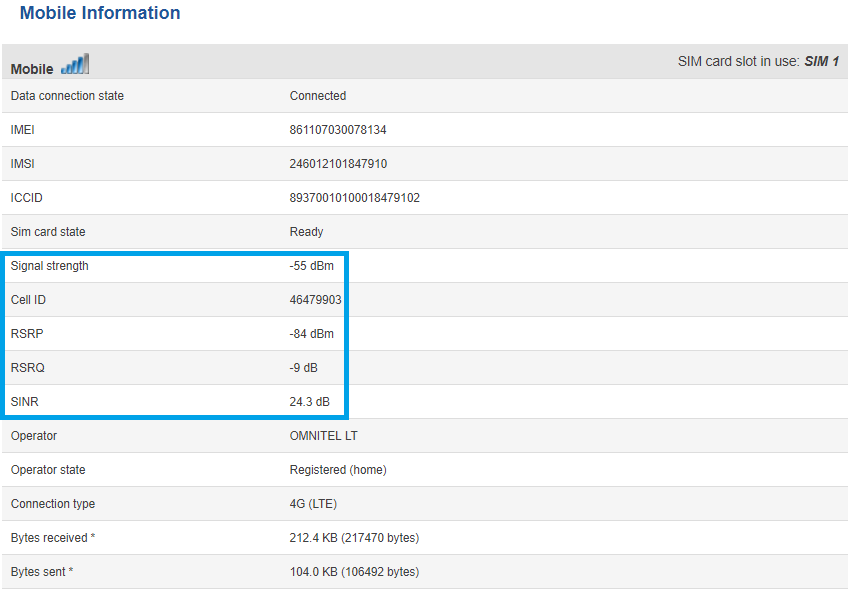
To get more detail about signal quality, you may want to check the Mobile Information section, which is located in '''Status -> Network -> Mobile'''. The Mobile Information window contains information about your mobile connection. Concerning signal quality, it displays Signal Strength ('''RSSI'''), '''RSRP''', '''RSRQ''' and '''SINR'''. | |||
[[Image:Status network mobile.PNG]] | |||
===SSH and CLI=== | |||
To get the most detailed information about your signal quality values you can use ''gsmctl'' commands when logged in via CLI or SSH. | |||
Revision as of 08:42, 29 September 2017
Summary
This chapter is an overview of recommended signal strength levels for different mobile service modes.
Signal Measurement
Signal strength values are defined by a few different measurements which vary even more for different service modes. These measurements are as follows:
- RSSI
- RSRP
- RSRQ
- RSCP
- SINR
- EC/IO
More on these measurements in separate service mode sections.
2G (GSM)
2G (GSM) Signal strength is defined by only one value: RSSI – Received Signal Strength Indicator;
| RSSI | Signal strength |
|---|---|
| >= -70 dBm | Excellent |
| -70 dBm to -85 dBm | Good |
| -86 dBm to -100 dBm | Fair |
| < -100 dBm | Poor |
| -110 dBm | No signal |
3G (WCDMA, TDSCDMA, CDMA, EVDO, CDMA-EVDO)
For 3G service mode, there are three relevant measurements:
- RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator
- EC/IO - indicates the downlink carrier-to-interference ratio (signal quality)
- RSCP - indicates the Received Signal Code Power
The RSSI standard values for 3G are basically the same as 2G
| RSSI | Signal strength |
|---|---|
| >= -70 dBm | Excellent |
| -70 dBm to -85 dBm | Good |
| -86 dBm to -100 dBm | Fair |
| < -100 dBm | Poor |
| -110 dBm | No signal |
| EC/IO | Signal quality |
|---|---|
| 0 to -6 | Excellent |
| -7 to -10 | Good |
| -11 to -20 | Fair to poor |
4G (LTE)
For 4G service mode, there are four relevant measurements:
- RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator
- RSRP - the Reference Signal Received Power is the power of the LTE Reference Signals spread over the full bandwidth and narrowband
- RSRQ - Reference Signal Received Quality is a C/I type of measurement and it indicates the quality of the received reference signal (similar to EC/IO)
- SINR - Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (A minimum of -20 dB SINR is needed to detect RSRP/RSRQ). Indicates the throughput capacity of the channel. As the name implies, SINR is the strength of the signal divided by
the strength of any interference
| RSRP | Signal strength |
|---|---|
| >= -80 dBm | Excellent |
| -80 dBm to -90 dBm | Good |
| -90 dBm to -100 dBm | Fair to poor |
| <= -100 dBm | No signal |
| RSSI | Signal quality |
|---|---|
| >= -10 dB | Excellent |
| -10 dB to -15 dB | Good |
| -15 dB to -20 dB | Fair to poor |
| <= -20 dB | No signal |
| SINR | Signal strength |
|---|---|
| >= 20 dB | Excellent |
| 13 dB to 20 dB | Good |
| 0 dB to 13 dB | Fair to poor |
| <= 0 dB | No signal |
RSSI for LTE is a calculated from several other signal related measurements: RSSI = wideband power = noise + serving cell power + interference power. For example, a 4G LTE modem might report an RSSI of -68 dBm, but:
RSRP = -102 dBm
RSRQ = -16 dB
SNR = -1.8 dB
In this case, the signal quality is actually very poor. This could be due to the device being some distance away from the LTE transmitter. It’s also possible that something is interfering with the signal, such as a building or other obstructions between the device and the tower.
| RSSI | Signal strength |
|---|---|
| > -65 dBm | Excellent |
| -65 dBm to -75 dBm | Good |
| -75 dBm to -85 dBm | Fair |
| -85 dBm to -95 dBm | Poor |
| <= -95 dBm | No signal |
How do I check the signal quality on a RUT device?
WebUI
The fastest and easiest way to find out your RSSI is by checking the Overview window of your router's WebUI (web user interface). The Overview window can be reached simply by accessing your router's WebUI (the default log in information is: address: 192.168.1.1; Username: admin; Password: admin01). Once you've logged in, you will be redirected to Overview window automatically. The Overview window contains widgets that display various information summaries about the status of your router. The RSSI value can be checked by looking at the Mobile widget that is located in the top right corner of the Overview window by default.
To get more detail about signal quality, you may want to check the Mobile Information section, which is located in Status -> Network -> Mobile. The Mobile Information window contains information about your mobile connection. Concerning signal quality, it displays Signal Strength (RSSI), RSRP, RSRQ and SINR.
SSH and CLI
To get the most detailed information about your signal quality values you can use gsmctl commands when logged in via CLI or SSH.