Template:Networking rutxxx configuration examples l2tp pover ipsec windows: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<li>Select <i>Role: Server</i>.</li> | <li>Select <i>Role: Server</i>.</li> | ||
<li>Enter a <i>custom configuration name</i>.</li> | <li>Enter a <i>custom configuration name</i>.</li> | ||
<li>Click the | <li>Click the <i>Add New</i> button.</li> | ||
<li>Click the | <li>Click the <i>Edit</i> button next to the newly created L2TP instance.</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li>[[File:{{{file_l2tp_add}}}|border|class=tlt-border]] | </li>[[File:{{{file_l2tp_add}}}|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<li> | <li>Configure the L2TP server instance:</li> | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
<li><i>Enable</i> the L2TP instance.</li> | <li><i>Enable</i> the L2TP instance.</li> | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 12 March 2020
Introduction
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the [[Media:{{{fw_version}}}_WEBUI.bin|{{{fw_version}}}]] firmware version.
Because of the lack of confidentiality inherent in the Layer 2 Networking Protocol (L2TP) protocol, Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is often used to secure L2TP packets by providing confidentiality, authentication and integrity. The combination of these two protocols is generally known as L2TP over IPsec (or simply L2TP/IPsec).
This article provides a guide on how to configure L2TP/IPsec on RUTxxx routers and how to connect them with a Windows 10 client.
It should also be noted that this guide is aimed at more advanced users and, therefore, skips some of the more self-explanatory steps in order to preserve the overall coherence of the article. For example, instead of showing how to add new instances step by step, it is only mentioned in a short sentence. If you feel this lack of information impedes your ability to configure the setup, we suggest you check out our separate configuration guides on IPsec and L2TP for reference.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- One RUTxxx routers of any type (excluding RUT850)
- A Public Static or Public Dynamic IP addresses
- At least one end device with Windows 10
Configuration scheme:
[[File:{{{file_scheme}}}|border|class=tlt-border]]
The figure above depicts the L2TP/IPsec scheme. - The router with the Public IP address (RUT1) acts as the L2TP/IPsec server and the Windows 10 device acts as client. L2TP connects the networks of RUT1 and Windows 10 client and IPsec provides the encryption for the L2TP tunnel.
When the scheme is realized, L2TP packets between the endpoints are encapsulated by IPsec. Since the L2TP packet itself is wrapped and hidden within the IPsec packet, the original source and destination IP address is encrypted within the packet.
Router configuration
If you have familiarized yourself with the configuration scheme and have all of the devices in order, we can start configuring the routers using instructions provided in this section. To summarize, we'll be configuring an L2TP server and an IPsec Transport instance (server) on RUT1; an a Windows 10 VPN connection (client).
L2TP Server (RUT1)
- Login to the router's WebUI and navigate to the Services → VPN → L2TP page and do the following:
- Select Role: Server.
- Enter a custom configuration name.
- Click the Add New button.
- Click the Edit button next to the newly created L2TP instance.
[[File:{{{file_l2tp_add}}}|border|class=tlt-border]]
- Configure the L2TP server instance:
- Enable the L2TP instance.
- Enter a User name and Password for authentication for the client.
- Optionaly, set a fixed IP for this client (if left empty, client will receive first free IP from the IP range).
- Don't forget to Save the changes.
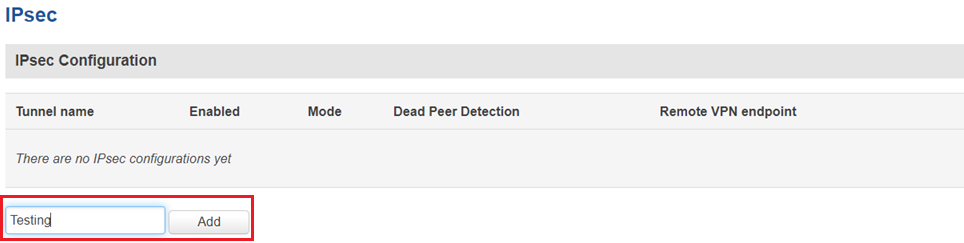
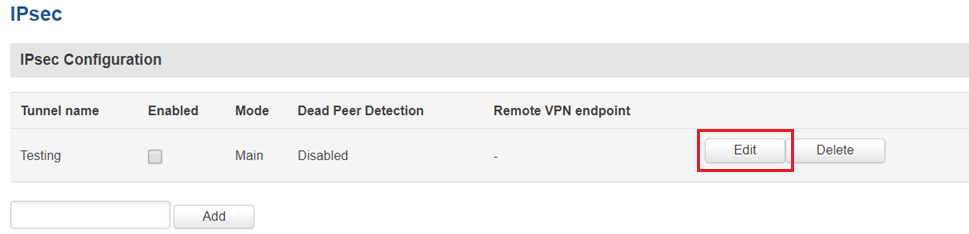
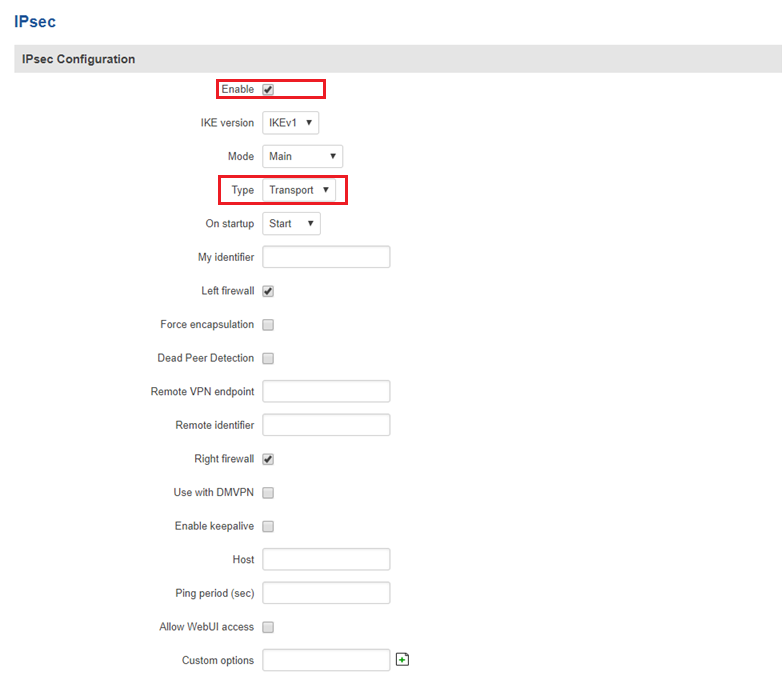
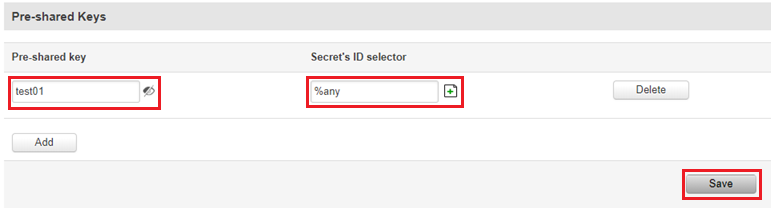
IPsec
You must configure a working IPsec Transport connection. This subsection contains instructions on how to do just that. Other used parameters will be defaults; You can find explanations for those parameters in the VPN manual page, IPsec section.
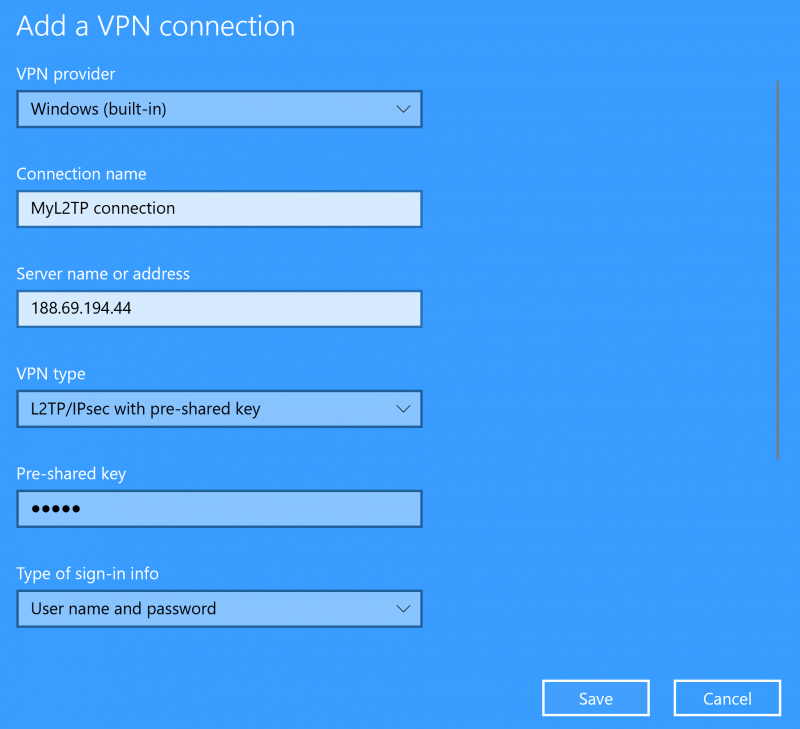
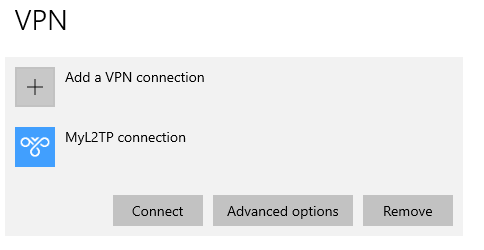
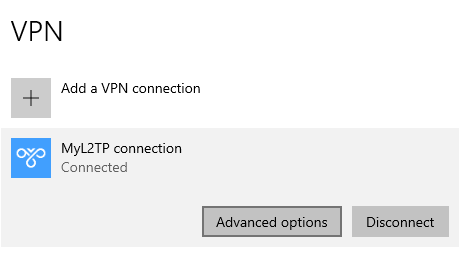
Windows 10 client Configuration
See also
- Other types of VPNs suported by RUTxxx devices:
[[Category:{{{name}}} Configuration Examples]]