Domnev: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<p style="color: | <p style="color:#0054B6">The information in this page is updated in accordance with [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.03.1'''] firmware version .</p> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
This article contains instructions on how to send M-Bus data to the server using various protocols. | This article contains instructions on how to send M-Bus data to the server using various protocols. | ||
Revision as of 10:21, 2 February 2023
The information in this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.03.1 firmware version .
Introduction
This article contains instructions on how to send M-Bus data to the server using various protocols.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's take a look at the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- TRB143;
- M-Bus device;
- Server;
- An end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone) for configuration;
If you're having trouble finding any page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Basic" button under "Mode," which is located at the top-right corner of the WebUI.

Node-RED installation and setup
We are going to set up Node-RED in a Linux virtual machine. For Node-RED to work, you would need to install Node.js version 14.00 or higher. If you already have Node.js installed, verify the Node.js version using this command:
node -v
If you do not have Node.js installed, run these commands to install it:
sudo apt install curl curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo -E bash – sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
Once we have Node.js installed, we can install Node-RED. Use this command to install:
sudo npm install -g –unsafe-perm node-red
Use the command node-red to start a local server. Here is how the terminal should look like if the server starts correctly:
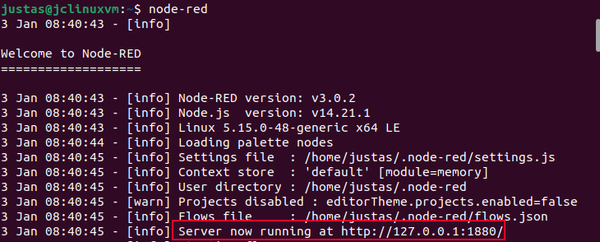
Once you have the local server running, use the local IP and port number in your internet browser. In this case, we are using 127.0.0.1:1880:
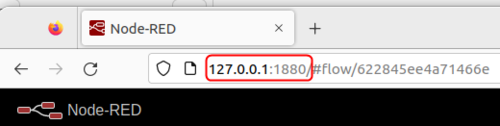
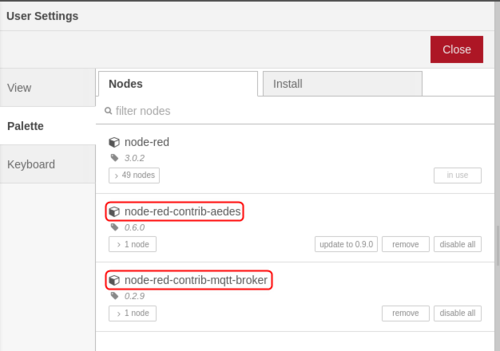
For MQTT usage, we are going to need MQTT-specific nodes. Use the side menu to navigate to the Manage Palette section and install these nodes:
- node-red-contrib-aedes
- node-red-contrib-mqtt-broker
Configuration
M-Bus Data to Server via MQTT
This section contains information on how to send M-Bus data to the server on Node-RED using the MQTT protocol.
The M-Bus meter is directly connected to TRB143. Gateway reads the M-Bus data and send it to the server using MQTT protocol.
Data to Server configuration
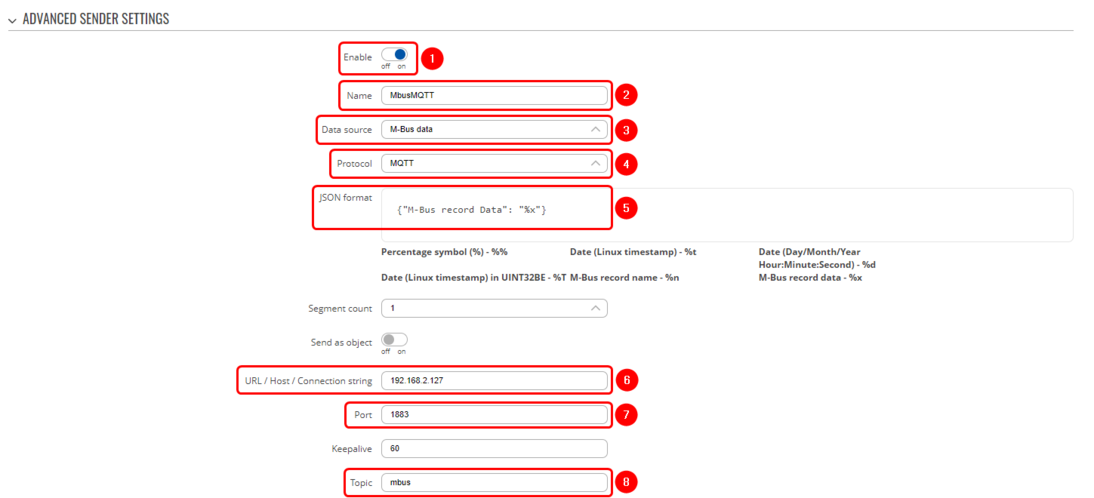
The Data to Server feature provides you with the possibility to set up data senders that collect data from various sources and periodically send it to remote servers. This section will walk you through configuring the Data to Server to send M-Bus data to the Node-RED server. To configure Data to Server, access the router's WebUI and navigate to Services, then Data to Server:
- Enable instance;
- Name: Enter desired instance name;
- Data source: M-bus;
- Protocol: MQTT;
- JSON format: Enter what data you would like to send;
- URL/Host/Connection string: Enter address of server;
- Port: Enter server port;
- Topic: Enter desired topic name
M-Bus configuration
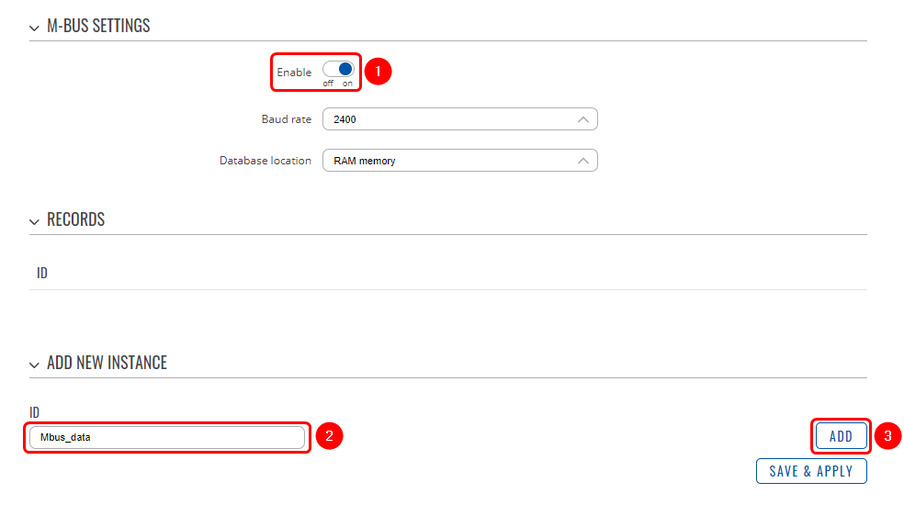
The M-Bus Settings section is used to configure the general service functionality. To set up a new M-Bus instance, go to Services → M-Bus:
- Enable M-Bus;
- ID: Enter desired instance name;
- Add;
After this, you should be redirected to the configuration page for the M-Bus instance:
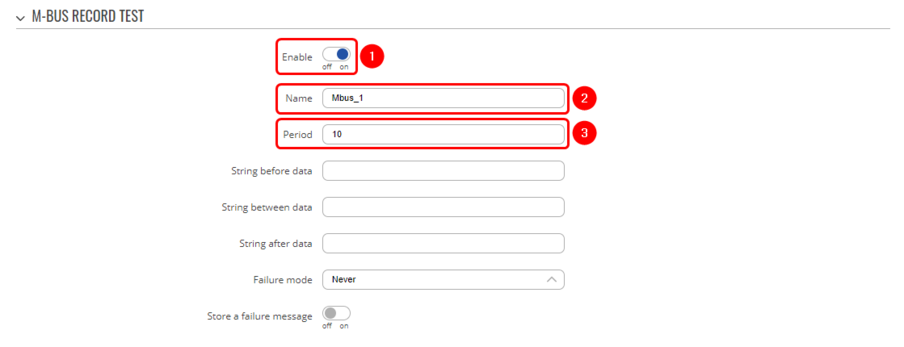
- Enable instance;
- Name: Enter your desired name;
- Period: Enter desired period;
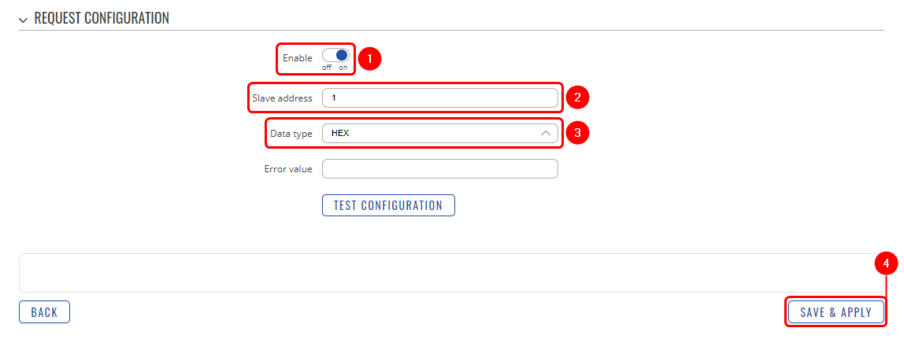
At the bottom of the M-Bus instance, you should see the Request Configuration section. It is used to configure requests from M-Bus devices.
- Enable request configuration;
- Slave address: Enter desired slave address;
- Data type: Select desired data type (this time we will be using HEX);
- Save & apply changes.
Node-RED configuration
Below you can see the Node-Red block diagram that is used to receive data and its configuration:
- aedes broker block - Broker;
- MQTT in block - mbus;
- Debug - debug 2;
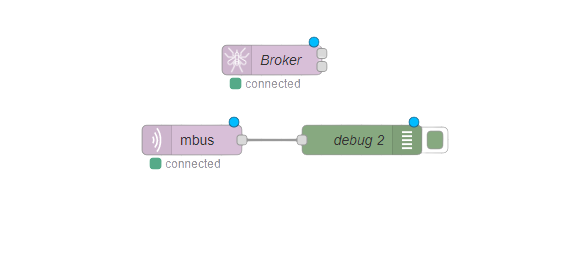
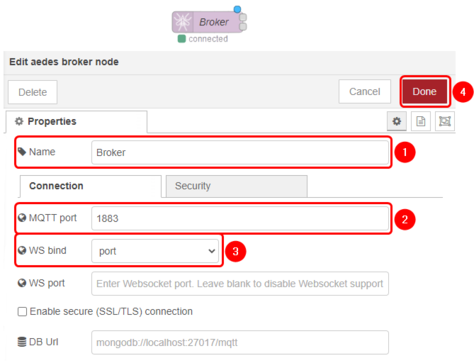
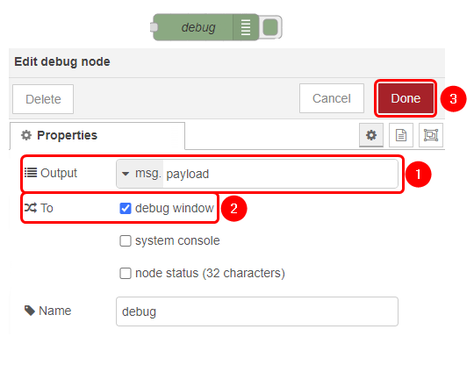
Configure the aedes broker block and broker blocks accordingly:
|
|
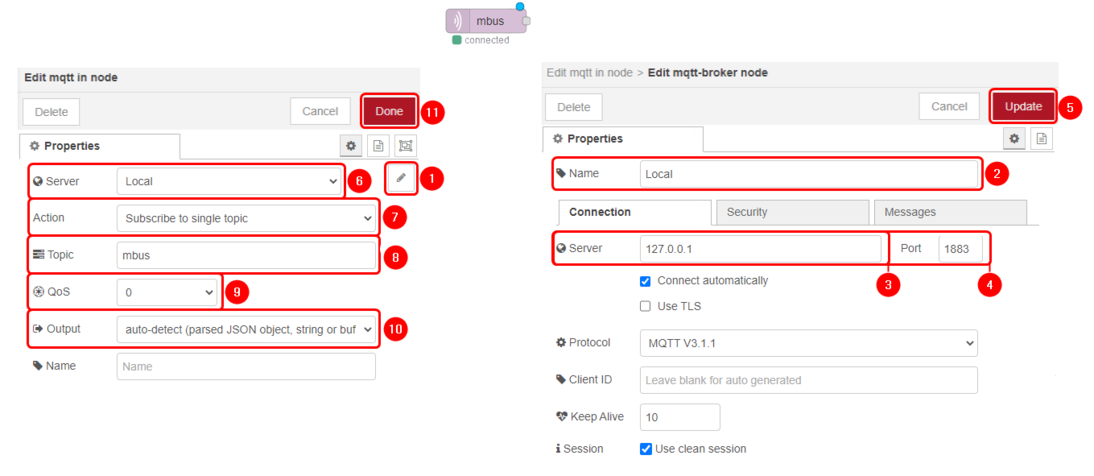
- Edit: Configure MQTT-Broker node;
- Name: Enter desired MQTT-Broker nodes name;
- Server: 127.0.0.1 as we will be using Node-RED as MQTT-Broker;
- Port: 1883;
- Update: Save the changes;
- Server: Select MQTT-Broker that you have just created;
- Action: Subscribe to single topic;
- Topic: Enter the topic that you have set in Data to Server configuration;
- Qos: 0;
- Output: Auto-Detect;
- Update: Save the changes;
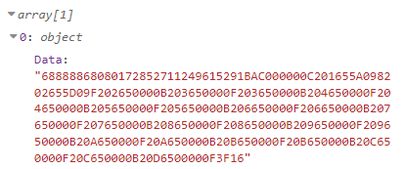
Results
If you have taken all of the steps described above, the configuration is complete. Below you can see M-Bus data output in HEX format.
M-Bus Data to Server Via HTTP
This section contains information on how to send M-Bus data to the server on Node-RED using the HTTP(S) protocol.
File:M-bus topology HTTP data.png
The M-Bus meter is directly connected to TRB143. Gateway reads the M-Bus data and send it to the server using HTTP(S) protocol.
Data to Server configuration
To set up Data to Server, navigate to Services → Data to Server:
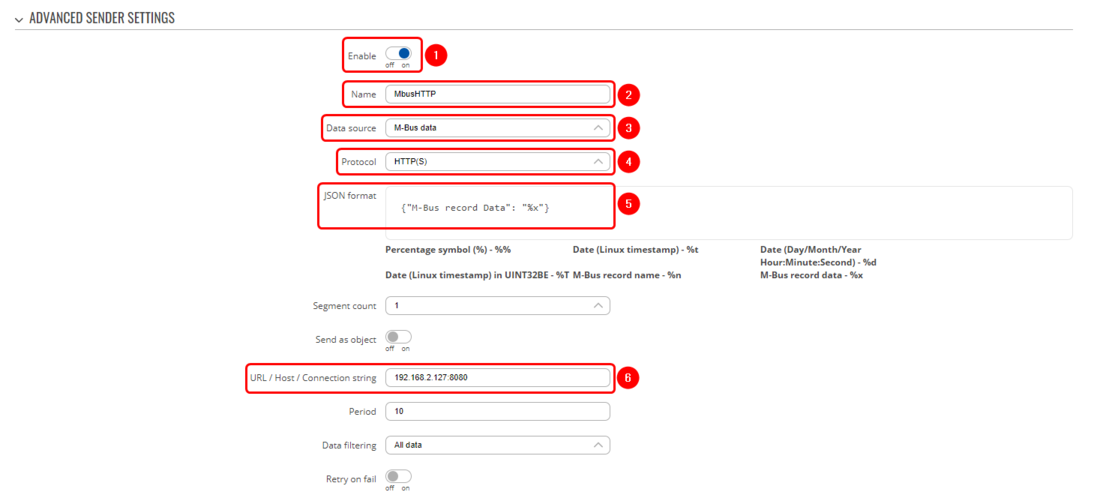
- Enable instance;
- Name: Enter desired instance name;
- Data source: M-bus;
- Protocol: HTTP(S);
- JSON format: Enter what data you would like to send;
- URL/Host/Connection string: Enter address of server and port;
M-Bus configuration
Go to Services → M-Bus → the instance you have created → edit. After that, scroll down to Request configuration → edit. There you will be able to change the data type.
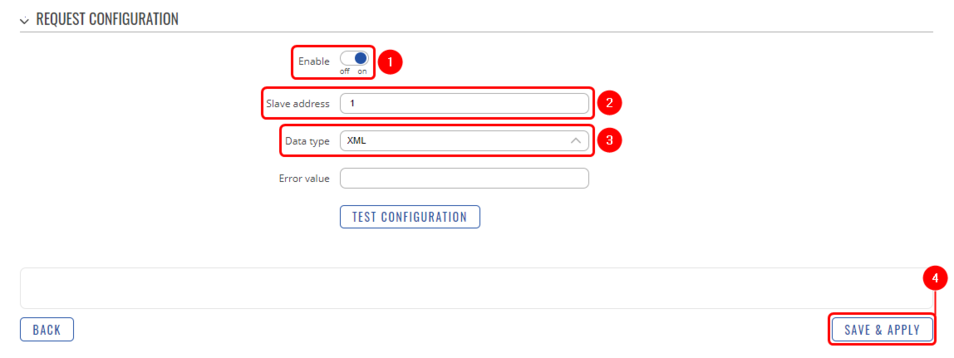
- Enable request configuration;
- Slave address: Enter desired slave address;
- Data type: Select desired data type (this time we will be using XML);
- Save & apply changes.
Node-RED configuration
Below you can see the Node-Red block diagram that is used to receive data and its configuration:
- TCP in block - tcp:8080;
- Debug - debug;
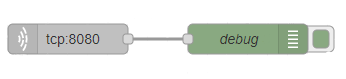
Configure TCP in and debug blocks accordingly:
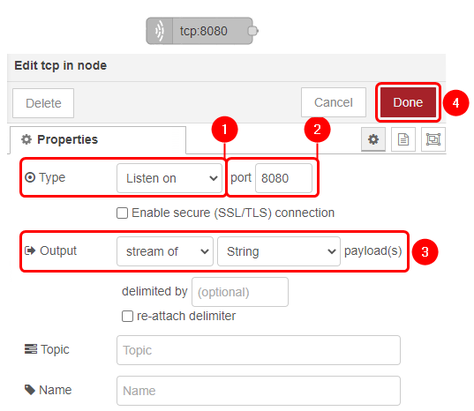
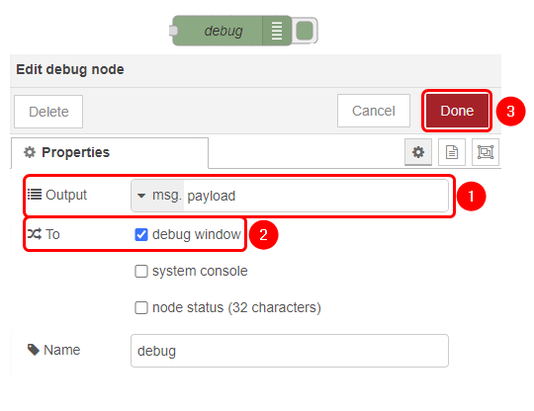
|
|
Results
If you have taken all of the steps described above, the configuration is complete. Below you can see M-Bus data output in XML format.
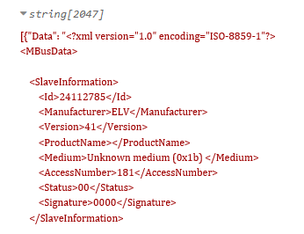
MQTT broker
This section contains information on how to send M-Bus data to the server on Node-RED using a Teltonika router as a MQTT broker.
File:M-bus topology TRBroker.png
The M-Bus meter is directly connected to TRB143. Gateway acts as MQTT Broker, reads the M-Bus data and sends it to the MQTT Subscriber.
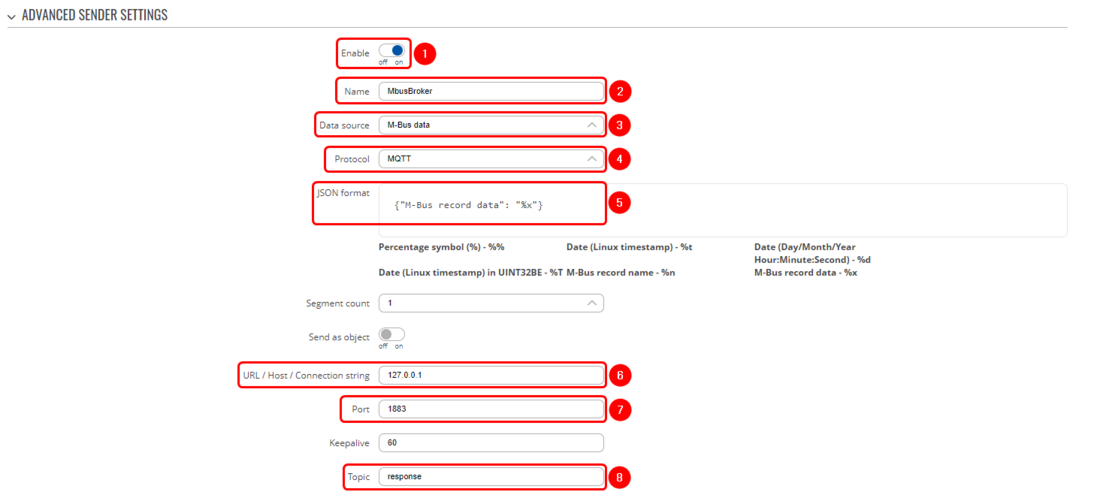
Data to Server configuration
To set up Data to Server, navigate to Services → Data to Server:
- Enable instance;
- Name: Enter desired instance name;
- Data source: M-bus;
- Protocol: MQTT;
- JSON format: Enter what data you would like to send;
- URL/Host/Connection string: Localhost IP;
- Port: enter server port;
- Topic: enter desired topic name;
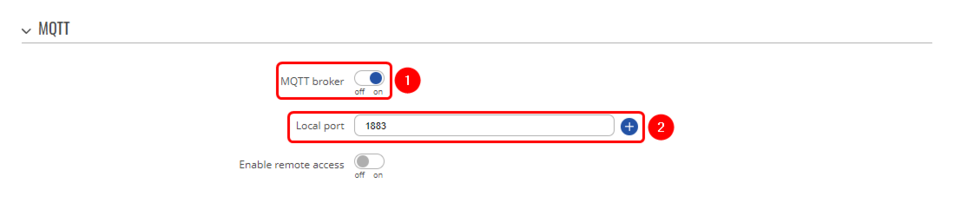
MQTT broker configuration
The MQTT Broker is an entity that listens for connections on the specified port and relays received messages to MQTT client. To set up MQTT Broker go to Services → MQTT → Broker:
- MQTT broker: On;
- Local port: 1883;
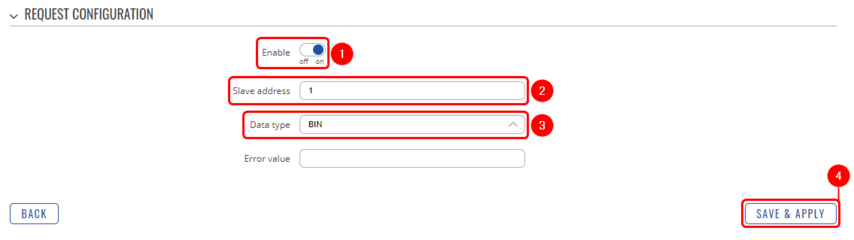
M-Bus configuration
Go to Services → M-Bus → the instance you have created → edit. After that, scroll down to Request configuration → edit. There, you will be able to change the data type.
- Enable request configuration;
- Slave address: Enter desired slave address;
- Data type: Select desired data type (this time we will be using BIN);
- Save & apply changes.
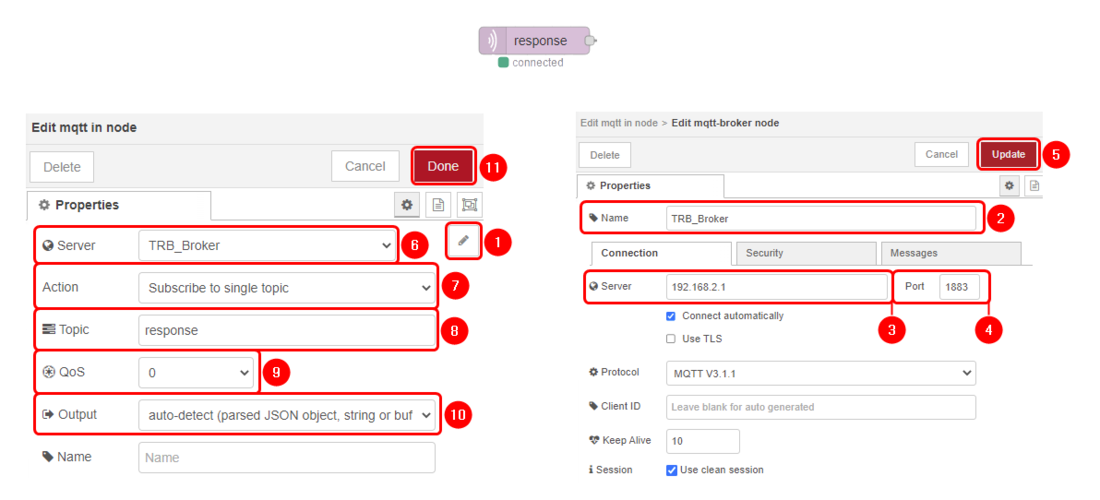
Node-RED configuration
Below you can see the Node-Red block diagram that is used to receive data and its configuration:
- MQTT in block - mbus;
- Debug - debug;
Configure debug block:
 |
|
|---|---|
|
|
- Edit: Configure MQTT-Broker node;
- Name: Enter desired MQTT-Broker nodes name;
- Server: 127.0.0.1 as we will be using Node-RED as MQTT-Broker;
- Port: 1883;
- Update: Save the changes;
- Server: Select MQTT-Broker that you have just created;
- Action: Subscribe to single topic;
- Topic: Enter the topic that you have set in Data to Server configuration;
- Qos: 0;
- Output: Auto-Detect;
- Update: Save the changes;
Results
If you have taken all of the steps described above, the configuration is complete. Below you can see M-Bus data output in BIN format.