TLS Certificates LV Demo: Difference between revisions
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
#Click [[File:Tls certificates generate button.png|62px]] button | #Click [[File:Tls certificates generate button.png|62px]] button | ||
# | # | ||
[[File:Tls certificates ca | [[File:Tls certificates ca p3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
# | # | ||
Revision as of 09:38, 16 September 2024
Main Page > FAQ > Security > TLS Certificates LV DemoSummary
Some services (such as OpenVPN, MQTT, etc.) on Teltonika Networks devices can be secured using TLS for encryption and authentication. This page discusses where one can obtain TLS certificates and key for this purpose.
Certificate generation
If you are using a third party service that requires TLS, all necessary files should be provided by the provider of that service. However, if you are setting up your own solution you may find use in of the TLS certificate generation methods described below.
Teltonika Networks device
The easiest way to generate certificates and keys is by using the Certificate Generation page that is available in the device's WebUI:
- System → Administration → Certificates
Generation of Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate and Key
The first step is to generate a Certificate Authority (CA) certificate, which will be used to sign both server and client certificates.
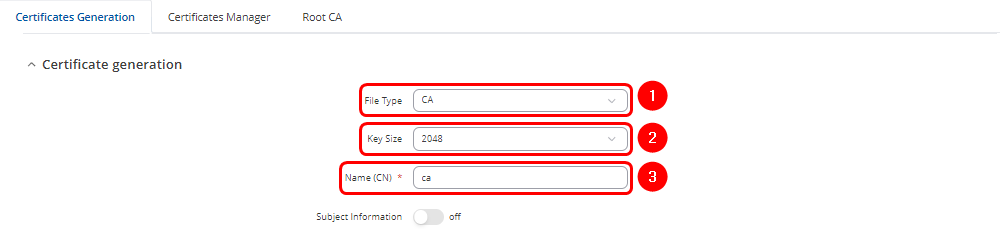
- Choose the file type as CA.
- On Teltonika routers, users can select from four Key Size options, ranging from 512 bits to 4096 bits.
- Enter the Common Name. This usually represents the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the server (e.g., example.com), but it can be any name of your choice.
- By enabling Subject Information, you can provide details about the entity to which the certificate is issued (Optional):
- A. Country Code (CC): The two-letter country code (e.g., LT for Lithuania).
- B. State or Province Name (ST): The name of the state or province (e.g., California).
- C. Locality Name (L): The city or locality (e.g., San Francisco).
- D. Organization Name (O): The name of the organization or company (e.g., Teltonika).
- E. Organizational Unit Name (OU): The name of the department or unit within the organization (e.g., IT Department).
- These fields help to clearly identify the organization or individual associated with the certificate.
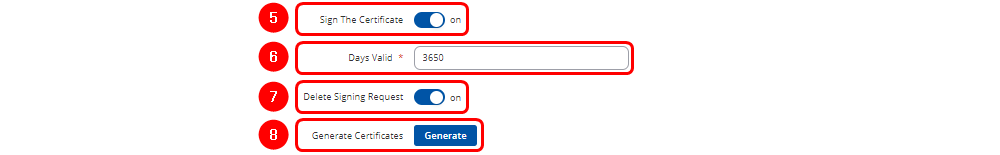
- Select the "On" option next to "Sign the Certificate." If not enabled, the Root CA will not sign or generate the new CA.
- Enter the period of how long CA certificate will be valid
- "Delete Signing Request" can be enabled, as it is not required after generation.
- Click
 button
button
Generation of Server Certificate and Key
A server certificate, signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), is used to authenticate the server and facilitate secure, encrypted communications with clients. Generating a server certificate follows similar steps to those for creating a CA certificate.
- Select Server file type.
- Select Key Size
- Enter Common Name of the Server
- Subject Information of the server(Optional)
- Select the "On" option next to "Sign the Certificate".
- Define how long the certificate will be valid.
- The system should automatically detect the CA certificate and key files from "Certificates Manager" tab.
- "Delete Signing Request" (Optional)
- Click
 button
button
File:Tls certificates server gen p1.png
Generation of Client Certificate and Key
A client certificate, signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), is used to authenticate the client and facilitate secure, encrypted communications with other clients and servers. Generating a server certificate follows similar steps to those for creating a CA certificate.
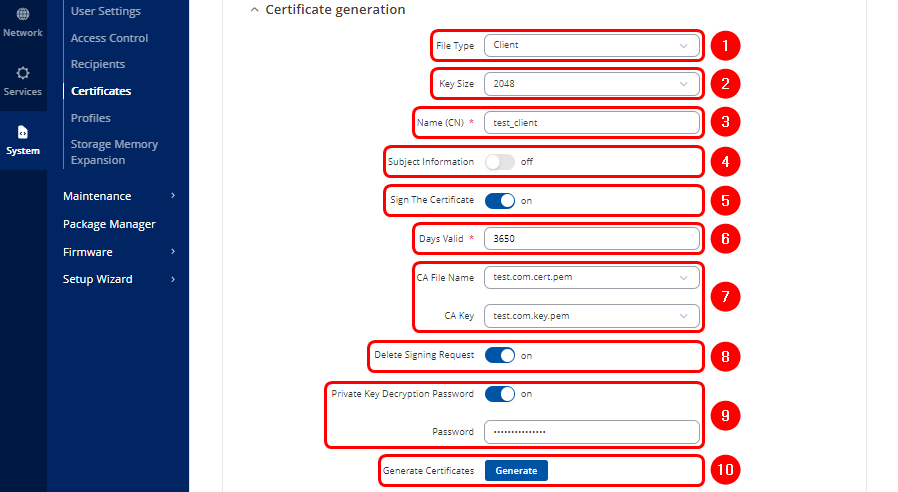
- Select Client file type.
- Select Key Size
- Enter Common Name of the Client
- Subject Information of the Client(Optional)
- Select the "On" option next to "Sign the Certificate".
- Define how long the certificate will be valid.
- The system should automatically detect the CA certificate and key files from the "Certificates Manager" tab.
- "Delete Signing Request" (Optional)
- "Private Key Decryption password" (Optional)
- Click
 button
button
Generation of DH Parameters
The DH parameters refers to the parameters used in the Diffie-Hellman key exchange. This cryptographic protocol allows two parties to generate a shared secret over an untrusted communication channel securely. In practical use, such as with VPNs, TLS/SSL, or routers, DH parameters are used to securely generate session keys for encrypting data. Generating a DH Parameters follows similar steps:
File:Tls certificates dh gen.png
Computer
You can also use third party software to generate the certificates on your computer. Guides are available for: