Wireless distribution system (WDS): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<p style="color:red">The information in this page is updated in accordance with [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07. | <p style="color:red">The information in this page is updated in accordance with [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.09.1'''] firmware version.</p> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Introduction | Introduction | ||
Revision as of 14:20, 23 September 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.09.1 firmware version.
Introduction
Introduction Wireless distribution system (WDS) enables access points to connect wirelessly within an IEEE 802.11 network. This system allows the expansion of a wireless network through multiple access points without needing a wired backbone. A key advantage of WDS is its ability to maintain the MAC addresses of client frames when transmitting between access points. This article provides an extensive configuration example of a basic WDS usage scenario with two RUTxxx devices. If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.

Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- Two RUTxxx routers
- Router's LANs should be in same subnet
- An end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone)
Configuration scheme:
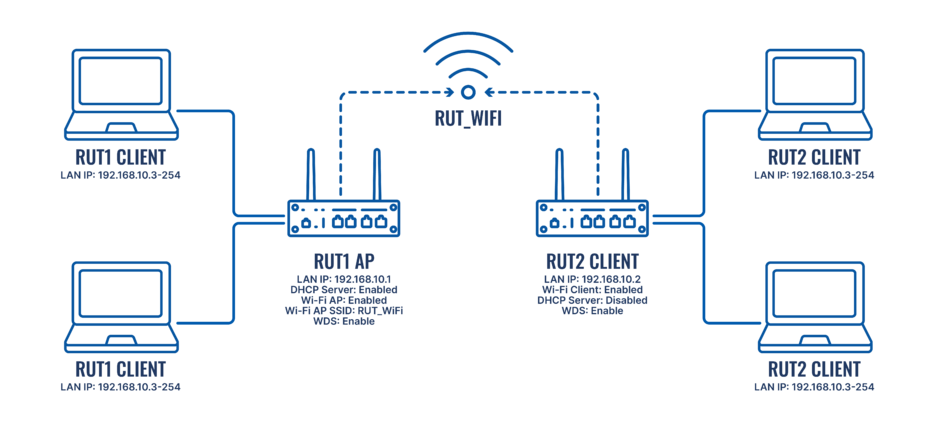
The scheme depicts two RUTxxx routers - RUT1 and RUT2. RUT1 is configured as Access Point Mode with SSID: RUT_WiFi. RUT2 is configured as Client mode (AP) and connected to Wi-Fi with SSID: RUT_WiFi. RUT2's DHCP Server is disabled. This is done so that the end devices connected to RUT2 get IP addresses from RUT1's DHCP Server with the help of WDS. So in short, this type of configuration combines devices into a single network, allowing them to communicate with each other.
NOTE: the parameters displayed in the scheme above will be used in further examples of this guide. Parameters like LAN IP addresses and WiFi SSID should be chosen in accordance with your own needs.
Router configuration
If you have familiarized yourself with the configuration scheme and have all of the devices in order, you can start configuring your routers using instructions provided in this section.
RUT1
The configuration for RUT1 is fairly simple. You only need to make sure that the router has:
- An active WiFi Access Point (AP) з включеним WDS
- An active DHCP Server
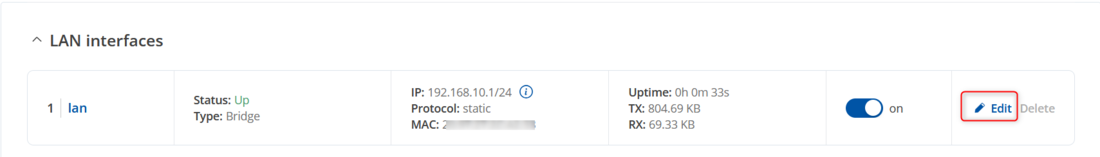
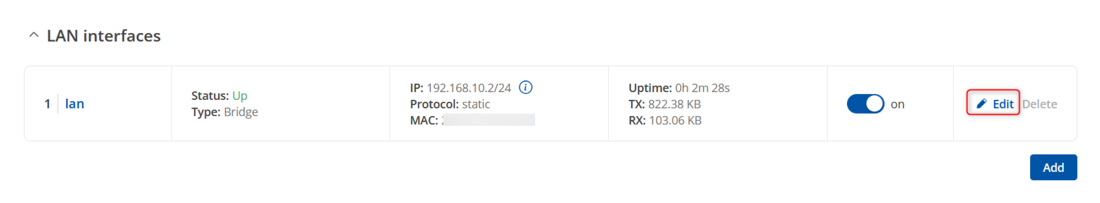
If you need to change the ip lan by logging in to the router's WebUI and visiting the Network → lan → lan settings click Edit button on the right side of interface for lan settings.
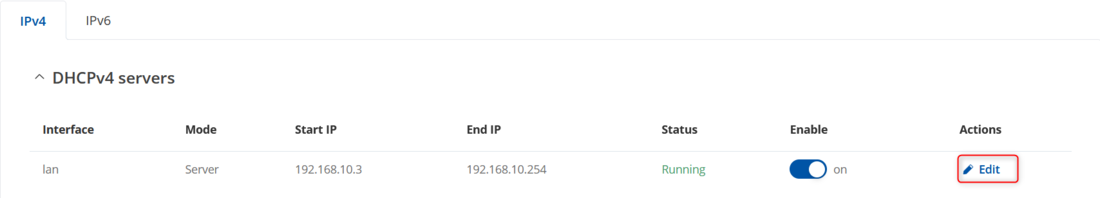
A WiFi Access Point (AP) and DHCP Server are enabled by default on RUTxxx routers, but if you wish to make changes, you can find the configuration pages for the services in Network → DHCP → Server settings click Edit button on the right side of interface for DHCP settings.
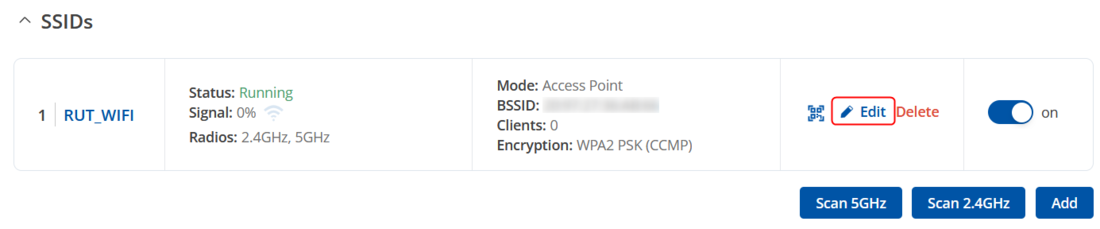
Got to Network → Wireless → SSIDs section and click Edit button on the right side of a wireless network for WiFi settings.
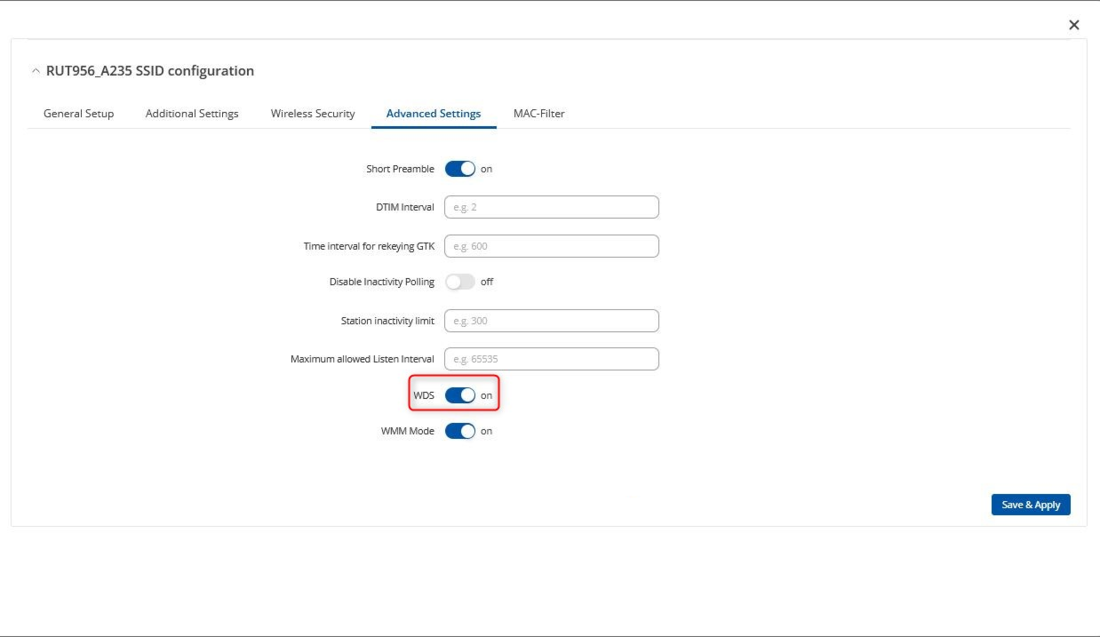
Go to the Advanced Settings tab and turn on WDS.
RUT2
The key things you need to configure in RUT2 are:
- Scan WiFi and connect to RUT1 WiFi Access Point
- Change network from auto(wifi0) to lan
- Enable WDS in Advanced Settings
- Change default IPv4 address to 192.168.10.2 and Disable DHCP server
NOTE: in this case, the steps should be taken in the order they are presented in, because if you disable RUT2's DHCP Server first, you may lose access to your router. So let's begin by setting up WiFi.
WiFi
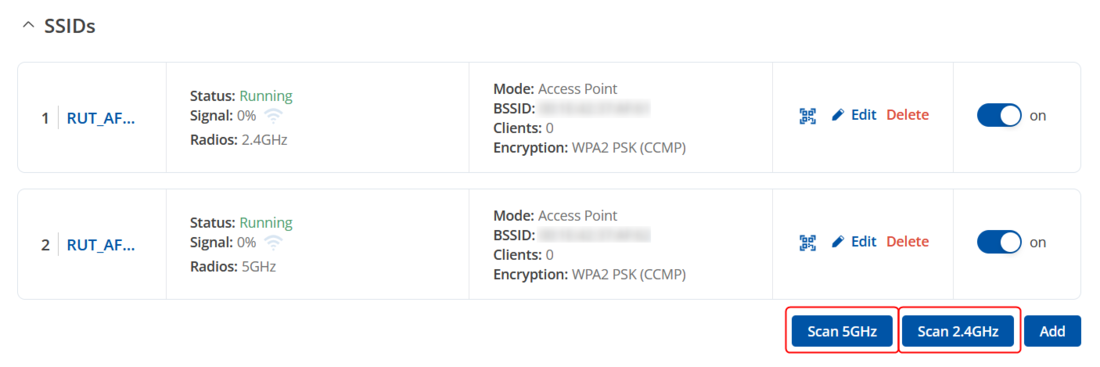
- To set up WiFi, login to the router's WebUI and navigate to the Network section found the Wireless tab by side (Network → Wireless → SSIDs)
- To begin configuring WiFi Client first click the 'Scan' button to scan the surrounding area and attempt to connect to a new wireless access point. You can choose whether to scan 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz wireless networks:
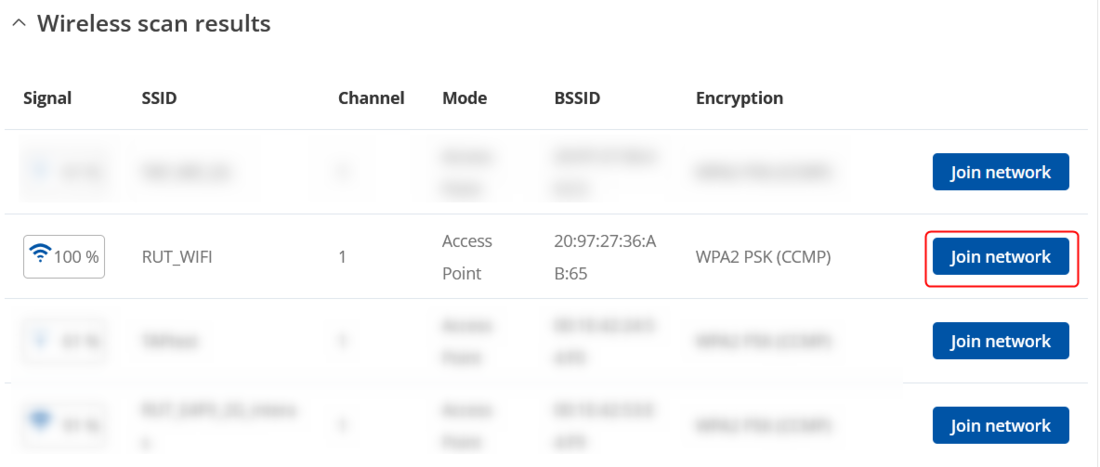
- Once the scan is complete, you will be presented with a list of nearby WiFi Access Points. Locate and choose RUT1's Access Point and click "Join network":
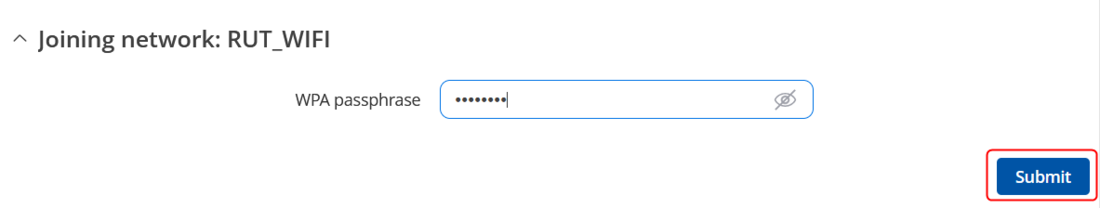
- You will be redirected again to following window, where you will need to enter WPA passphrase or other security password depending on AP that you are connecting to.
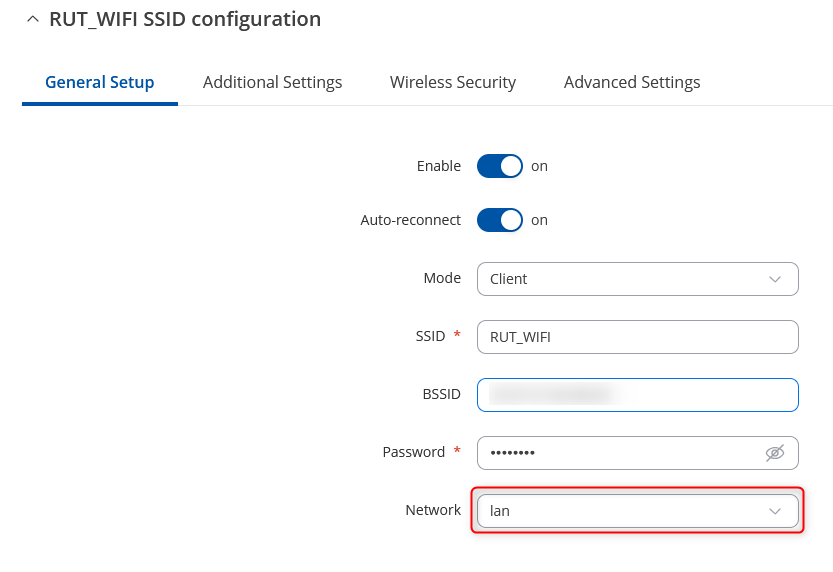
- Next window that opens will be Wireless client Configuration. Values there, mostly, should be left unchanged to avoid connection problems, because they are dictated by Access Point. Next window that opens will be Wireless client Configuration. Values there, mostly, should be left unchanged to avoid connection problems, because they are dictated by Access Point. The only thing you need to change is to select lan in network:
Go to the Advanced Settings tab and turn on WDS.
- After we configured WiFi settings, we will need to change lan IPv4 address and disable DHCP settings on our LAN interface. Go to Network → LAN and click on the button Edit:
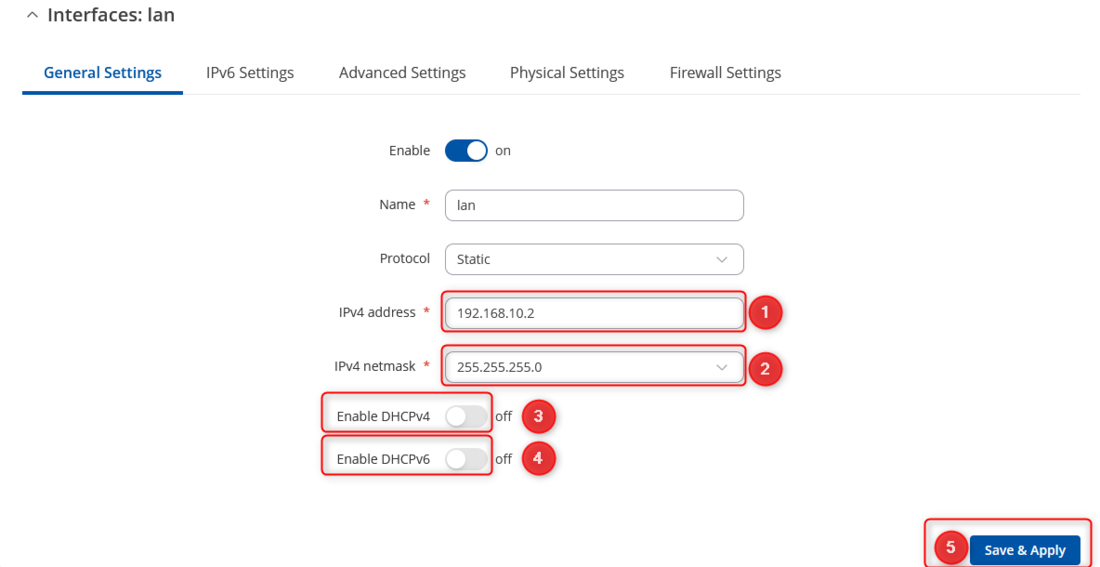
- After you clicked Edit button settings window will appear. Change IPv4 address and IPv4 netmask, disable DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 settings.
- Change IPv4 address
- Change IPv4 netmask
- Disable DHCPv4
- Disable DHCPv6
- Save
Testing the set up
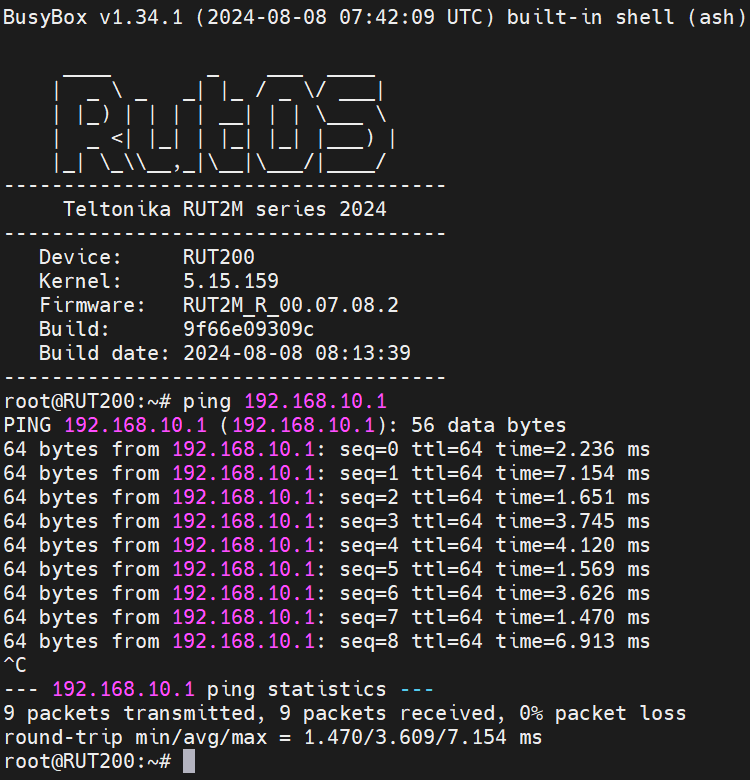
If you've taken all of the steps described above, the configuration is done. But as with any other configuration, it is always wise to test the set up in order to make sure that it works properly. To test this particular set up, login to any of the routers go to System → Maintenance → CLI. Login with user name: root and the router's admin password. You should then be able to ping the other router or any of the end devices that you have connected to either of the two routers. To execute a ping command, type ping <devices_ip> into the console and press the Enter key:
Replace <devices_ip> with an actual IP address of a device that is in your network and if the ping requests are successful it means the configuration is working. You can check the IP addresses of the devices connected to your network in RUT1's Status → Routes section.