Locking Devices to a Mobile Cell
Overview
All mobile carrier cells are assigned a unique ID, which is broadcasted to all connected devices. It is usually irrelevant information for the end user, as cell switching on mobile phones and routers has become very good. But sometimes in remote areas, it is beneficial to lock the LTE router to a single cell, as automatic mode may choose a cell with fewer or slower bands, as it only really looks for the best signal. For now, only some devices with Quectel modems support this feature.
Compatible modems
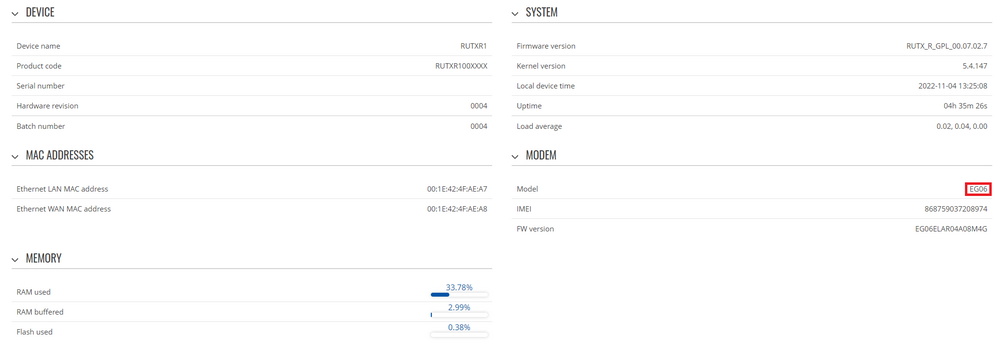
Not all modems support cell locking. To find out if your device is compatible, in your device WebUI, go to Status → System page. Under the Modem section, you'll see the Model row:
If the model starts with EG or EC, and not SLM or RG, this feature should work. However to make sure it's supported, command gsmctl -A 'AT+QNWLOCK=?' should not return ERROR, when ran via SSH or CLI. The response should look something like this:
When to use cell locking
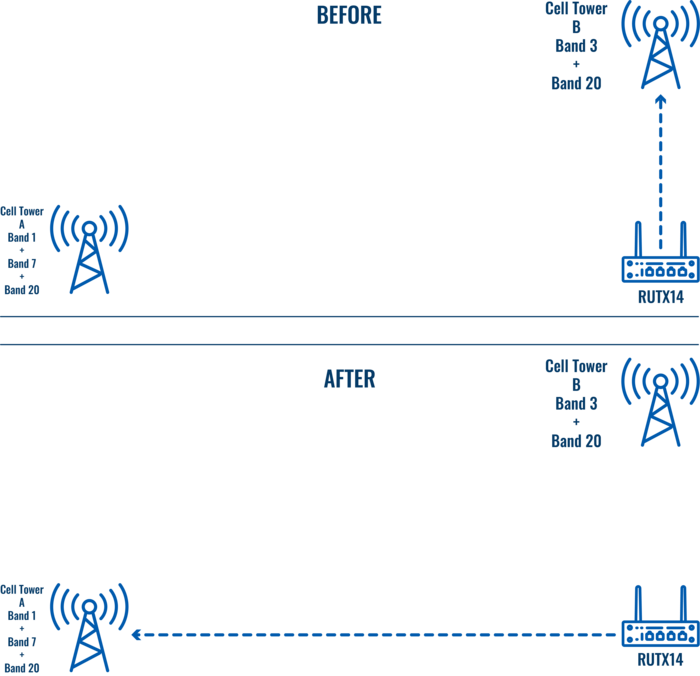
Let's say you're setting up RUTX14, which supports Carrier Aggregation of up to 3 bands, and you have two cell towers within a similar distance. Let's say Cell A transmits on bands 1, 7, and 20, while Cell B transmits on bands 3 and 20.
Since the signal from Cell B is a little stronger, the router will connect to two bands, and the bandwidth will be lower than using three bands. This means much lower speeds and reduced throughput.
If we lock the router into only using Cell A, we might get a little worse signal, but much better speeds due to using 3 bands at the same time.
Another use case could be to avoid overloaded cells. In some areas, even when the signal to a cell is great, speeds can be disappointing. This can be caused by lacking carrier infrastructure and overloaded cell towers. In this case, cell locking could be useful to connect to a cell tower with a worse signal, yet achieve better speeds.
Note: It is always recommended to use Band Lock and only resort to Cell locking if Band Lock does not resolve the issue.
Cell lock configuration
While we do not support this function via our WebUI just yet, it can quite easily be done using AT commands. AT commands are the "native language" for mobile modems, which the router uses to communicate with the modem.
A few notes before we get started:
- The described method works with Teltonika RUT/RUTX/TCR/TRB series devices, that contain Quectel modems;
- Using this command will lock the device into LTE-only mode;
- Rebooting the device might remove the cell lock;
- It is not recommended to perform these actions while the device is connected remotely as if it loses connection, it will not be recoverable!
Configuring LTE-only mode
To start, we'll set the router to LTE-only mode, by using the command:
gsmctl -A 'AT+QCFG="NWSCANMODE",3,1'
Where:
- 3 - LTE-only mode;
- 1 - Take effect immediately after executing the command.
This may cause the router to lose connection for a few seconds, so before continuing to the next step, please make sure the router is connected to the network.
Note: Do not use WebUI to change this setting. It has to be done via AT commands.
Finding the serving cell details
To know if our changes had any effect, we'll check the current cell we're connected to, by using a command:
gsmctl -A 'AT+QENG="SERVINGCELL"'
The output should look something like this:

- 139B15 - currently serving cell ID in hexadecimal form. This ID is unique to each cell. It is only used as a reference point in this configuration.
- 459 - PCI or Physical Cell Identity. PCI is necessary for a modem to communicate with a cell tower. This is one of the variables we will use when setting up cell locking.
- 1850 - LTE EARFCN stands for E-UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number. This will be the second variable when setting up cell locking.
Finding the neighbouring cells details
To check the neighboring cells, that we can connect to, this command should be used:
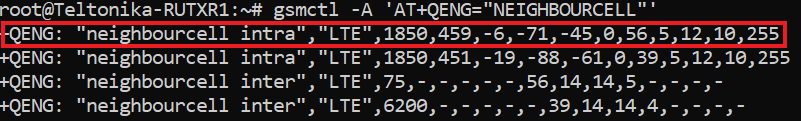
gsmctl -A 'AT+QENG="NEIGHBOURCELL"'
And the output should look like this:
Here's an explanation of the first line for each value:
- LTE - network generation;
- 1850 - EARFCN value. EARFCN is used to determine the channel frequency and bandwidth, thus it can be useful to determine the band of neighbouring cell. This can be achieved using EARFCN calculator;
- 459 - PCI;
- -6 - RSRQ (dB);
- -71 - RSRP (dBm);
- -45 - Signal Strength - RSSI (dBm).
The explanation for the last 3 measurements can be found on our Mobile signal strength recommendations page. From these outputs, the most fitting cell should be picked, and its EARFCN and PCI value should be noted.
Locking to a selected cell
Once we pick out the cell that we prefer, we can execute this command, with <EARFCN> and <PCID> replaced with desired variables from the previous commands (< and > are not needed):
gsmctl -A 'AT+QNWLOCK="common/lte",2,<EARFCN>,<PCI>'
Output from the command should be OK, if it's not, please double-check the spelling.
Verifying the change
To verify that the cell change occurred, wait around 30 seconds and again run the command gsmctl -A 'AT+QENG="SERVINGCELL"'
The output values for PCI and EARFCN should now match the ones used in the previous command. If not, please double check, that you have not set the same cell as the router was connected to before.
Note: After changing SIM card settings, please verify that the cell lock is still in place, as some settings could cause the cell lock to reset.
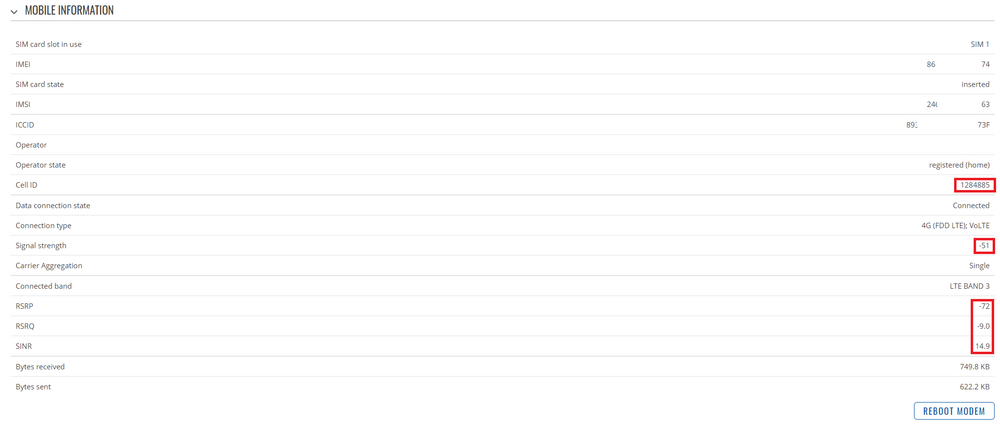
Cell ID and signal strength values can also be checked by going to Status -> Network -> Mobile in the router's WebUI:
Please keep in mind that Cell ID is displayed in its decimal form on WebUI.
Reverting to an automatic cell selection
If you decide that this feature is no longer needed, it can always be reverted back to automatic cell selection.
First, let's set cell selection back to auto using this command:
gsmctl -A 'AT+QNWLOCK="common/lte",0'
Then, we need to bring the device service mode back to Auto, by using this command:
gsmctl -A 'AT+QCFG="NWSCANMODE",0,1'
And that's it! Your router should be back to fully automatic mode.
External links
OpenCellid - database of cells and their locations;
CellMapper - database of cells, their locations as well as EARFCN and PCI data;