L2TP configuration examples
Introduction
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs. It does not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself. Rather, it relies on an encryption protocol that it passes within the tunnel to provide privacy.
This article provides an extensive configuration example with details on how to create a connection between an L2TP Server and Client, both of which configured on RUTxxx routers.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- Two RUTxxx routers of any type (excluding RUT850)
- A SIM card with a Public Static or Public Dynamic IP address for the L2TP Server
- An end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone) to configure the routers
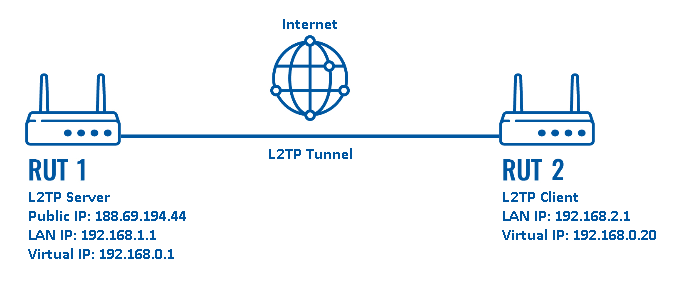
Configuration scheme:
As indicated by the figure above, the configuration we are trying to achieve here is very basic: it concerns two RUTxxx routers - RUT1 and RUT2. One functions as an L2TP Server, the other - an L2TP Client. They are connected into a virtual network via an L2TP Tunnel.
Router configuration
If you have familiarized yourself with the configuration scheme and have all of the devices in order, we can start configuring the routers using instructions provided in this section.
L2TP Server (RUT1)
As mentioned in the prerequisites section, the router that acts as the server must have a Public Static or Public Dynamic IP address (more information on the subject can be found here). If that is in order, we should start configuring the server.
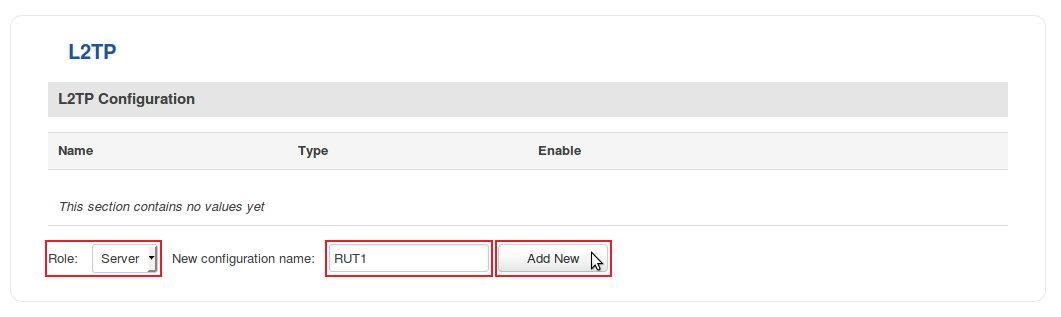
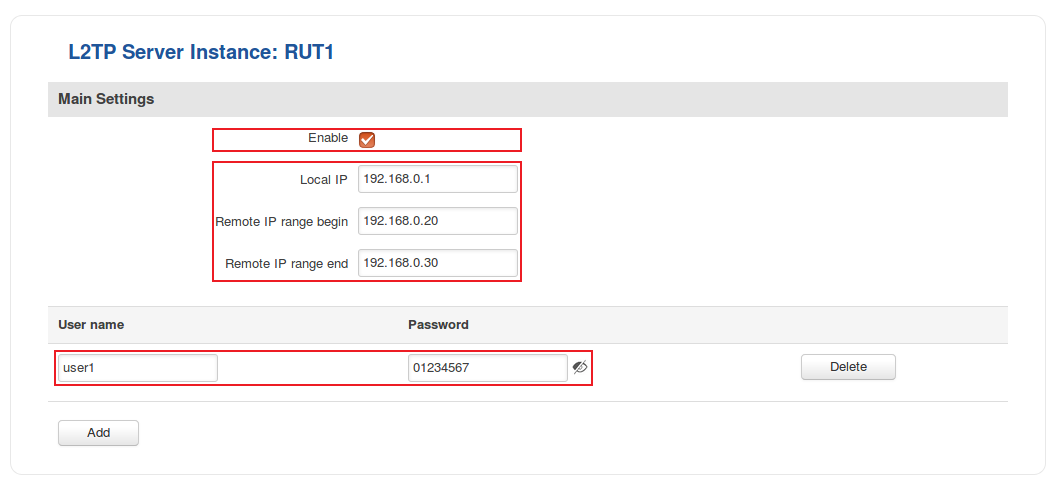
- Login to the router's WebUI and go to Services → VPN → L2TP. Select Role: Server, enter a name for the new instance and click the "Add" button: