TRB142 RS232
Main Page > TRB Gateways > TRB142 > TRB142 Manual > TRB142 WebUI > TRB142 Services section > TRB142 RS232
Summary
The RS232 function is designed to utilize the serial interface of the device. Serial interfaces provide a possibility for legacy devices to gain access to IP networks. This chapter is an overview of the RS232 section.
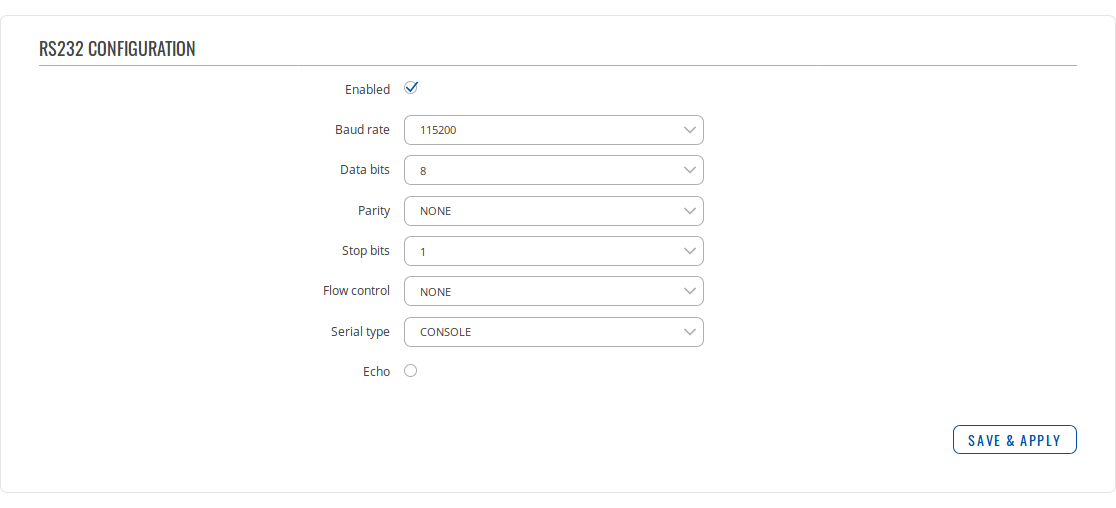
RS232 Configuration
The RS232 Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of the RS232 serial connection. Parameters used should be selected in accordance with the needs of the user and the type of device connected via the RS232 port.
The figure below is an example of the RS232 Configuration section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; Default: no | Enables the RS232 service |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200; Default: 115200 | Data rate for serial data transmission (in bits per second) |
| Data bits | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8; Default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character |
| Parity | None | Odd | Even; Default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Stop bits | 1 | 2; Default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used |
| Flow control | None | RTS/CTS | Xon/Xoff; Default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking.
|
| Serial type | Console | Over IP | Modem | Modbus gateway | NTRIP client; Default: Console | Serial connection type. More information on each serial type can be seen below or by clicking on a link in the value section |
| Echo | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles RS232 echo ON or OFF. RS232 echo is a loopback test usually used to check whether the RS232 cable is working properly |
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | yes | no; Default: no | When checked, enables the RS232 service |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200; Default: 115200 | Sets the data rate for serial data transmission (in bits per second) |
| Data bits | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8; Default: 8 | The number of data bits for each character |
| Parity | None | Odd | Even; Default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check. None (N) - no parity method is used Odd (O) - the parity bit is set in a way that the number of "logical ones (1s)" has to be odd Even (E) - the parity bit is set in a way that the number of "logical ones (1s)" has to be even |
| Stop bits | 1 | 2; Default: 1 | |
| Flow control | None | RTS/CTS | Xon/Xoff; Default: None | |
| Serial type | Console | Over IP | Modem | Modbus gateway | NTRIP client; Default: Console | Specifies the serial connection type. |
| Echo | yes | no; Default: no |
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|