Domnev1
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.09 firmware version .
Summary
This article contains instructions on how to configure Port Foward functionality on most of the Teltonika Networks devices (with the exception of TAP and TSW series)
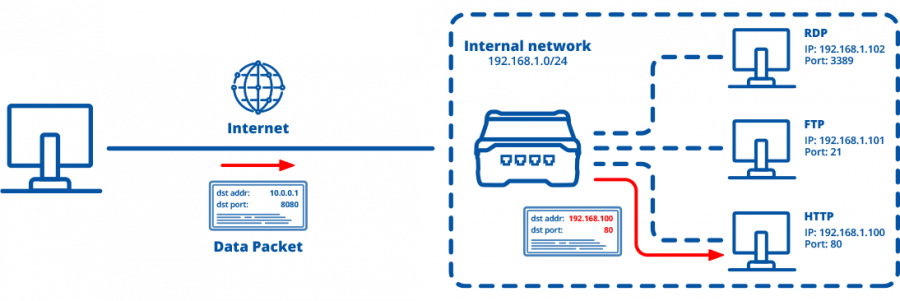
Port Forwarding is the process of redirecting data packets to another destination. In Teltonika-Networks devices this is a feature of the iptables firewall, NAT table, PREROUTING chain. When a packet matches a port forwarding rule, the destination and/or port values are changed in the packet header.
Configuration overview & prerequisites
Before we begin, let's take a look at the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Configuring port forwarding on Teltonika devices is a simple process that involves just a few steps and can easily be replicated across various devices. The number of devices involved will depend on the specific use case, but the setup can be scaled seamlessly. In the example below, we will use the RUTX50 as the primary device with mobile internet connectivity, acting as the gateway and DHCP server. This setup allows us to remotely access third-party devices connected to RUTX50 over the internet.
Prerequisites:
- A device from the RUT, RUTX, RUTM, RUTC or TRB series gateway;
- A device which we will be reaching through port forward
- A PC, Laptop, tablet or a smartphone
- The Teltonika Networks device must have a SIM card with a Public Static or Public Dynamic IP address (more on IP address types here) to make remote access possible
- (Optional) If the router's SIM card has a Public Dynamic IP address, you may want to additionally configure a Dynamic DNS hostname
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Router configuration
First, let's overview what configurations we'll be needing to set up:
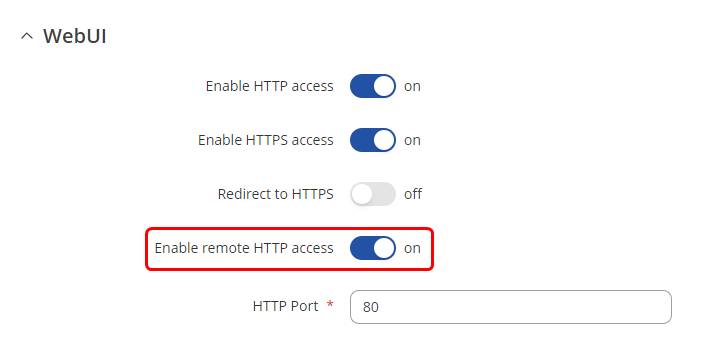
- Enable remote HTTP access, so that the router can be reached from a remote location
- Specify an Access Point Name (APN) for the SIM card in use, so that the router will obtain a Public IP address
- Configure a Port Forwarding rule that redirects all connections from one Port to the camera's IP address:Port
- (Optional) Configure Dynamic DNS hostname
Enabling remote HTTP(S) access
To enable remote HTTP access, log in to the router's WebUI and navigate to the System → Administration → Access Control tab. Once in the Administration-Access Control, find the Enable remote HTTP access field and put a check mark next to it:
WARNING: once you set up any type of remote access, your router becomes vulnerable to malicious attacks from unknown hosts throughout the Internet. It is highly recommended that once you enable remote access, you also change the router's default password to a string, custom password. You can change the router's password in System → Administration → General → Administrator Password
Step 2: Set an APN
Note: If you have a Public IP address already, you can skip this step.
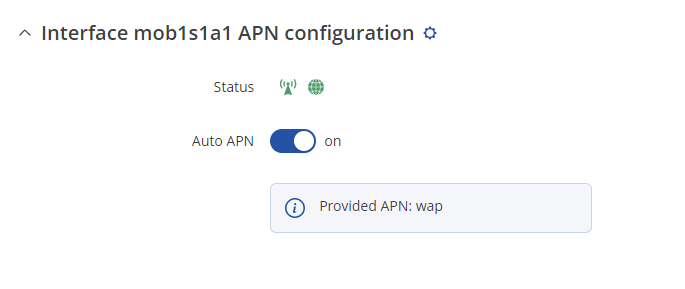
To set the APN, while in the router's WebUI, navigate to the Network → Mobile → General → Interface mob1s1a1 APN configuration:
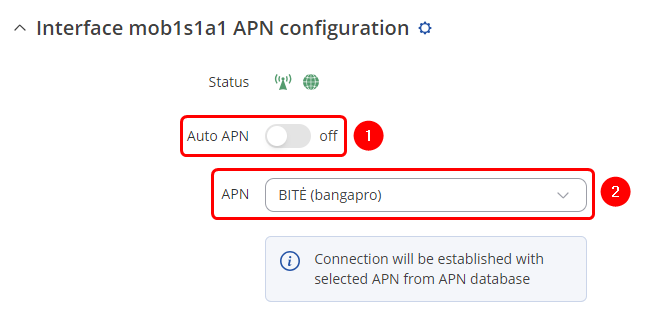
Once in the Interface mob1s1a1 APN configuration window, edit your mobile interface, find the APN field and enter you Internet Service Provider's APN:
- Disable the Auto APN option
- Choose the correct APN, which gives out a public IP address (for more information about that contact your Internet Service Provider)
Additional notes on APN:
- NOTE 1: don't use the exact APN value as seen in the example above as it will not work with your SIM card. APN depends on your Internet Service Provider (ISP), therefore, your ISP should provide you with their APN or, in many case, you can find your ISP's APN with an online search.
- NOTE 2: furthermore, it should be noted that not all SIM cards support this functionality. Static or Dynamic Public IP addresses (obtained through APN) are a paid service and setting any APN value for a SIM card that doesn't support this service will most likely result in losing your data connection. If this is the case, it can be fixed by simply deleting the APN, but it also means that remote access through mobile WAN IP will most likely not work on your SIM card.
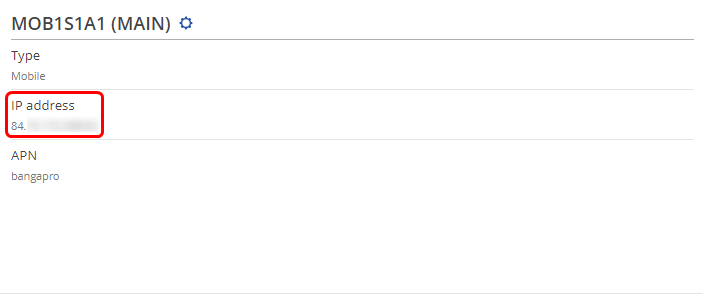
- NOTE 3: in some cases the SIM card doesn't require an APN in order to obtain a Public IP address. If that is the case for you, simply check what your router's mobile WAN IP address is - if it's already a Public IP address, then you don't need to set an APN. The easiest way to find what your mobile WAN IP address is to log in to the router's WebUI and check the MOB1S1A1 widget in the Overview page:
Step 3: Configure Port Forwarding
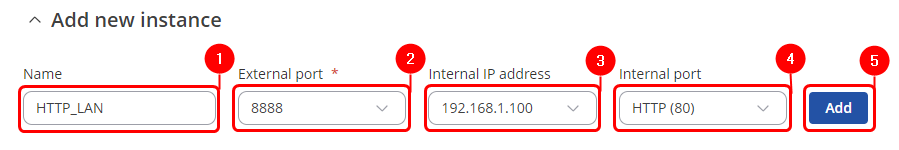
Navigate to the Port Forwards tab by going to Network → Firewall → Port Forwards. Scroll down to the bottom of the page and locate the New Port Forward Rule section. Set the following parameters:
- Custom name for the port forward.
- External port(s): 8888 (LAN device HTTP port)
- Internal IP: 192.168.1.100 (LAN device IP address)
- Internal port(s): 80
- Click on Add button.
After you have added the new rule, you will redirected to that rule's configuration window. Make sure to enable a rule. Everything else should already be in order so just click Save & Apply and your rule will be created.
(Optional) Step 4: Configure Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS or DynDNS) is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name System (DNS), often in real time, with the active DDNS configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses or other information.
Dynamic DNS configuration is optional here, but it is recommended if your SIM card has a Dynamic Public IP address. You can find more information on what a Dynamic Public IP address is here, but in short it means that your WAN IP address is Dynamic and, therefore, it may change over time (usually when disconnecting/reconnecting or re-registering to a network). Dynamic DNS assigns a hostname to your IP address and constantly updates that hostname, which means that even if your IP address changes, DDNS will assign the same hostname to your new IP, making your router reachable via the same hostname at any time.
You must use an external DDNS service to create a hostname and assign it to your IP. RUT routers support many such services. You can find a complete list of supported DDNS services in the Services → Dynamic DNS section of the router's WebUI. You can also find guides on how to configure some of these services in our wiki:
The guides contain information on how to configure both the router and the third party service. Choose one according to your liking.
Testing the set up
See Also
Most Teltonika-Networks devices have the port forwarding feature. Configuration is described in the user manual Firewall page for each device.