Overlapping subnets with IPsec solution
Introduction
This article provides an extensive configuration example with details on how to solve overlapping subnets when using IPsec.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Prerequisites:
- Two RUTxxx routers of any type (excluding RUT850)
- A SIM card with a Public Static or Public Dynamic IP address for the IPsec server
- An end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone) to configure the routers
Configuration scheme:
Router configuration
If you have familiarized yourself with the configuration scheme and have all of the devices in order, we can start configuring the routers using instructions provided in this section.
Basic tunnel
First of, lets configure a simple connection between two IPsec instances, i.e., RUT1 and RUT2.
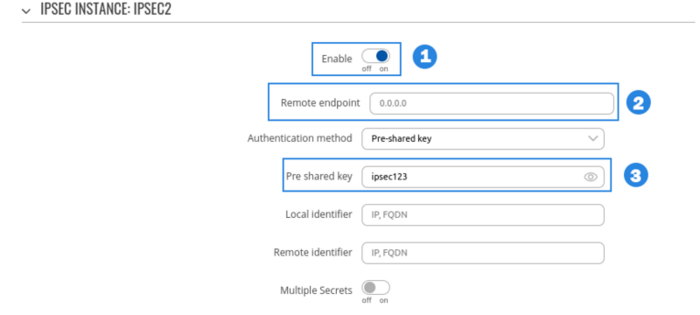
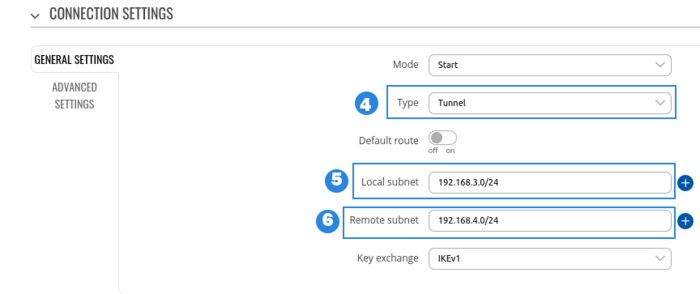
RUT1 configuration
- Enable instance.
- Remote endpoint (Only one side of IPsec needs to have it configured)
- Write Pre shared key(a shared password used for authentication between the peers. The value of this field must match on both instances).
- Select Type to tunnel
- Write Local subnet (an IP address/Subnet mask of the router on which the IPsec instance is configured).
- Write Remote subnet
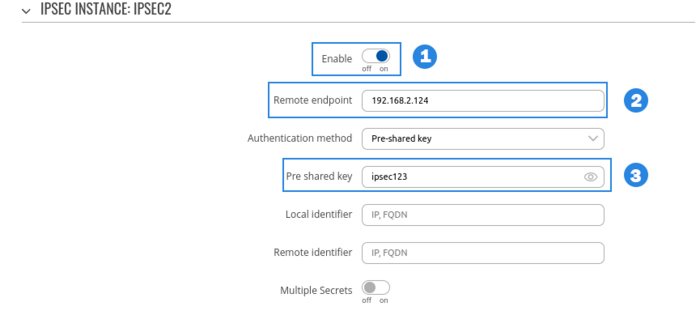
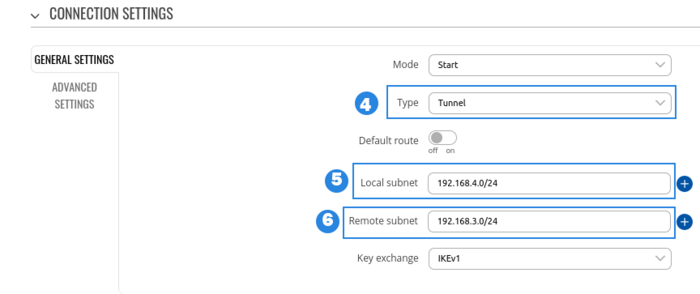
RUT2 configuration
- Enable instance.
- Add Remote endpoint
- Write Pre shared key (a shared password used for authentication between the peers. The value of this field must match on both instances).
- Select Type to tunnel
- Write Local subnet (an IP address/Subnet mask of the router on which the IPsec instance is configured).
- Write Remote subnet
Check IPsec tunnel status
If you've followed all the steps presented above, your configuration should be finished. But as with any other configuration, it is always wise to test the setup in order to make sure that it works properly. This can be verified by running ipsec status command in RUT CLI, you should see tunnel being installed between virtual networks:
root@Teltonika-RUTX12:~# ipsec status
Security Associations (1 up, 0 connecting):
ipsec-ipsec_c[1]: ESTABLISHED 32 MINUTES AGO, 192.168.2.124[192.168.2.124]...192.168.2.145[192.168.2.145]
ipsec-ipsec_c{1}: INSTALLED, TUNNEL, reqid 1, ESP SPIs: ca6d4767_i c3f5534b_o
ipsec-ipsec_c{1}: 192.168.3.0/24 === 192.168.4.0/24
Firewall configuration
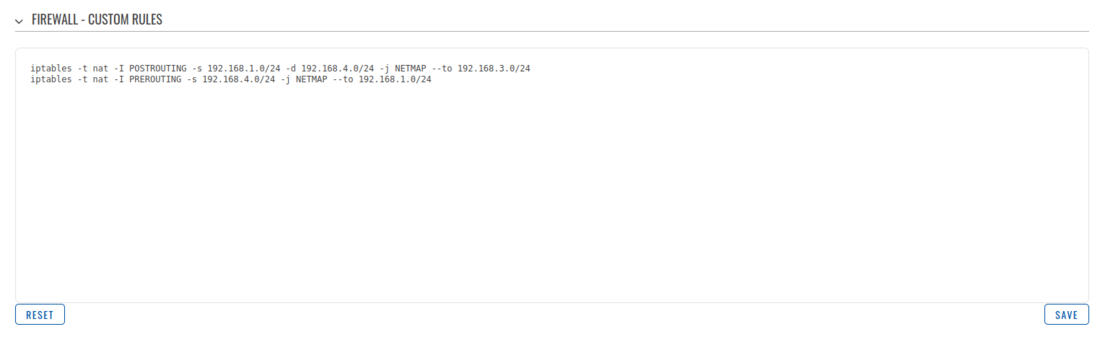
After establishing IPsec tunnel it's necessary to map LAN network IP addresses to virtual IPsec network addresses, for this we'll use iptables NETMAP target. Insert these IPtables rules into WebUI -> Network -> Firewall -> Custom rules.
RUT1 Firewall configuration
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.4.0/24 -j NETMAP --to 192.168.3.0/24 iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -s 192.168.4.0/24 -j NETMAP --to 192.168.1.0/24
RUT2 Firewall configuration
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.3.0/24 -j NETMAP --to 192.168.4.0/24 iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -s 192.168.3.0/24 -j NETMAP --to 192.168.1.0/24
POSTROUTING rule checks if outgoing packet destination IP belongs to remote IPsec virtual IP range, if yes, it will change packet source IP from LAN IP to virtual IPsec IP. PREROUTING rule checks if incoming packet source IP belongs to remote IPsec virtual IP range, if yes, it will change incoming packet destination IP from virtual IPsec IP to LAN IP.
Now LAN to LAN communication should be possible between end devices but to enable RUT to RUT communication additionally it'll be needed to install route on each device.
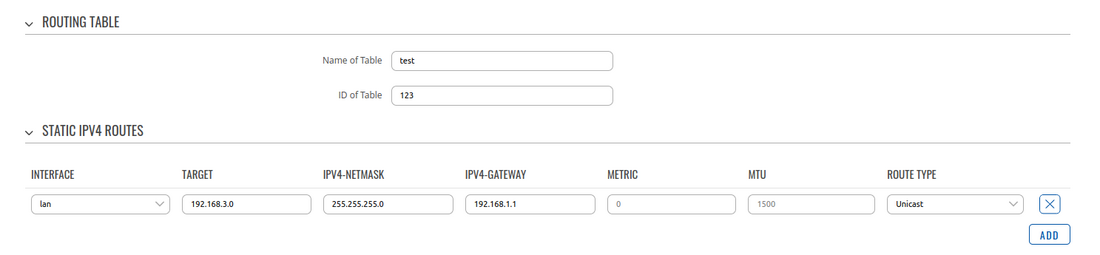
Routing update
To have permanent static route navigate to WebUI -> Network -> Routing -> Advanced static routes. Add new routing table and insert static route where:
- Interface is LAN
- Target is remote IPsec virtual network
- Gateway is LAN IP