VLAN: Tag-Based RUTX
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.08 firmware version .
Summary
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer (OSI layer 2). LAN is the abbreviation for local area network and in this context virtual refers to a physical object recreated and altered by additional logic. VLANs work by applying tags to network packets and handling these tags in networking systems - creating the appearance and functionality of network traffic that is physically on a single network but acts as if it is split between separate networks. In this way, VLANs can keep network applications separate despite being connected to the same physical network, and without requiring multiple sets of cabling and networking devices to be deployed.
VLANs allow network administrators to group hosts together even if the hosts are not on the same network switch. This can greatly simplify network design and deployment, because VLAN membership can be configured through software. Without VLANs, grouping hosts according to their resource needs necessitates the labor of relocating nodes or rewiring data links. It also has benefits in allowing networks and devices that must be kept separate to share the same physical cabling without interacting, for reasons of simplicity, security, traffic management, or economy. For example, a VLAN could be used to separate traffic within a business due to users, and due to network administrators, or between types of traffic, so that users or low priority traffic cannot directly affect the rest of the network's functioning. Many Internet hosting services use VLANs to separate their customers' private zones from each other, allowing each customer's servers to be grouped together in a single network segment while being located anywhere in their datacenter. Some precautions are needed to prevent traffic "escaping" from a given VLAN, an exploit known as VLAN hopping.
This chapter is an overview of the VLAN function of RUTX devices.
Configuration in Router's web interface
Vlan Tag Configuration
Open router‘s WebUI and navigate to Network → VLAN → Port Based configuration:
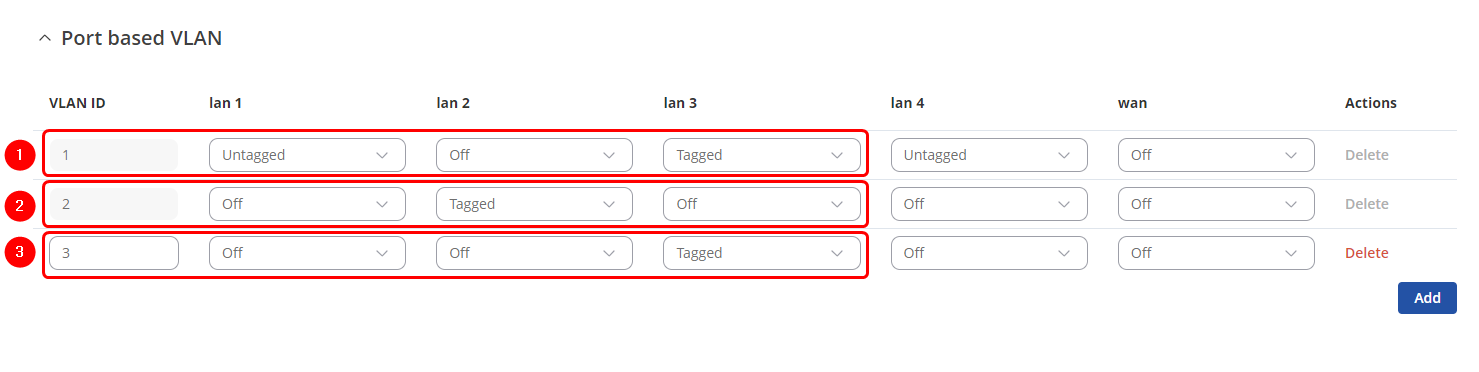
Port based VLAN
Add new VLANs by clicking ![]() and Make following changes:
and Make following changes:
- VLAN ID: 1 | lan1: Untagged | Lan2: Off | Lan3: Tagged
- VLAN ID: 2 | lan1: Off | Lan2: Tagged | Lan3: Off
- VLAN ID: 3 | lan1: Off | Lan2: Off | Lan3: Tagged
Lan Configuration
Open router’s WebUI → Network → LAN click ![]() on current available LAN interface configuration:
on current available LAN interface configuration:
LAN Interface Configuration
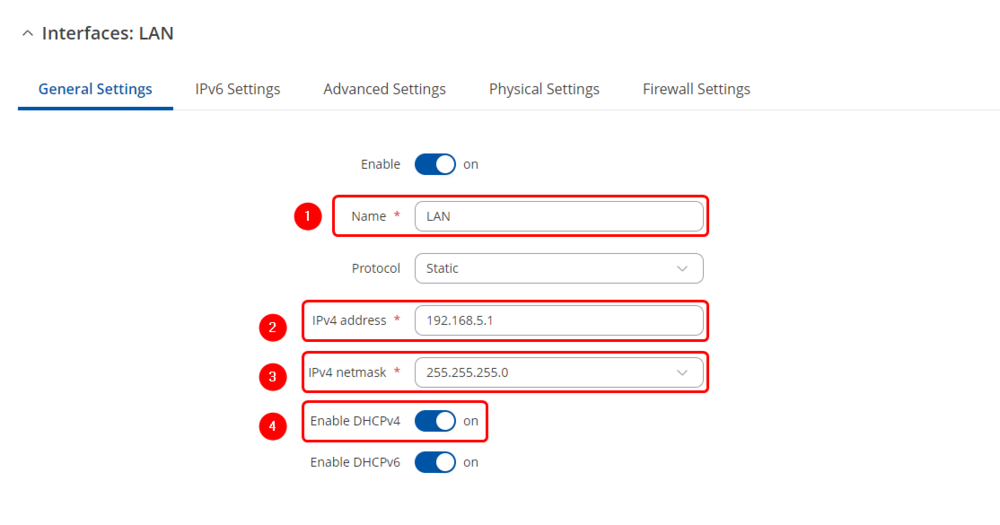
General Settings
Make the following changes:
- Enter Name: LAN
- Enter IPv4 address: 192.168.5.1
- Enter IPv4 net mask: 255.255.255.0
- Enable DHCPv4: on
LAN 2 Interface Configuration
Click ![]() button in new window make following changes:
button in new window make following changes:
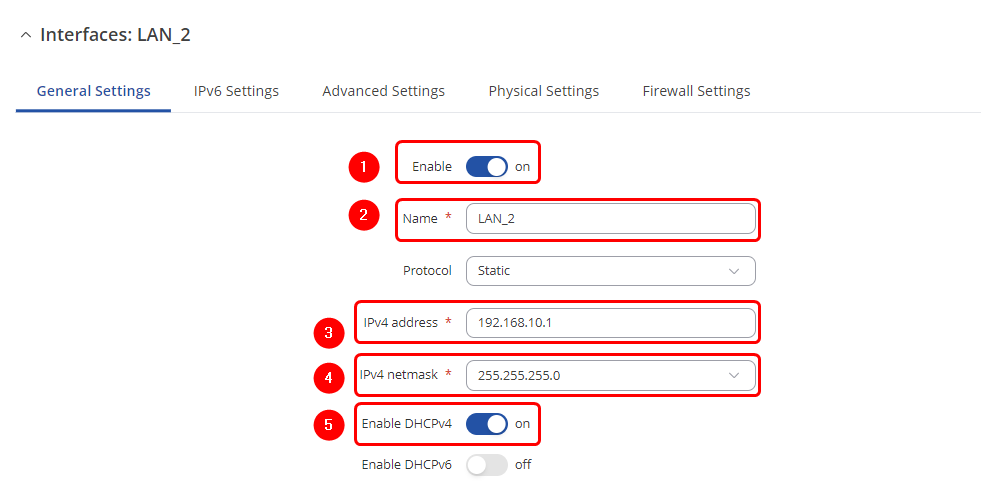
General Settings
- Enable Interface: On
- Enter Name: LAN_2
- Enter IPv4 address: 192.168.10.1
- Enter IPv4 net mask: 255.255.255.0
- Enable DHCPv4: on
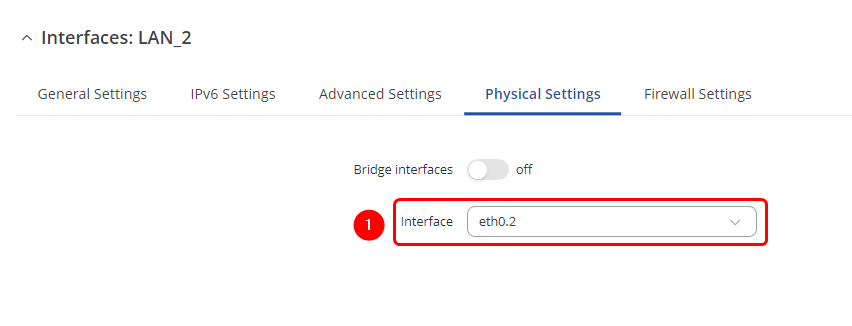
Physical Settings
Make the following changes:
- Select Interface : eth0.2
LAN 3 Interface Configuration
Click ![]() button in new window make following changes:
button in new window make following changes:
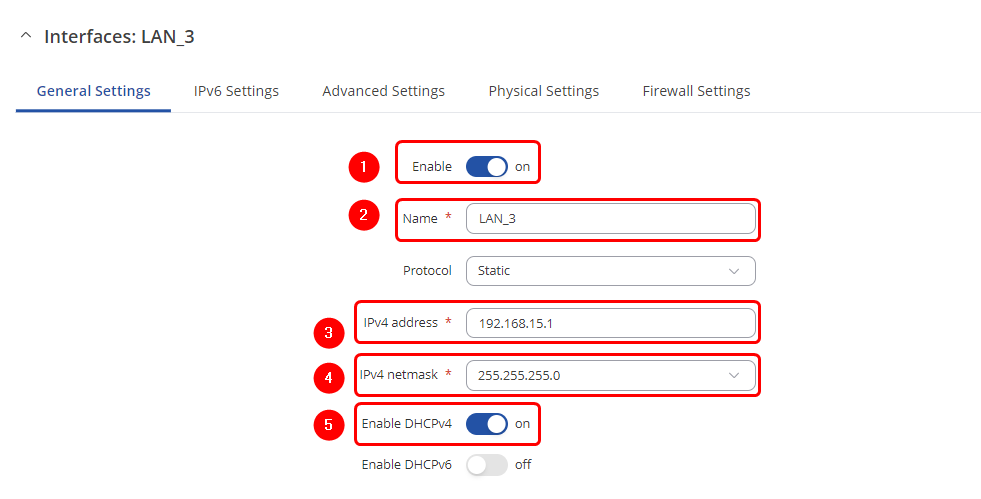
General Settings
- Enable Interface: On
- Enter Name: LAN_3
- Enter IPv4 address: 192.168.15.0
- Enter IPv4 netmask: 255.255.255.0
- Enable DHCPv4: on
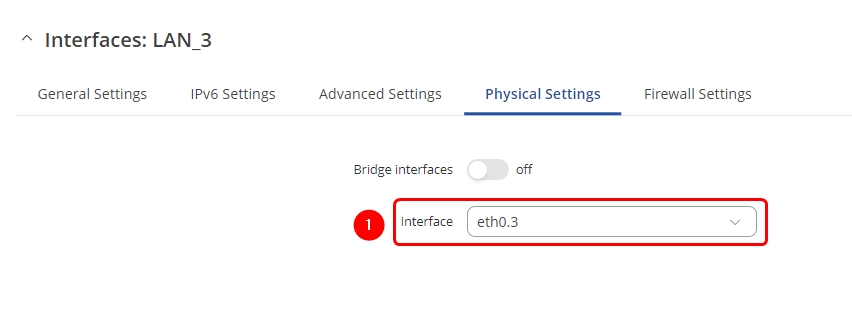
Physical Settings
Make the following changes:
- Select Interface : eth0.3
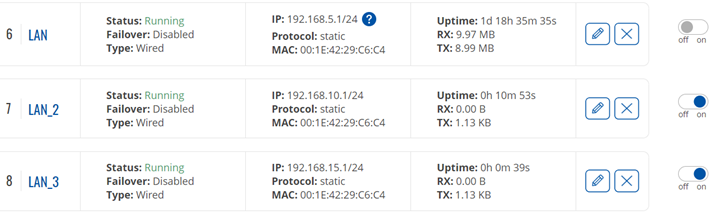
Lan Interfaces After Successful Configuration
Testing VLAN Tag Configuration
Change your wired connection from your PC to your device LAN 3 port.
PC Network Settings
How to Assign Tagged Vlan To Your PC Ethernet Interface
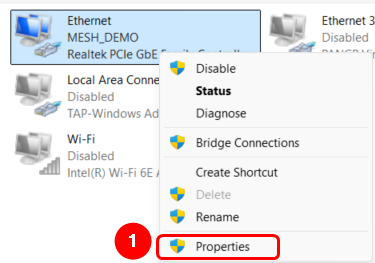
Open network settings on your PC:
1. Open network Ethernet interface "Properties".
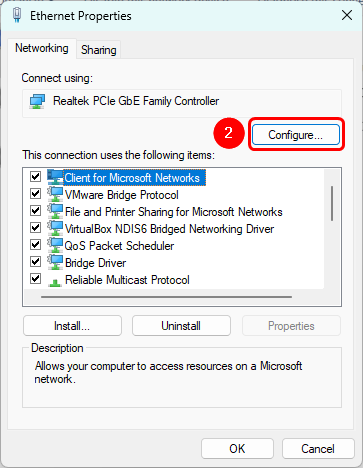
2. Click "Configure" inside "Ethernet Properties".
3. Select "Advanced" tab in the new window.
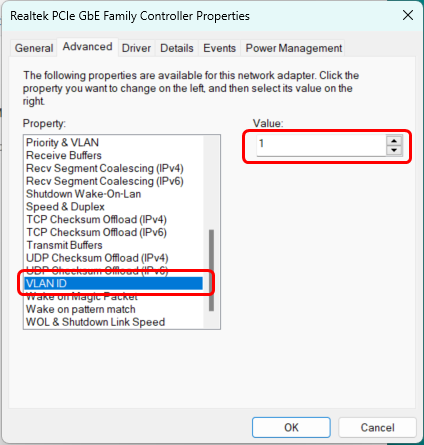
4. Set "VLAN ID" to values that were assigned to LAN3 port in the VLAN configuration (WebUI -> Network -> VLAN -> Port Based -> Port based VLAN -> VLAN ID) in this case values are "1" and "3" . Depending on the "VLAN ID" tag vlaue your network device will be assigned to different LAN network.
5. After setting new "VLAN ID" always execute command in your PC's Command Prompt: ipconfig/renew
Network Configuration Depending On The VLAN ID
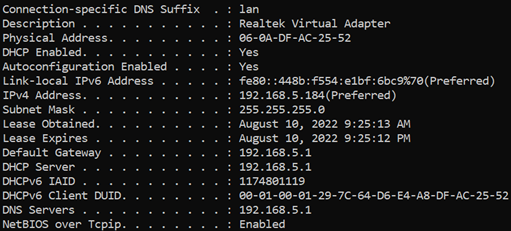
VLAN ID 1
Open Command Prompt on your pc and enter the command "ipconfig /all". You will see that you now have an IP address from the LAN network.
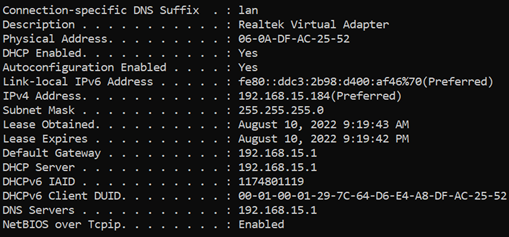
VLAN ID 3
Open Command Prompt on your pc and enter the command "ipconfig /all". You will see that you now have an IP address from the LAN_3 network.