Noip IPv6 DDNS Configuration
Summary
This article will guide you through configuring an IPv6 DDNS AAAA record on noip.com and creating an instance on RUT routers.
Prerequisite
To use the IPv6 DDNS service, you must have a Static or Dynamic IPv6 Global Unicast Address (GUA) configured in your router WAN interface. Otherwise, it will not work. You can click on the following link to get more information about IPv6 Addressing.
| Prefix | Range | Designation and explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 2000::/3 | 2000::/64 - 3FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/64 | They are globally routable and reachable IPv6 addresses on the Internet; analogously considered the equivalent of public IPv4 addresses. The operators of networks using these addresses can be found using the Whois servers of the RIRs listed in the registry at: https://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv6-unicast-address-assignments/ipv6-unicast-address-assignments.xhtml |
Step 1: noip.com configuration
First, access the website by entering www.noip.com/login in your internet web browser's URL bar.
Login screen
Login into noip.com system using your credentials. If you don't have a registered account, then you need to create one. You can do that by clicking Register.
Create host
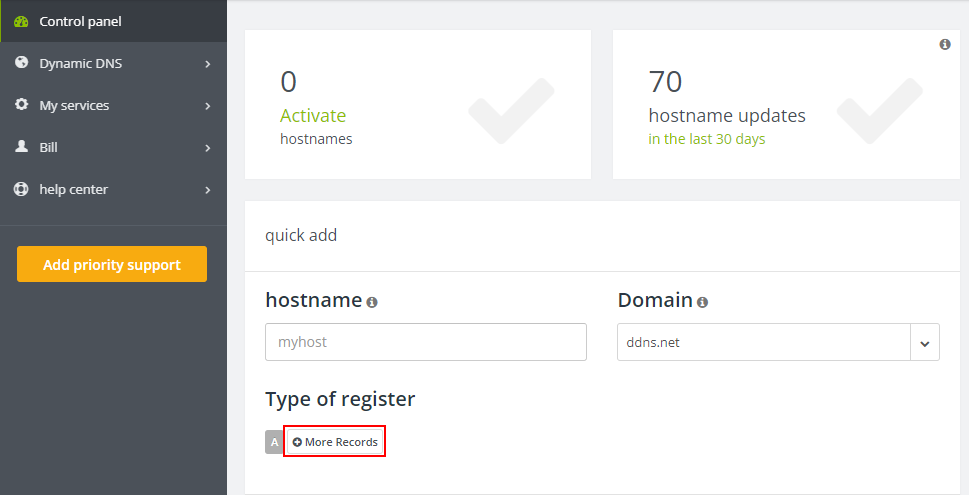
After successfully logging into your account, in the control panel dashboard go to the "quick add" section and select More Records
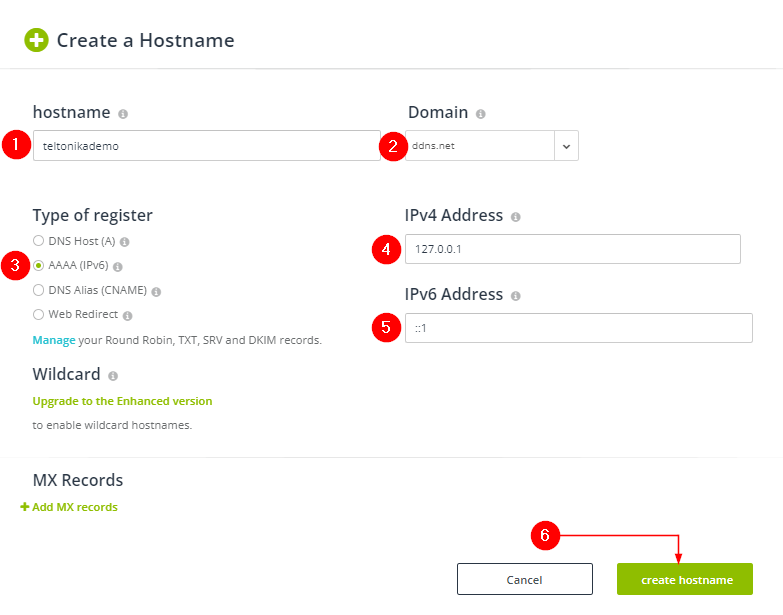
A new window will prompt in your web browser; fill out the information according to your hostname and domain of preference, select the AAAA record, enter the loopback address for each Internet protocol accordingly and click on create hostname.
Record Validation
Check the record you just have created has an Active button below the hostname. Don't worry about the warning signal displayed in the Last Update field; it's just to inform you that no dynamic update has been detected yet.

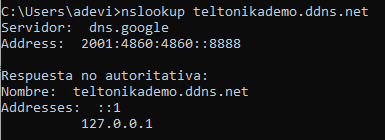
Note: For further verifications, you can send a query to check the DNS records for your given domain name by introducing at your laptop command prompt or shell terminal the nslookup command as shown below: