Difference between revisions of "Domnev"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <p style="color:red">The information in this page is updated in accordance with [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07 | + | <p style="color:red">The information in this page is updated in accordance with [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.4'''] firmware version .</p> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
This article contains instructions on how to set up BACnet on Teltonika Networks devices. | This article contains instructions on how to set up BACnet on Teltonika Networks devices. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
=== Server === | === Server === | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | For the server, Yet Another BACnet Explorer (YABE) is used. | + | For the server, Yet Another BACnet Explorer (YABE) is used. It is an open-source BACnet Explorer that is designed to be lightweight, fast, and easy to use. |
Open the software and '''click''' on the '''green plus sign (top left)''' to add a new device. Then a new window will pop up; there, select the '''local endpoint IP address '''and click '''Start'''. Everything else can be left as is or changed to suit your needs. | Open the software and '''click''' on the '''green plus sign (top left)''' to add a new device. Then a new window will pop up; there, select the '''local endpoint IP address '''and click '''Start'''. Everything else can be left as is or changed to suit your needs. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
== BACnet/IP via LTE configuration == | == BACnet/IP via LTE configuration == | ||
| − | |||
[[File:BACnet Topology 2.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|876x321px]] | [[File:BACnet Topology 2.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|876x321px]] | ||
| Line 65: | Line 64: | ||
Navigate to '''Services → BACnet''' and '''enable''' the '''instance'''. | Navigate to '''Services → BACnet''' and '''enable''' the '''instance'''. | ||
| − | [[File:BACnet enable instance.png|border|center|class=tlt-border| | + | [[File:BACnet enable instance.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|818x210px]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== Firewall ==== | ==== Firewall ==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | Open the RUT1 WebUI and navigate to '''Network → Firewall → Port Forwards'''. Create a port forward rule to forward UDP packets from RUT2 WAN to the RUT1 LAN address port. | |
[[File:Router1 firewall port forward.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|797x617px]] | [[File:Router1 firewall port forward.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|797x617px]] | ||
| Line 90: | Line 81: | ||
# '''Internal port''' - YABE port | # '''Internal port''' - YABE port | ||
| − | + | YABE port can be found looking through the traffic with Wireshark on your PC or TCP dump on RUT1 or RUT2. | |
| − | If you restart the YABE software or delete and recreate a new communication device, YABE may use a different port number, in which case you must change the port forward configuration in the router connected to your PC. | + | '''Note''': If you restart the YABE software or delete and recreate a new communication device, YABE may use a different port number, in which case you must change the port forward configuration in the router connected to your PC. |
=== Router 2 === | === Router 2 === | ||
| Line 109: | Line 100: | ||
[[File:BACnet_enabled_BBMD_fixed.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|797x234px]] | [[File:BACnet_enabled_BBMD_fixed.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|797x234px]] | ||
| − | + | The created port forward rule should look like this: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[File:BACnet firewall router2.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|864x620px]] | [[File:BACnet firewall router2.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|864x620px]] | ||
| − | + | Everything else can be left as default or changed according to your needs. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Server === | === Server === | ||
Revision as of 14:02, 15 March 2023
The information in this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.4 firmware version .
Introduction
This article contains instructions on how to set up BACnet on Teltonika Networks devices.
BACnet provides a standardized way for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other and integrate seamlessly into a building automation system. This allows building managers and operators to monitor and control various building systems from a central location, optimizing energy efficiency, reducing operating costs, and improving occupant comfort and safety.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's take a look at the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- Two RUT955;
- Controller;
- BACnet Server;
- An end device (PC, Laptop) for configuration;
If you're having trouble finding any page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Basic" button under "Mode," which is located at the top-right corner of the WebUI.
Note: This is additional software that can be installed from the Services → Package Manager page.
BACnet/Ethernet configuration
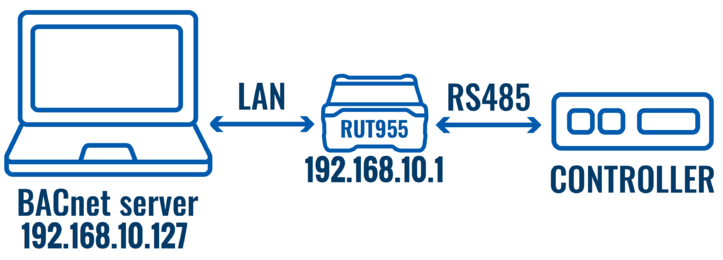
The controller is directly connected to RUT955 via RS485; The router forwards the data from the controller to the BACnet server to the PC.
BACnet
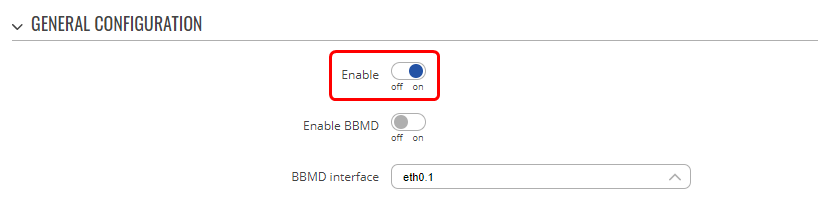
Install the BACnet package on RUT955 and navigate to Services → BACnet and enable the instance. Everything else can be left as is or changed to suit your needs.
Server
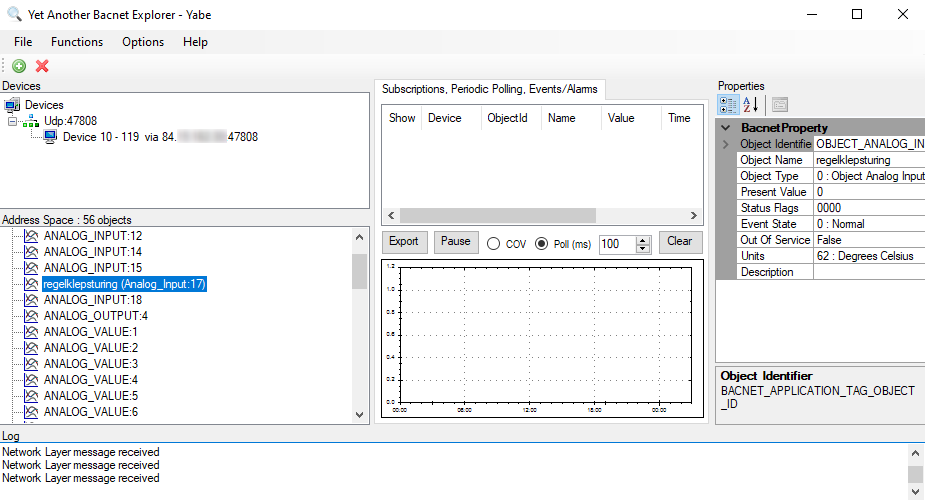
For the server, Yet Another BACnet Explorer (YABE) is used. It is an open-source BACnet Explorer that is designed to be lightweight, fast, and easy to use.
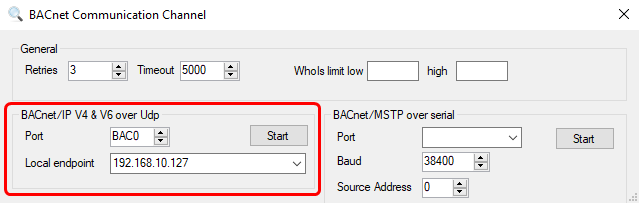
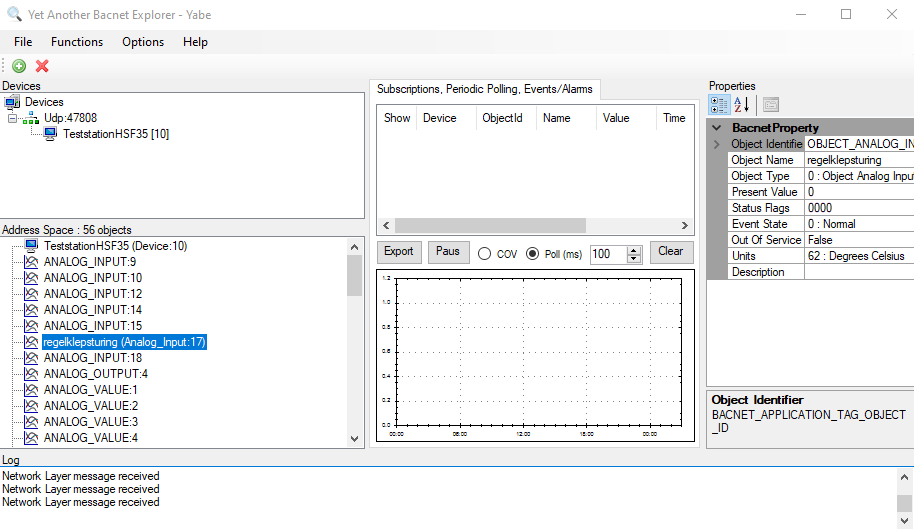
Open the software and click on the green plus sign (top left) to add a new device. Then a new window will pop up; there, select the local endpoint IP address and click Start. Everything else can be left as is or changed to suit your needs.
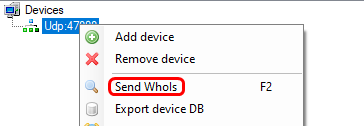
Select the newly created communication node and right-click on it to send WhoIs request (application might send these automatically).
Results
In cases of success, you see the connected BACnet device and its parameters.
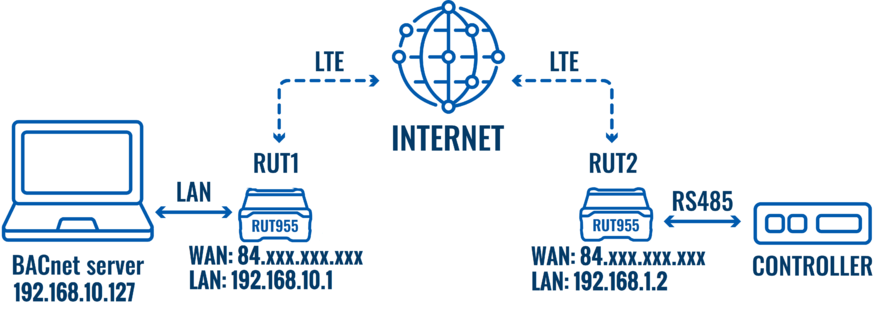
BACnet/IP via LTE configuration
In this topology, there are two RUT955 routers - RUT1 and RUT2. RUT1 is connected to the server via LAN, and RUT2 is connected to the controller via RS485. RUT2 transmits data to RUT1, which then forwards it to the BACnet server.
For this configuration, you must have a public IP address. You can read more on this in our article on Private and Public IP Addresses.
Router 1
BACnet
Navigate to Services → BACnet and enable the instance.
Firewall
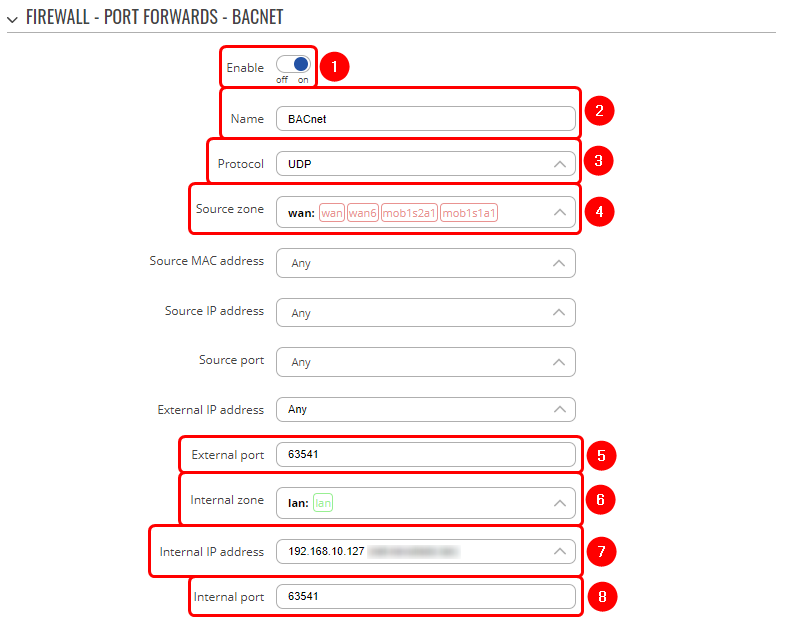
Open the RUT1 WebUI and navigate to Network → Firewall → Port Forwards. Create a port forward rule to forward UDP packets from RUT2 WAN to the RUT1 LAN address port.
- Enable instance
- Name - enter desired name
- Protocol - UDP
- Source zone - WAN
- External port - YABE port
- Internal zone - LAN
- Internal IP address - PC LAN IP
- Internal port - YABE port
YABE port can be found looking through the traffic with Wireshark on your PC or TCP dump on RUT1 or RUT2.
Note: If you restart the YABE software or delete and recreate a new communication device, YABE may use a different port number, in which case you must change the port forward configuration in the router connected to your PC.
Router 2
BACnet
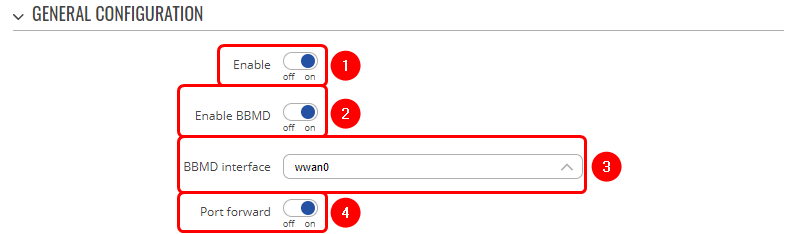
Bacnet BBMD – stands for "BACnet Broadcast Management Device." A BBMD is a device that manages the routing of BACnet broadcast messages across different IP subnets. When a BACnet device sends a broadcast message, it is typically sent to all devices on the same subnet, but not to devices on other subnets. However, sometimes it is necessary for broadcast messages to be sent to devices on multiple subnets. This is where a BBMD comes in. Navigate to Services → BACnet, there:
- Enable BACnet
- Enable BBMD
- BBMD interface - select the interface with Public IP.
- Enable Port forward - this will automatically create a port forward rule.
The created port forward rule should look like this:
Everything else can be left as default or changed according to your needs.
Server
Open the software and click on the green plus sign (top left) to add a new device. Then a new window will pop up; there, select the local endpoint IP address and click start. Everything else cane be left as default or changed according to your needs.
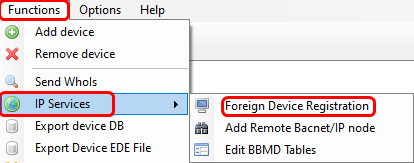
Then select the node and go to Meniu → Functions → IP services → Foreign device registration and enter the public IP address of RUT2 (the one connected to controller).
Results
In case of success, you see the device connected via gateway.
BACnet/IP via RMS VPN configuration
If having a public IP is not an option, RMS VPN could be used as an alternative to access your device over the internet. RMS VPN is a service designed for remote efficient, low-cost management of large-scale networks. In contrast to point-to-point VPN services, RMS VPN enables the instant creation of encrypted VPN tunnels for secure access to multiple endpoints.
RMS VPN
A guide on how to set up an RMS VPN hub can be found here.
Both RUT1 and RUT2 have to be added to the RMS VPN Hub.
RUT1 & RUT2
Once RMS VPN Hub is set up, follow the RUT1 and RUT2 configuration described above.
See also
BACnet on RUT955
Port-forward on RUT955