Difference between revisions of "Domnev"
| (103 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <p style="color:red">The information | + | <p style="color:red">The information on this page is updated in accordance with the [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.4'''] firmware version .</p> |
| − | == | + | __TOC__ |
| − | + | ==Summary== | |
| + | In this guide, the MQTT Serial Gateway function will be configured using third-party MQTT Broker services (in this example, ''Flespi.io''). | ||
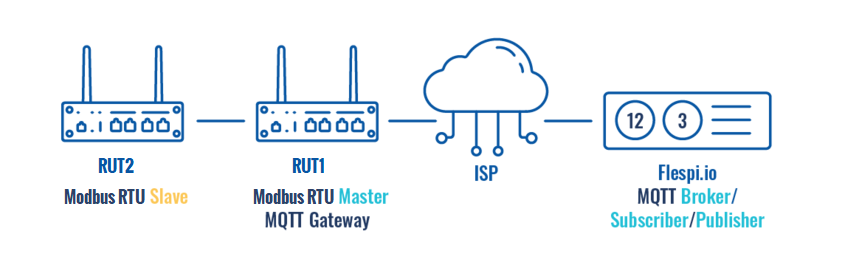
| − | ==Configuration overview | + | ==Configuration overview & prerequisites== |
| + | *Two devices with serials ports - one acts as Modbus RTU Master, another as Modbus RTU Slave; | ||
| + | *Flespi.io account to act as an MQTT Broker/Publisher/Subscriber (for first configuration example); | ||
| − | + | [[File:MQTT Serial gateway topology v2.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|847x279px]] | |
| − | + | RUT2 will act as a Modbus RTU slave and RUT1 as a Modbus RTU Master. On RUT1, MQTT Serial Gateway will be configured to transfer Modbus data over MQTT. Flespi.io platform will serve as an MQTT Broker | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==RUT2 configuration== | |
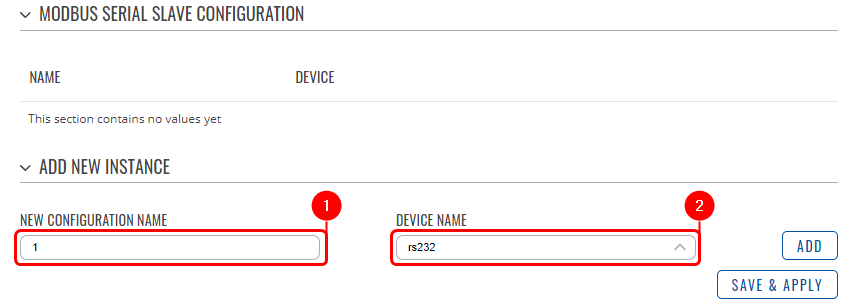
| − | + | ===Configuring Modbus RTU Slave=== | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Go to Services → Modbus → Modbus RTU Slave and create a new instance. | ||
| + | # Enter the '''desired instance name'''; | ||
| + | # Select the '''desired serial interface'''. | ||
| − | = | + | [[File:Modbus RTU Slave.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|855 × 308px]] |
| − | + | ==RUT1 configuration== | |
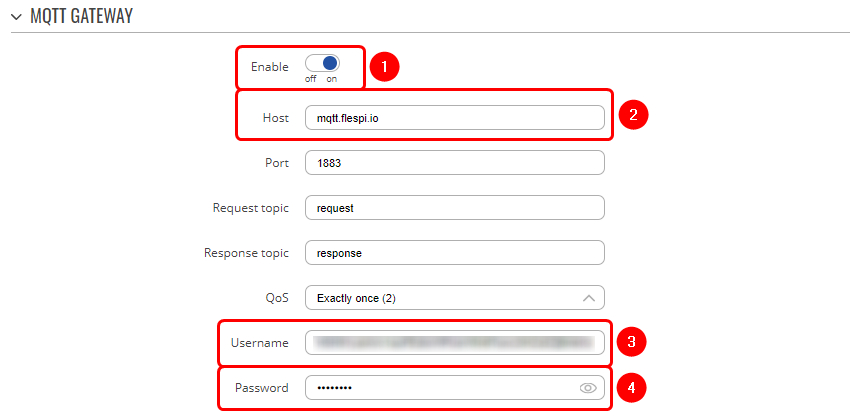
| − | + | ===Configuring MQTT Gateway=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | Go to '''Services → Modbus → MQTT Gateway''' and there: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | # '''Enable''' the '''instance'''; | |
| − | + | # '''Enter Host''' (copied from flespi connection settings without 'wss://' and port); | |
| − | + | # '''Enter Username''' (Copied from flespi Connection settings generated '''token'''); | |
| + | # '''Enter Password'''. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:MQTT Gateway config.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|862 × 412px]] |
| − | + | '''Note''': ''Everything else can be left as default or changed according to your needs.'' | |
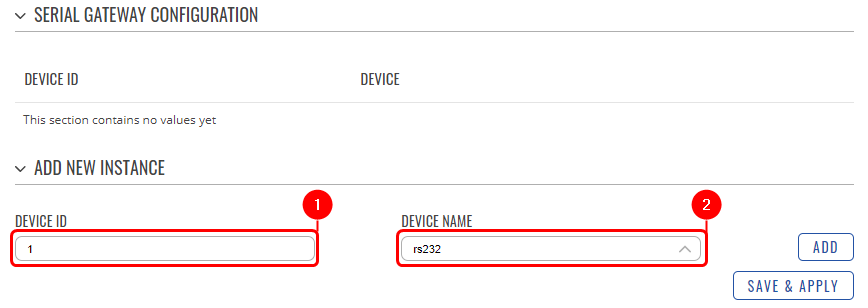
| − | === | + | ===Configuring Serial Gateway=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | [[File: | + | Under the MQTT Gateway configuration, create the Serial Gateway: |
| + | # Enter the '''desired device ID'''; | ||
| + | # Select the '''desired serial interface'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Serial gateway config.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|868×308px]] | ||
| − | + | ===Configuring Flespi.io MQTT Broker=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | '''Log in''' or '''create an account''' on '''https://flespi.io'''; | |
| + | |||
| + | #Navigate to '''MQTT Board''' on the '''left side''' menu; | ||
| + | #On the right-hand panel, top right corner, next to the name of the MQTT board, '''press the cogwheel-looking icon''' to open ''Connection Settings''; | ||
| + | #In the opened window, press '''"Get flespi token"''' to generate a username; | ||
| + | #Enter the '''Client name'''; | ||
| + | #Copy the Host address; | ||
| + | #Copy '''Username'''; | ||
| + | #Create a '''password'''. | ||
| − | + | Once done, save all the changes. | |
| − | + | [[File:Flespi board.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|1102x729px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Message format for MQTT publisher=== | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Modbus request data sent in the MQTT payload should be generated in accordance with the following format: | ||
| − | + | <pre>1 <COOKIE> <SERIAL_DEVICE_ID> <TIMEOUT> <SLAVE_ID> <MODBUS_FUNCTION> <FIRST_REGISTER> <REGISTER_COUNT> </pre> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The table below explains what each option means: | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |1. Format version | |
| − | + | |'''1''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | ==== | + | |2. Cookie |
| + | |from '''0''' to '''2<sup>64</sup> -1''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |3. Serial device ID | ||
| + | |a string used to identify a serial device. Must match with <u>Device ID</u> field in MQTT Gateway page Serial gateway configuration section | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4. Timeout | ||
| + | |timeout for Modbus connection, in seconds. Range [1..999]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5. Slave ID | ||
| + | |Indicates to which slave request is sent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6. Modbus function | ||
| + | |Modbus task type that will be executed. Possible values are: | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li><b>1</b> - read coils;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>2</b> - read input coils;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>3</b> - read holding registers;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>4</b> - read input registers;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>5</b> - set single coil;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>6</b> - write to a single holding register;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>15</b> - set multiple coils;</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>16</b> - write to multiple holding registers.</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |7. First register | ||
| + | |number (not address) of the first register/coil/input (in range [1..65536]) from which the registers/coils/inputs will be read/written to. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |8. Registry count | ||
| + | | <li><b>1</b> - <u>coil count</u> (in range [1..2000]); must not exceed the boundary (first coil number + coil count <= 65537);</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>2</b> - <u>input count</u> (in range [1..2000]); must not exceed the boundary (first input number + input count <= 65537);</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>3</b> - <u>holding register count</u> (in range [0..125]); must not exceed the boundary (first register number + holding register count <= 65537);</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>4</b> - <u>input register count</u> (in range [0..125]); must not exceed the boundary (first register number + input register count <= 65537);</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>5</b> - <u>coil value</u> (in range [0..1]);</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>6</b> - <u>holding register value</u> (in range [0..65535]);</li> | ||
| + | <li><b>15</b> - <u>coil count</u> (in range [1..1968]); must not exceed the boundary (first coil number + coil count <= 65537); and <u>coil values</u> separated with commas, without spaces (e.g., <i>1,2,3,654,21,789</i>); there must be exactly as many values as specified (with coil count); each value must be in the range of [0..1]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ====Examples==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |Setting relay (on) (Relay address is 202, which means 'Number of first register will be 203) | |
| − | + | |'''1 1 1 1 1 6 203 1''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | [[ | + | |Getting temperature |
| + | |'''1 1 1 1 1 3 6 2''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Modbus parameters are held within registers. The register numbers and corresponding system values can be found [[RUT955_Monitoring_via_Modbus#Get_Parameters|'''in this article''']]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Testing MQTT Publisher and Subscriber on flespi.io== | ||
| + | ====Adding Flespi Subscriber==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | To test the Modbus Serial Gateway functionality, '''log into''' your '''Flespi account''' → '''MQTT Board''' and '''add a Subscriber''': | ||
| − | + | #Press '''''<nowiki/>'+'''''' button on the top right corner | |
| − | + | #Select '''''<nowiki/>'Subscriber'''''' | |
| − | + | # In the topic field enter '''''<nowiki/>'response'''''' | |
| − | + | #Press '''''<nowiki/>'Subscribe'''''' button | |
| − | |||
| − | # ''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | # ''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
| − | |||
| − | # ''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | # '' | ||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Flespi subscriber.png|border|class=tlt-border|496x204px]] [[File:Flespi subscriber setup.png|border|class=tlt-border|496x205px]] | ||
| + | ====Adding Flespi Subscriber==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Also, you will need to '''add a Publisher''': | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | #Press '''''<nowiki/>'+'''''' button on the top right corner | |
| − | + | #Select '''''<nowiki/>'Publisher'''''' | |
| − | + | #In the topic field enter '''''<nowiki/>'request'''''' | |
| − | + | #In the message field enter message, for this example '''''<nowiki/>'Getting temperature'''''' is used | |
| + | #Press '''''<nowiki/>'Publish'''''' button | ||
| − | = | + | [[File:Flespi publisher.png|border|class=tlt-border|495x238px]] [[File:Flespi publisher setup.png|border|class=tlt-border|494x239px]] |
| − | + | ====Flespi Subscriber output==== | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | Check the response in the '''''<nowiki/>'Subscriber'''''' tab, you should receive a message similar to the one below. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Flespi response.png|border|center|class=tlt-border|500x305px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In the output, we can see that router's '''temperature''' is '''44 degrees Celsius'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| − | * [[ | + | *[[RUT955 Monitoring via Modbus#Get Parameters]] |
| − | + | *[[RUT955_Modbus#MQTT_Gateway|MQTT Gateway and Modbus]] | |
| − | * [[ | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| + | [https://flespi.io/#/ Flespi.io] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:14, 13 September 2023
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.4 firmware version .
Summary
In this guide, the MQTT Serial Gateway function will be configured using third-party MQTT Broker services (in this example, Flespi.io).
Configuration overview & prerequisites
- Two devices with serials ports - one acts as Modbus RTU Master, another as Modbus RTU Slave;
- Flespi.io account to act as an MQTT Broker/Publisher/Subscriber (for first configuration example);
RUT2 will act as a Modbus RTU slave and RUT1 as a Modbus RTU Master. On RUT1, MQTT Serial Gateway will be configured to transfer Modbus data over MQTT. Flespi.io platform will serve as an MQTT Broker
RUT2 configuration
Configuring Modbus RTU Slave
Go to Services → Modbus → Modbus RTU Slave and create a new instance.
- Enter the desired instance name;
- Select the desired serial interface.
RUT1 configuration
Configuring MQTT Gateway
Go to Services → Modbus → MQTT Gateway and there:
- Enable the instance;
- Enter Host (copied from flespi connection settings without 'wss://' and port);
- Enter Username (Copied from flespi Connection settings generated token);
- Enter Password.
Note: Everything else can be left as default or changed according to your needs.
Configuring Serial Gateway
Under the MQTT Gateway configuration, create the Serial Gateway:
- Enter the desired device ID;
- Select the desired serial interface.
Configuring Flespi.io MQTT Broker
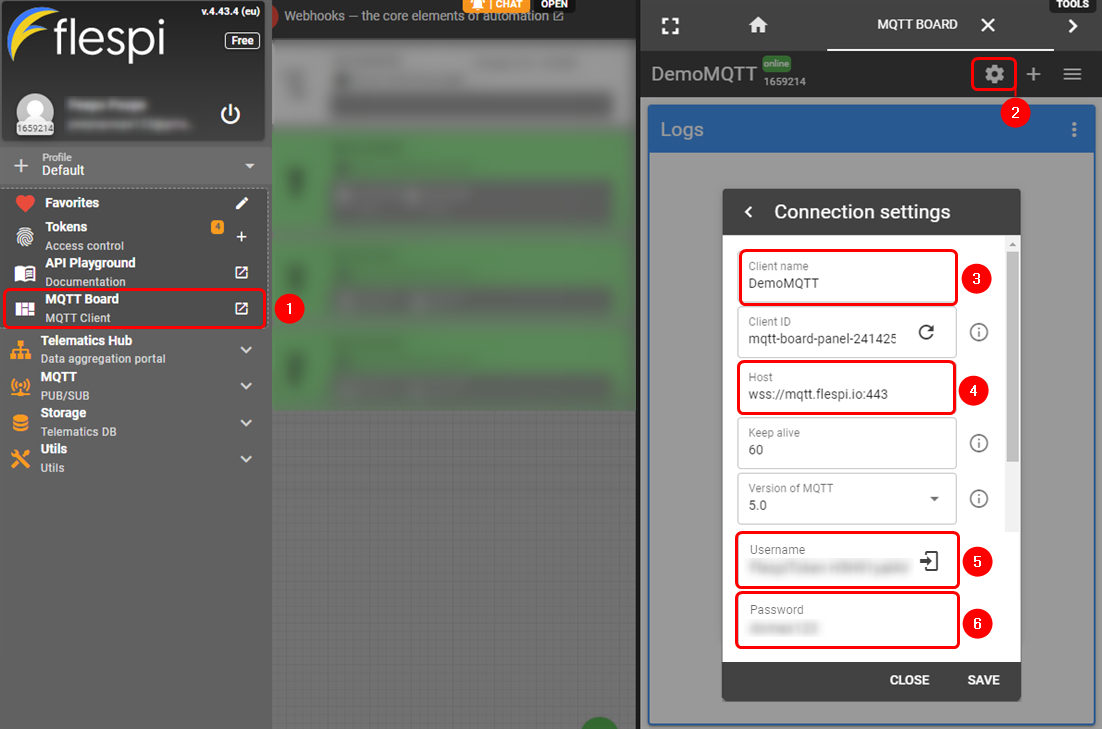
Log in or create an account on https://flespi.io;
- Navigate to MQTT Board on the left side menu;
- On the right-hand panel, top right corner, next to the name of the MQTT board, press the cogwheel-looking icon to open Connection Settings;
- In the opened window, press "Get flespi token" to generate a username;
- Enter the Client name;
- Copy the Host address;
- Copy Username;
- Create a password.
Once done, save all the changes.
Message format for MQTT publisher
Modbus request data sent in the MQTT payload should be generated in accordance with the following format:
1 <COOKIE> <SERIAL_DEVICE_ID> <TIMEOUT> <SLAVE_ID> <MODBUS_FUNCTION> <FIRST_REGISTER> <REGISTER_COUNT>
The table below explains what each option means:
| 1. Format version | 1 |
| 2. Cookie | from 0 to 264 -1 |
| 3. Serial device ID | a string used to identify a serial device. Must match with Device ID field in MQTT Gateway page Serial gateway configuration section |
| 4. Timeout | timeout for Modbus connection, in seconds. Range [1..999]. |
| 5. Slave ID | Indicates to which slave request is sent |
| 6. Modbus function | Modbus task type that will be executed. Possible values are:
|
| 7. First register | number (not address) of the first register/coil/input (in range [1..65536]) from which the registers/coils/inputs will be read/written to. |
| 8. Registry count |
Examples
| Setting relay (on) (Relay address is 202, which means 'Number of first register will be 203) | 1 1 1 1 1 6 203 1 |
| Getting temperature | 1 1 1 1 1 3 6 2 |
Modbus parameters are held within registers. The register numbers and corresponding system values can be found in this article.
Testing MQTT Publisher and Subscriber on flespi.io
Adding Flespi Subscriber
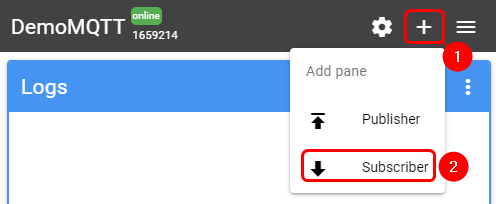
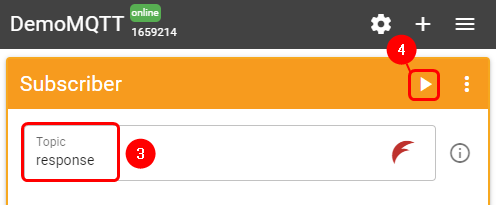
To test the Modbus Serial Gateway functionality, log into your Flespi account → MQTT Board and add a Subscriber:
- Press '+' button on the top right corner
- Select 'Subscriber'
- In the topic field enter 'response'
- Press 'Subscribe' button
Adding Flespi Subscriber
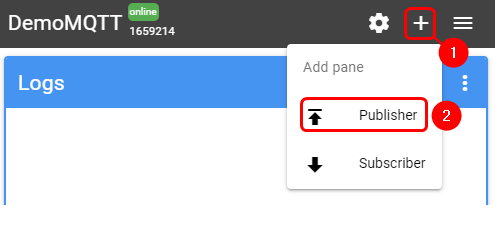
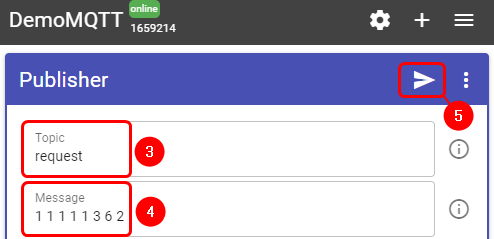
Also, you will need to add a Publisher:
- Press '+' button on the top right corner
- Select 'Publisher'
- In the topic field enter 'request'
- In the message field enter message, for this example 'Getting temperature' is used
- Press 'Publish' button
Flespi Subscriber output
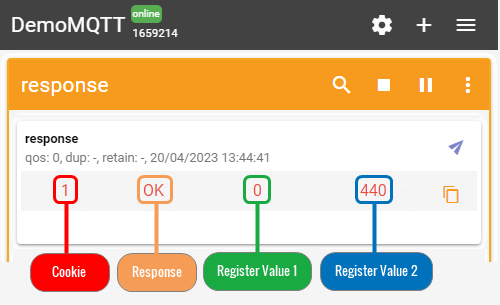
Check the response in the 'Subscriber' tab, you should receive a message similar to the one below.
In the output, we can see that router's temperature is 44 degrees Celsius.