Difference between revisions of "TAP 100 and TAP 200 Wireless Mesh Configuration"
| (57 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <p style="color:red">The information on this page is updated in accordance with the [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.07.1'''] firmware version .</p> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Mesh networking is a revolutionary approach to wireless connectivity, offering numerous benefits that make it increasingly popular in various applications. At its core, mesh networking involves interconnected nodes that communicate with each other to create a network. Here's why it's used and why it's so valuable: | Mesh networking is a revolutionary approach to wireless connectivity, offering numerous benefits that make it increasingly popular in various applications. At its core, mesh networking involves interconnected nodes that communicate with each other to create a network. Here's why it's used and why it's so valuable: | ||
| − | + | #Flexibility and Scalability: Mesh networks adapt and scale easily. | |
| − | + | #Redundancy and Reliability: Multiple paths ensure uninterrupted connectivity. | |
| − | + | #Coverage and Range Extension: Nodes relay signals to extend coverage. | |
| − | + | #Self-Healing and Self-Organizing: Mesh networks adjust routes for continuous connectivity. | |
| − | + | #Cost-Effectiveness: Mesh networks reduce installation and maintenance costs. | |
| − | + | #Ad Hoc and Temporary Deployments: Ideal for quick setups in various scenarios. | |
| − | + | #IoT and Smart Home Applications: Efficiently connect and manage devices.requirements without compromising performance. | |
Overall, mesh networking represents a versatile and robust solution for wireless connectivity, offering unparalleled flexibility, reliability, and scalability across a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, mesh networks are poised to play an increasingly essential role in powering the connected world of tomorrow. | Overall, mesh networking represents a versatile and robust solution for wireless connectivity, offering unparalleled flexibility, reliability, and scalability across a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, mesh networks are poised to play an increasingly essential role in powering the connected world of tomorrow. | ||
| − | ==Prerequisites== | + | |
| + | ==Prerequisites & Topology== | ||
| + | |||
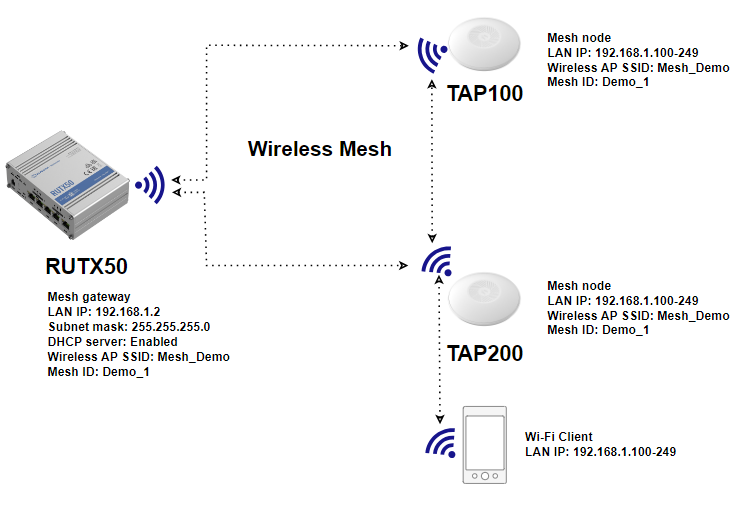
Configuring a wireless mesh network with Teltonika devices is straightforward and requires just a few steps, which can be replicated across multiple devices. The number of devices needed depends on the specific use case, but the setup provided can be effortlessly expanded to accommodate many devices. In the example below, we will utilize RUTX50 as the node with mobile internet connectivity, serving as the mesh gateway and DHCP server. The access points (TAP100 and TAP200) will function as mesh nodes. | Configuring a wireless mesh network with Teltonika devices is straightforward and requires just a few steps, which can be replicated across multiple devices. The number of devices needed depends on the specific use case, but the setup provided can be effortlessly expanded to accommodate many devices. In the example below, we will utilize RUTX50 as the node with mobile internet connectivity, serving as the mesh gateway and DHCP server. The access points (TAP100 and TAP200) will function as mesh nodes. | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''Before proceeding with the confuration, ensure that all requirements are met:''' | ||
| + | #Ensure that the firmware version of the Access Points (TAP100 and TAP200) is 00.07.07.1 or later, as the TAP functionality was not available in versions prior to this. | ||
| + | #The devices suitable for this configuration are from the RUT, RUTX, and TAP series. | ||
| + | #Make sure the gateway has access to the internet and DHCP enabled. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Correct Topology.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] |
The test configuration utilizes the RUTX50 router along with the TAP100 and TAP200 access points. The RUTX50 unit is connected to the internet via mobile internet connectivity, although other connection types are feasible. After proper setup, all mesh devices should establish communication among themselves via wireless mesh, directly or through other devices in the mesh network. This enables an expansion of the Wi-Fi coverage radius. | The test configuration utilizes the RUTX50 router along with the TAP100 and TAP200 access points. The RUTX50 unit is connected to the internet via mobile internet connectivity, although other connection types are feasible. After proper setup, all mesh devices should establish communication among themselves via wireless mesh, directly or through other devices in the mesh network. This enables an expansion of the Wi-Fi coverage radius. | ||
Configration | Configration | ||
| − | |||
==Configuration== | ==Configuration== | ||
| + | |||
{{Template:Networking_rutos_manual_basic_advanced_webui_disclaimer | {{Template:Networking_rutos_manual_basic_advanced_webui_disclaimer | ||
| series = RUTX | | series = RUTX | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Gateway LAN Configuration=== |
| + | ---- | ||
This router requires internet access. The specified settings should be activated by default. | This router requires internet access. The specified settings should be activated by default. | ||
| − | + | Open router’s '''WebUI → Network → LAN''' click [[File:Pencil2.png]]on current available LAN interface configuration: | |
| − | # | + | |
| − | # | + | ====General Settings==== |
| − | # | + | ---- |
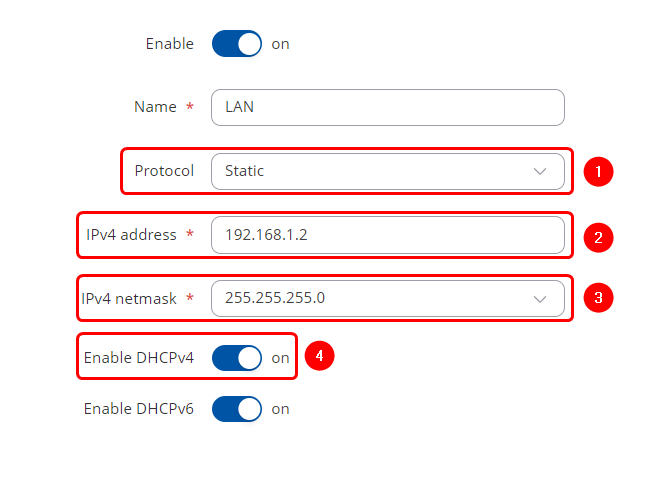
| − | # | + | Make the following changes: |
| + | # Select Protocol: '''Static''' | ||
| + | # Enter IPv4 address: '''192.168.1.2''' | ||
| + | # Enter IPv4 netmask: '''255.255.255.0''' | ||
| + | # Enable DHCPv4: '''on''' | ||
| + | [[File:Gateway_Lan_Configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Mesh Node Common Configuration=== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | '''''The following settings need to be applied to all of devices in the wireless mesh network including mesh gateway(RUTX50) and AP nodes(TAP100/200).''''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Open router‘s '''WebUI''' and navigate to '''Network → Wireless → SSIDs''' click [[File:Pencil2.png]]on current available 2.4Ghz Wireless interface configuration: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Wi-Fi General Setup==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
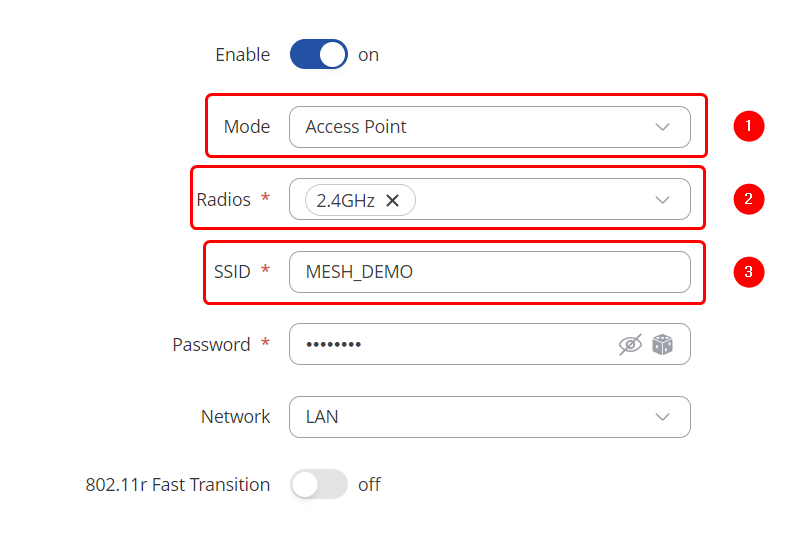
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Select Mode: '''Access Point''' | ||
| + | # Select Radios: '''2.4GHZ''' | ||
| + | # Enter SSID: '''MESH_DEMO''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SSIDs General Settings.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Wi-Fi Wireless Security==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
| + | # Select Encryption: '''WPA3-SAE''' | ||
| + | # Enter Password: '''Password''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Wireless Security.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Mesh General Setup==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | In router‘s WebUI, Navigate to '''Network → Wireless section → SSIDs'''. click [[File:Add Button.png]] and create new interface. Frequency band must match in all nodes. | ||
| + | |||
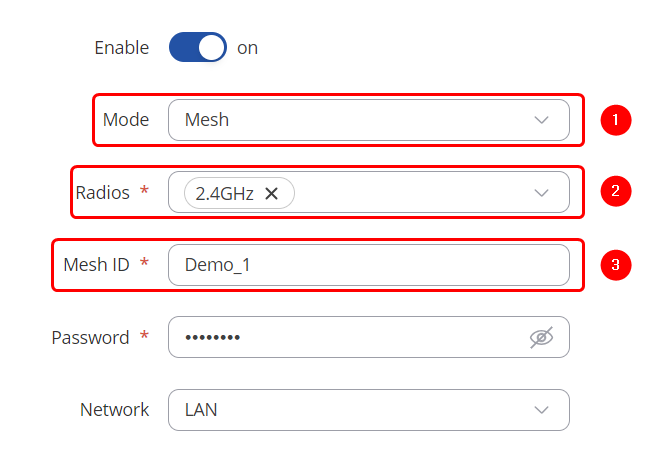
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Select Mode: '''Mesh''' | ||
| + | # Select Radios: '''2.4GHZ''' | ||
| + | # Enter SSID: '''Demo_1''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Mesh General Settings.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Mesh Additional Settings==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
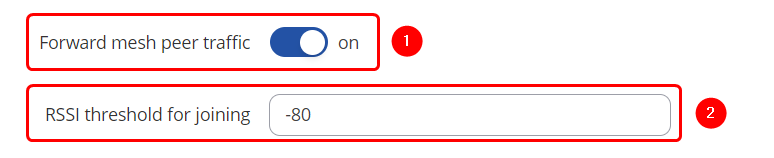
| + | # Enable Forward mesh peer traffic: '''on''' | ||
| + | # Enter RSSI threshold for joining: '''-80''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Mesh Additional Settings.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Mesh Wireless Security==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
| + | # Select Encryption: '''WPA3-SAE''' | ||
| + | # Enter Password: '''Password''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Wireless Security.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Radio General Setup==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | In router‘s WebUI, Navigate to '''Network → Wireless section → Radio → Wifi 2.4GHZ settings'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
| + | |||
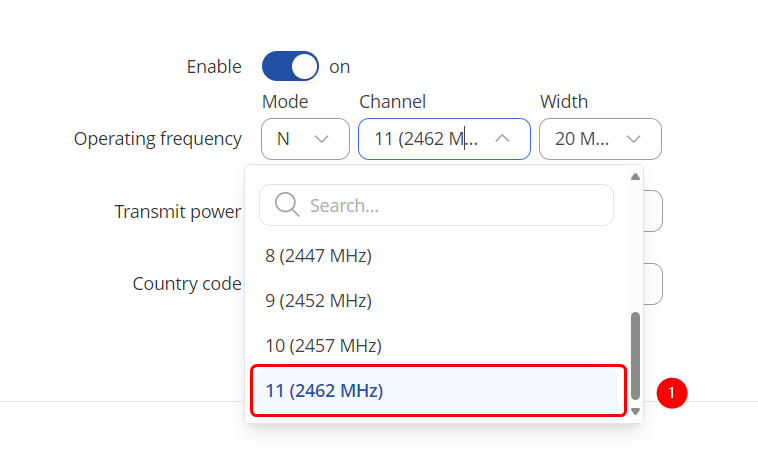
| + | # Select Channel: '''11 (2462 Mhz)''' | ||
| + | [[File:Mesh Channel Selection.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Mesh Node DHCP setup==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | In order to avoid conflicts, TAP100/200 needs to be leasing their LAN IP from mesh gateway. These settings should also be set last, otherwise access to TAP100/200 will be lost. Open '''WebUI → Network → IP Settings → Network configuration.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Make the following changes: | ||
| + | |||
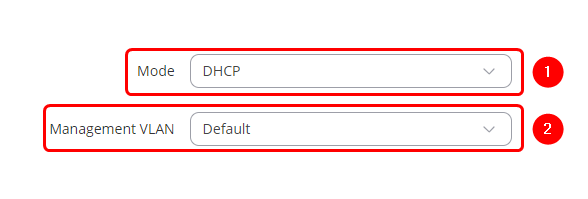
| + | # Select Protocol: '''DHCP''' | ||
| + | # Select Management VLAN: '''Default''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:TAP_NETWORK_CONFIGURATION.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Configuration Testing=== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connect to gateway(RUTX50) '''WebUI''', enter '''Network → Wireless → SSIDs → WIFI 2.4GHZ''' tab. Demo_1 mesh interfaces should display two clients, in this case that would be TAP100 and TAP200 devices in the mesh network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Devices In Mesh.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
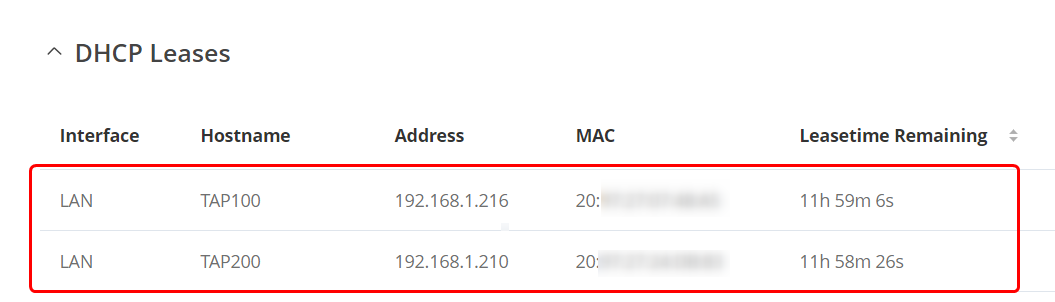
| + | Open '''Status → Network → LAN''' tab. There should be displayed leases given to TAP100 and TAP200. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MESH LEASE.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
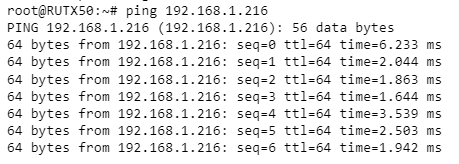
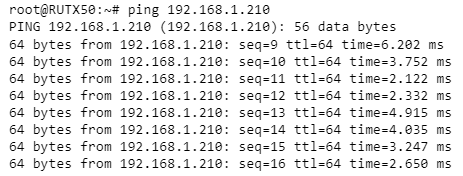
| + | Devices TAP100/200 can be reached from mesh gateway without ethernet connecton. Try pinging devices. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PING TAP 100.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:PING TAP 200.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | |||
| + | # [https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/network/wifi/mesh/80211s https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/network/wifi/mesh/80211s] | ||
| + | # [https://www.cwnp.com/uploads/802-11s_mesh_networking_v1-0.pdf https://www.cwnp.com/uploads/802-11s_mesh_networking_v1-0.pdf] | ||
| + | # [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/Wireless_Mesh_configuration_example https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/Wireless_Mesh_configuration_example] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:13, 15 May 2024
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.07.1 firmware version .
Introduction
Mesh networking is a revolutionary approach to wireless connectivity, offering numerous benefits that make it increasingly popular in various applications. At its core, mesh networking involves interconnected nodes that communicate with each other to create a network. Here's why it's used and why it's so valuable:
- Flexibility and Scalability: Mesh networks adapt and scale easily.
- Redundancy and Reliability: Multiple paths ensure uninterrupted connectivity.
- Coverage and Range Extension: Nodes relay signals to extend coverage.
- Self-Healing and Self-Organizing: Mesh networks adjust routes for continuous connectivity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Mesh networks reduce installation and maintenance costs.
- Ad Hoc and Temporary Deployments: Ideal for quick setups in various scenarios.
- IoT and Smart Home Applications: Efficiently connect and manage devices.requirements without compromising performance.
Overall, mesh networking represents a versatile and robust solution for wireless connectivity, offering unparalleled flexibility, reliability, and scalability across a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, mesh networks are poised to play an increasingly essential role in powering the connected world of tomorrow.
Prerequisites & Topology
Configuring a wireless mesh network with Teltonika devices is straightforward and requires just a few steps, which can be replicated across multiple devices. The number of devices needed depends on the specific use case, but the setup provided can be effortlessly expanded to accommodate many devices. In the example below, we will utilize RUTX50 as the node with mobile internet connectivity, serving as the mesh gateway and DHCP server. The access points (TAP100 and TAP200) will function as mesh nodes.
Before proceeding with the confuration, ensure that all requirements are met:
- Ensure that the firmware version of the Access Points (TAP100 and TAP200) is 00.07.07.1 or later, as the TAP functionality was not available in versions prior to this.
- The devices suitable for this configuration are from the RUT, RUTX, and TAP series.
- Make sure the gateway has access to the internet and DHCP enabled.
The test configuration utilizes the RUTX50 router along with the TAP100 and TAP200 access points. The RUTX50 unit is connected to the internet via mobile internet connectivity, although other connection types are feasible. After proper setup, all mesh devices should establish communication among themselves via wireless mesh, directly or through other devices in the mesh network. This enables an expansion of the Wi-Fi coverage radius. Configration
Configuration
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Gateway LAN Configuration
This router requires internet access. The specified settings should be activated by default.
Open router’s WebUI → Network → LAN click ![]() on current available LAN interface configuration:
on current available LAN interface configuration:
General Settings
Make the following changes:
- Select Protocol: Static
- Enter IPv4 address: 192.168.1.2
- Enter IPv4 netmask: 255.255.255.0
- Enable DHCPv4: on
Mesh Node Common Configuration
The following settings need to be applied to all of devices in the wireless mesh network including mesh gateway(RUTX50) and AP nodes(TAP100/200).
Open router‘s WebUI and navigate to Network → Wireless → SSIDs click ![]() on current available 2.4Ghz Wireless interface configuration:
on current available 2.4Ghz Wireless interface configuration:
Wi-Fi General Setup
Make the following changes:
- Select Mode: Access Point
- Select Radios: 2.4GHZ
- Enter SSID: MESH_DEMO
Wi-Fi Wireless Security
Make the following changes:
- Select Encryption: WPA3-SAE
- Enter Password: Password
Mesh General Setup
In router‘s WebUI, Navigate to Network → Wireless section → SSIDs. click ![]() and create new interface. Frequency band must match in all nodes.
and create new interface. Frequency band must match in all nodes.
Make the following changes:
- Select Mode: Mesh
- Select Radios: 2.4GHZ
- Enter SSID: Demo_1
Mesh Additional Settings
Make the following changes:
- Enable Forward mesh peer traffic: on
- Enter RSSI threshold for joining: -80
Mesh Wireless Security
Make the following changes:
- Select Encryption: WPA3-SAE
- Enter Password: Password
Radio General Setup
In router‘s WebUI, Navigate to Network → Wireless section → Radio → Wifi 2.4GHZ settings.
Make the following changes:
- Select Channel: 11 (2462 Mhz)
Mesh Node DHCP setup
In order to avoid conflicts, TAP100/200 needs to be leasing their LAN IP from mesh gateway. These settings should also be set last, otherwise access to TAP100/200 will be lost. Open WebUI → Network → IP Settings → Network configuration.
Make the following changes:
- Select Protocol: DHCP
- Select Management VLAN: Default
Configuration Testing
Connect to gateway(RUTX50) WebUI, enter Network → Wireless → SSIDs → WIFI 2.4GHZ tab. Demo_1 mesh interfaces should display two clients, in this case that would be TAP100 and TAP200 devices in the mesh network.
Open Status → Network → LAN tab. There should be displayed leases given to TAP100 and TAP200.
Devices TAP100/200 can be reached from mesh gateway without ethernet connecton. Try pinging devices.