TRB145 Modbus
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version TRB1_R_00.07.09.1.
Summary
Modbus is a serial communications protocol. Simple and robust, it has become a de facto standard communication protocol and is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices.
This manual page provides an overview of the Modbus functionality in TRB145 devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
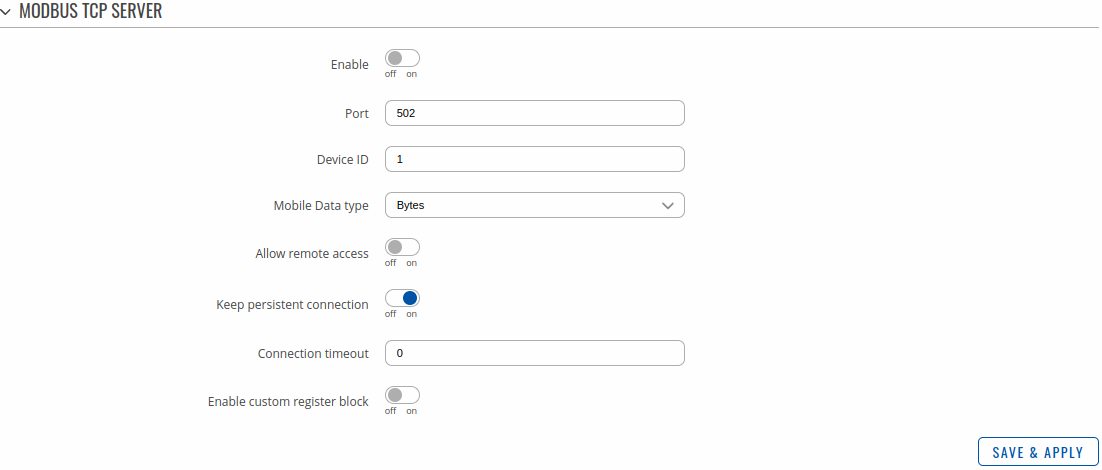
Modbus TCP Server
A Modbus TCP Server listens for connections from a TCP Client (client) and sends out a response or sets some system related parameter in accordance with the given query. This provides the user with the possibility to set or get system parameters.
The figure below is an example of the Modbus TCP window section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that window:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns Modbus TCP on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 502 | TCP port used for Modbus communications. |
| Device ID | integer [0..255]; default: 1 | The device's Modbus server ID. When set to 0, it will respond to requests addressed to any ID. |
| Mobile Data type | Bytes | Kilobytes | Megabytes; default: Bytes | Selects mobile data unit representation type. |
| Allow remote access | off | on; default: off | Allows remote Modbus connections by adding an exception to the device's firewall on the port specified in the field above. |
| Keep persistent connection | off | on; default: onn | Allows keep the connection open after responding a Modbus TCP client request. |
| Connection timeout | integer [0..60]; default: 0 | Sets TCP timeout in seconds after which the connection is forcefully closed. |
| Enable custom register block | off | on; default: off | Allows the usage of custom register block. |
| Register file path | path; default: /tmp/regfile | Path to file in which the custom register block will be stored. Files inside /tmp or /var are stored in RAM. They vanish after reboot, but do not degrade flash memory. Files elsewhere are stored in flash memory. They remain after reboot, but degrade flash memory (severely, if operations are frequent). |
| First register number | integer [1025..65536]; default: 1025 | First register in custom register block |
| Register count | integer [1..64512]; default: 128 | Register count in custom register block |
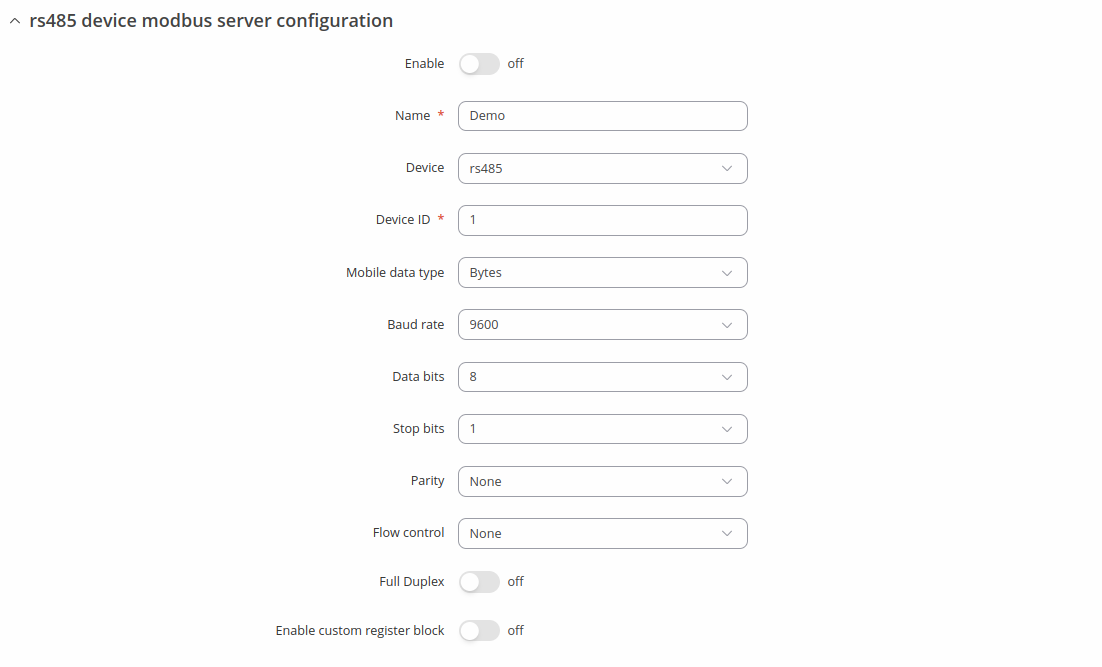
Modbus Serial Server
A Modbus Serial Server listens for connections from a serial client and sends out a response or sets some system related parameter in accordance with the given query. This provides the user with the possibility to set or get system parameters.
Modbus Serial Server Configuration
The Modbus Serial Server Configuration section is used to configure serial servers. By default, the list is empty. To add a new server instance, enter the instance name, select serial interface and click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added server instance configuration page.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables this Modbus Serial Server instance configuration. |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the serial server instance. Used for management purposes only. |
| Device | RS485; default: RS485 | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Device ID | integer [0..255]; default: 1 | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Mobile Data type | Bytes | Kilobytes | Megabytes; default: Bytes | Selects mobile data unit representation type. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200| 230400 | 460800 | 921600 | 1000000 | 3000000; default: 9600 | Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second). |
| Data bits | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | Even | Odd | None; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None ; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. |
| RS485: Full Duplex | off | on; default: off | Enables RS485 full duplex. |
| Enable custom register block | off | on; default: off | Allows the usage of custom register block. |
| Register file path | path; default: /tmp/regfile | Path to file in which the custom register block will be stored. Files inside /tmp or /var are stored in RAM. They vanish after reboot, but do not degrade flash memory. Files elsewhere are stored in flash memory. They remain after reboot, but degrade flash memory (severely, if operations are frequent). |
| First register number | integer [1025..65536]; default: 1025 | First register in custom register block |
| Register count | integer [1..64512]; default: 128 | Path to file in which the custom register block will be stored. Files inside /tmp or /var are stored in RAM. They vanish after reboot, but do not degrade flash memory. Files elsewhere are stored in flash memory. They remain after reboot, but degrade flash memory (severely, if operations are frequent). |
Modbus Registers
Get Parameters
Modbus parameters are held within registers. Each register contains 2 bytes of information. For simplification, the number of registers for storing numbers is 2 (4 bytes), while the number of registers for storing text information is 16 (32 bytes).
The register numbers and corresponding system values are described in the table below:
| required value | register address | register number | number of registers | representation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System uptime | 1 | 2 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile signal strength (RSSI in dBm) | 3 | 4 | 2 | 32 bit integer |
| System temperature (in 0.1 °C) | 5 | 6 | 2 | 32 bit integer |
| System hostname | 7 | 8 | 16 | Text |
| GSM operator name | 23 | 24 | 16 | Text |
| Router serial number | 39 | 40 | 16 | Text |
| Router name | 71 | 72 | 16 | Text |
| Network registration info | 103 | 104 | 16 | Text |
| Network type | 119 | 120 | 16 | Text |
| Current WAN IP address | 139 | 140 | 2 | 8 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data received today (SIM1) | 185 | 186 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data sent today (SIM1) | 187 | 188 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data received this week (SIM1) | 189 | 190 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data sent this week (SIM1) | 191 | 192 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data received this month (SIM1) | 193 | 194 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data sent this month (SIM1) | 195 | 196 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data received last month (SIM1) | 487 | 488 | 4 | 64 bit unsigned integer (Big Endian Notation) |
| Mobile data sent last month (SIM1) | 491 | 492 | 4 | 64 bit unsigned integer (Big Endian Notation) |
| Mobile data received last 24h (SIM1) | 197 | 198 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data sent last 24h (SIM1) | 199 | 200 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data received last 7 days (SIM1) | 292 | 293 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data sent 7 days (SIM1) | 294 | 295 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data received last week (SIM1) | 503 | 504 | 4 | 64 bit unsigned integer (Big Endian Notation) |
| Mobile data sent last week (SIM1) | 507 | 508 | 4 | 64 bit unsigned integer (Big Endian Notation) |
| Mobile data received last 30 days (SIM1) | 296 | 297 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Mobile data sent last 30 days (SIM1) | 298 | 299 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| PIN 3 status (4 PIN connector) | 324 | 325 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| PIN 4 status (4 PIN connector) | 325 | 326 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| PIN 3 direction | 326 | 327 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| PIN 4 direction | 327 | 328 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| Modem ID | 328 | 329 | 8 | Text |
| IMSI | 348 | 349 | 16 | Text |
| Unix timestamp | 364 | 365 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Local ISO time | 366 | 367 | 12 | Text |
| UTC time | 378 | 379 | 12 | Text |
| LAN IP | 394 | 395 | 2 | 8 bit unsigned integer |
| Add SMS | 397 | 398 | 90 | Text |
Set Parameters
The Modbus daemon can also set some device parameters.
| value to set | register address | register number | register value | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hostname | 7 | 8 | Hostname (in decimal form) | Changes hostname |
| Device name | 71 | 72 | Device name (in decimal form) | Changes device name |
| Switch mobile data connection (ON/OFF*) | 204 | 205 | 1 | 0 | Turns mobile data connection ON or OFF |
| Reboot | 206 | 207 | 1 | Reboots the router |
| Change APN | 207 | 208 | APN code | Changes APN. The number of input registers may vary depending on the length of the APN, but the very first byte of the set APN command denotes the number of the SIM card for which to set the APN. This byte should be set to:
|
| Switch PIN 3 state | 324 | 325 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 3 ON or OFF, when output is selected |
| Switch PIN 4 state | 325 | 326 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 4 ON or OFF, when output is selected |
| Switch PIN 3 direction | 326 | 327 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 3 direction between INPUT (0) or OUTPUT (1) |
| Switch PIN 4 direction | 327 | 328 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 4 direction between INPUT (0) or OUTPUT (1) |
| Change LAN IP | 394 | 395 | IPv4 (in decimal form) | Changes device LAN IP |
| Send SMS | 396 | 397 | 1|0 | Sends an SMS with content defined in Add SMS (397) register |
| Add SMS | 397 | 398 | Message (in decimal form) | Define SMS content which will be sent using Send SMS (396) register. The register array is split into two parts that represent the recipient's "phone number" (first 10 registers) and the "SMS message contents" (remaining 80 registers). |
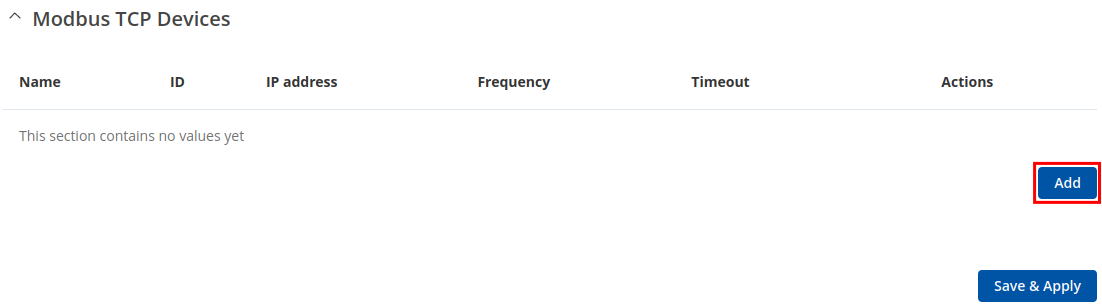
Modbus TCP Client
A Modbus Client device can request data from Modbus servers. The Modbus TCP Client section is used to configure Modbus TCP servers and enable Client.
Notice the Global section config. It is used to outright turn the service off or on if any active configurations are present.
Clicking the Cog icon opens a modal window. The global configuration slider can be set and it's state saved.
By default, the server list is empty and client is disabled. To add a new server, click the 'Add' button
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added server's configuration page.
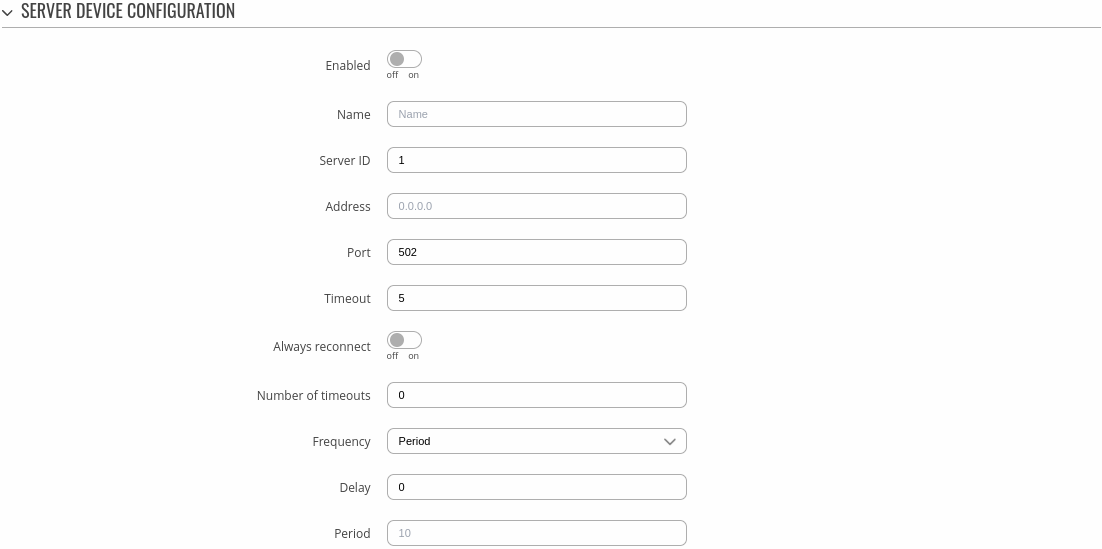
Server Device Configuration
The Server Device Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of Modbus TCP servers that the Client (this TRB145 device) will be querying with requests. The figure below is an example of the Server Device Configuration and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns communication with the server device on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Server device's name, used for easier management purposes. |
| Server ID | integer [0..255]; default: none | Server ID. Each server in a network is assigned a unique identifier ranging from 1 to 255. When the client requests data from a server, the first byte it sends is the Server ID. When set to 0, the server will respond to requests addressed to any ID. |
| IP address | ip4; default: none | Server device's IP address. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Server device's Modbus TCP port. |
| Timeout | integer [1..30]; default: 5 | Maximum response wait time. |
| Always reconnect | off | on; default: off | Create new connection after every Modbus request. |
| Number of timeouts | integer [0..10]; default: 1 | Skip pending request and reset connection after number of request failures. |
| Frequency | Period | Schedule; default: Period | |
| Delay | integer [0..999]; default: 0 | Wait in milliseconds after connection initialization. |
| Period | integer [1..99999]; default: none | Interval in seconds for sending requests to this device |
Requests Configuration
A Modbus request is a way of obtaining data from Modbus servers. The client sends a request to a server specifying the function code to be performed. The server then sends the requested data back to the Modbus client.
Note: Modbus TCP Client uses Register Number instead of Register Address for pointing to a register. For example, to request the Uptime of a device, you must use 2 in the First Register field.
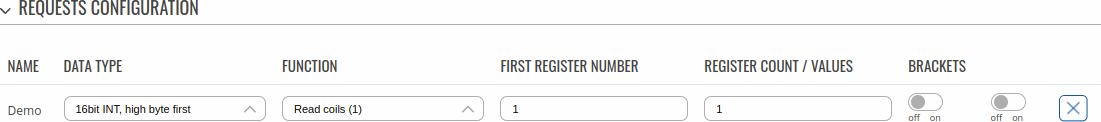
The Request Configuration list is empty by default. To add a new Request Configuration loon to the Add New Instance section. Enter a custom name into the 'Name' field and click the 'Add' button:
The new Request Configuration should become visible in the list:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: Unnamed | Name of this Request Configuration. Used for easier management purposes. |
| Data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float (various Byte order) | 32bit INT (various Byte order) | 32bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit INT (various Byte order) | 64bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit float (various Byte order) | ASCII | Hex | Bool | PDU; default: 16bit INT, high byte first | Defines how read data will be stored. |
| Function | Read coils (1) | Read input coils (2) | Read holding registers (3) | Read input registers (4) | Set single coil (5) | Set single coil register (6) | Set multiple coils (15) | Set multiple holding registers (16); default: Read holding registers (3) | Specifies the type of register being addressed by a Modbus request. |
| First Register | integer [0..65535]; default: 1 | First Modbus register from which data will be read. |
| Register Count / Values | integer [1..2000]; default: 1 | Number of Modbus registers that will be read during the request. |
| Remove Brackets | off | on; default: off | Removes the starting and ending brackets from the request (only for read requests). |
| off/on slider | off | on; default: off | Turns the request on or off. |
| Delete [ X ] | - (interactive button) | Deletes the request. |
Additional note: by default the newly added Request Configurations are turned off. You can use the on/off slider to the right of the Request Configuration to turn it on:
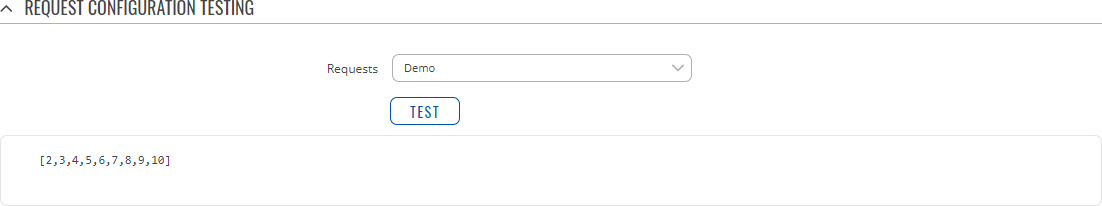
After having configured a request, you should see a new 'Request Configuration Testing' section appear. It is used to check whether the configuration works correctly. Simply click the 'Test' button and a response should appear in the box below. Note: to use test buttons, you need to enable Client section. A successful response to a test may look something like this:
Alarms Configuration
Alarms are a way of setting up automated actions when some Modbus values meet user-defined conditions. When the Modbus TCP Client (this TRB145 device) requests some information from a server device it compares that data to with the parameters set in an Alarm Configuration. If the comparison meets the specified condition (more than, less than, equal to, not equal to), the Client performs a user-specified action, for example, a Modbus write request or switching the state of an output.
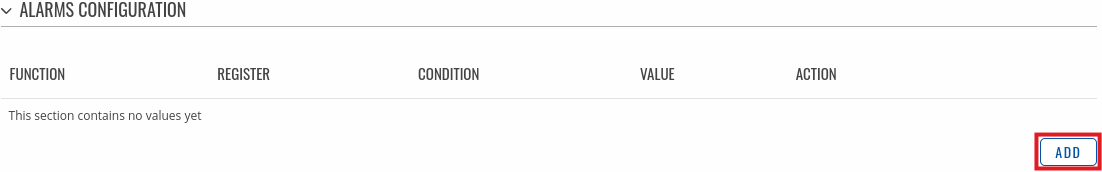
The figure below is an example of the Alarms Configuration list. To create a new Alarm, click the 'Add' button.
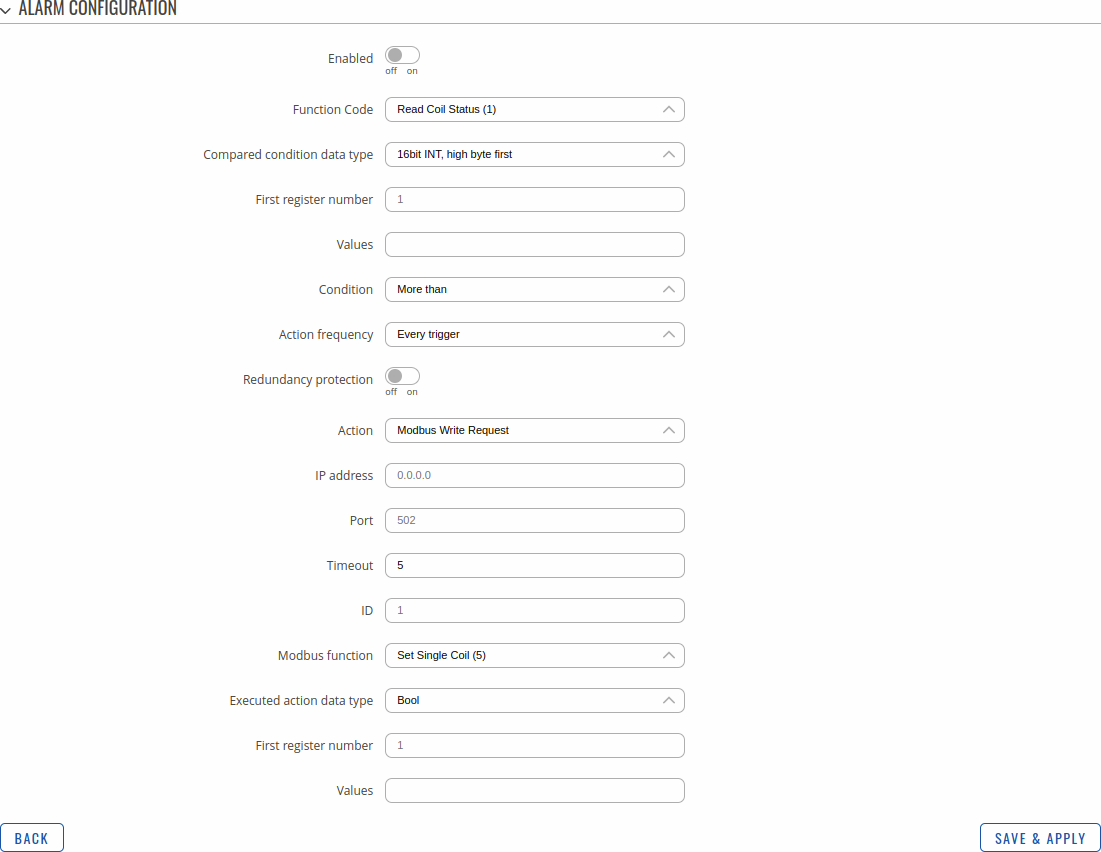
After adding the Alarm you should be redirected to its configuration page which should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns the alarm on or off. |
| Function code | Read Coil Status (1) | Read Input Status (2) | Read Holding Registers (3) | Read Input Registers (4); default: Read Coil Status (1) | Modbus function used for this alarm's Modbus request. The Modbus TCP Client (this TRB145 device) perform this request as often as specified in the 'Period' field in Server Device Configuration. |
| Compared condition data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float (various Byte order) | 32bit INT (various Byte order) | 32bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit INT (various Byte order) | 64bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit float (various Byte order) | ASCII | Hex | Bool; default: 16bit INT, high byte first | Select data type that will be used for checking conditions. |
| First register number | integer [1..65536]; default: none | Number of the Modbus coil/input/holding-register/input-register to read from. |
| Values | various; default: none | The value against which the read data will be compared. |
| Condition | More than | Less than | Equal to | Not Equal to | Less or equal | More or equal; default: More than | When a value is obtained it will be compared against the value specified in the following field. The comparison will be made in accordance with the condition specified in this field. |
| Action frequency | Every trigger | First trigger; default: Every trigger | Describes how frequently the specified action will be taken. |
| Redundancy protection | off | on; default: off | Protection against executing a configured action too often. |
| Redundancy protection period | integer [1..86400]; default: none | Duration to activate redundancy protection for, measured in seconds. This field becomes visible only when 'Redundancy protection' is turned on. |
| Action | Ubus event | SMS | MODBUS Write Request| Trigger output | MQTT message; default: MODBUS Write Request | Action that will be taken if the condition is met. Possible actions:
|
| SMS: Message | string; default: none | SMS message text. |
| SMS: Phone number | phone number; default: none | Recipient's phone number. |
| MODBUS Write Request: IP address | ip | host; default: none | Modbus server's IP address. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Modbus server's port. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Timeout | integer [1..30]; default: 5 | Maximum time to wait for a response. |
| MODBUS Write Request: ID | integer [1..255]; default: none | Modbus server ID. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Modbus function | Set Single Coil (5) | Set Single Register (6) | Set Multiple Coils (15) | Set Multiple Registers (16); default: Set Single Coil (5) | A function code specifies the type of register being addressed by a Modbus request. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Executed action data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float (various Byte order) | 32bit INT (various Byte order) | 32bit UNIT (various Byte order) 64bit INT (various Byte order) | 64bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit float (various Byte order) | ASCII | Hex | Bool; default: Bool | Select data type that will be used for executing action. |
| MODBUS Write Request: First register number | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Begins reading from the register specified in this field. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Values | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Register/Coil values to be written (multiple values must be separated by space character). |
| Trigger output: Output | Configurable Input/Output (3) | Configurable Input/Output (4); default: Configurable Input/Output (3) | Selects which output will be triggered. |
| Trigger output: I/O Action | Turn On | Turn Off | Invert; default: Turn On | Selects the action performed on the output. |
| MQTT message: JSON format | string; default: none | Below this field you can find special codes that begin with the '%' sign. Each code represents a piece information related to the status of the device. Include these codes in the field for dynamic information reports. Possible values: Local time, Unix time, Router name, Device name, Serial number, Current FW version, LAN IP address, Monitoring status, UTC time in ISO, WAN IP address, New line, Modbus server ID, Modbus server IP, First register number, Register value, Mobile IP addresses, Signal strength, Operator name, Network type, Data connection state, Network state, IMSI, IMEI, Modem model, Modem serial number, SIM pin state, SIM state, RSCP, ECIO, RSRP, SINR, RSRQ, ICCID, CELLID, Neighbour cells, Network info, Network serving, WAN MAC address, Analog Current Loop (6,9), Analog Input (6,9), Input (3), Digital Input (1), Output (4), Isolated Output (3,4,8), Isolated Input (2,7), Relay (5,10) |
| MQTT message: Hostname | host | ip; default: none | Broker’s IP address or hostname. |
| MQTT message: Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Broker's port number. |
| MQTT message: Keepalive | positive integer; default: none | The number of seconds after which the broker should send a PING message to the client if no other messages have been exchanged in that time |
| MQTT message: Topic | string; default: none | The name of the topic that the broker will subscribe to. |
| MQTT message: Client ID | positive integer; default: none | Client ID to send with the data. If empty, a random client ID will be generated |
| MQTT message: QoS | At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: At most once (0) | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
| MQTT message: Use root CA | off | on; default: off | Use root CA for verifying the servers certificates |
| MQTT message: Use TLS | off | on; default: off | Turns the use of TLS/SSL for this MQTT connection on or off. |
| MQTT message: Use credentials | off | on; default: off | Turns the use of username and password for this MQTT connection on or off. |
Modbus Serial Client
The Modbus Serial Client page is used to configure the device as a Modbus RTU Client. Modbus RTU (remote terminal unit) is a serial communication protocol mainly used in communication via serial interfaces.
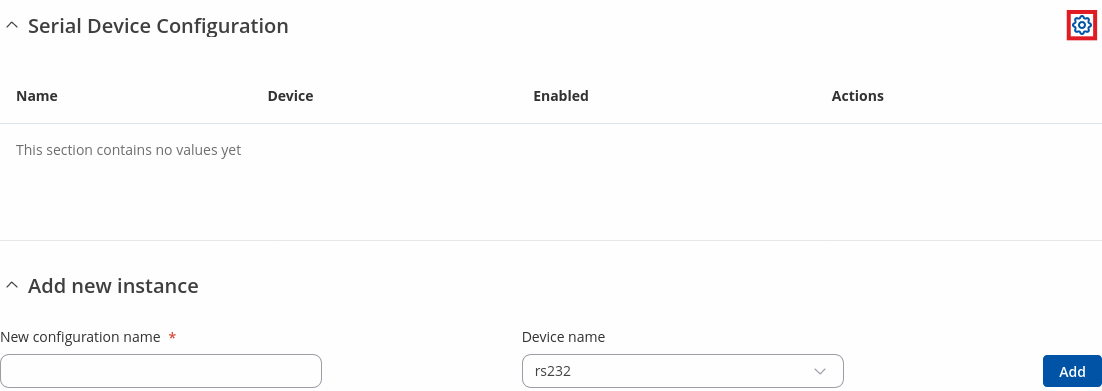
Notice the Global section config. It is used to outright turn the service off or on if any active configurations are present.
Clicking the Cog icon opens a modal window. The global configuration slider can be set and it's state saved.
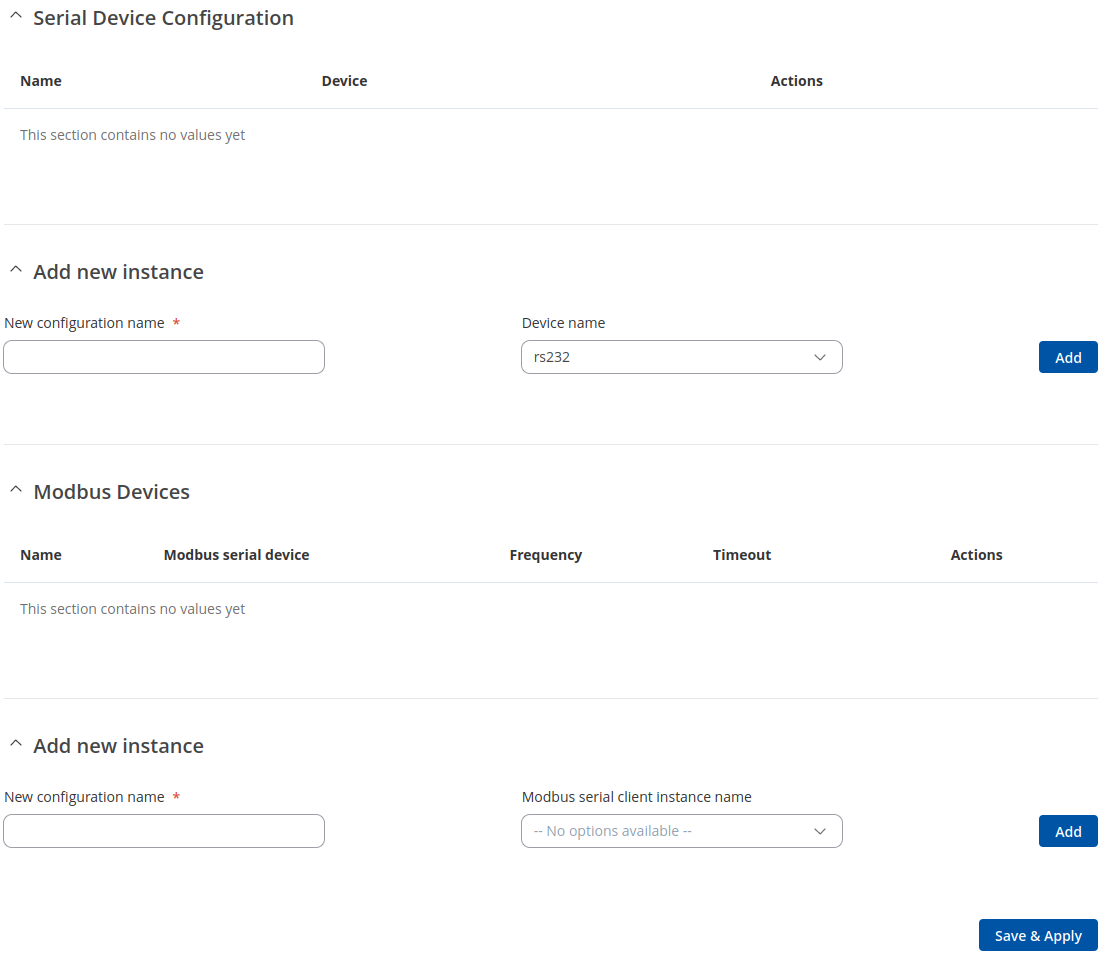
Modbus Serial Device Configuration
This section is used to create Modbus Serial Client's server device instances. You may create a Serial Device instance for each supported serial interface.
By default there are no instances created. To add a new serial device configuration, enter an instance name and click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added device's configuration page.
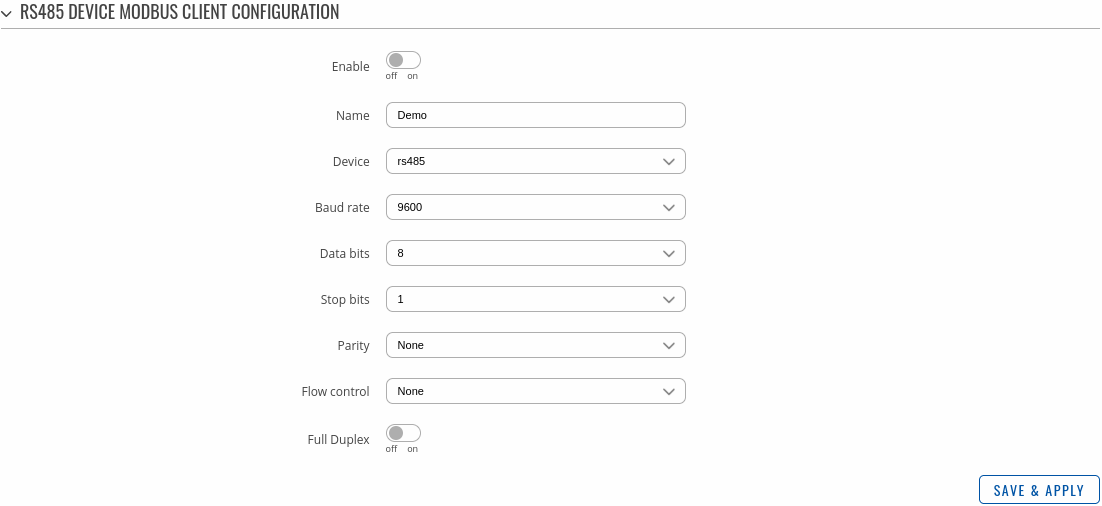
RS Device Modbus Client Configuration
This section is used to configure the Modbus Serial Client's server device interface settings.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables this Modbus Serial Device instance configuration. |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the serial device instance. Used for management purposes only. |
| Device | RS485; default: RS485 | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200| 230400 | 460800 | 921600 | 1000000 | 3000000; default: 9600 | Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second). |
| Data bits | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | Even | Odd | None; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None ; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. |
| RS485: Full Duplex | off | on; default: off | Enables RS485 full duplex. |
Modbus Server Device Configuration
This section is used to create server instances that the Client (this TRB145 device) will be querying with requests.
By default there are no instances created. To add a new server configuration, enter an instance name, select a serial device instance and click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added server's configuration page.
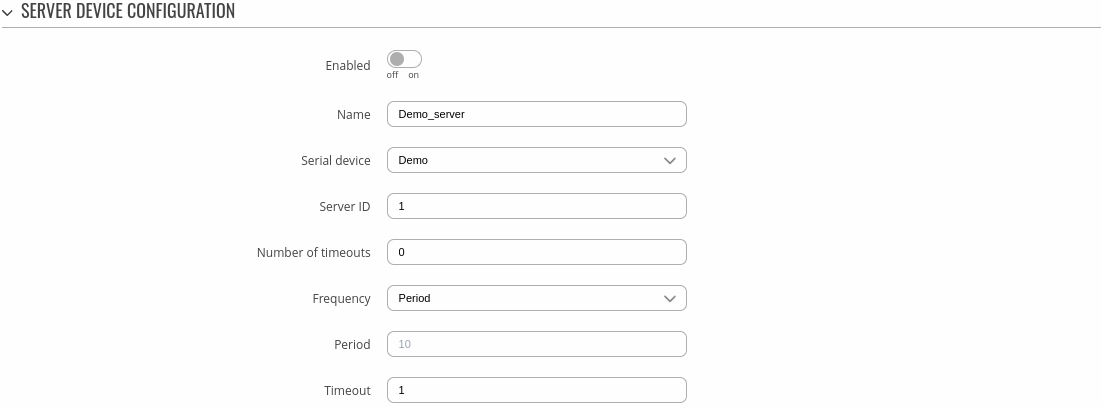
Server Device Configuration
The Server Device Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of Modbus RTU servers that the Client (this TRB145 device) will be querying with requests. The figure below is an example of the Server Device Configuration and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns communication with the server device on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Server device's name, used for easier management purposes. |
| Serial device | serial device instance; default: none | Specifies which serial device will be used on this server. |
| Server ID | integer [0..255]; default: 1 | Server ID. Each server in a network is assigned a unique identifier ranging from 1 to 255. When the client requests data from a server, the first byte it sends is the Server ID. When set to 0, the server will respond to requests addressed to any ID. |
| Number of timeouts | integer [0..10]; default: 0 | Skip pending request and reset connection after number of request failures. |
| Frequency | Period | Schedule; default: Period | |
| Period | integer [1..99999]; default: none | Interval at which requests are sent to the server device. |
| Timeout | integer [1..60]; default: 1 | Maximum response wait time. |
Requests Configuration
A Modbus request is a way of obtaining data from Modbus servers. The client sends a request to a servers specifying the function code to be performed. The server then sends the requested data back to the Modbus client.
Note: Modbus Serial Client uses Register Number instead of Register Address for pointing to a register. For example, to request the Uptime of a device, you must use 2 in the First Register field.
The Request Configuration list is empty by default. To add a new Request Configuration loon to the Add New Instance section. Enter a custom name into the 'Name' field and click the 'Add' button:
The new Request Configuration should become visible in the list:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: Unnamed | Name of this Request Configuration. Used for easier management purposes. |
| Data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float (various Byte order) | 32bit INT (various Byte order) | 32bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit INT (various Byte order) | 64bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit float (various Byte order) | ASCII | Hex | Bool | PDU; default: 16bit INT, high byte first | Defines how read data will be stored. |
| Function | Read coils (1) | Read input coils (2) | Read holding registers (3) | Read input registers (4) | Set single coil (5) | Set single coil register (6) | Set multiple coils (15) | Set multiple holding registers (16); default: Read holding registers (3) | Specifies the type of register being addressed by a Modbus request. |
| First Register | integer [0..65535]; default: 1 | First Modbus register from which data will be read. |
| Register Count / Values | integer [1..2000]; default: 1 | Number of Modbus registers that will be read during the request. |
| Remove Brackets | off | on; default: off | Removes the starting and ending brackets from the request (only for read requests). |
| off/on slider | off | on; default: off | Turns the request on or off. |
| Delete [ X ] | - (interactive button) | Deletes the request. |
Additional note: by default the newly added Request Configurations are turned off. You can use the on/off slider to the right of the Request Configuration to turn it on:
After having configured a request, you should see a new 'Request Configuration Testing' section appear. It is used to check whether the configuration works correctly. Simply click the 'Test' button and a response should appear in the box below. Note: to use test buttons, you need to enable Client section. A successful response to a test may look something like this:
Modbus Client Alarms
Alarms are a way of setting up automated actions when some Modbus values meet user-defined conditions. When the Modbus Serial Client (this TRB145 device) requests some information from a server device it compares that data to with the parameters set in an Alarm Configuration. If the comparison meets the specified condition (more than, less than, equal to, not equal to), the Client performs a user-specified action, for example, a Modbus write request or switching the state of an output.
The figure below is an example of the Modbus Client Alarms list. To create a new Alarm, click the 'Add' button.
After this you should be redirected to that Alarm's configuration page which should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns the alarm on or off. |
| Function code | Read Coil Status (1) | Read Input Status (2) | Read Holding Registers (3) | Read Input Registers (4); default: Read Coil Status (1) | Modbus function used for this alarm's Modbus request. The Modbus TCP Client (this TRB145 device) perform this request as often as specified in the 'Period' field in Server Device Configuration. |
| Compared condition data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float (various Byte order) | 32bit INT (various Byte order) | 32bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit INT (various Byte order) | 64bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit float (various Byte order) | ASCII | Hex | Bool; default: 16bit INT, high byte first | Select data type that will be used for checking conditions. |
| First register number | integer [1..65536]; default: none | Number of the Modbus coil/input/holding-register/input-register to read from. |
| Values | various; default: none | The value against which the read data will be compared. |
| Condition | More than | Less than | Equal to | Not Equal to | Less or equal | More or equal; default: More than | When a value is obtained it will be compared against the value specified in the following field. The comparison will be made in accordance with the condition specified in this field. |
| Action frequency | Every trigger | First trigger; default: Every trigger | Describes how frequently the specified action will be taken. |
| Redundancy protection | off | on; default: off | Protection against executing a configured action too often. |
| Redundancy protection period | integer [1..86400]; default: none | Duration to activate redundancy protection for, measured in seconds. This field becomes visible only when 'Redundancy protection' is turned on. |
| Action | SMS | MODBUS Write Request| Trigger output; default: MODBUS Write Request | Action that will be taken if the condition is met. Possible actions:
|
| SMS: Message | string; default: none | SMS message text. |
| SMS: Phone number | phone number; default: none | Recipient's phone number. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Timeout | integer [1..30]; default: 5 | Maximum time to wait for a response. |
| MODBUS Write Request: ID | integer [1..255]; default: none | Modbus server ID. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Modbus function | Read Single Coil (5) | Set Single Register (6) | Set Multiple Coils (15) | Set Multiple Registers (16); default: Set Single Coil (5) | A function code specifies the type of register being addressed by a Modbus request. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Executed action data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float (various Byte order) | 32bit INT (various Byte order) | 32bit UNIT (various Byte order) | 64bit INT (various Byte order) | 64bit UINT (various Byte order) | 64bit float (various Byte order) | ASCII | Hex | Bool; default: Bool | Select data type that will be used for executing action. |
| MODBUS Write Request: First register number | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Begins reading from the register specified in this field. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Values | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Register/Coil values to be written (multiple values must be separated by space character). |
| Trigger output: Output | Configurable Input/Output (3) | Configurable Input/Output (4); default: Configurable Input/Output (3) | Selects which output will be triggered. |
| Trigger output: I/O Action | Turn On | Turn Off | Invert; default: Turn On | Selects the action performed on the output. |
MQTT Modbus Gateway
The MQTT Modbus Gateway function is used to transfer Modbus data (send requests, receive responses) over MQTT. When it is enabled, the device (this TRB145) subscribes to a REQUEST topic and publishes on a RESPONSE topic on a specified MQTT broker. It translates received MQTT message payload to a Modbus request and relays it to the specified Modbus TCP server.
When the MQTT Gateway receives a response from the server, it translates it to an MQTT message and publishes it on the RESPONSE topic.
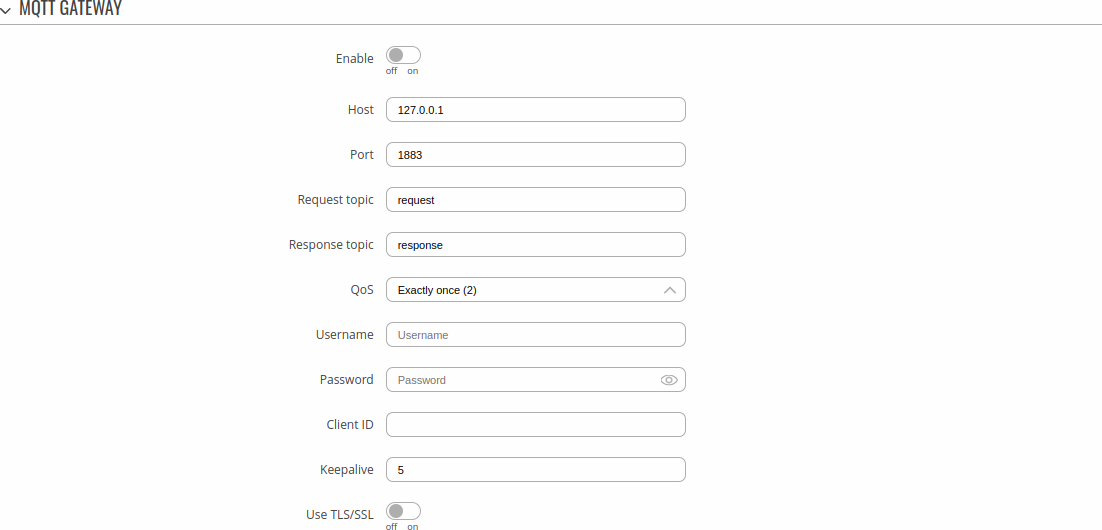
Below is an example of the MQTT Gateway page. Refer to the table for information on MQTT Gateway configuration fields.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns MQTT gateway on or off. |
| Host | ip | host; default: 127.0.0.1 | IP address or hostname of an MQTT broker. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Port number of the MQTT broker. |
| Request topic | alphanumeric string; default: request | MQTT topic for sending requests. |
| Response topic | alphanumeric string; default: response | MQTT topic for subscribing to responses. |
| QoS | At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: Exactly once (2) | Specifies quality of service. |
| Username | string; default: none | Username for authentication to the MQTT broker. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password for authentication to the MQTT broker. |
| Client ID | integer; default: none | Specifies client ID for MQTT broker. |
| Keepalive | integer; default: 5 | Keepalive message to MQTT broker (seconds) |
| Use TLS/SSL | off | on; default: off | Turns TLS support on or off |
| TLS type | cert | psk; default: cert | Selects the type of TLS encryption |
| TLS insecure | off | on; default: off | Disables TLS security |
| Certificate files from device | off | on; default: off | Choose this option if you want to use certificate files generated on device. |
| CA file | string; default: none | Upload/select certificate authority file. |
| Certificates file | string; default: none | Upload/select certificate file. |
| Key file | string; default: none | Upload/select certificate key file. |
| PSK | string; default: none | Specifies the pre-shared key. |
| Identity | string; default: none | Specifies identity. |
Serial Gateway Configuration
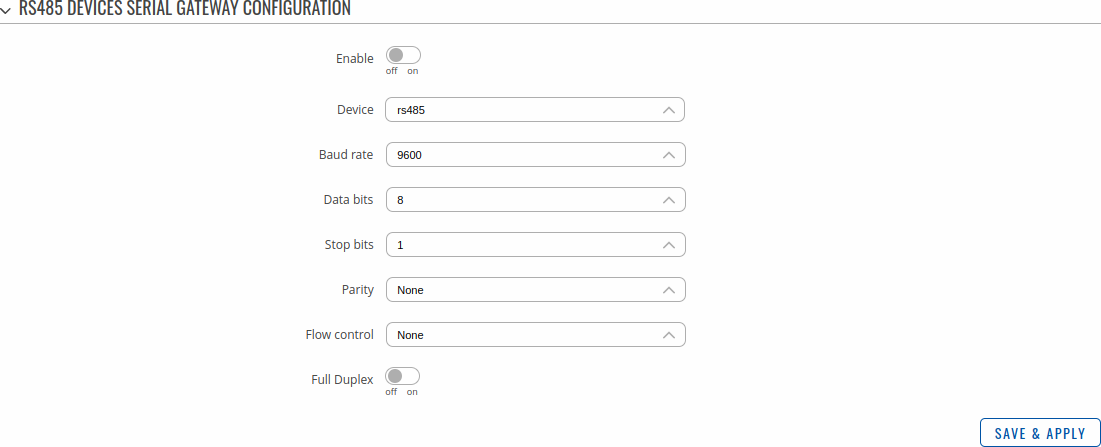
Serial Gateway Configuration section displays Serial gateway instances currently existing on the router.
By default the list is empty. To create a new gateway instance, enter the ID of serial device, select serial interface and click the 'Add' button.
After this you should be redirected to instance's configuration page which should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables this Serial Gateway instance configuration. |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the gateway instance. Used for management purposes only. |
| Device | RS485; default: RS485 | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200| 230400 | 460800 | 921600 | 1000000 | 3000000; default: 9600 | Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second). |
| Data bits | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | Even | Odd | None; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None ; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. |
| RS485: Full Duplex | off | on; default: off | Enables RS485 full duplex. |
Request messages
Note: MQTT Gateway uses Register Number instead of Register Address for pointing to a register. For example, to request the Uptime of a device, you must use 2 in the Register Number field.
Modbus request data sent in the MQTT payload should be generated in accordance with the one of the following formats:
- TCP:
0 <COOKIE> <IP_TYPE> <IP> <PORT> <TIMEOUT> <SERVER_ID> <MODBUS_FUNCTION> <FIRST_REGISTER> <REGISTER_COUNT/VALUES>
- Serial:
1 <COOKIE> <SERIAL_DEVICE_ID> <TIMEOUT> <SERVER_ID> <MODBUS_FUNCTION> <FIRST_REGISTER> <REGISTER_COUNT/VALUES>
- MODBUS TCP connection management messages:
2 <COOKIE> <CONNECTION_INDEX> <ACTION>
2 <COOKIE> <CONNECTION_INDEX> 0 <IP_TYPE> <IP> <PORT> <TIMEOUT>
Explanation:
- Cookie - a 64-bit unsigned integer in range [0..264-1]). A cookie is used in order to distinguish which response belongs to which request, each request and the corresponding response contain a matching cookie: a 64-bit unsigned integer.
- IP type - host IP address type. Possible values:
- 0 - IPv4 address;
- 1 - IPv6 address;
- 2 - hostname that will be resolved to an IP address.
- IP - IP address of a Modbus TCP server. IPv6 must be presented in full form (e.g., 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
- Port - port number of the Modbus TCP server.
- Timeout - timeout for Modbus connection, in seconds. Range [1..999].
- Server ID - Modbus TCP server ID. Range [1..255].
- Modbus function - Modbus task type that will be executed. Possible values are:
- 1 - read coils;
- 2 - read input coils;
- 3 - read holding registers;
- 4 - read input registers;
- 5 - set single coil;
- 6 - write to a single holding register;
- 15 - set multiple coils;
- 16 - write to multiple holding registers.
- First register - number (not address) of the first register/coil/input (in range [1..65536]) from which the registers/coils/inputs will be read/written to.
- Register count/value - this value depends on the Modbus function:
- 1 - coil count (in range [1..2000]); must not exceed the boundary (first coil number + coil count <= 65537);
- 2 - input count (in range [1..2000]); must not exceed the boundary (first input number + input count <= 65537);
- 3 - holding register count (in range [0..125]); must not exceed the boundary (first register number + holding register count <= 65537);
- 4 - input register count (in range [0..125]); must not exceed the boundary (first register number + input register count <= 65537);
- 5 - coil value (in range [0..1]);
- 6 - holding register value (in range [0..65535]);
- 15 - coil count (in range [1..1968]); must not exceed the boundary (first coil number + coil count <= 65537); and coil values separated with commas, without spaces (e.g., 1,2,3,654,21,789); there must be exactly as many values as specified (with coil count); each value must be in the range of [0..1].
- 16 - register count (in range [1..123]); must not exceed the boundary (first register number + register count <= 65537); and register values separated with commas, without spaces (e.g., 1,2,3,654,21,789); there must be exactly as many values as specified (with register count); each value must be in the range of [0..65535].
- Serial device ID - a string used to identify a serial device. Must match with Device ID field in MQTT Gateway page Serial gateway configuration section.
- Connection index - a number used to identify a connection on which an action will be preformed (in range [0..7]).
- Action - a connection action. Possible values are:
- 0 - OPEN. This will open a closed connection, reopen an already open connection with the same parameters or close an already open connection and open a new one with new parameters.
- 1 - CLOSE. This will close an open connection and do nothing to the closed one.
- 2 - STATUS. This will respond with either OK 1 for an open connection or OK 0 for a closed connection.
Response messages
A special response message can take one of the following forms:
<COOKIE> OK - for functions 6 and 16 <COOKIE> OK <VALUE> <VALUE> <VALUE>... - for function 3, where <VALUE> <VALUE> <VALUE>... are read register values <COOKIE> ERROR: ... - for failures, where ... is the error description
Examples
Below are a few examples of controlling/monitoring the internal Modbus TCP Server on TRB145.
Reboot the device
- Request:
0 65432 0 192.168.1.1 502 5 1 6 206 1
- Response:
65432 OK
Retrieve uptime
- Request:
0 65432 0 192.168.1.1 502 5 1 3 2 2
- Response:
65432 OK 0 5590
If you're using Eclipse Mosquitto (MQTT implementation used on TRB145), Publish/Subscribe commands may look something like this:
Retrieve uptime
- Request:
mosquitto_pub -h 192.168.1.1 -p 1883 -t request -m "0 65432 0 192.168.1.1 502 5 1 3 2 2"
- Response:
mosquitto_sub -h 192.168.1.1 -p 1883 -t response 65432 OK 0 5590
Modbus TCP over Serial Gateway
The Modbus TCP over Serial gateway serial type allows redirecting TCP data coming to a specified port to an RTU specified by the Server ID. The Server ID can be specified by the user or be obtained directly from the Modbus header.
Modbus TCP over Serial Gateway Configuration
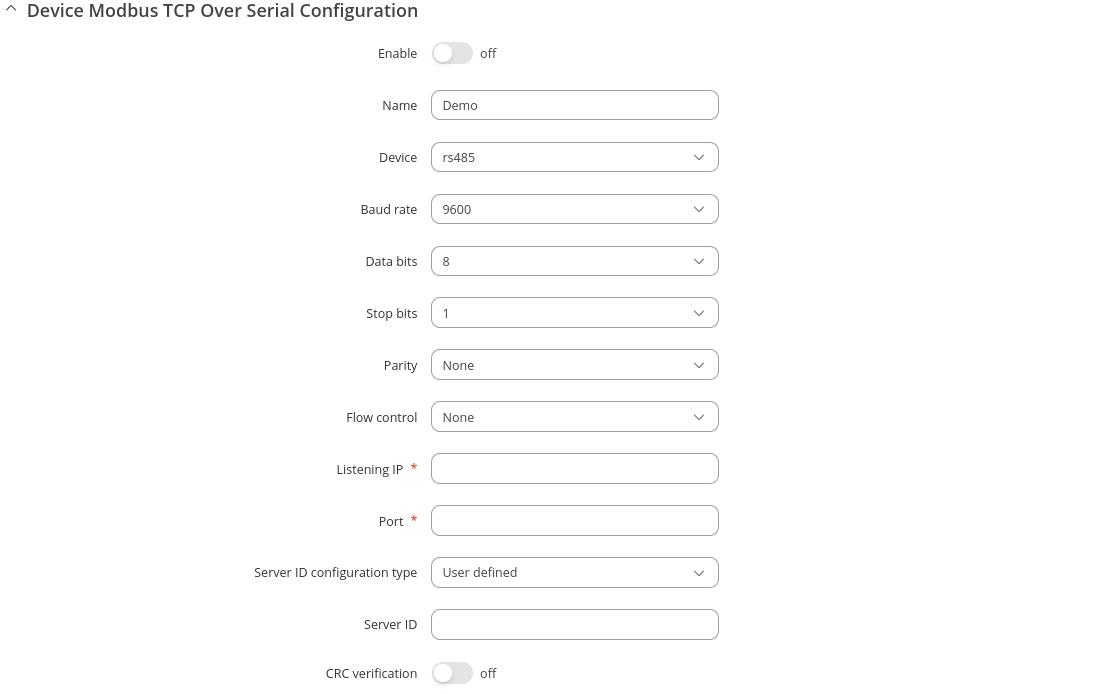
Modbus TCP over Serial Gateway Configuration section displays gateway instances currently existing on the router.
By default the list is empty. To create a new gateway instance, enter the name of instance, select serial interface and click the 'Add' button.
After this you should be redirected to instance's configuration page which should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables this Modbus TCP over Serial Gateway instance configuration. |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the gateway instance. Used for management purposes only. |
| Device | RS485; default: RS485 | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200| 230400 | 460800 | 921600 | 1000000 | 3000000; default: 9600 | Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second). |
| Data bits | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | Even | Odd | None; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. |
| Listening IP | ip; default: none | IP address to listen for incoming connections. (0.0.0.0) value may be used to listen for incoming connections on any interface or IP address. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Port number to listen for incoming connections. |
| Server ID configuration type | User defined | Obtained from TCP; default: User defined | Specifies whether server IDs are user defined or automatically obtained from TCP. |
| Server ID | integer; default: none | Specifies the server ID of range of permitted server IDs. The way this field is named and its function depends on the value of the Server ID configuration field. A range of IDs can be specified by placing a hyphen (-) between two integer numbers. For example, if you permit server IDs in the range of 10 to 20, you would specify it as: 10-20 You can also specify multiple values that are not connected in a range using commas (,). For example, to specify 6, 50 and 100 as permitted server IDs, you would have to use: 6,50,100 |
| Permitted server IDs | range of integers; default: 1-247 | Read Server ID field description. |
| CRC verification | off | on; default: off | Checks if sent serial message is not disturbed. |
| RS485: Full Duplex | off | on; default: off | Enables RS485 full duplex. |
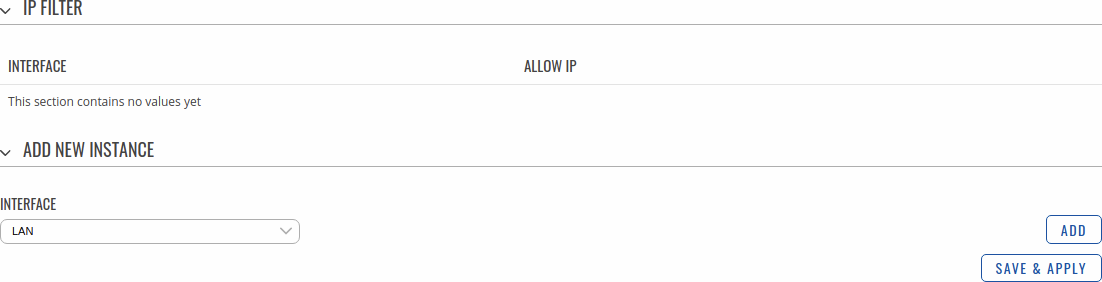
IP Filter
The IP Filter section is used for configuring which network is allowed to communicate with the device. You may add a new instance by selecting the Interface and pressing Add.
Then enter the IP address and save.
See also
- Monitoring via Modbus - detailed examples on how to use Modbus TCP