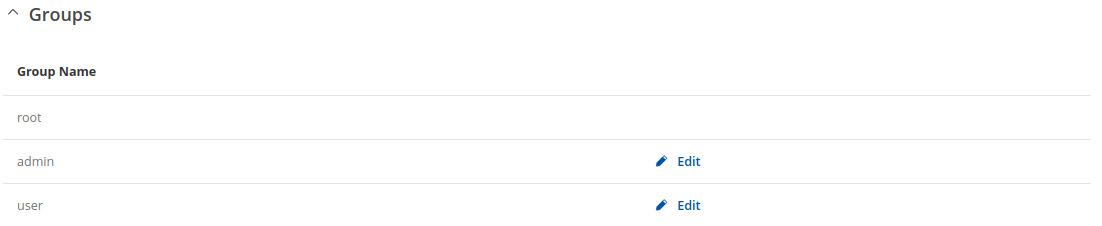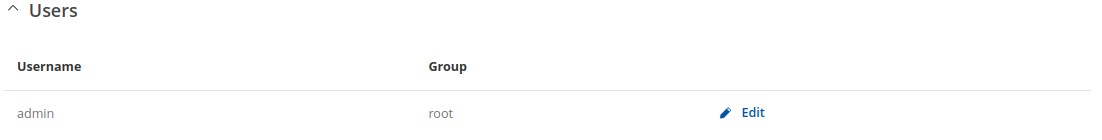NTP001 Administration
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version NTP_R_00.01.01.
Summary
This page is an overview of the Administration section of NTP001 devices.
General
The General section is used to set up some of device managerial parameters, such as changing device name. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Device name and hostname | ||
| Device name | string; default: NTP001 | Device model name. |
| Hostname | string; default: NTP001 | Device hostname. This can be used for communication with other LAN hosts. |
| LED Indication | ||
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Turns on/off LEDs indication. |
| Reset Button Configuration | ||
| Min time | integer [0..60]; default: none | Minimum time (in seconds) the button needs to be held to perform an action. |
| Max time | integer [1..60]; default: none | Maximum time (in seconds) the button can be held to perform an action, after which no action will be performed. |
User Settings
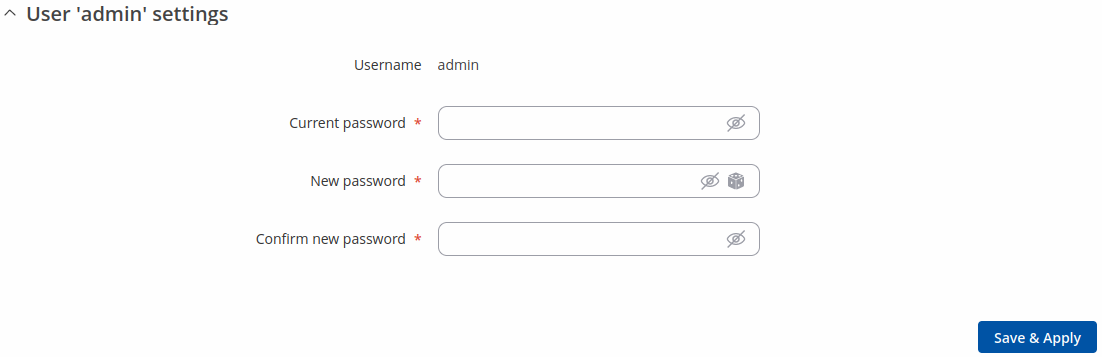
Change Password
The User settings section is used to change the password of the current user.
System Users
The System Users page is used to add new user accounts that can access the device with different user credentials than the default ones. The newly added users can be assigned to one of two groups, either of which can be modified to limit WebUI read/write access rights for users belonging to each specific group.
This page is unrelated to SSH users. By default, there is one SSH user named "root" and it shares the same password as the default WebUI user named "admin".
This manual page provides an overview of the Users page in NTP001 devices.
Groups
The Groups section lists available user groups of which there are three:
- root - highest level of authority. Key elements that define this group:
- has unlimited read/write access;
- additional users cannot be added to this group;
- access rights for this group cannot be modified.

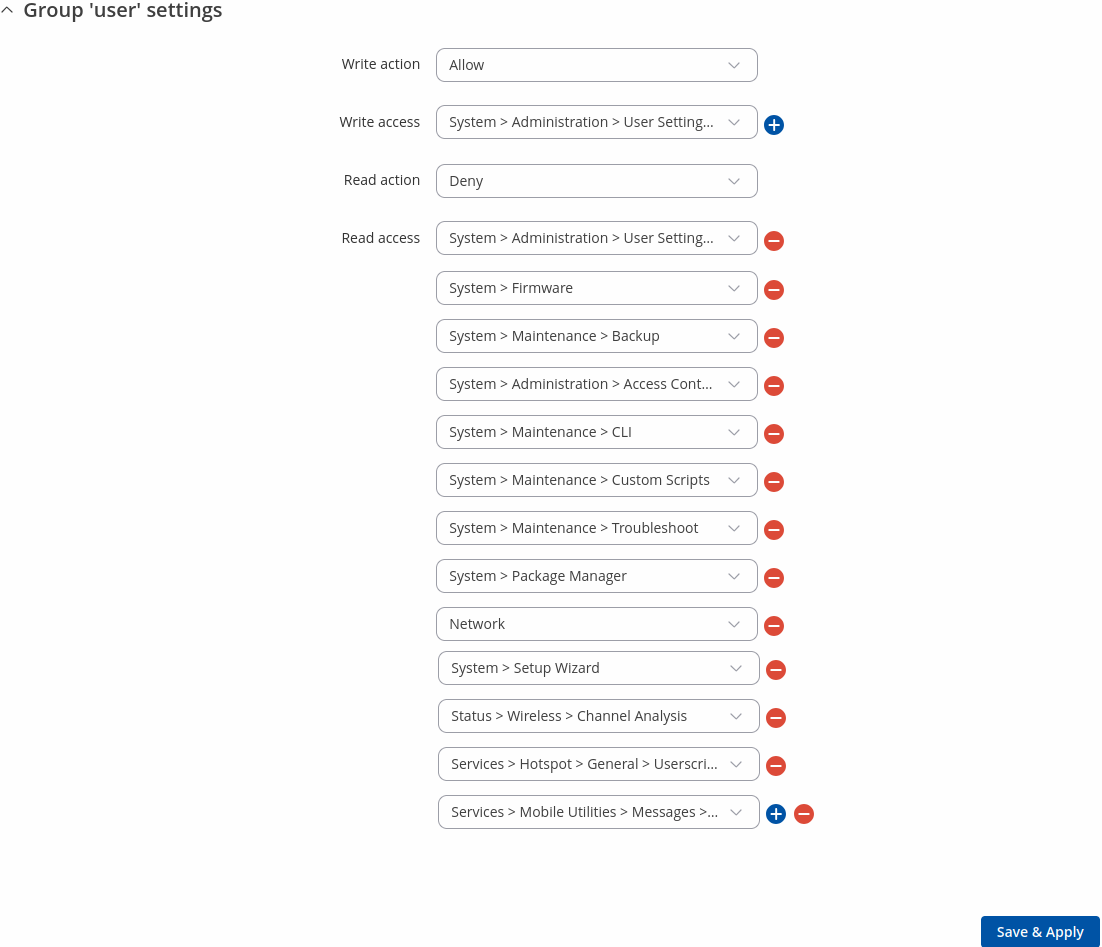
- admin - second highest level of authority. Key elements that define this group:
- limited read access; by default, users belonging to this group cannot view these pages:
- System → Administration → Users Settings → System Users
- System → Administration → Profiles
- System → Maintenance → Backup
- System → Firmware
- System → Maintenance → CLI
- System → Setup Wizard
- System → Maintenance → Custom Scripts
- limited write access; by default, users belonging to this group cannot view these pages:
- System → Administration → Users Settings → System Users
- System → Maintenance → Backup
- System → Firmware
- System → Maintenance → CLI
- System → Setup Wizard
- System → Maintenance → Custom Scripts
- System → Administration → Access Control → General
- System → Administration → Profiles
- access rights can be modified.

- limited read access; by default, users belonging to this group cannot view these pages:
- user - lowest level of authority. Key elements that define this group:
- no write access;
- limited read access; by default, users belonging to this group cannot view these pages:
- System → Administration → Users Settings → System Users
- System → Firmware
- System → Maintenance → Backup
- System → Administration → Access Control
- System → Maintenance → CLI
- System → Maintenance → Custom Scripts
- System → Maintenance → Troubleshoot
- System → Package Manager
- Network
- System → Setup Wizard
- Services → Hotspot → General → Userscripts
- access rights can be modified.

Additional note: you can view and/or edit settings for each group by clicking the 'Edit' button next to them. More on information on how to edit group access settings is located in the following section of this manual page.
Group Settings (edit group)
A group's parameters can be set in its Group Settings page. To access the Groups Settings page, click the 'Edit' button next to the group's name. Below is an example of the Group Settings section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Write action | Allow | Deny; default: Allow | Specifies whether to deny or allow write access for users belonging the group. |
| Write access | path(s) to page(s); default:
|
Controls the ability of users to change and execute the contents (e.g. Network > Lan). |
| Read action | Allow | Deny; default: Deny | Specifies whether to deny or allow read access for users belonging the group. |
| Read access | path(s) to page(s); default: in the picture above | Path(s) to the page(s) to which the selected "Read action" will be applied. Click the plus symbol to add more entries. |
Examples
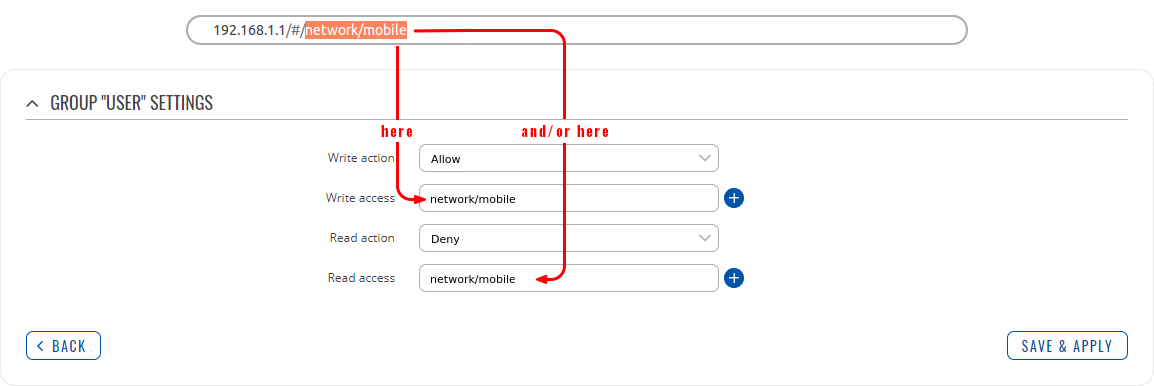
The easiest way to master the syntax is to navigate to page that you want to generate a path for and the copy the path from the URL of that page.
For example, to specify the path to the Network → Mobile page, navigate to the page, copy the page's URL address starting from the symbol "#" and paste it into one of the access fields:
However, the VPN window contains links to many different types of VPN pages. If you want to specify only one of them, you can do it as well. For example, to to specify the path to the IPsec page, add "/ipsec" to the path string:
services/vpn/ipsec
An asterisk (*) in the path string means that the every page from that point on is included in that path. For example, to generate a path that includes pages in the Services menu tab:
services/*
Or to simply include everything in the entire WebUI (if this path is combined with Read action: Deny, users from that group will not be able to login to the WebUI):
*
Users
The Users section lists all created users and provides the possibility to change their passwords and the group they belong to (with the exception of the default user "admin" which always belongs to the root group).
By default, there is only one user called "admin":
User Settings (edit user)
Each user's password and group parameters can be set in their User Settings pages. To access the User Settings page, click the 'Edit' button next to the user's name.
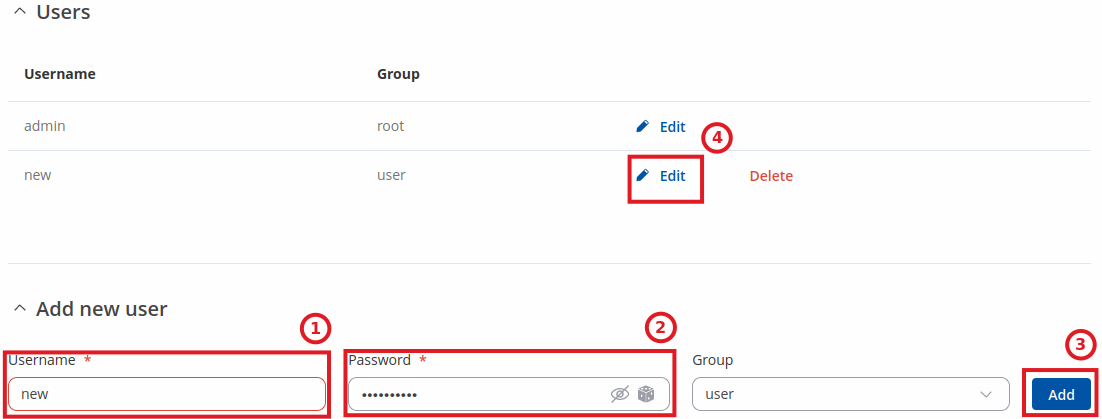
However, you may want to add a new user at first. This can be done from the Add New User section below:
- create a username;
- create a password for the user (must contain at least 8 characters, including at least one upper case letter and one digit);
- click the 'Add' button;
- click the 'Edit' next to newly added user.
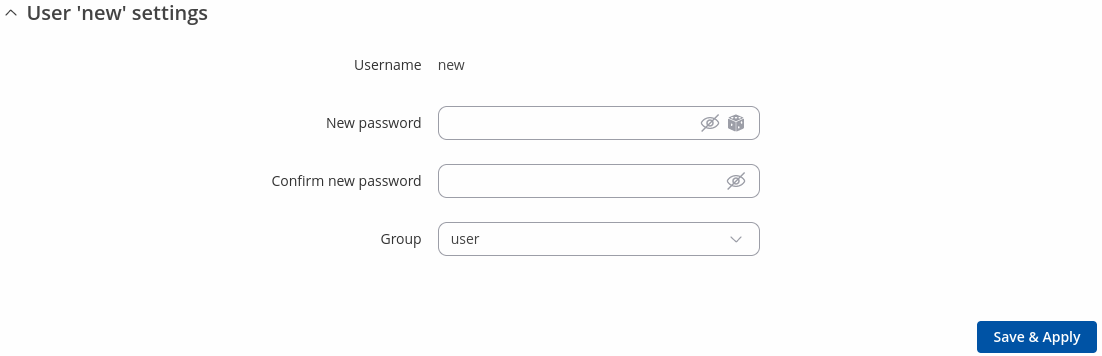
Below is an example of a newly added user's settings page:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Username | string; default: none | Displays the user's name. |
| New password | string; default: none | |
| Confirm new password | string; default: none | Repeat the new password. |
| Group | admin | user; default: user | The group to which the user belongs. |
| Enable SSH access | off | on; default: off | Enables SSH access (only for 'root' users). |
Add New User
The Add New User section is used to create additional users that can access the WebUI. After a new user is added, it will appear in the Users section.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Username | string; default: none | A custom name for the new user. |
| Password | string; default: none |
Access Control
General
The Access Control page is used to manage remote and local access to device.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SSH | ||
| Enable SSH access | off | on; default: on | Turns SSH access from the local network (LAN) on or off. |
| Port | integer [1..65535]; default: 22 | Selects which port to use for SSH access. |
| Authentication type | Password | Key-based only | Use both; default: Password |
|
| Public keys | string; default: none | Public keys for ssh key-based authentication. Each individual key must be specified on a new line |
| WebUI | ||
| Enable HTTP access | off | on; default: on | Turns HTTP access from the local network (LAN) to the device's WebUI on or off. |
| Enable HTTPS access | off | on; default: on | Turns HTTPS access from the local network (LAN) to the device's WebUI on or off. |
| Redirect to HTTPS | off | on; default: off | Redirects connection attempts from HTTP to HTTPS. |
| HTTP Port | integer [1..65535]; default: 80 | Selects which port to use for HTTP access. |
| HTTPS Port | integer [1..65535]; default: 443 | Selects which port to use for HTTPS access. |
| CLI | ||
| Enable CLI | off | on; default: on | Turns CLI access from the local network (LAN) on or off. |
| Port range | Port ranges with values from 1 to 65535 are accepted. E.g. 232-254.; default: 4200-4220 | Selects which ports to use for CLI access. |
| Shell limit | integer [1..10]; default: 5 | Maximum number of active CLI connections. |
Security
The Security tab provides the possibility to enable/disable blocking IP's service and delete blocked devices from the list.
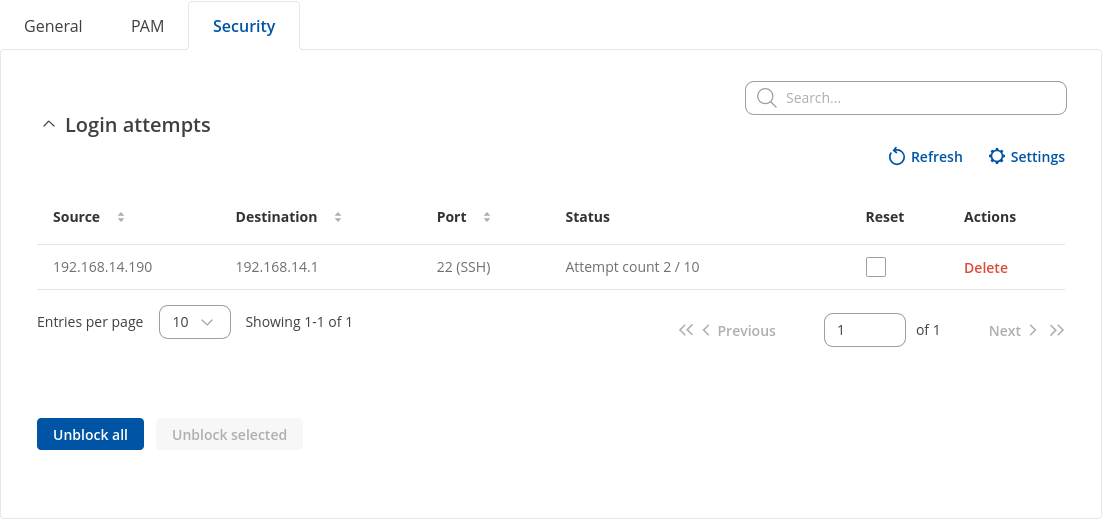
Login Attempts
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Source | IP address | Shows the IP address from which the connection failed. |
| Destination | IP address | Shows yours device IP adress |
| Port (protocol) | Port number | Shows the port number from which the connection failed. |
| Status | Attempt count | Blocked | Shows the number of failed attempts to connect to device. Indicates whether the source address is blocked or not. |
| Reset | Check box | Allows you to select multiple IP addresses. |
| Actions | -(interactive button) | Allows you to select multiple IP addresses. |
| Unblock all | -(interactive button) | Deletes instance. |
| Unblock selected | -(interactive button) | Unblocks selected source adresses from the list. |
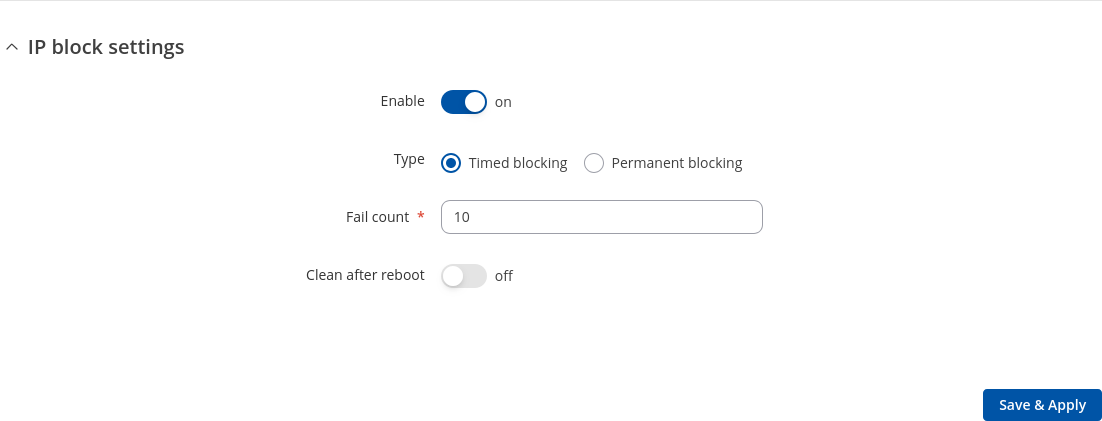
IP Block Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Enable or disable blocking IP's if they have reached the set amount of failed times. |
| Type | Timed blocking | Permanent blocking; default: Timed blocking | You can choose an option of a blocking type. |
| Fail count | integer [1..1000]; default: 10 | An amount of times IP address can try to access SSH or WebUI before being blocked. |
| Clean after reboot | off | on; default: off | If enabled, blocked loging attempts list will be cleared on device reboot. |
Certificates
The Certificates page is used for convenient TLS certificate and key generation and management. Generated files can be exported and used on other machines or locally on this device with functions that use TLS/SSL.
Certificate Generation
The Certificate Generation tab provides the possibility to generate TLS certificates required for secure authentication and communication encryption used by some of the devices services.
There are six distinct generation methods (denoted by the selected 'File Type').
- Simple - generates and signs a set of 2048 bit certificate and key files that include:
- Certificate Authority (CA)
- Server certificate & key
- Client certificate & key
- DH Parameters
- CA - generates a Certificate Authority (CA) file. A CA is a type of certificate file that certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. In other words, it assures clients that they are connecting to a trusted server and vice versa.
- Server - generates a server certificate and key. A server certificate validates a server's identity to connecting clients, while a key is responsible for encryption.
- Client - generates a client certificate and key. A client certificate validates a client's identity to the server that it's connecting to, while a key is responsible for encryption.
- DH Parameters - generates a Diffie-Hellman (DH) parameters file. DH parameters are used in symmetric encryption to protect and define how OpenSSL key exchange is performed.
- Let's encrypt - generates SSL certificate.
- SCEP - generates SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) certificate.
Generation Parameters
Generating each type of file requires setting some parameters. This section provides an overview for parameters used in Simple and TLS certificate generation.
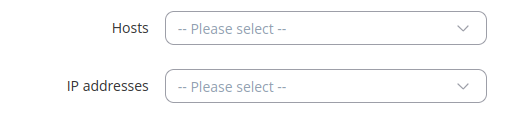
Simple file parameters
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hosts | string; default: none | Appends hostnames to certificates. |
| IP addresses | IPv4 address; default: none | Appends IPv4 addresses to certificates. |
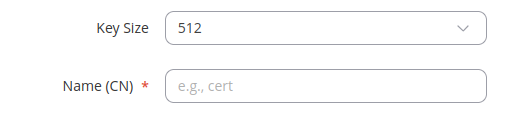
TLS parameters or simply parameters that apply to each (CA, Server, Client, DH) file type are the size and common name of the generated file(s).
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Key Size | integer; default: 2048 | Generated key size in bits. Larger keys provide more security but take longer to generate. A 2048 bit is the preferred option. |
| Name (CN) | string; default: cert | Common Name (CN), aka Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is a parameter that defines the name of the certificate. It should be chosen with care as it is not only used for easier management. For example, the Common Name should typically hostname of the server. It may also be used to differentiate clients in order to apply client-specific settings. |
Subject information is not mandatory but can be used as user-friendly way to identify the ownership of certificate files by including such information as the owner's location and company name.
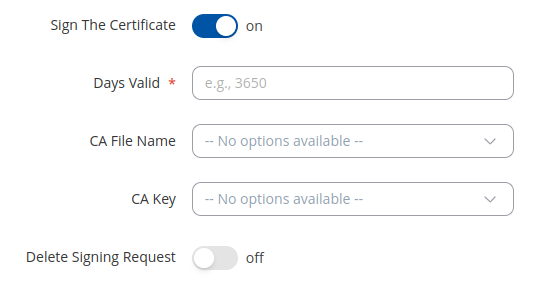
The Sign the certificate slider control whether the certificate will be signed automatically or manually after the generation is complete.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Days Valid | integer; default: 3650 | Length of the signature's validity. |
| CA File Name | filename; default: none | Selects which CA file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| CA key | filename; default: none | Selects which CA key file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| Delete Signing Request | off | on; default: off | Generation creates additional 'signing request' files (which appear under the Certificate Manager tab) that are later used to sign the generated certificates. When this option is set to 'on', the device deletes the signing request files after the signing process is complete. |
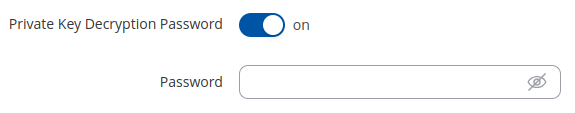
A Private Key Decryption Password is a parameter used to decrypt private keys protected by a password.
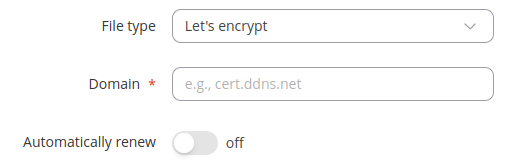
Let's encrypt - This section provides an overview of the parameters used to generate SSL certificates.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Domain | domain name; default: none | Hostname that is linked to the device's public IP address. |
| Automatically renew | off | on; default: off | Certificates will be automatically renewed every 60 days. |
SCEP - This section provides an overview of the parameters used to create certificates for the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Key Size | 512 | 1024 | 2048 | 4096 | ; default: none | Certificate key size. |
| Common name | string; default: none | Common name of the certificate. |
| SCEP server URL | url; default: none | URL of the SCEP server. |
| Challenge | string; default: none | It's recommended to use a high-entropy shared-secret authentication string, such as a base64-encoded key from EAP or DNP3-SA protocols, for the initial SCEP certificate generation. |
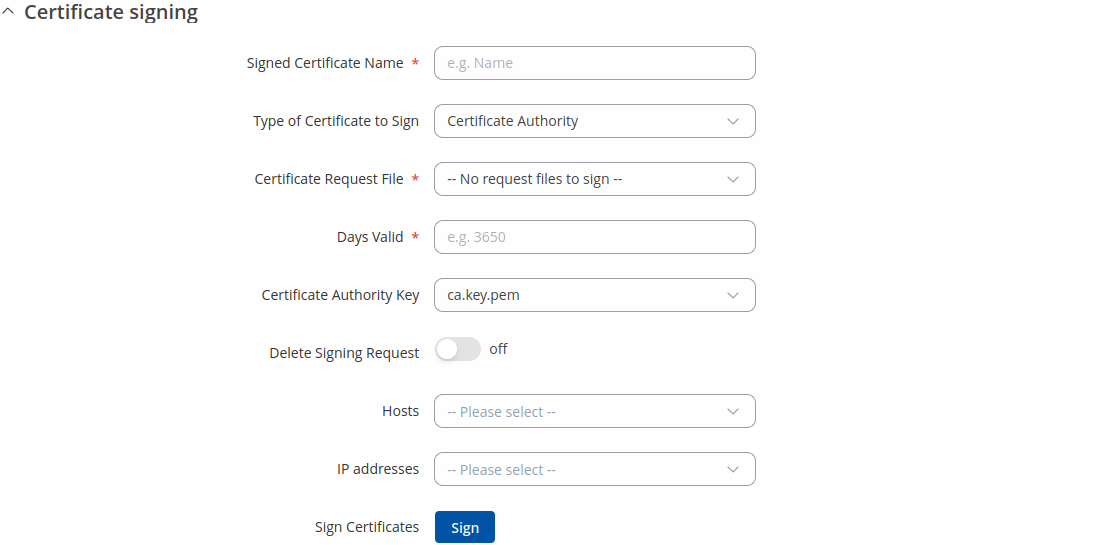
Certificate Signing
The Certificate Signing section is used to validate (sign) unsigned certificates.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Signed Certificate Name | string; default: none | Name of the signed certificate. |
| Type of Certificate to Sign | Certificate Authority | Client Certificate | Server Certificate; default: Certificate Authority | Specifies what type of file will be signed. |
| Certificate Request File | file; default: none | Specifies the signing request file linked to the certificate. |
| Days Valid | integer; default: none | Length of the signature's validity. |
| Certificate Authority File | filename; default: none | Selects which CA file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| Certificate Authority Key | filename; default: none | Selects which CA key file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| Delete Signing Request | off | on; default: off | Generation creates additional 'signing request' files (which appear under the Certificate Manager tab) that are later used to sign the generated certificates. When this option is set to 'on', the device deletes the signing request files after the signing process is complete. |
| Hosts | string; default: none | Appends hostnames to certificates. |
| IP addresses | IPv4 address; default: none | Appends IPv4 addresses to certificates. |
| Sign | - (interactive button) | Signs the certificate on click. |
Certificate Manager
The Certificate Manager page displays information on all certificate and key files stored on the device and provides the possibility export these files for use on another machine or import files generated elsewhere.
Certificate Import
The Certificate Import section provides the possibility to import certificates and files generated on another machine. To upload such a file simply click 'Browse' and locate the file on your computer, it should then start uploading automatically.
Certificates, Keys & Requests
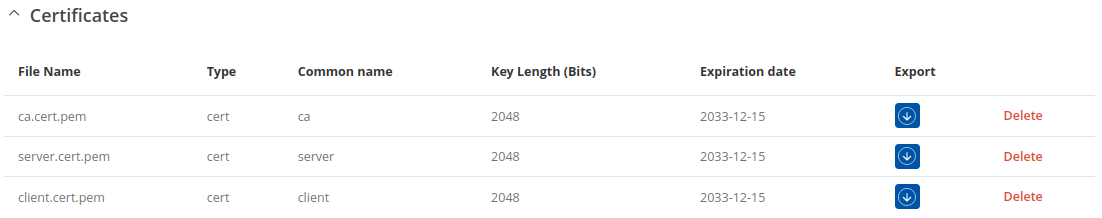
The Certificates, Keys and Requests section display files generated on or imported to the device along with the most important information related to them.
By default, the lists are empty. A set certificates generated using 'Simple' file type would look something like this:
The 'Export' buttons are used to download the files from the device onto your local machine. The 'X' buttons located to the right of each entry are used to delete related files.
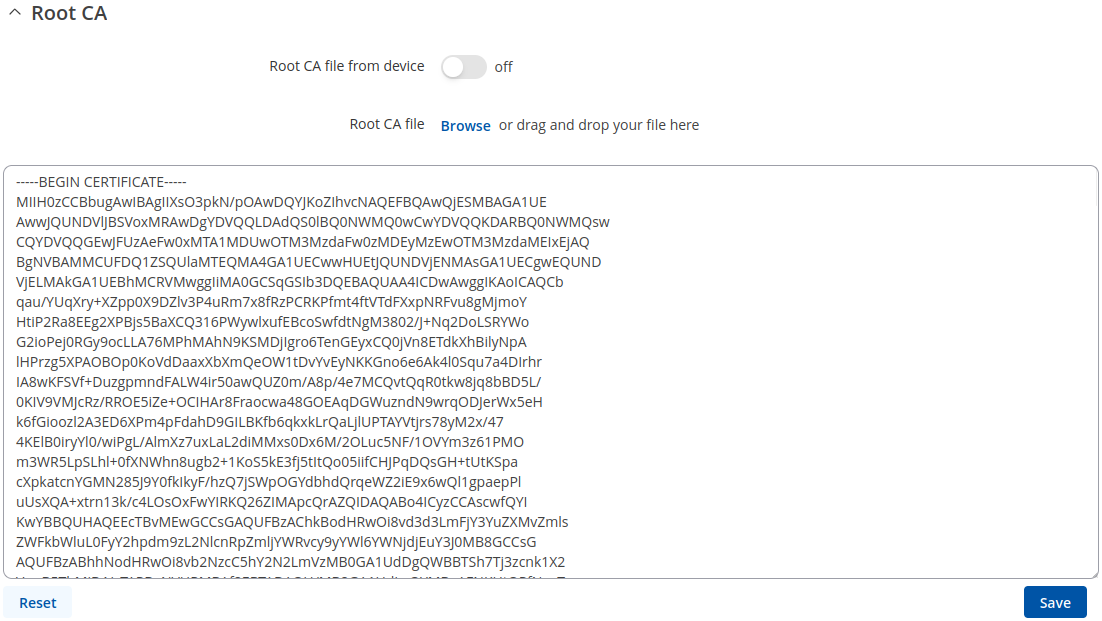
Root CA
The Root CA section is used to add a root CA certificate file to the device. There is a default file already preloaded on the device which will be overwritten by any uploaded file. The certificates must be in .pem format, maximum file size is 10 KB. These certificates are only needed if you want to use HTTPS for your services and the default file should be sufficient in most cases.
Profiles
Summary
Configuration profiles provide a way to create multiple distinct device configuration sets and apply them to the device based on current user requirements. This chapter is an overview of the Profiles page in NTP001 devices.
Configuration Profiles
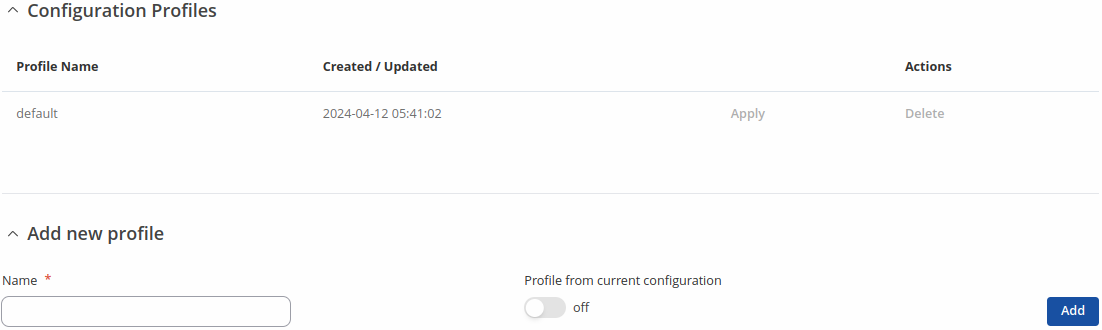
This section displays user defined configuration profiles:
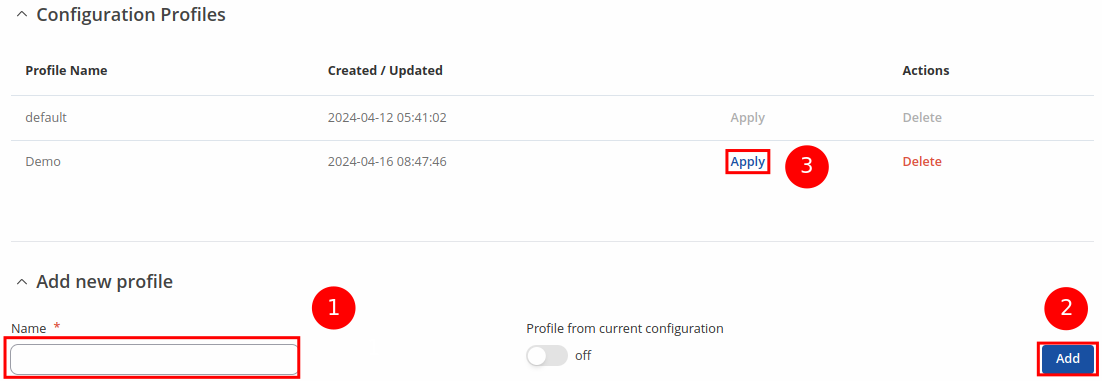
To create a new profile, configure the device in accordance with your needs, go to this page, enter a custom name for the profile and click the 'Add' button. You can also choose to create a profile without any previous configurations. A new profile with the given name will appear in the "configuration profiles" list:
The 'Apply' button applies the adjacent configuration on the device.
Scheduler
The Profile Scheduler provides a possibility to set up a schedule of when the device should use one profile configuration or another.
Check Profile Scheduler Instance Example to get a better understanding at how Profile Scheduler Instances works.
General Configuration
The General Configuration section is used to enable the Scheduler itself. Created instances won't work unless this option is turned on.
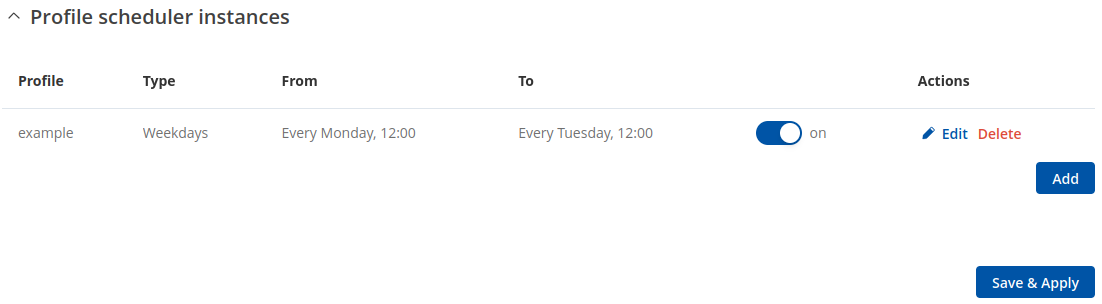
Profile Scheduler Instances
The Profile Scheduler Instances section allows you to create profile Instances to be enabled during specific time intervals. To add a new Instance click Add button.
Note: new Instance can only be created if there is at least one custom profile created.
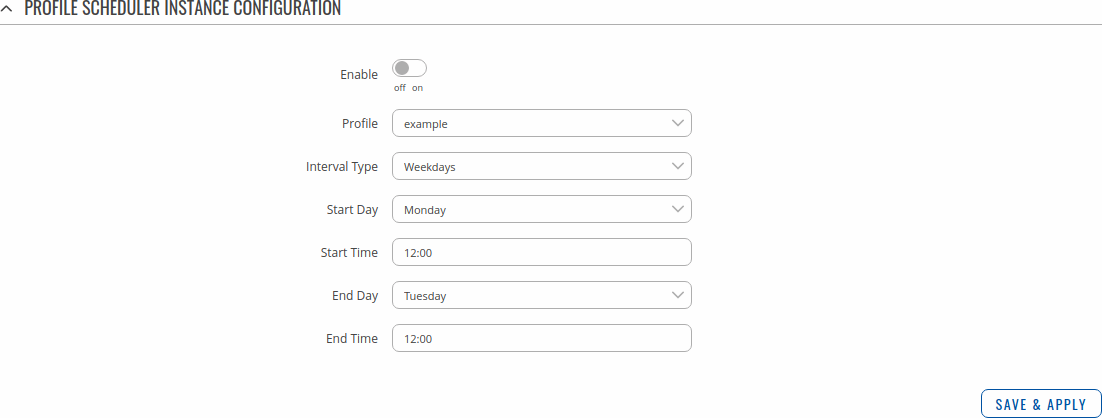
Profile Scheduler Instance Configuration
This page is used to configure profile, time and day of selected scheduler instance. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Profile Scheduler Instance Configuration fields:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enable selected instance for scheduler. |
| Profile | profiles; default: none | Select profile which will be applied during specified time interval. |
| Interval Type | Weekdays | Month Days; default: Weekdays | Depending on your needs select whether you want to configure weekdays or specific month days. |
| Start Time | time; default: 12:00 | Enter time of the start of interval in which scheduler will switch profiles. |
| End Time | time; default: 12:00 | Enter time of the end of interval in which scheduler will switch profiles back. |
| Interval Type: Weekdays | ||
| Start Day | Weekday [Monday..Sunday]; default: Sunday | Select a day of the start of interval in which scheduler will switch profiles. |
| End Day | Weekday [Monday..Sunday]; default: Sunday | Select a day of the end of interval in which scheduler will switch profiles back. |
| Interval Type: Month Days | ||
| Start Day | Day of month [1..31]; default: 1 | Select a day of the start of interval in which scheduler will switch profiles. |
| End Day | Day of month [1..31]; default: 1 | Select a day of the end of interval in which scheduler will switch profiles back. |
| Force last day | off | on; default: off | Force intervals to accept last day of month as valid option if selected day doesn't exist in ongoing month. |
Profile Scheduler Instance Example
Scheduler will use profile instance if it is enabled and it's time interval matches device's date, otherwise default profile will be used.
Example - we have 3 profiles in total:
- default
- Profile A
- Profile B
We create profile instances for Profiles A and B:
- Profile A: 08:00 - 11:00
- Profile B: 13:00 - 20:00
During 11:00 - 13:00 and 20:00 - 08:00 default profile will be used.