RUT230 Graphs (legacy WebUI)
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version RUT2XX_R_00.01.14.7.
Notice: This device has entered it's EOL (End of Life) cycle. For more information, visit our EOL policy here. Temporarily, some content in this page might not match features found in firmware listed above.
Note: this user manual page is for RUT230's old WebUI style available in earlier FW versions. Click here for information based on the latest FW version.
Summary
The Graphs page contains various graphs that display various statistical data changes in real time.
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Graphs page for RUT230 devices.
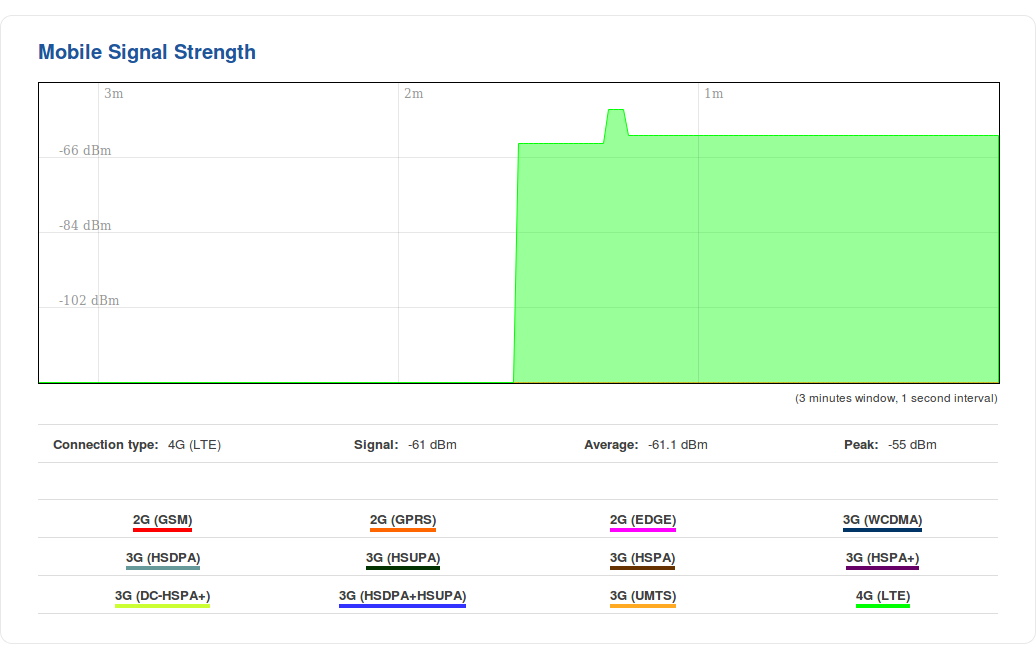
Mobile Signal
The Mobile Signal Strength graph displays mobile signal strength (RSSI, measured in dBm) value changes over a period of 3 minutes. The figure below is an example of the Mobile Signal Strength graph:
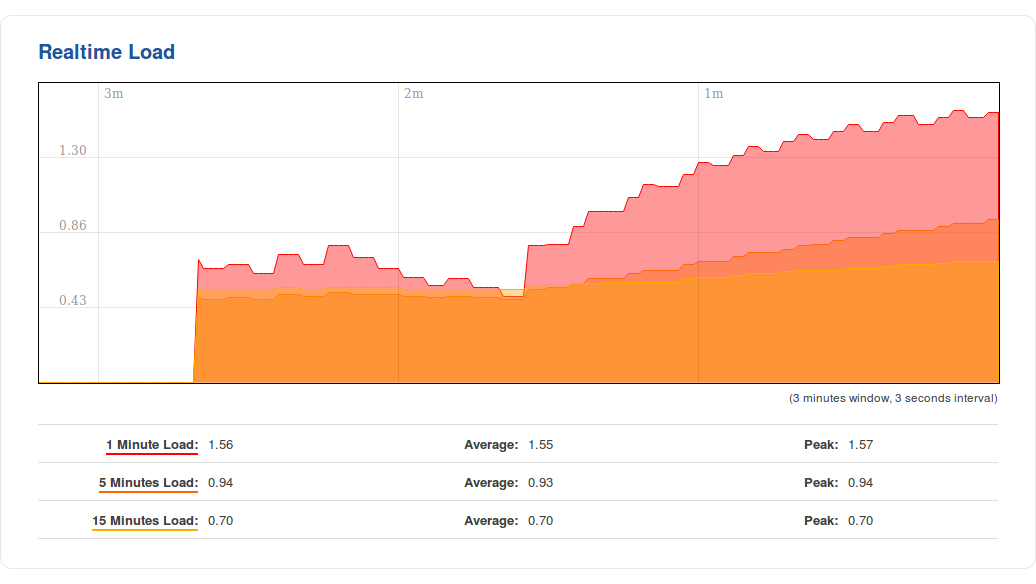
Load
The Realtime Load section displays a tri-graph that illustrates average CPU load values in real time. The graph consists out of three color coded graphs, each one corresponding to the average CPU load over 1 (red), 5 (orange) and 15 (yellow) most recent minutes.
The figure below is an example of the Realtime Load graph:
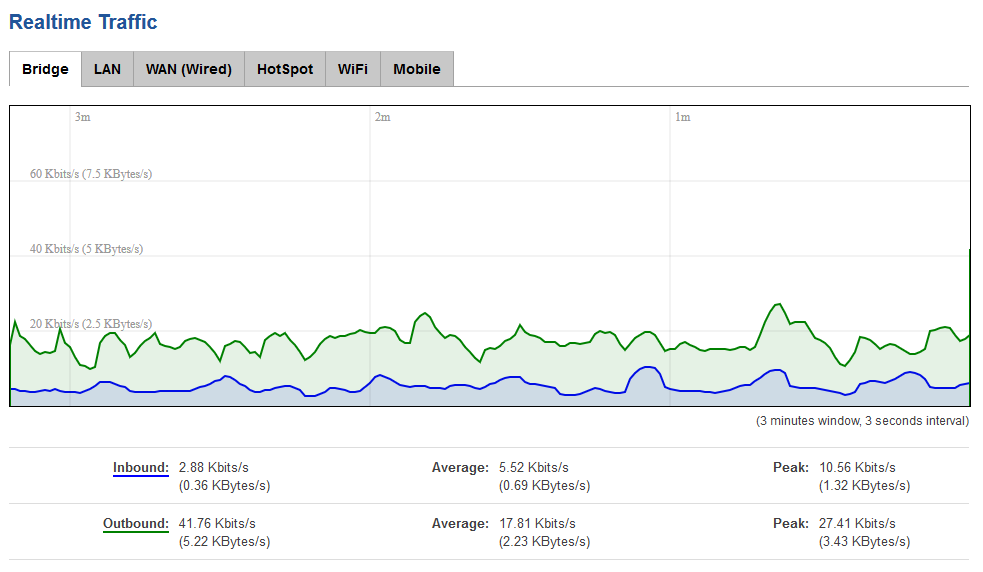
Traffic
The Realtime Traffic graphs provide users with the possibility to monitor average inbound and outbound traffic over the course of 3 minutes; each new measurement is taken every 3 seconds. The graphs consist out of two color coded graphs: the green graph shows the outbound traffic, the blue graph shows the inbound traffic. Although not graphed, the page also displays peak loads and averages of inbound and outbound traffic.
The figure below is an example of the Realtime traffic graph for the Bridge connection:
| GRAPH | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Bridge | Cumulative graph, which encompasses wired Ethernet LAN and the wireless network |
| LAN | Displays traffic that passes through the LAN network interface(s) in graph form |
| WiFi | Displays traffic that passes through the WiFi interface in graph form |
| WAN (Wired) | WAN (WiFi) | Mobile | Displays traffic that passes through the current active WAN connection in graph form |
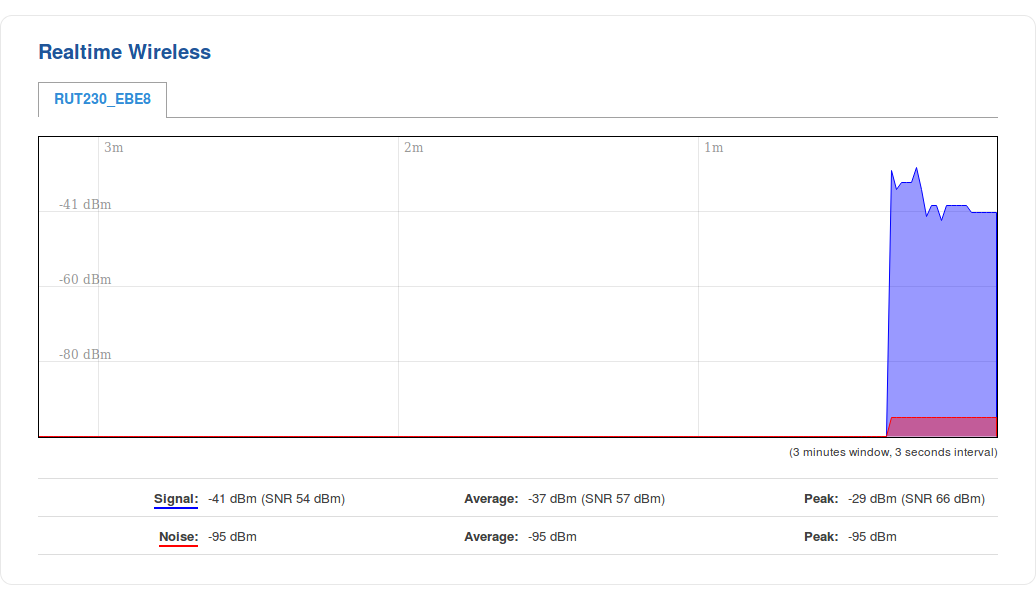
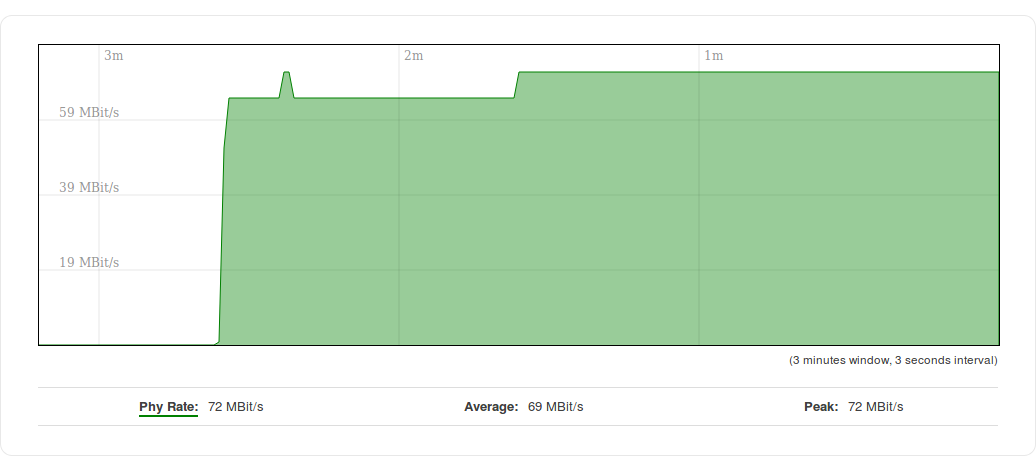
Wireless
The Realtime Wireless graph displays the wireless radio signal strength, signal noise, average and peak signal levels and the theoretical maximum channel permeability. The graph below the WiFi signal graph displays the Phy Rate for the wireless connection.
The figures below are examples of both Wireless graphs:
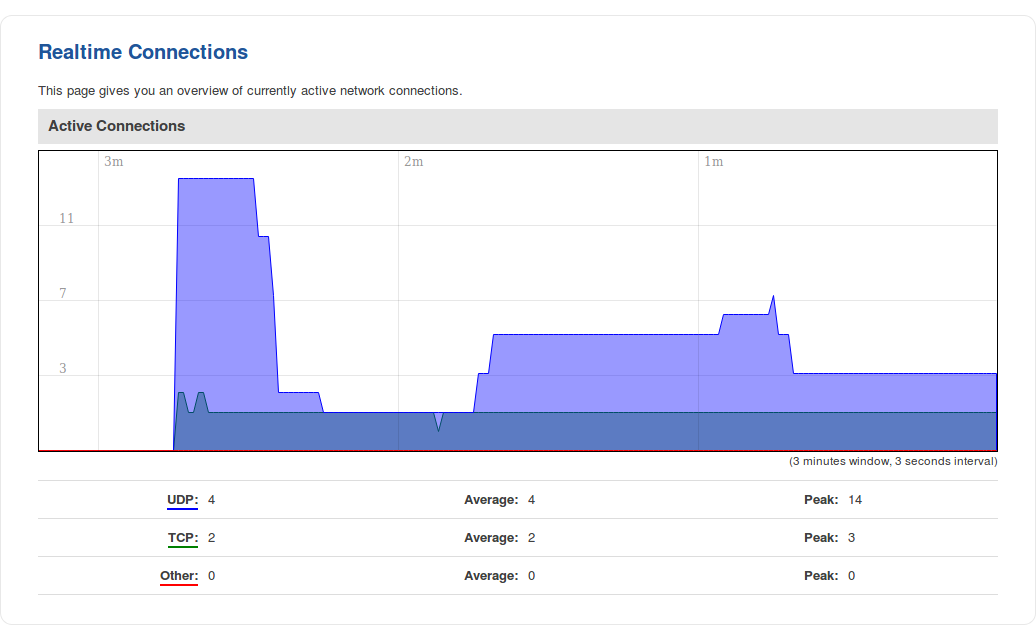
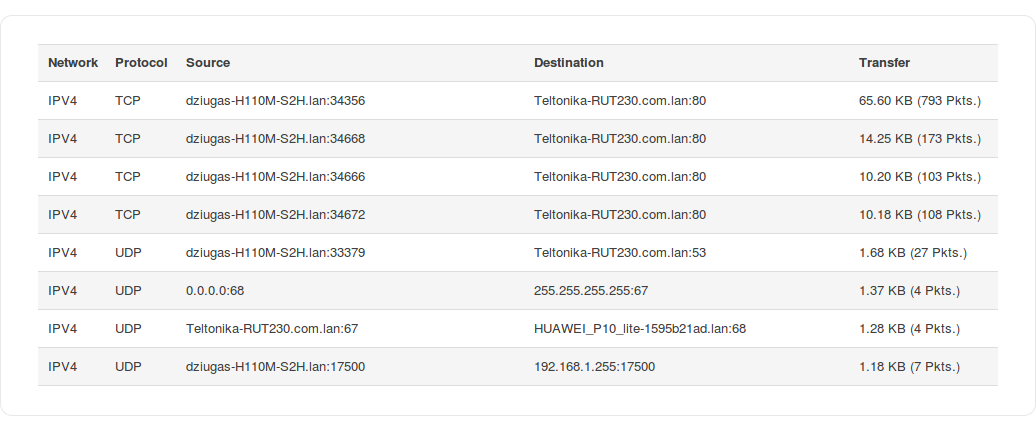
Connections
The Realtime Connections graph displays currently active network connections with the information about network, protocol, source and destination addresses and transfer speed. The table below the graph displays basic information on active connections.
The figures below are examples of both of the Realtime Connections graph and the corresponding table: