RUT2xx NordVPN configuration example
NordVPN is a personal virtual private network (VPN) service provider. It is supported on various different devices and RUT2xx routers are one of those.
Introduction
This article contains step-by-step instructions on how to set up NordVPN VPN connection using RUT2xx routers.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- One RUT2xx router
- An end device to configure the router (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone)
- NordVPN account and subscription
Please bear in mind that from June 14th, 2023, you will no longer be able to use your NordVPN email/username and password to authenticate your connection, and you will need to set up service credentials manually on your Nord Account. More details about the changes to the login process can be found here.
Choosing and downloading server files
In order to setup your router to connect to NordVPN server you will need to download OVPN configuration files. Those can be found at NordVPN website. It is necessary to choose a server which can provide the best possible performance, visit this website and it will automatically show you which server will provide you the best experience. Also when it comes to choosing TCP or UDP you need to decide what you are trying to achieve. TCP is reliable, data sent using this protocol is guaranteed to be delivered to the receiver. If data is lost in transit it will recover the data and resend it. TCP will also check packets for errors and track packets so that data is not lost or corrupted, but that effects internet speed. UDP is unreliable, it does not provide guaranteed delivery and a datagram packet may become corrupt or lost in transit, but you will get greater internet speed.
RUT2xx configuration
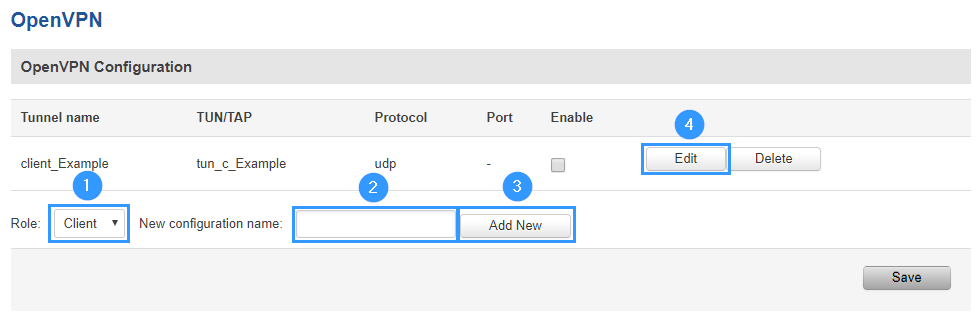
Access RUT2xx WebUI and go to Services > VPN > OpenVPN. There create a new configuration by selecting role Client, writing New configuration name and pressing Add New button. It should appear after a few seconds. Then press Edit.
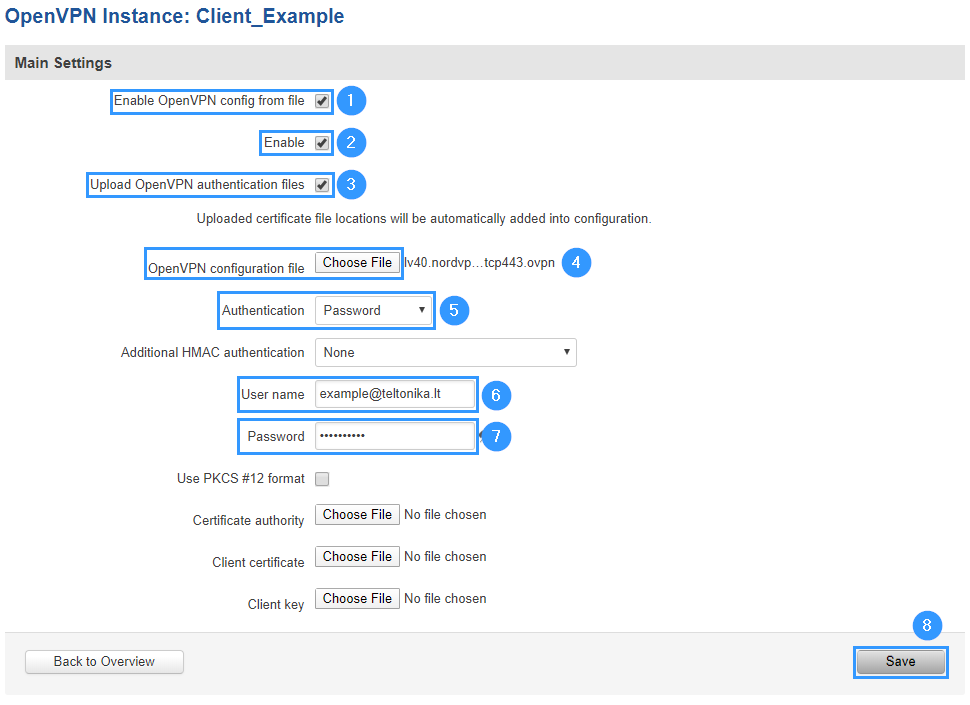
Now apply the following configuration.
- Enable OpenVPN config from file feature.
- Enable instance.
- Allow Upload OpenVPN authentication files.
- Upload OpenVPN configuration file (the one you downloaded from NordVPN website).
- Set Authentication to Password.
- NordVPN service username.
- NordVPN service password.
- Press Save.
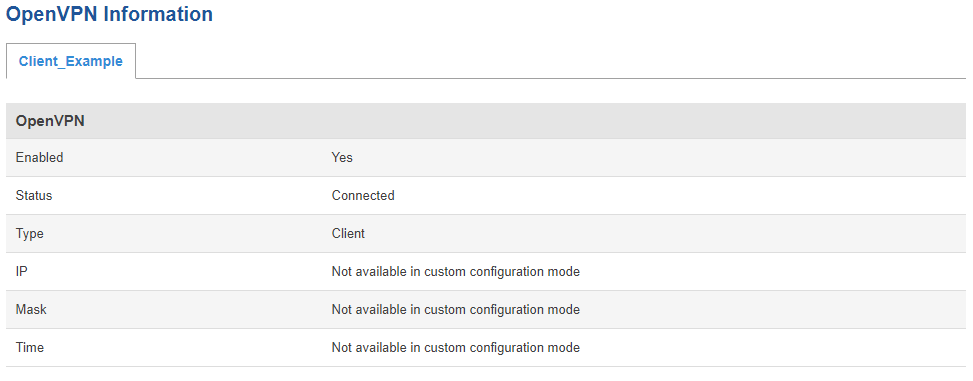
You will be forwarded back to OpenVPN configuration window.
You can check whether you applied the configuration correctly. Go to Status > Network > OpenVPN it should indicate as Connected. (It might not connect instantly so please wait for a moment).
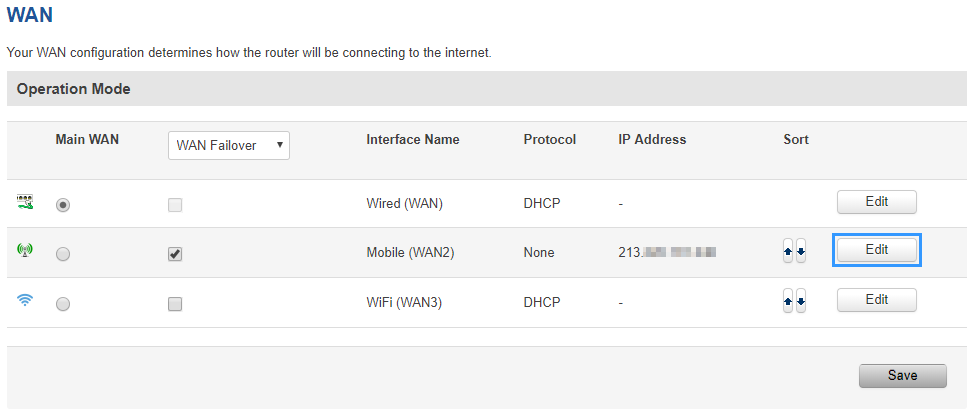
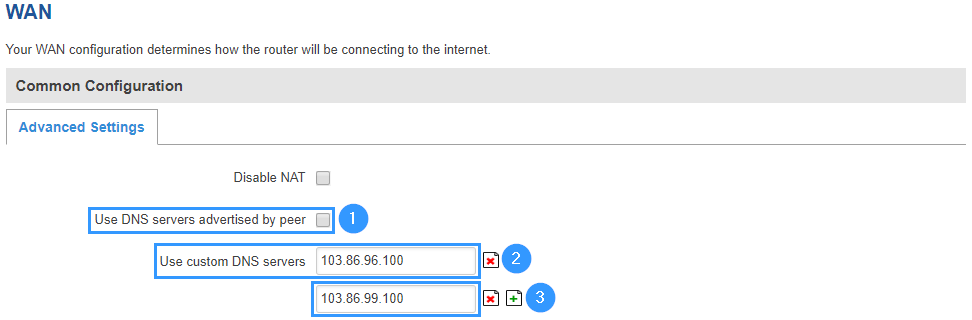
Now you need to configure your router to use NordVPN DNS servers. In order to do that go to Network > WAN, there click Edit on a WAN source you are using (in this example we used mobile WAN source).
Now to set DNS servers follow the steps below.
- Disable DNS servers advertised by peer.
- Add first DNS server: 103.86.96.100.
- Add second DNS server: 103.86.99.100.
- Press Save & Apply.
Testing configuration
If configured correctly all of your internet traffic now should go through VPN server. One of the easiest ways to check whether everything is working correctly is to check whether your public IP address has changed. You can do so by simply visiting a website such as www.whatismyipaddress.com and comparing your IP address before and after you connect to server also there you can find information about IP location, so when you connect to server it should change to a different address/country. Or you can visit NordVPN website and there on the very top of the website you can indicate whether you are protected or not.
External links
Disclaimer:
Any of the trademarks, service marks, collective marks, design rights or similar rights that are mentioned, used or cited in the articles are the property of their respective owners.