WireGuard Configuration Example
The information in this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.17.4 firmware version.
Introduction
WireGuard is a modern, lightweight, and secure VPN solution that relies on trusted cryptography. This guide provides an example of setting up a basic WireGuard tunnel between two Teltonika devices.
Prerequisites
For this example you need:
Expected Outcome
A tunnel will be established between RUTX50 (WG1) and RUTX14 (WG2). The assigned tunnel IP addresses will be:
- WG1 (server): 172.16.10.1
- WG2 (client): 172.16.10.2
WG1 (Server) configuration
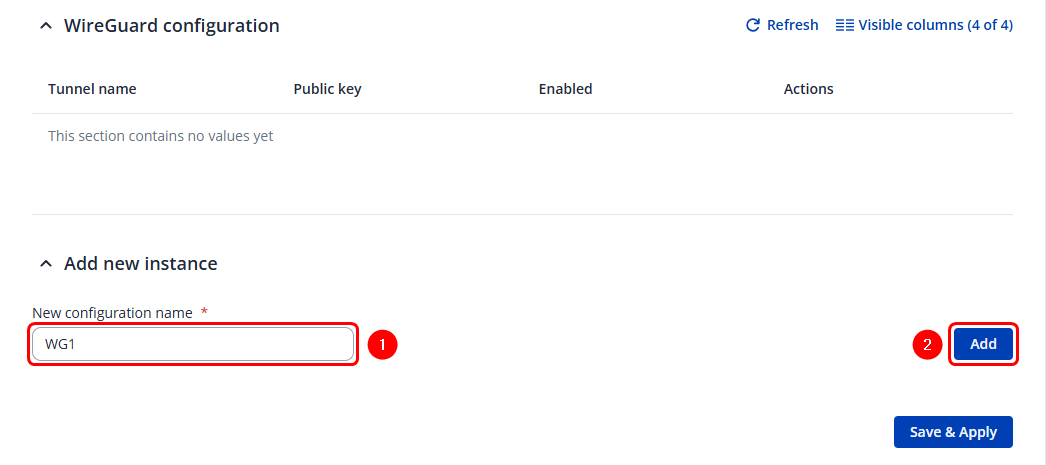
Creating new wireguard instance
To create Instance:
Instance configuration
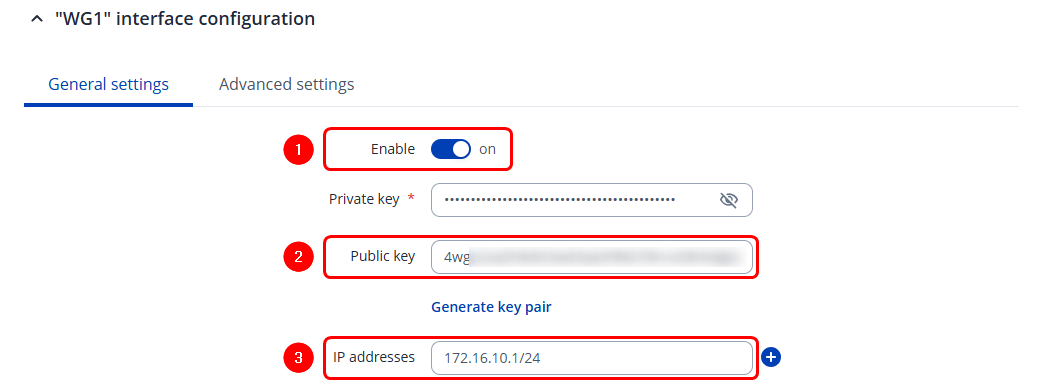
In the pop-up configuration window, open the General settings tab:
- Enable the instance
- Copy the Public Key (make sure to copy all of it), this will be required in WG2 (client) configuration
- Enter Wireguard IP address for this device
Peer configuration
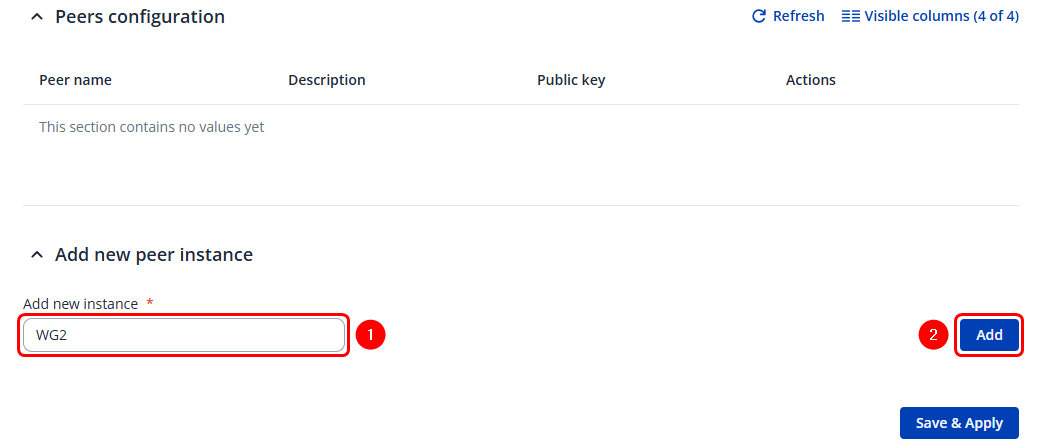
The next step is to configure the Peers that this instance will connect to.
To create a Peer:
In the pop-up configuration window, select the General settings tab:
- Enter the Public Key of the WireGuard peer device
- Enter the WireGuard tunnel IP address for the peer device (WG2) in the Allowed IPs section
- Add an additional Allowed IPs entry if you want to reach Peer device's (WG2) LAN subnet (optional)
- Enable "Route alowed IPs"
- Save the configuration
WG2 (Client) configuration
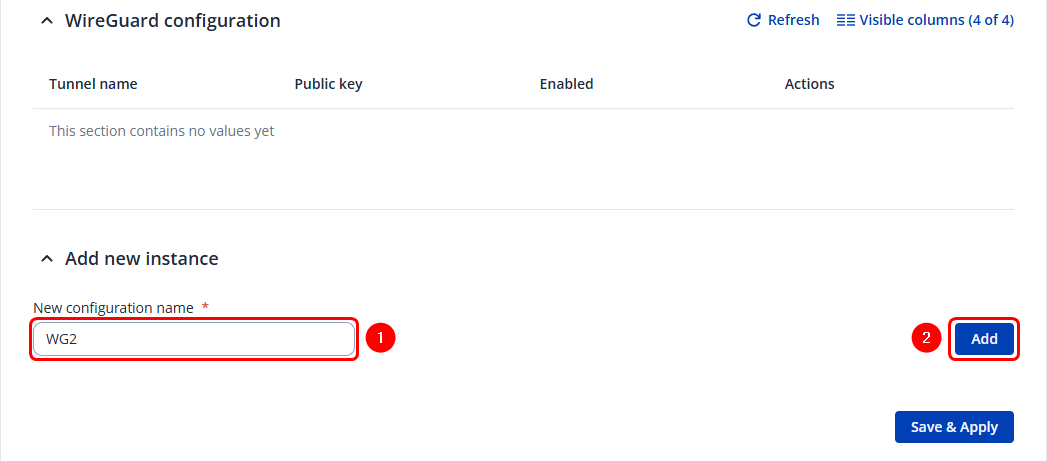
Creating new wireguard instance
To create Instance:
Instance configuration
In the pop-up configuration window, select the General settings tab:
- Enable the instance
- Copy the Public Key (make sure to copy all of it), this will be required in WG1 (server) configuration
- Enter Wireguard tunnel IP address for this device
Peer configuration
The next step is to configure the Peers that this instance will connect to.
To create a Peer:
In the pop-up configuration window, select the General settings tab:
- Enter the Public Key of the WireGuard peer device
- Enter the Public IP address of the WireGuard peer/server (WG1)
- Enter the WireGuard tunnel IP address for the peer device in the Allowed IPs section
- Add Allowed IPs entry if you want to reach Peer device's (WG2) LAN subnet (optional)
- Enable "Route alowed IPs"
- Save the configuration
Testing Configuration
To check the Wireguard tunnel connection and test it you need to open Command Line Interface and log in.
Once in the Command Line, enter the following command:
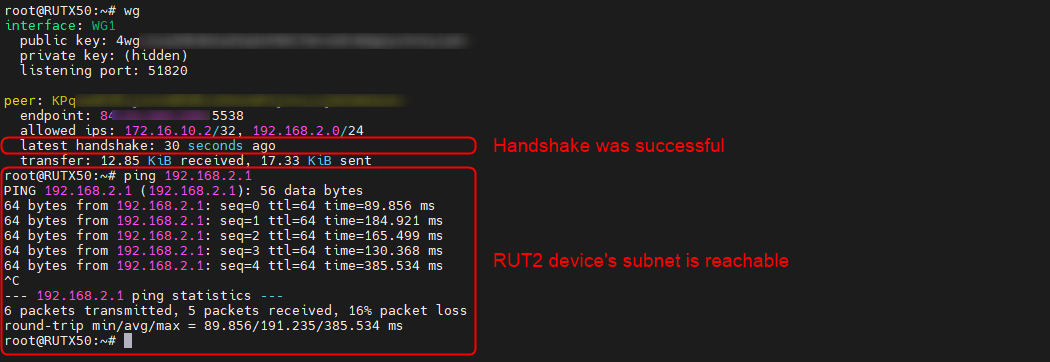
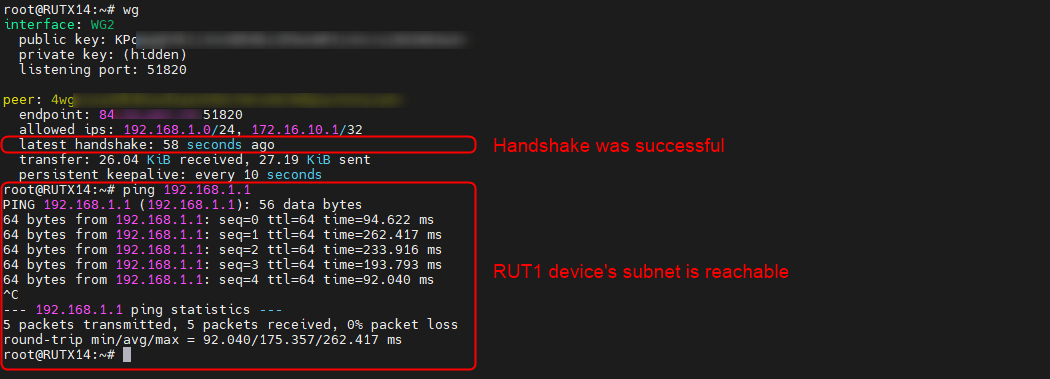
wg
If the latest handshake line is visible, it indicates that a connection between your devices has been successfully established. Furthermore, if the peer’s LAN subnet IP was added to the Allowed IPs section, you should also be able to ping devices within that subnet.
WG1:
WG2: