Monitoring via JSON-RPC linux RutOS
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.4 firmware version .
Introduction
JSON-RPC is a remote procedure call protocol encoded in JSON. It is a very simple protocol (and very similar to XML-RPC), defining only a few data types and commands. JSON-RPC allows for notifications (data sent to the server that does not require a response) and for multiple calls to be sent to the server which may be answered out of order.
This article provides a guide on how to use JSON-RPC on RUTxxx routers.
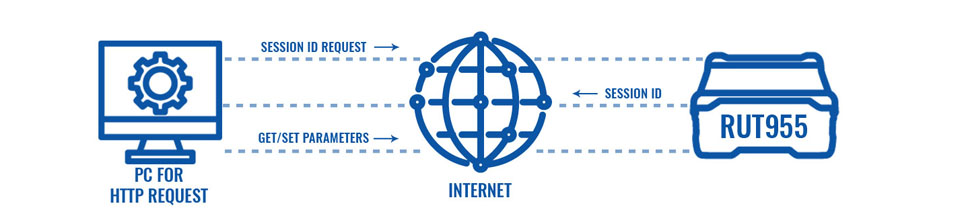
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- A PC with HTTP request software.
- An Internet connection. (This example is based on a local configuration, but also can be used via wired WAN or a remote installation with Public IP)
- One RUTxxx series router.
Using JSON-RPC (Linux)
This section describes how to use JSON-RPC commands with a Linux OS system. To find the guide for Windows users, jump to this section here.
Obtaining a session ID
To log in to the router via JSON-RPC you must first obtain a Session ID. To do so, you must send an HTTP POST request to the router. Open the Linux Terminal app and execute this command:
curl -d "{ \"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [ \"00000000000000000000000000000000\", \"session\", \"login\", { \"username\": \"admin\", \"password\": \"admin01\" } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
The section highlighted in orange is the router's admin password. admin01 is the default value, replace it with your router's password. The address highlighted in green is the router's IP address. Replace this value with your router's IP. If you're trying to reach the router from LAN, use the local IP address (default: 192.168.1.1), if you're trying to reach the router from WAN, use the router's WAN IP address.
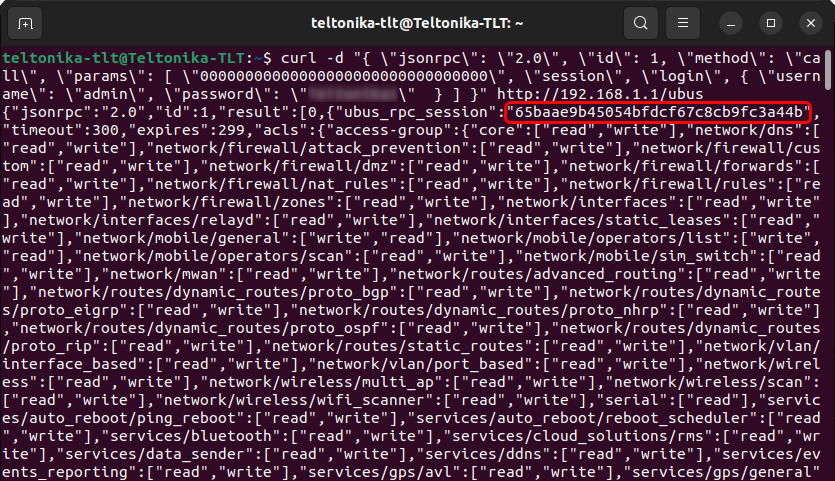
The picture above depicts the process of obtaining a Session ID. The ID itself is encapsulated in a red rectangle. Copy this ID as you will need it to authenticate yourself when using other commands.
Getting router parameters
Now that you have obtained a Session ID, you can issue commands to the router. Lets start with commands that return information about the router.
Getting signal levels
This is a command that returns the router's signal levels value:
curl -d "{ \"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [\"a74c8e07646f0da2bfddce35bf3de1f3\", \"file\", \"exec\", { \"command\":\"gsmctl\", \"params\": [\"-q\"] } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
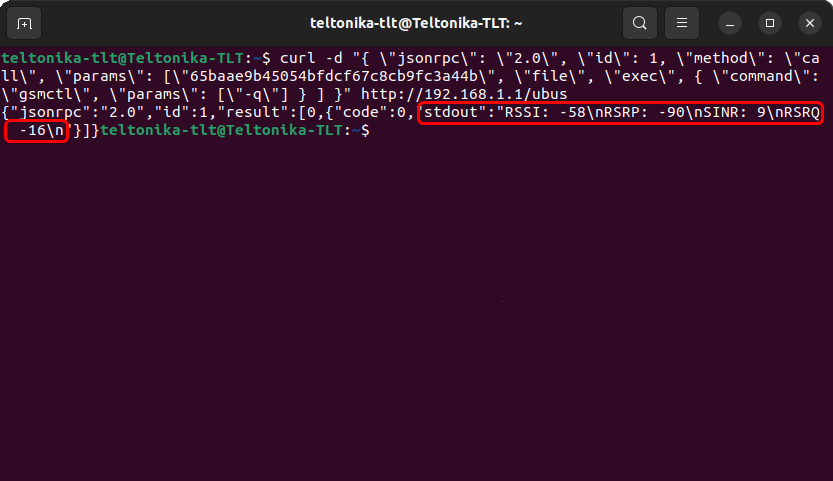
Highlighted in red is the Session ID. Replace it with the Session ID that was provided to you. Highlighted in orange is the command that we used for our query and highlighted in green is the parameter for the command: gsmctl -q.
The picture bellow is a visual representation of this example. Encapsulated in a red rectangle is the answer to the gsmctl -q:
You can issue almost any Linux command in a similar manner. For example, if you wish to get a list of file names contained in the config folder, the Linux command to do so would be ls /etc/config, which, translated to JSON-RPC, would be:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [\"a74c8e07646f0da2bfddce35bf3de1f3\", \"file\", \"exec\", {\"command\":\"ls\", \"params\": [\"/etc/config\"] } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
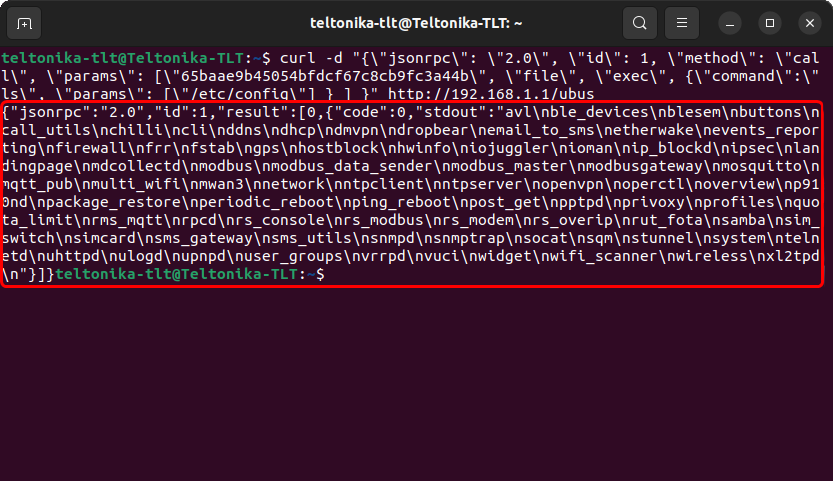
The answer is encapsulated in an red rectangle.
Setting router parameters
This section will describe how to use uci set commands in order to set or change various router parameters via JSON-RPC. For more general information about the usage and syntax of UCI commands, check out our UCI command usage guide.
UCI SET
The uci set command is used to set router parameters. As an example, lets try to change the router's LAN IP address. The command to do so looks like this:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\", \"id\":1, \"method\":\"call\", \"params\":[\"590bde71578da2fabfe77ba86c00e4e5\", \"uci\", \"set\", { \"config\":\"network\", \"type\":\"interface\", \"match\": {\"ipaddr\":\"192.168.1.1\"}, \"values\": {\"ipaddr\":\"192.168.11.1\"} } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
The sections highlighted in orange describe the config file's name and section (in this case, network config and interface section). Highlighted in red is the option in the config file that you wish to change (in this case, the router's LAN IP address, ipaddr). Finally, highlighted in green is the value that will to replace the old value (in this case, change the router's LAN IP address to 192.168.11.1). If the command was issued successfully, you should see a Response like this:
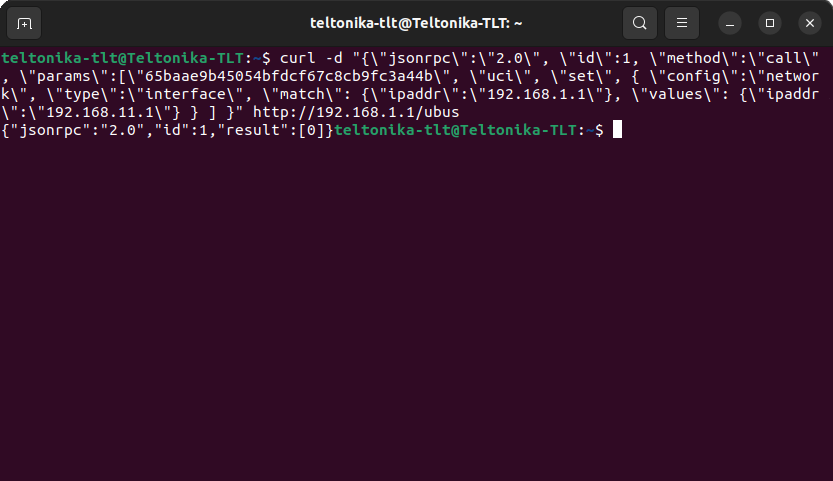
UCI COMMIT
In order to commit the changes from RAM to flash memory, you must execute a uci commit command. Continuing from the example above, lets commit the changes made to the network config. The command to do so looks like this:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\", \"id\":1, \"method\":\"call\", \"params\":[\"9704f676709d9dedc98d7718c4e3e7d2\", \"uci\", \"commit\", {\"config\":\"network\"} ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
When committing changes, you will need to specify the name of the file where the changes took place (in this case, network, which is highlighted in orange). If the commit was successful, you should see the same message as before:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0]}
RELOAD_CONFIG
In order for the changes to take effect, use the reload_config command which restarts all of the router's services. The reload_config command looks like this:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\",\"id\":1, \"method\":\"call\", \"params\":[\"428a9fa57f1a391db0bd1b865fa16bb5\", \"file\", \"exec\", {\"command\": \"reload_config\"} ] }" http://192.168.56.1/ubus
The command itself is highlighted in orange.
Setting Multiple Parameters
This next example describes how to set multiple parameters in a single config file with one command. Lets change the default configuration of the Ping Reboot function (ping_reboot config file):
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\", \"id\":1, \"method\":\"call\", \"params\":[\"558a9b03c940e52f373f8c02498952e3\", \"uci\", \"set\", {\"config\":\"ping_reboot\", \"match\":{\"enable\":\"0\", \"host\":\"8.8.8.8\", \"packet_size\":\"56\"}, \"values\":{\"enable\":\"1\", \"host\":\"8.8.4.4\", \"packet_size\":\"64\"} } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
The command above will enable the Ping Reboot function, set the host to ping to 8.8.4.4 and ping packet size to 64. The default values are highlighted in orange and the new ones are highlighted in green.
Note: Remember always to use the commands in the order (set, commit, reload_config)
Some Additional Commands
If the commands found in the guide above did not suffice your needs, this section provides a list of additional ones. The commands presented in this section will be for both Linux and Windows operating systems. They should be used as syntax examples for your own purposes.
WiFi clients list
This command returns a list of devices connected to your WLAN and some additional information about the connection.
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "call", "params":
[
"86fc586fa1471622473434ff0176fd66", "iwinfo", "assoclist",
{
"device":"wlan0"
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{ \"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [ \"86fc586fa1471622473434ff0176fd66\", \"iwinfo\", \"assoclist\", {\"device\":\"wlan0\"} ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
The response should look something like this:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0,{"results":
[{"mac":"E4:02:9B:XX:XX:XX","signal":-32,"noise":-88,"inactive":10,"rx":
{"rate":1000,"mcs":0,"40mhz":false,"short_gi":false},"tx":
{"rate":72200,"mcs":7,"40mhz":false,"short_gi":true}},
{"mac":"D8:C7:71:XX:XX:XX","signal":-12,"noise":-88,"inactive":400,"rx":
{"rate":1000,"mcs":0,"40mhz":false,"short_gi":false},"tx":
{"rate":72200,"mcs":7,"40mhz":false,"short_gi":true}}]}]}
To obtain these values, the Linux iwinfo command and assoclist parameter (red) are used. Highlighted in green are the devices connected to the router via WiFi as identified by their MAC addresses. The response information about the connection with the device, such as signal strength, noise, time of inactivity (idle time), rx, tx rate, etc., is highlighted in blue.
WiFi information
This command returns information on your WiFi Access Point.
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "call", "params":
[
"a70ceeba344b6046625d8bcec132796c", "iwinfo", "info",
{
"device":"wlan0"
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{ \"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [ \"a70ceeba344b6046625d8bcec132796c\", \"iwinfo\", \"info\", {\"device\":\"wlan0\"} ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
Response:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0,
{"phy":"phy0","ssid":"HAL9000","bssid":"00:1E:42:XX:XX:XX","country":"00","mode":"Master","channel":6,"frequency":2437,"txpower":20,
"quality":22,"quality_max":70,"signal":22,"noise":-61,"bitrate":72200,"encryption":
{"enabled":false},"hwmodes":["b","g","n"],"hardware":{"name":"Generic MAC80211"}}]}
As with the clients list command described above, to obtain this information the Linux iwinfo command is used, but this time with the info parameter (red). The relevant information, such as WiFi SSID, WiFi MAC address, WiFi channel, Encryption type, etc., is highlighted in blue
Manufacturing information
This command returns information about the device's manufacturing details like device's Product Code, Serial Number MAC Address, etc.
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "call", "params":
[
"805725a19ab0fba6c2b44ecf2f952fb9","file", "exec",
{
"command":"mnf_info", "params":["--name", "--batch"]
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{ \"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [ \"805725a19ab0fba6c2b44ecf2f952fb9\",\"file\", \"exec\",{ \"command\":\"mnf_info\", \"params\":[\"--name\", \"--batch\"] } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
Response:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0,{"code":0,"stdout":""RUT955003XXX\n0105\n001e4216d666\n"}]}
To obtain the manufacturing information the mnf_info (highlighted in red) command is used. In this case a query was sent asking for the device's Product Code (name), Serial Number (sn) and MAC Address (mac) (highlighted in red in the query; returned values highlighted in blue). Using mnf_info, you can "ask" the router for any type of manufacturing information. Here is the list of possible mnf_info parameters:
- --mac - returns the router's LAN MAC address
- --maceth - returns the router's WAN MAC address
- --name - returns the router's Product Code
- --wps - returns the router's WPS PIN number
- --sn - returns the router's Serial number
- --batch - returns the router's Batch number
- --hwver - returns the router's Hardware Revision number
- --simpin - returns the router's SIM card's PIN (as it is specified in the Mobile section)
- --blver - returns the router's Bootloader version
GPS Data
This command returns the device's GPS GPS latitude and longitude.
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "call", "params":
[
"456f77f6b686bf5972daa3a26bee60b0","file", "exec",
{
"command":"gpsctl", "params":["-ix"]
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\",\"id\":1,\"method\":\"call\",\"params\":[\"5363304b3ed4ee0806f101295fc52e93\",\"file\",\"exec\",{\"command\":\"gpsctl\",\"params\":[\"-ix\"]}]}" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
Response:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0,{"code":0,"stdout":"-23.612625\n-46.626355\n"}]}
The blue part in the code are the Latitude and Longitude.
Firmware number
This command returns the device's Firmware version number.
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "call", "params":
[
"85ea4cb00398d8387b22d8fa6f75f753", "file", "read",
{
"path":"/etc/version"
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{ \"jsonrpc\": \"2.0\", \"id\": 1, \"method\": \"call\", \"params\": [ \"85ea4cb00398d8387b22d8fa6f75f753\",\"file\", \"read\",{ \"path\":\"/etc/version\"} ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
Response:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0,{"data":"RUTXXX_R_00.07.02.0\n"}]}
This command (file, read, highlighted in red) is an alternative to the Linux cat command. All you need is to specify the path (in this case /etc/version, highlighted in red) to the file that you wish to read.
Reboot
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"call","params":
[
"5cd4b143b182c07bc578ae3310d6280e","file","exec",
{
"command":"reboot","params":["config"]
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\",\"id\":1,\"method\":\"call\",\"params\":[\"5cd4b143b182c07bc578ae3310d6280e\",\"file\",\"exec\",{\"command\":\"reboot\",\"params\":[\"config\"]}]}" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
Response: The success response for this command is an empty message. If the response contains no data, the command was executed successfully.
Set SIM card information
In this last example we'll try to change the mobile connection's MTU and Service mode values.
Windows:
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0", "id":1, "method":"call", "params":
[
"558a9b03c940e52f373f8c02498952e3", "uci", "set",
{
"config":"simcard", "type":"sim1", "match":
{
"service":"auto",
"mtu":"1500"
},
"values":
{
"service":"lte-only",
"mtu":"1476"
}
}
]
}
Linux:
curl -d "{\"jsonrpc\":\"2.0\", \"id\":1, \"method\":\"call\", \"params\":[\"558a9b03c940e52f373f8c02498952e3\", \"uci\", \"set\", {\"config\":\"simcard\", \"type\":\"sim1\", \"match\":{\"service\":\"auto\", \"mtu\":\"1500\"}, \"values\":{\"service\":\"lte-only\", \"mtu\":\"1476\"} } ] }" http://192.168.1.1/ubus
Response:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":[0]}
The command used is uci set (highlighted in red). The config file name is simcard, section sim1, options mtu and service (configs, sections and options highlighted in orange). The response shown above is a positive response, but don't forget to execute uci commit and reload_config afterwards or else your changes will not take effect.
See Also
You may learn more about UCI commands here.