RUTX QinQ configuration
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.19.4 firmware version .
Introduction
QinQ, also known as VLAN stacking or IEEE 802.1ad, is a networking technique that allows multiple VLAN tags to be inserted into a single Ethernet frame. This enables service providers and enterprise networks to transport customer VLAN traffic transparently across a shared infrastructure without altering the original VLAN configuration.
In a QinQ scenario, a Customer VLAN (C-VLAN) tag is preserved, while an additional Service VLAN (S-VLAN) tag is added by the provider network. This approach significantly expands VLAN scalability and simplifies network segmentation, especially in multi-tenant, metropolitan, and industrial environments.
QinQ is commonly used in scenarios where traffic from different customers, sites, or departments must be isolated while being carried over the same backbone network. Typical applications include ISP aggregation networks, industrial automation, smart grid deployments, and large enterprise interconnections.
Teltonika Networks devices that support QinQ can be configured to operate as edge or transport devices, enabling seamless VLAN encapsulation, traffic separation, and interoperability with existing Layer 2 infrastructures.
Topology
QinQ Basic Configuration
Port Based VLAN configuration
Step 1: Create and assign Customer and Service VLANs on the physical ports
The first step is to create and assign the Customer VLAN (C-VLAN) and the Service VLAN (S-VLAN) to their corresponding physical interfaces.
In this use case example:
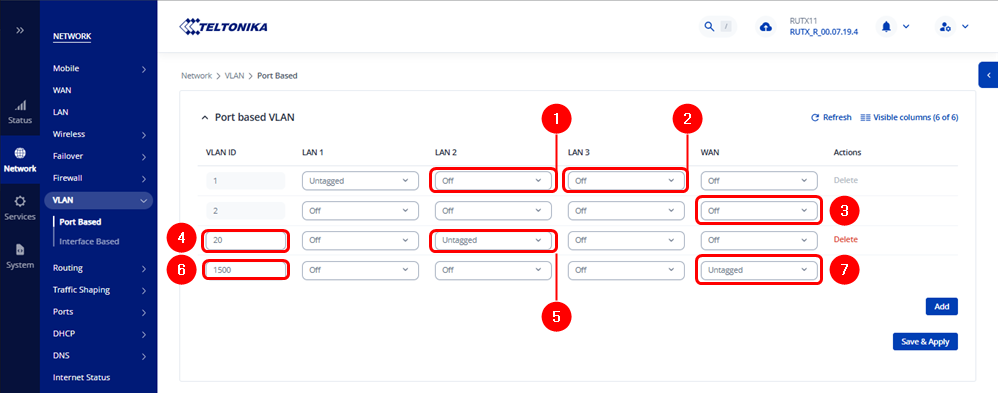
- VLAN 20 is used as the Customer VLAN (C-VLAN) and is assigned to the LAN2 port.
- VLAN 1500 is used as the Service VLAN (S-VLAN) and is assigned to the WAN port.
Note: If more than one Customer VLAN (C-VLAN) is required, each VLAN can be assigned to a different physical port in untagged (access) mode, or multiple C-VLANs can be carried over the same port using tagged (trunk) mode.
To properly create and assign the VLANs, please locate the following path: WebUI → Network → VLAN → Port Based, and follow the standard VLAN configuration procedure described here and use the image below as a reference.
Interface Based VLAN configuration
Step 2: QinQ encapsulation configuration
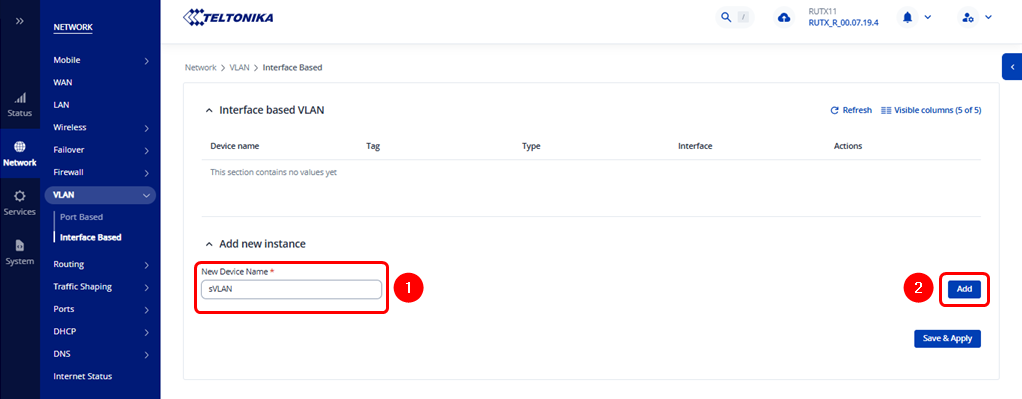
Navigate to the following path: WebUI → Network → VLAN → Interface Based, and add a new instance belonging to the Service VLAN (sVLAN) as shown below:
Then, configure the Service VLAN (S-VLAN) tag, set the protocol/type to 802.1ad, and select the appropriate parent interface.
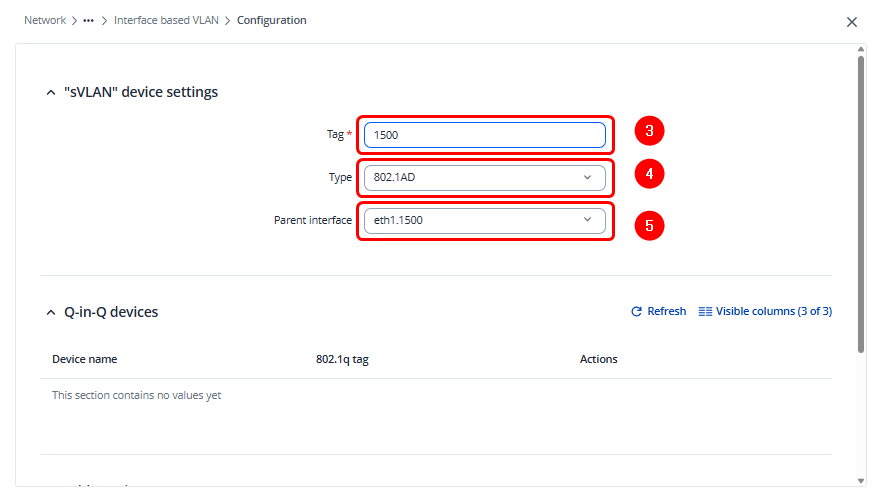
Note: On RUTX series devices, the Service VLAN (S-VLAN) must be selected as the parent interface in the format eth1.XXXX. On RUT series devices, the only available option is eth0.XXXX, which must be used as the parent interface for the Service VLAN.
Add a new instance in the Q-in-Q Devices section. For clarity, it is recommended to use a naming convention that allows you to easily identify the Customer VLAN, for example: cVLANXX
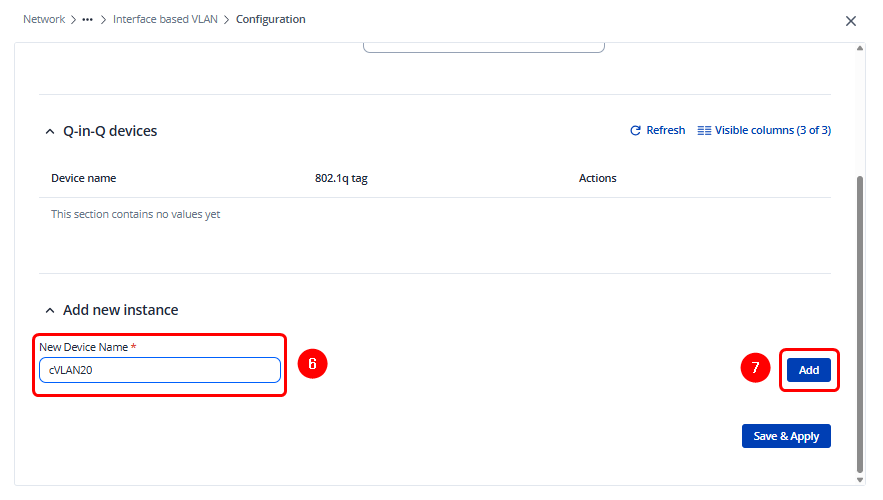
Then, specify the VLAN tag (C-VLAN ID) that will be assigned to this instance and save the configuration.
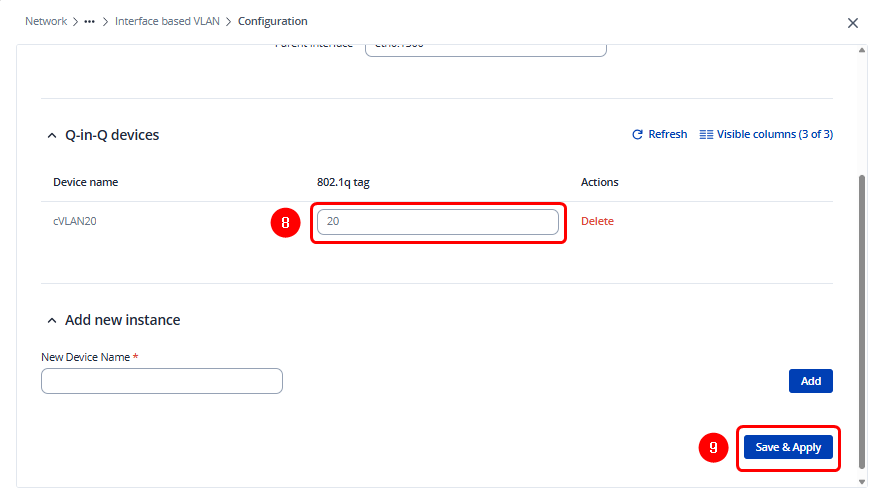
Note: If more than one Customer VLAN (C-VLAN) is required, additional instances must be created.
LAN interface configuration
Step 3: Bind the QinQ interface to the LAN interface
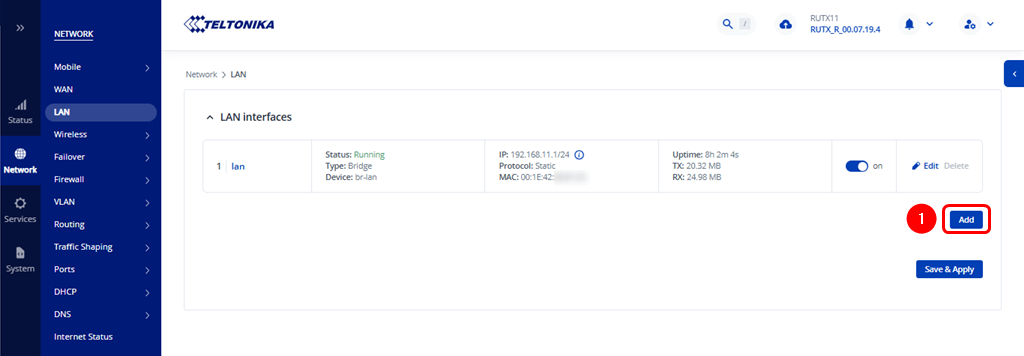
Navigate to WebUI → Network → LAN and add a new LAN instance.
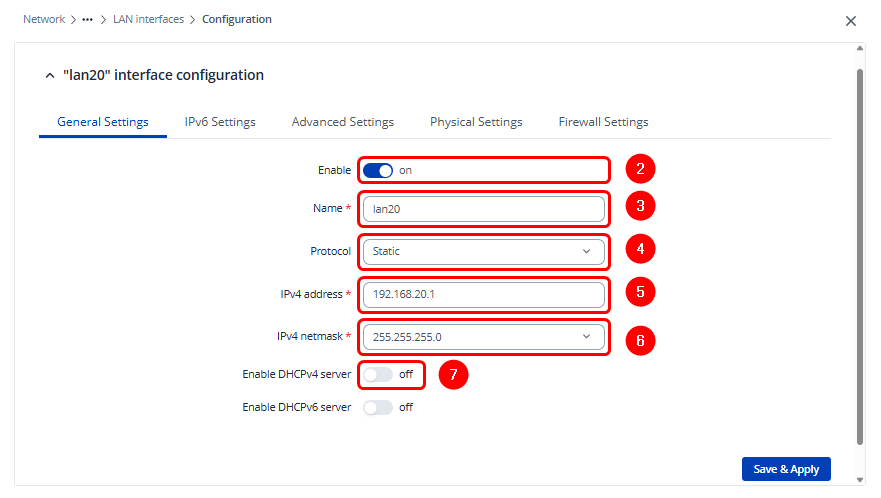
Enable the instance and assign a descriptive name that allows easy identification. Configure the appropriate IPv4 address and netmask, and disable the DHCPv4 server option if the router is not intended to act as a DHCP server.
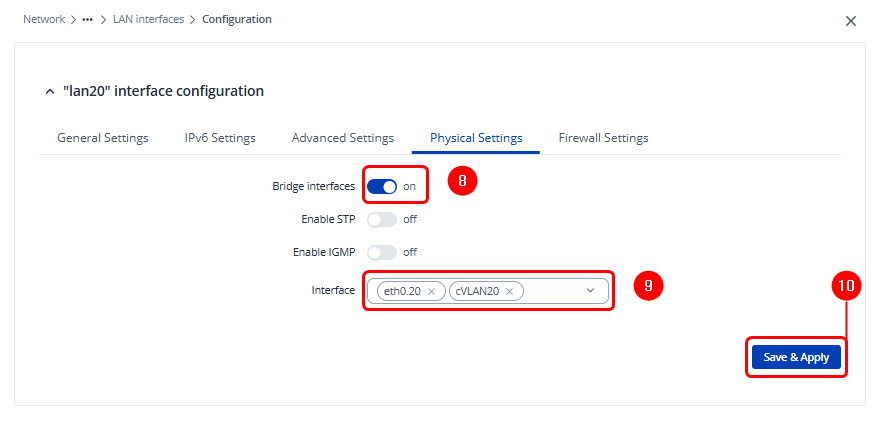
Next, open the Physical Settings tab. Enable the Bridge option and bind together the physical Customer VLAN (VLAN 20) with the interface created during the Q-in-Q encapsulation step. Finally, click Save & Apply to apply the configuration.
WAN interface configuration
Step 4: Bind the Service VLAN to the WAN interface
Browse to WebUI → Network → WAN. Disable the wan6 interface, then edit the wan interface by clicking the Edit button.
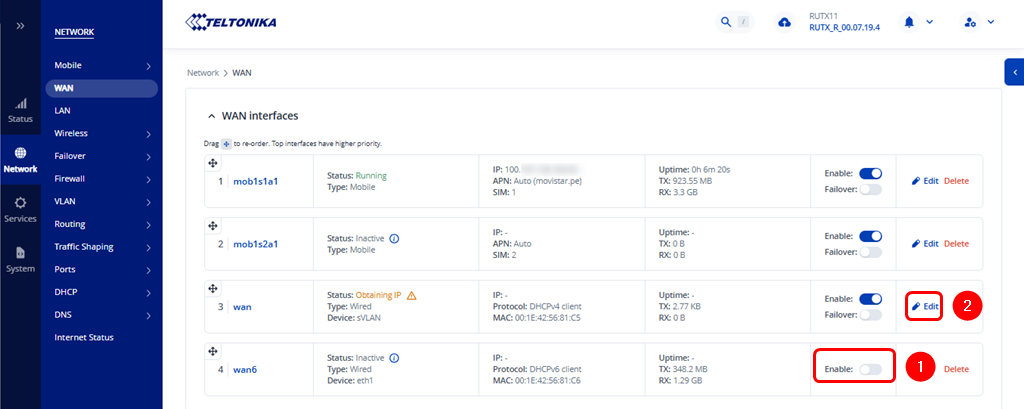
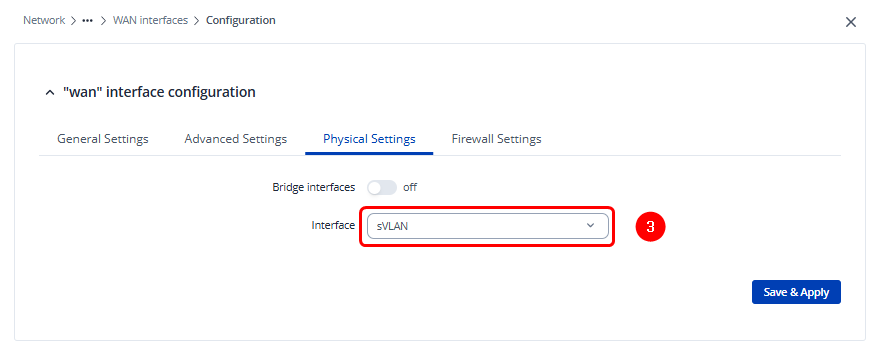
Open the Physical Settings tab and select the previously created Service VLAN (sVLAN) instance in the Interface field.
Next, switch to the Firewall Settings tab and change the Firewall zone to lan. Finally, click Save & Apply to apply the configuration.
Note: For this use case, the WAN General Settings protocol is set to None, as the interface will operate at Layer 2. However, if necessary, the user may modify these settings by following the standard configuration steps described here
Set-up verification
See Also
https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/VLAN_Set_Up
https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/RUTX11_VLAN
https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/RUTX11_LAN
https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/RUTX11_WAN#General_Setup
