Difference between revisions of "RUT955 Modbus"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
'''Modbus TCP''' interface allows the user to set or get router parameters like modem temperature, signal strength, etc. In other words, Modbus TCP allows you to control the router's behavior and get its status information. Modbus daemon acts as slave device. That means it accepts connections from the master (client) and sends out a response or sets some system related parameter. By the default Modbus will only accept connections through LAN interface. In order to accept connections through WAN interface also, Allow Remote Access must be checked. | '''Modbus TCP''' interface allows the user to set or get router parameters like modem temperature, signal strength, etc. In other words, Modbus TCP allows you to control the router's behavior and get its status information. Modbus daemon acts as slave device. That means it accepts connections from the master (client) and sends out a response or sets some system related parameter. By the default Modbus will only accept connections through LAN interface. In order to accept connections through WAN interface also, Allow Remote Access must be checked. | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:Rut9xx webui services modbus modbus tcp v1.png]] |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 5 November 2018
Main Page > RUT Routers > RUT955 > RUT955 Manual > RUT955 WebUI > RUT955 Services section > RUT955 ModbusSummary
Modbus is a serial communications protocol. Simple and robust, it has since become a de facto standard communication protocol and is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices. This chapter is an overview of the Modbus TCP functionality.
Modbus TCP
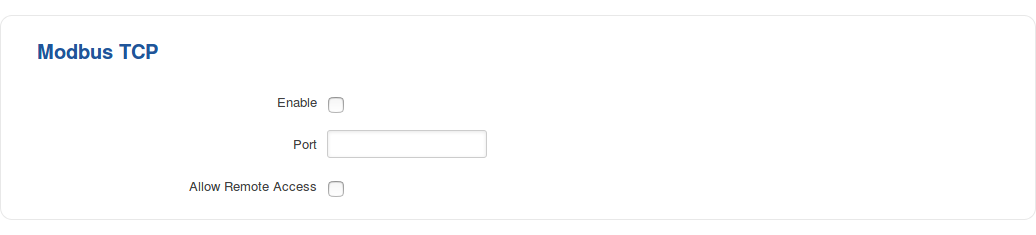
Modbus TCP interface allows the user to set or get router parameters like modem temperature, signal strength, etc. In other words, Modbus TCP allows you to control the router's behavior and get its status information. Modbus daemon acts as slave device. That means it accepts connections from the master (client) and sends out a response or sets some system related parameter. By the default Modbus will only accept connections through LAN interface. In order to accept connections through WAN interface also, Allow Remote Access must be checked.
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles Modbus TCP ON or OFF |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; Default: " " | Specifies which port to use for Modbus connections |
| Allow Remote Access | yes | no; Default: no | If enabled, allows Modbus access from remote devices (from WAN) |
Get Parameters
To obtain parameters from the system, the read holding registers command is used. Router parameters are held within registers. Each register contains 2 bytes of information. For simplification the number of registers for storing numbers is 2, while the number of registers for storing text information is 16. The register numbers and corresponding system values are described below:
| REQUIRED VALUE | REPRESANTATION | REGISTER NUMBERS | NUMBER OF REGISTERS |
|---|---|---|---|
| System uptime | 32 bit unsigned integer | 1 | 2 |
| GSM signal strength (dBm) | 32 bit integer | 3 | 2 |
| System temperature in 0.1 degrees Celcius | 32 bit integer | 5 | 2 |
| System hostname | Text | 7 | 16 |
| GSM operator name | Text | 23 | 16 |
| Router serial number | Text | 39 | 16 |
| Router MAC address | Text | 55 | 16 |
| Router name | Text | 71 | 16 |
| Current SIM card | Text | 87 | 16 |
| Network registration | Text | 103 | 16 |
| Network type | Text | 119 | 16 |
| Digital input 1 | 32 bit integer | 135 | 2 |
| Digital input | 32 bit integer | 137 | 2 |
| Current WAN IP address | 32 bit unsigned integer | 139 | 2 |
| Analog input | 32 bit integer | 141 | 2 |
Set Parameters
The Modbus daemon also supports setting of some system parameters. For this task the Write holding register command is used. System related parameters and how to use them are described below. The register number specifies where to start writing the required values. All commands, except “Change APN”, accepts only one input parameter. For the APN the number of input registers may vary. The very first byte of APN command denotes a number of SIM card for which set the APN. This byte should be set to 1 (in order to change APN for SIM card number 1) or to 2 (in order to change APN for SIM card number 2).
| VALUE TO SET | DESCRIPTION | REGISTER NUMBER | REGISTER VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital output 1 (on/off) | Change the state of the digital output number 1 | 201 | 1/0 |
| Digital output 2 (on/off) | Change the state of the digital output number 2 | 202 | 1/0 |
| Switch WiFi (on/off) | Allows to switch WiFi on or off | 210 | 1/0 |
| Switch mobile data connection (on/off) | Turns mobile data connection on or off | 211 | 1/0 |
| Switch SIM card (SIM1, SIM2, SIM1->SIM2 and SIM2->SIM1) | Allows to change SIM card in use, 3 possible options are supported | 212 | 0/1/2 |
| Change APN | Allows to change APN | 213 | APN code |
| Reboot | Reboots the router | 220 | 1 |
See also
You can find more information on how to use Modbus with RUT routers here: Monitoring via Modbus