How to set up a guest WiFi network
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.14.3 firmware version .
Introduction
Most of us are aware, that network security is critical. If your WiFi network is not properly secured, it makes you and all of your home or office resources vulnerable to a variety of security threats. To stay ahead of the curve, many companies and home users have guest WiFi. Unlike your regular WiFi network that you or your company members use, the guest WiFi network restricts what your guests can do in your network. It gives visitors access to the Internet connection, but nothing else making you or your company a lot more secure. This chapter is a guide on configuring a guest's WiFi.
Configuring the router
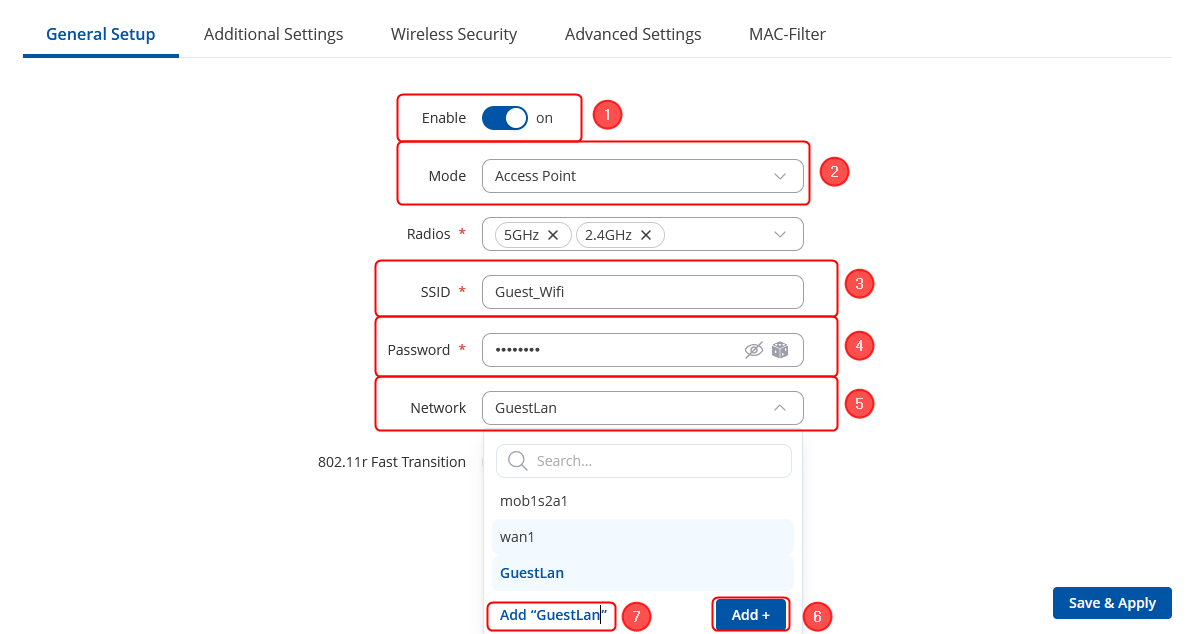
New WiFi AP
 |
|
|---|---|
|
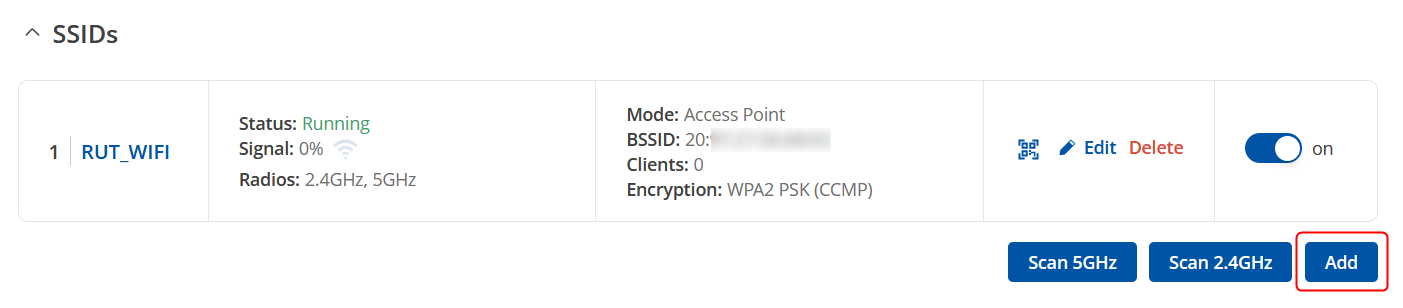
Login to the router's WebUI, navigate to the Network → Wireless → SSIDs page. Click Add. Then you will be forwarded to the configuration window. |
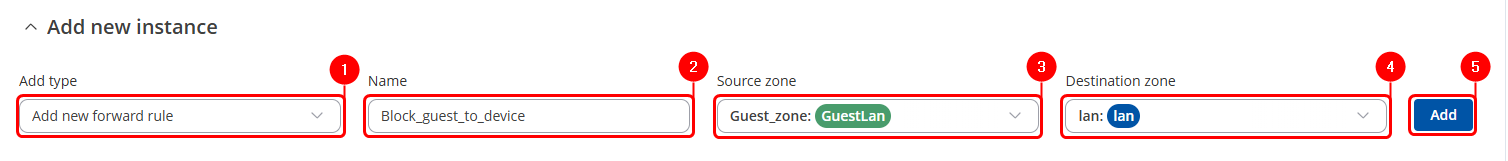
New LAN interface
 |
|
|---|---|
|
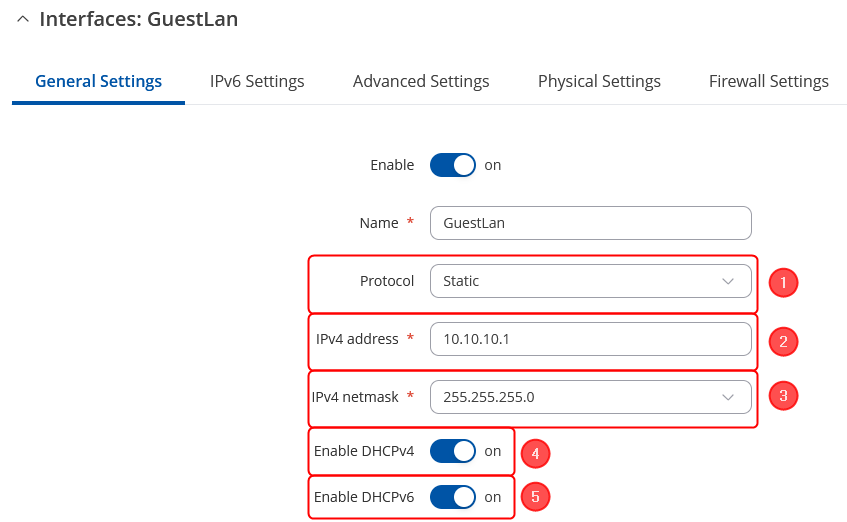
Once you have saved the Wireless interface, a new window should pop-up. Configure it as following:
|
 |
|
|---|---|
|
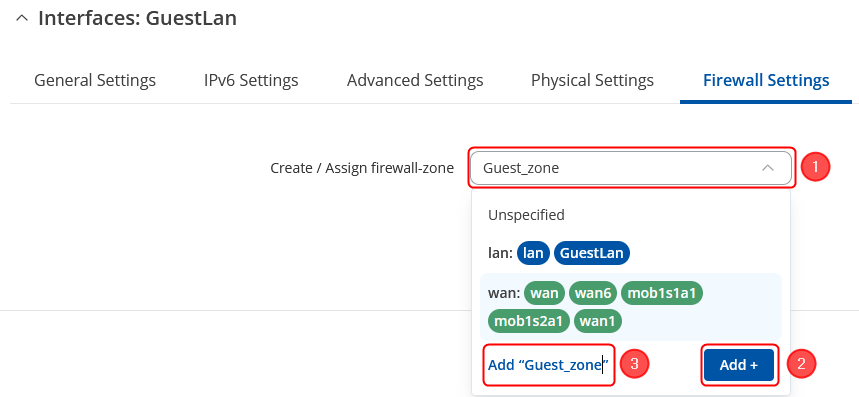
Then move to Firewall Settings section:
Save & Apply changes when done. |
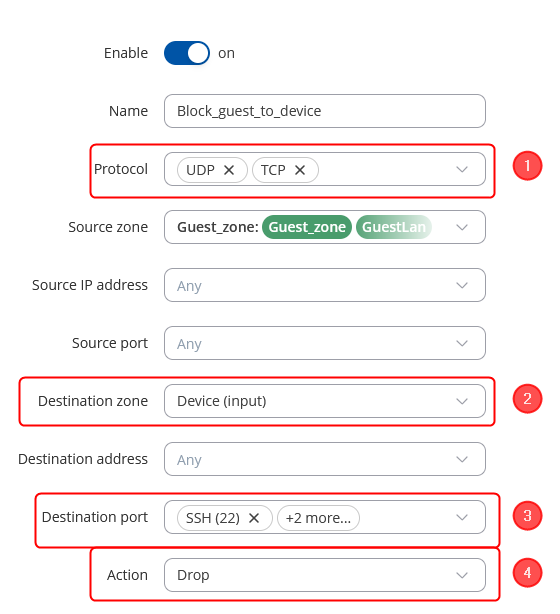
Firewall rules
 |
|
|---|---|
|
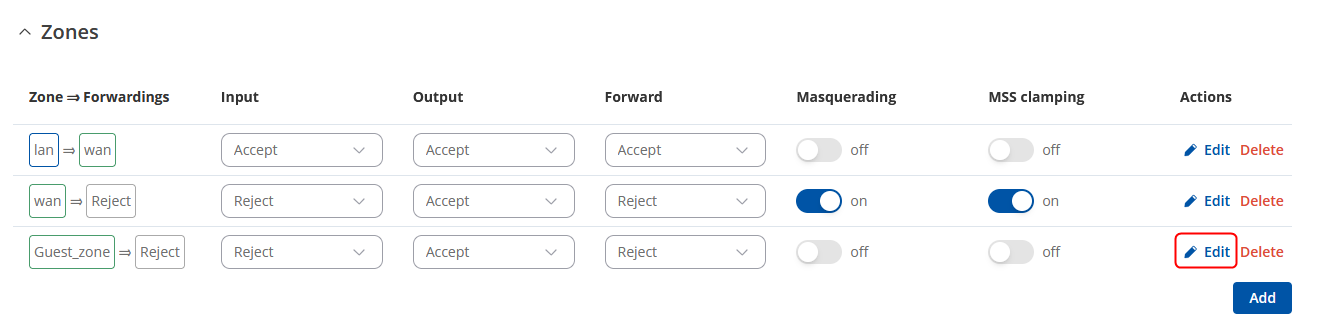
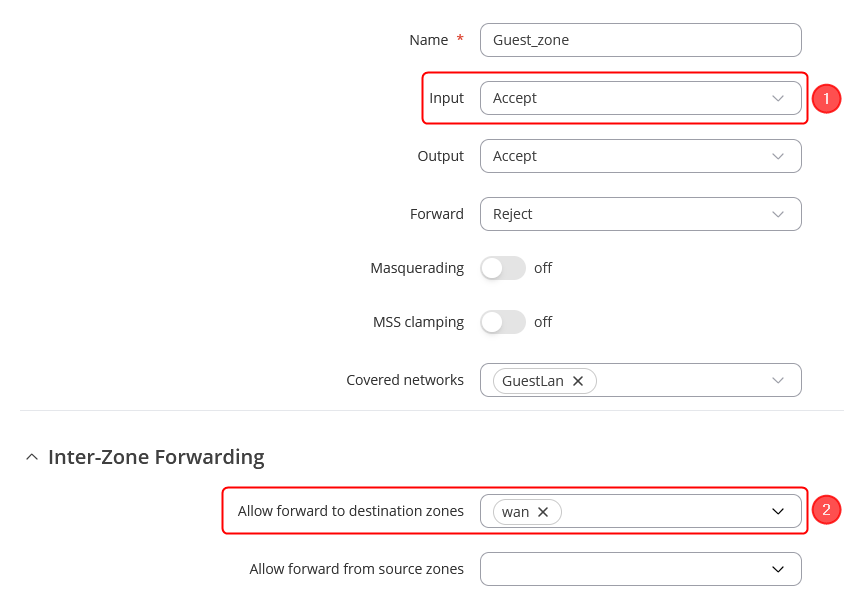
Navigate to Network → Firewall → Zones. There edit a new Zone rule that we added in LAN interface configuration, by pressing Edit button. Then you will be forwarded to the configuration window. |
 |
|
|---|---|
|
In the ZONE page, do the following:
When done, Save & Apply changes |
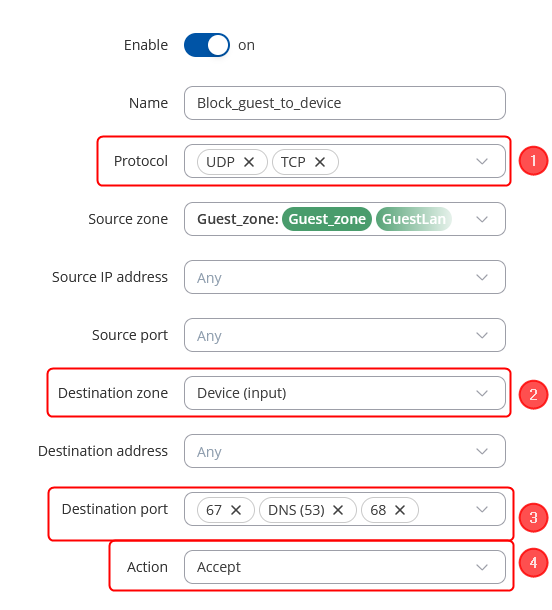
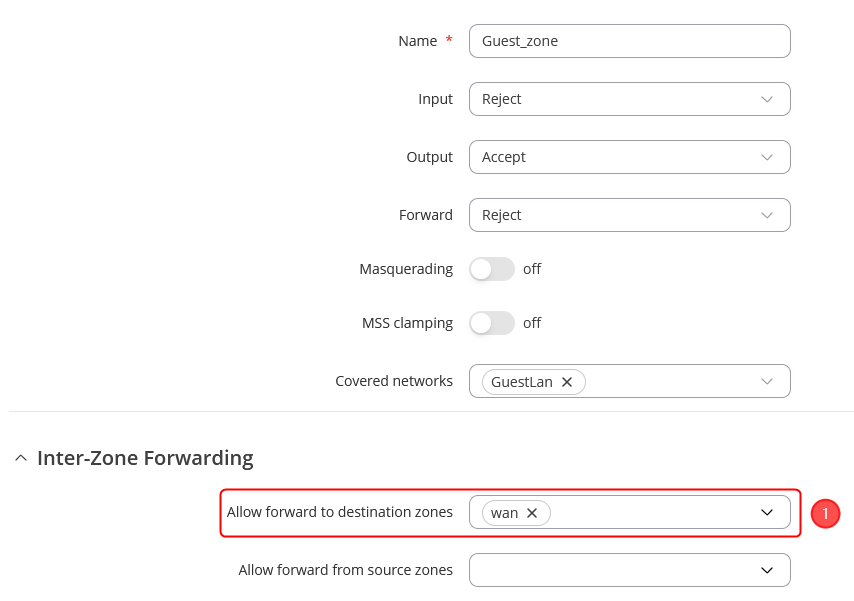
Alternative Firewall rules
 |
|
|---|---|
|
In the ZONE page, do the following:
When done, Save & Apply changes |
 |
|
|---|---|
|
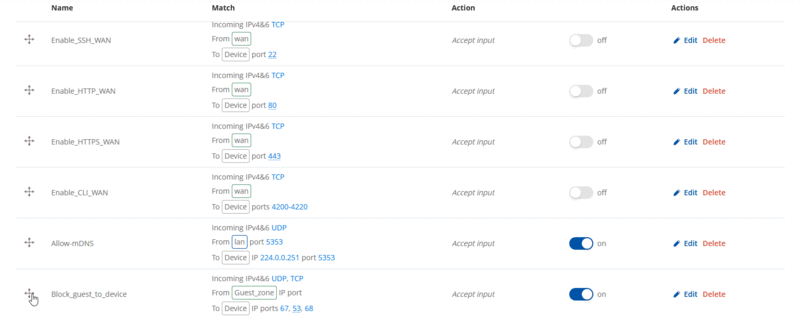
Then we will need to move up the traffic rule to the top, in order to be able to use these settings: |
Results
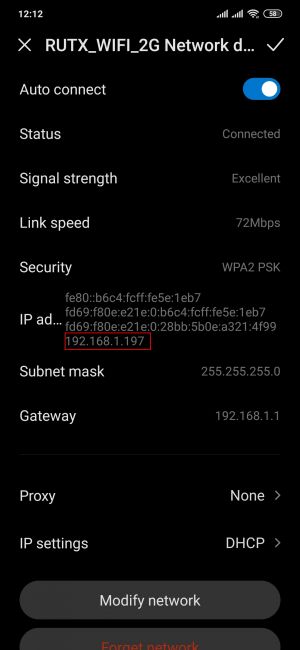
If you've followed all the steps presented above, your configuration should be finished. If you are near a RUT, that is, in a wireless zone, turn on WiFi on your device and view the available networks. You should see the available SSID - "RUTX_WiFi_2G" and "Guest_WiFi". Select one of them and enter the appropriate WiFi password.
 |
|
|---|---|
|
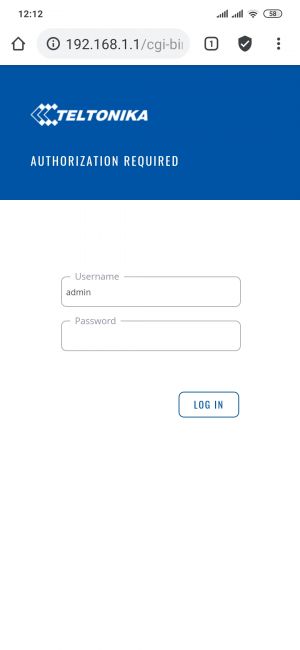
Wireless users connected to SSID: “RUTX_WIFI”, will be assign to “LAN”, and will get IP from main pool 192.168.1.0/24. |
 |
|
|---|---|
|
LAN users are able to access any data from pool 192.168.1.0/24. For example they can access Web UI. |
 |
|
|---|---|
|
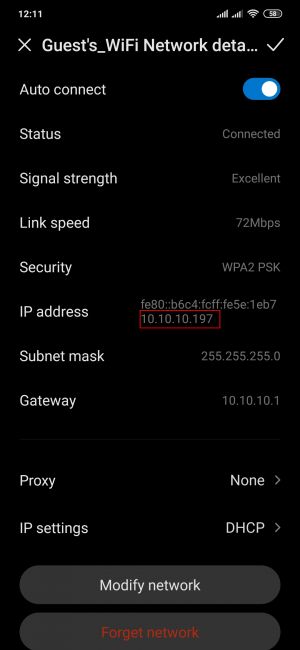
Wireless users connected to SSID: “GUEST'S_WIFI”, will be assign to LAN “Guest”, and will get IP from new pool 10.10.10.0/24. |
 |
|
|---|---|
|
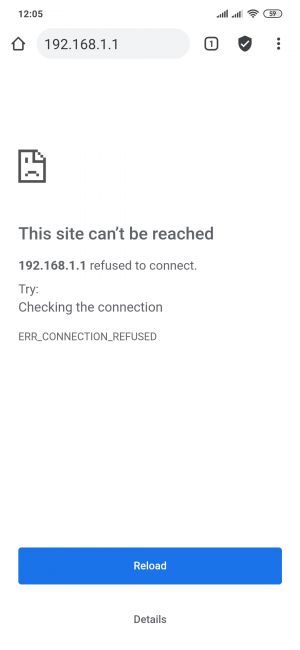
Guest hosts are unable to access any data from pool 192.168.1.0/24. And access to the routers Web UI or SSH is restricted. |