OpenVPN Access Control: Difference between revisions
m More informative testing |
m Fixes |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<p style="color:red">The information on this page is updated in accordance with the [https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/view/FW_%26_SDK_Downloads'''00.07.06.6'''] firmware version .</p> | |||
=Introduction= | |||
---- | |||
Normally, OpenVPN Client access is controlled by enabling or disabling the Client to Client button in OpenVPN Servers configuration, however, at times, more granular control is required. In this example, we will configure an OpenVPN server with 3 Clients: | Normally, OpenVPN Client access is controlled by enabling or disabling the Client to Client button in OpenVPN Servers configuration, however, at times, more granular control is required. In this example, we will configure an OpenVPN server with 3 Clients: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li> Client 1 will be able to communicate with Client 2 and OpenVPN server</li> | #<li> Client 1 will be able to communicate with Client 2 and OpenVPN server</li> | ||
<li> Client 2 will be able to communicate with Client 1 and OpenVPN server</li> | #<li> Client 2 will be able to communicate with Client 1 and OpenVPN server</li> | ||
<li> Client 3 will only be able to communicate with OpenVPN server, but not with any of other clients</li> | #<li> Client 3 will only be able to communicate with OpenVPN server, but not with any of other clients</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
=Topology= | |||
---- | |||
[[File:OpenVPN Topology v1.png| | [[File:OpenVPN Topology v1.png|border|center|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 25: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
=Generating certificates for an OpenVPN server= | |||
---- | |||
Navigate to '''System -> Administration -> Certificates''' | |||
1 |   1. Generate 2 certificates . Recommended key size is at least '''2048 bits''' for security reasons: | ||
   1.1. CA | |||
2 |    1.2 Server | ||
2. |   2.In Certificate Manager download Server certificate | ||
There are multiple methods of how certificates could be generated, you could follow this tutorial instead: | There are multiple methods of how certificates could be generated, you could follow this tutorial instead: | ||
[[How to generate TLS certificates (Windows)?]] | [[How to generate TLS certificates (Windows)?]] | ||
[[File:Certificate download | [[File:Certificate download v3.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border]] | ||
For any OpenVPN clients, You will need to generate “Client” certificates, download certificate and key, and send them to the client | For any OpenVPN clients, You will need to generate “Client” certificates, download certificate and key, and send them to the client | ||
=Creating an OpenVPN server= | |||
Connect to WebUI and enable Advanced mode | |||
[[File:Networking rutos manual webui basic advanced mode 75.gif|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | [[File:Networking rutos manual webui basic advanced mode 75.gif|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | ||
Navigate to '''Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN''' | |||
  1. Add a new OpenVPN instance with a Server role | |||
  2. Create an OpenVPN server with these settings | |||
[[File:OpenVPN server settings v3.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | |||
1) Client to client – disabled | |||
2) Virtual network IP address – 10.0.0.0 | |||
3) Virtual network netmask – 255.255.255.224 | |||
4) Certificate files from device - on | |||
Press '''"Save & Apply"''', enable OpenVPN server and check if the server is online | |||
[[File:OpenVPN server | [[File:OpenVPN server is online v2.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border]] | ||
=Connecting clients to the OpenVPN server= | |||
---- | |||
Navigate to '''Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN''' | |||
  1. Add a new OpenVPN instance with a Client role | |||
  2. Create an OpenVPN client with these settings | |||
[[File:OpenVPN Client1 v3.png|none|border|center|class=tlt-border]] | |||
   1) Remote host/IP address - Public IP of the OpenVPN server's router | |||
   2) Remote network IP address - 10.0.0.0 | |||
   3) Remote network netmask - 255.255.255.224 | |||
   4) Add the certificates from the OpenVPN server - Certificate Authority, Client certificate, and Client key which we downloaded in the Certificate Generation step | |||
  4. Press "Save & Apply", enable OpenVPN client and check if the connection is made | |||
[[File:OpenVPN Client1 connected v2.png|none| | [[File:OpenVPN Client1 connected v2.png|none|border|left|class=tlt-border]] | ||
Repeat this step for as many clients as You need. For this example, we will have 3 clients | |||
=Client to Client LAN network communication= | |||
---- | |||
==TLS Clients== | |||
---- | |||
1 |   1. On the OpenVPN server router, navigate to '''Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN''', Press "'''Edit'''" on the server, scroll down and add TLS clients | ||
Add clients which LAN address You want to have access to, in our case, we add all 3 clients | Add clients which LAN address You want to have access to, in our case, we add all 3 clients | ||
| Line 106: | Line 121: | ||
<li>Covered network - Which LAN subnet should clients be able to communicate with in the OpenVPN server</li> | <li>Covered network - Which LAN subnet should clients be able to communicate with in the OpenVPN server</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
==Firewall Zones== | |||
---- | |||
This step should be done on OpenVPN server and all clients that want their LAN subnets be accessible and to access other client's LAN subnets | This step should be done on OpenVPN server and all clients that want their LAN subnets be accessible and to access other client's LAN subnets | ||
  Navigate to '''Network -> Firewall -> General settings -> Zones''' and set OpenVPN zone to forward traffic to LAN | |||
[[File:OpenVPN to LAN zone forward.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | [[File:OpenVPN to LAN zone forward.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | ||
==Routes to LAN subnets== | |||
---- | |||
Create a route to other client LAN networks using WebUI. This step should be done on all <b>clients</b> that want their LAN subnets be accessible and to access other client's LAN subnets | Create a route to other client LAN networks using WebUI. This step should be done on all <b>clients</b> that want their LAN subnets be accessible and to access other client's LAN subnets | ||
1 |   1. Navigate to '''Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN''' press '''"Edit"''' on the OpenVPN client and add routes to other client LAN subnets. In this image, we are editing Client 1's configuration, to add routes to <b>Client 2's (192.168.20.0/24)</b> and <b>Client 3's (192.168.30.0/24)</b> LAN subnets. | ||
[[File:OpenVPN client routes.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | [[File:OpenVPN client routes.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | ||
=Controlling access with firewall= | |||
---- | |||
Navigate to '''Network -> Firewall -> Access Control''' and create a new deny rule. In this example, we are denying Client 3 from accessing any other clients and their LAN networks | |||
[[File:Deny Client3 rule.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | [[File:Deny Client3 rule.png|none|thumb|alt=|1000x1000px]] | ||
| Line 139: | Line 159: | ||
=Testing the setup= | |||
---- | |||
Client 1 to Client 2 | Client 1 to Client 2 | ||
Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.10.216 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.10.216 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
| Line 152: | Line 172: | ||
Client 1 to Client 3 | Client 1 to Client 3 | ||
Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.10.216 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.10.216 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
Request timed out. | Request timed out. | ||
| Line 162: | Line 180: | ||
Client 2 to Client 1 | Client 2 to Client 1 | ||
Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.20.193 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.20.193 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
Reply from 192.168.10.216: bytes=32 time=185ms TTL=125 | Reply from 192.168.10.216: bytes=32 time=185ms TTL=125 | ||
| Line 172: | Line 188: | ||
Client 2 to Client 3 | Client 2 to Client 3 | ||
Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.20.193 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.20.193 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
Request timed out. | Request timed out. | ||
| Line 182: | Line 196: | ||
Client 3 to Client 1 | Client 3 to Client 1 | ||
Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.30.178 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.30.178 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
Request timed out. | Request timed out. | ||
| Line 192: | Line 204: | ||
Client 3 to Client 2 | Client 3 to Client 2 | ||
Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.30.178 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.30.178 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
Request timed out. | Request timed out. | ||
| Line 207: | Line 217: | ||
Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=81ms TTL=62 | Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=81ms TTL=62 | ||
Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=107ms TTL=62 | Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=107ms TTL=62 | ||
Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
| Line 215: | Line 223: | ||
Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=132ms TTL=62 | Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=132ms TTL=62 | ||
Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=232ms TTL=62 | Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=232ms TTL=62 | ||
Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: | Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: | ||
| Line 226: | Line 232: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=See also= | |||
---- | |||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>[[OpenVPN_configuration_examples_RUT_R_00.07]]</li> | <li>[[OpenVPN_configuration_examples_RUT_R_00.07]]</li> | ||
| Line 239: | Line 247: | ||
=External links= | |||
---- | |||
https://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/howto.html - some additional information on OpenVPN | https://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/howto.html - some additional information on OpenVPN | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 29 March 2024
The information on this page is updated in accordance with the 00.07.06.6 firmware version .
Introduction
Normally, OpenVPN Client access is controlled by enabling or disabling the Client to Client button in OpenVPN Servers configuration, however, at times, more granular control is required. In this example, we will configure an OpenVPN server with 3 Clients:
- Client 1 will be able to communicate with Client 2 and OpenVPN server
- Client 2 will be able to communicate with Client 1 and OpenVPN server
- Client 3 will only be able to communicate with OpenVPN server, but not with any of other clients
Topology
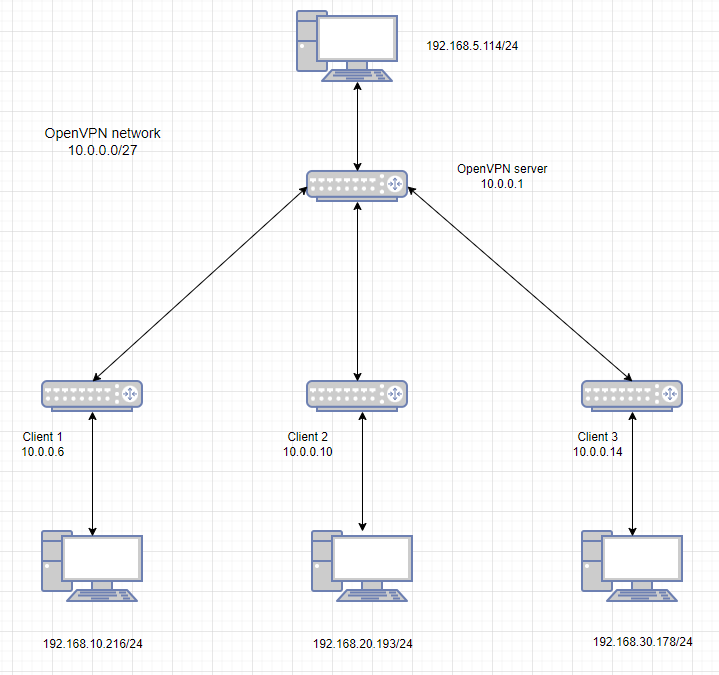
- OpenVPN server tunnel address - 10.0.0.1, OpenVPN subnet - 10.0.0.0/27, LAN device address - 192.168.5.114
- Client 1 VPN tunnel address - 10.0.0.6, LAN device address - 192.168.10.216
- Client 2 VPN tunnel address - 10.0.0.10, LAN device address - 192.168.20.193
- Client 3 VPN tunnel address - 10.0.0.14, LAN device address - 192.168.30.178
Generating certificates for an OpenVPN server
Navigate to System -> Administration -> Certificates
1. Generate 2 certificates . Recommended key size is at least 2048 bits for security reasons:
1.1. CA
1.2 Server
2.In Certificate Manager download Server certificate
There are multiple methods of how certificates could be generated, you could follow this tutorial instead:
How to generate TLS certificates (Windows)?
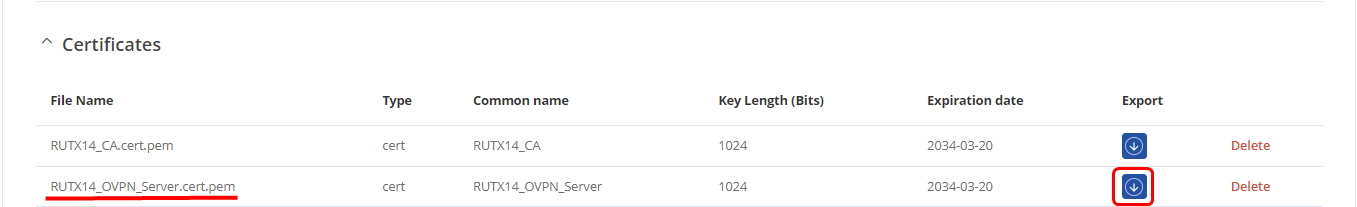
For any OpenVPN clients, You will need to generate “Client” certificates, download certificate and key, and send them to the client
Creating an OpenVPN server
Connect to WebUI and enable Advanced mode

Navigate to Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN
1. Add a new OpenVPN instance with a Server role
2. Create an OpenVPN server with these settings
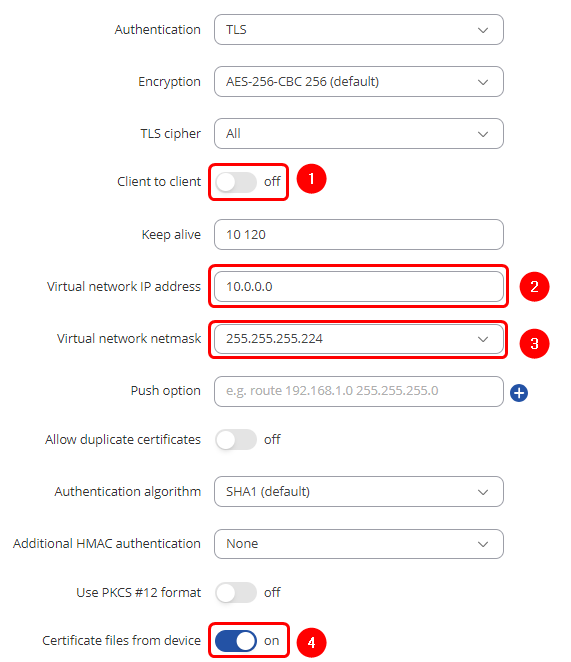
1) Client to client – disabled
2) Virtual network IP address – 10.0.0.0
3) Virtual network netmask – 255.255.255.224
4) Certificate files from device - on
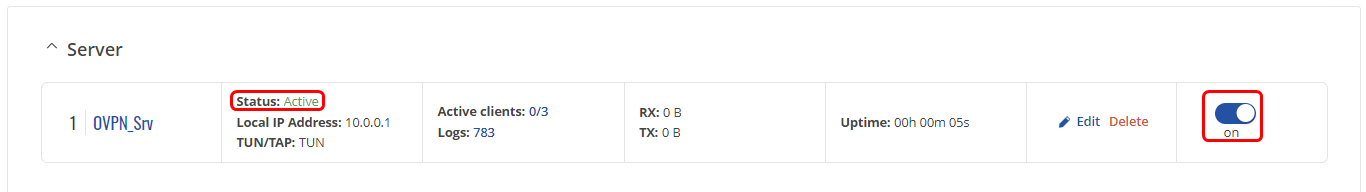
Press "Save & Apply", enable OpenVPN server and check if the server is online
Connecting clients to the OpenVPN server
Navigate to Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN
1. Add a new OpenVPN instance with a Client role
2. Create an OpenVPN client with these settings
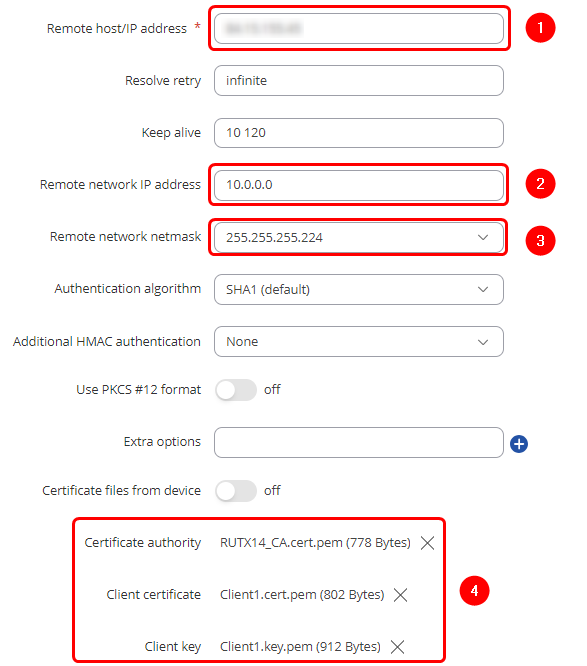
1) Remote host/IP address - Public IP of the OpenVPN server's router
2) Remote network IP address - 10.0.0.0
3) Remote network netmask - 255.255.255.224
4) Add the certificates from the OpenVPN server - Certificate Authority, Client certificate, and Client key which we downloaded in the Certificate Generation step
4. Press "Save & Apply", enable OpenVPN client and check if the connection is made
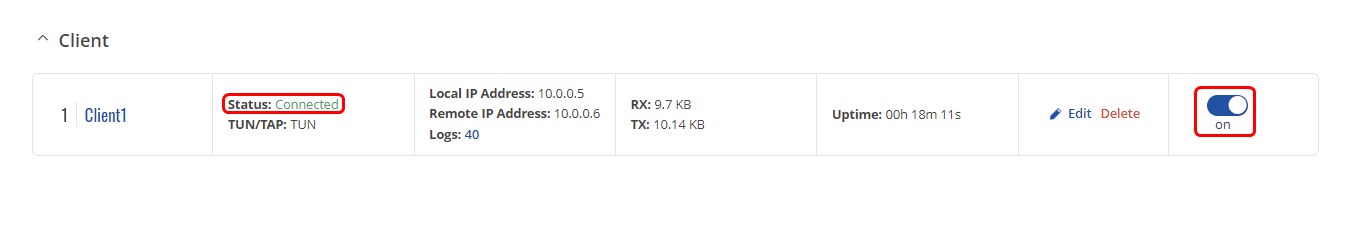
Repeat this step for as many clients as You need. For this example, we will have 3 clients
Client to Client LAN network communication
TLS Clients
1. On the OpenVPN server router, navigate to Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN, Press "Edit" on the server, scroll down and add TLS clients
Add clients which LAN address You want to have access to, in our case, we add all 3 clients
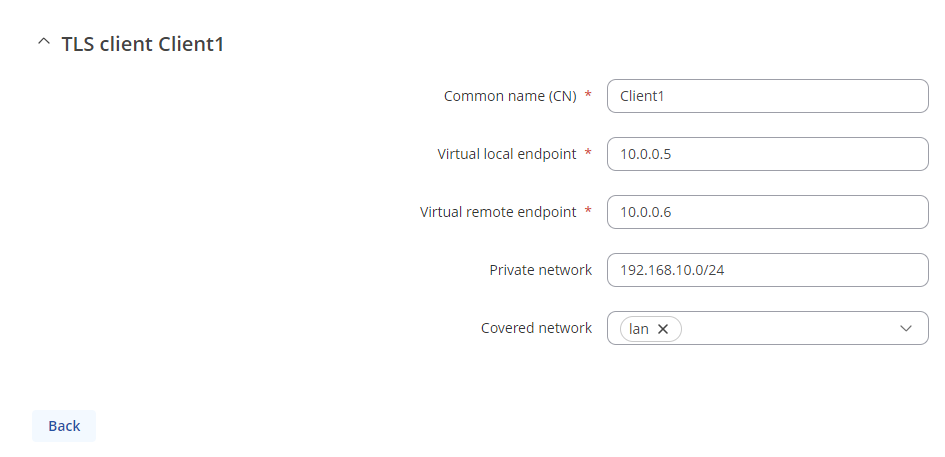
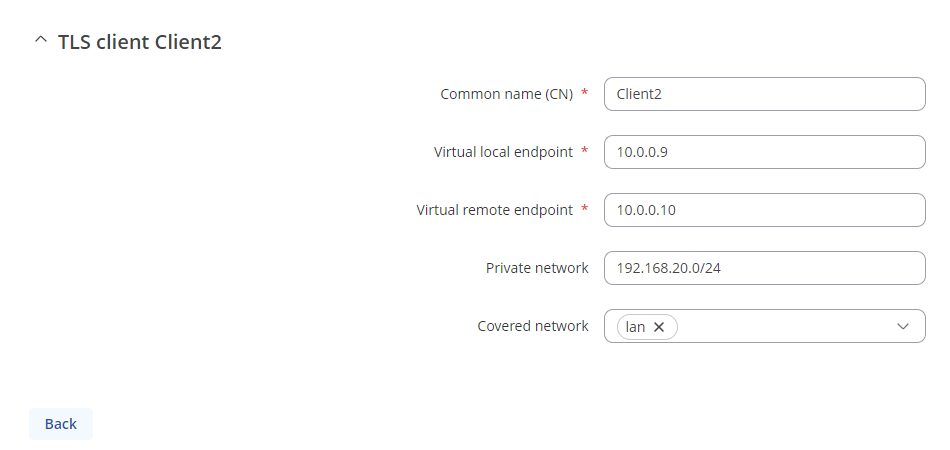
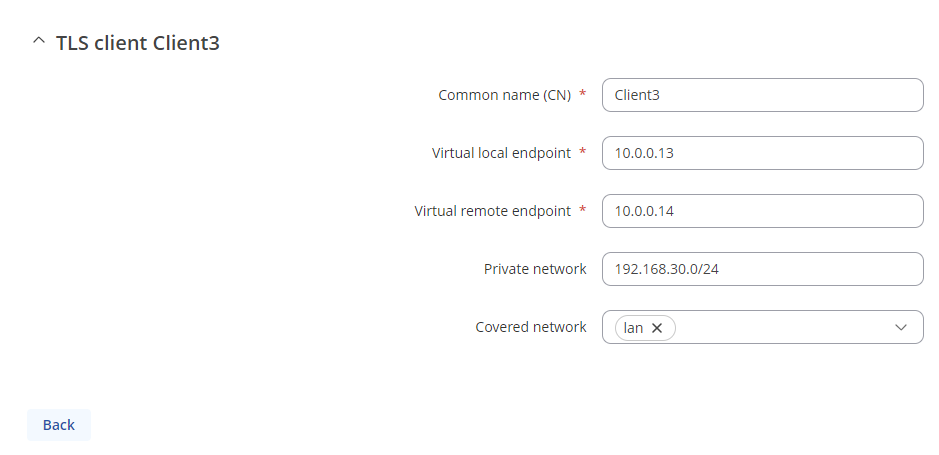
- Common name - common name of the certificate which was generated previously
- Virtual local endpoint - client’s local address in the virtual network
- Virtual remote endpoint - client’s remote address in the virtual network
- Private network - client's LAN subnet
- Covered network - Which LAN subnet should clients be able to communicate with in the OpenVPN server
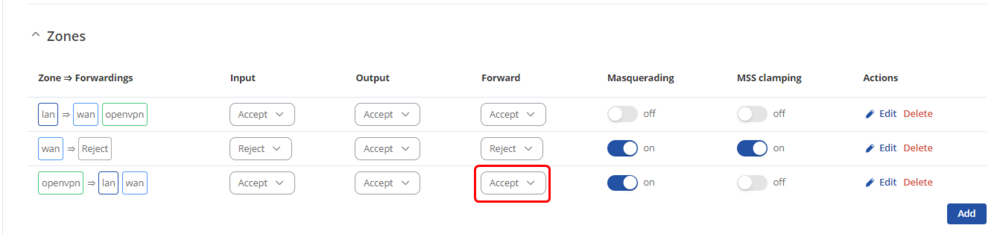
Firewall Zones
This step should be done on OpenVPN server and all clients that want their LAN subnets be accessible and to access other client's LAN subnets
Navigate to Network -> Firewall -> General settings -> Zones and set OpenVPN zone to forward traffic to LAN
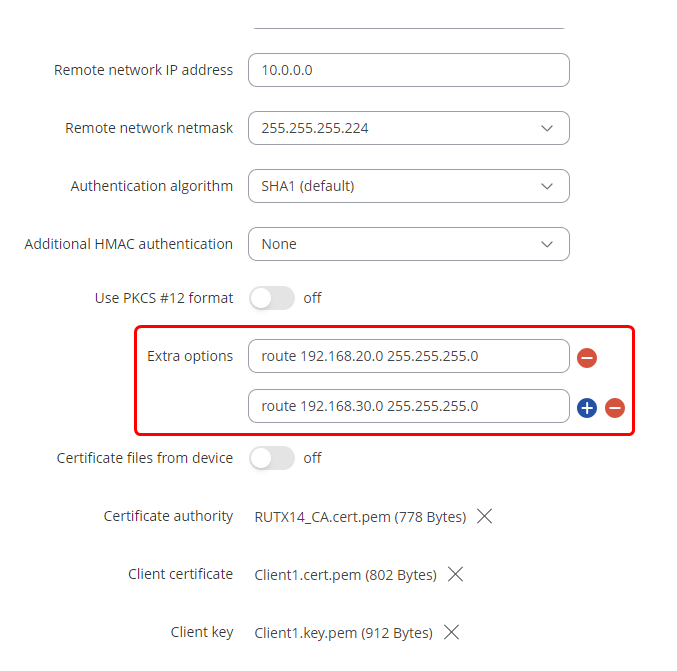
Routes to LAN subnets
Create a route to other client LAN networks using WebUI. This step should be done on all clients that want their LAN subnets be accessible and to access other client's LAN subnets
1. Navigate to Services -> VPN -> OpenVPN press "Edit" on the OpenVPN client and add routes to other client LAN subnets. In this image, we are editing Client 1's configuration, to add routes to Client 2's (192.168.20.0/24) and Client 3's (192.168.30.0/24) LAN subnets.
Controlling access with firewall
Navigate to Network -> Firewall -> Access Control and create a new deny rule. In this example, we are denying Client 3 from accessing any other clients and their LAN networks
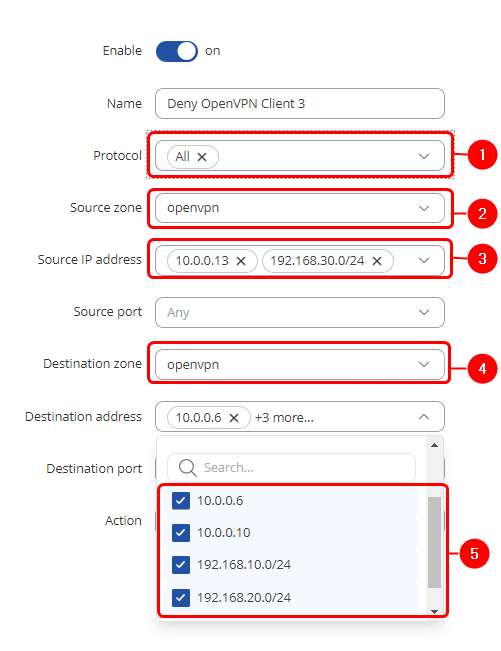
- Source interface - OpenVPN
- Destination interface - OpenVPN
- Source IP - OpenVPN remote IP and LAN subnet of client 3
- Destination IP - other client OpenVPN remote endpoints and LAN subnets
- Action - Deny
This rule will deny all traffic from Client 3 to other clients, but will not interact with traffic, if it's destination is OpenVPN server or it's LAN subnet
Testing the setup
Client 1 to Client 2
Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.10.216 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.20.194: bytes=32 time=172ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.20.194: bytes=32 time=114ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.20.194: bytes=32 time=113ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.20.194: bytes=32 time=294ms TTL=125
Client 1 to Client 3
Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.10.216 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out.
Client 2 to Client 1
Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.20.193 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.10.216: bytes=32 time=185ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.10.216: bytes=32 time=123ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.10.216: bytes=32 time=227ms TTL=125 Reply from 192.168.10.216: bytes=32 time=189ms TTL=125
Client 2 to Client 3
Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.20.193 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out.
Client 3 to Client 1
Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.30.178 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out.
Client 3 to Client 2
Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.30.178 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out.
And server can reach all of the clients and their LAN subnets
Pinging 192.168.10.216 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=264ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=138ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=81ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=107ms TTL=62 Pinging 192.168.20.193 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=61ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=376ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=132ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=232ms TTL=62 Pinging 192.168.30.178 from 192.168.5.114 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=226ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=327ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=111ms TTL=62 Reply from 192.168.5.114: bytes=32 time=80ms TTL=62
See also
- OpenVPN_configuration_examples_RUT_R_00.07
- How to generate TLS certificates (Windows)?
- OpenVPN client on Windows
- OpenVPN client on Linux
- OpenVPN server on Windows
- OpenVPN traffic split
- Configuration file .ovpn upload tutorial
- Firewall traffic rules
External links
https://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/howto.html - some additional information on OpenVPN
